1000+ Applied Mechanics and Graphic Statics MCQ for GMAT [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The moment of inertia of a circular lamina of diameter d, about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the lamina and passing through its centre, is
A. ?d4/12
B. ?d4/16
C. ?d4/24
D. ?d4/32
Answer : D
A. ?d4/12
B. ?d4/16
C. ?d4/24
D. ?d4/32
Answer : D
2. When a body falls freely under gravitational force, it possesses
A. Maximum weight
B. Minimum weight
C. No weight
D. No effect on its weight
Answer : C
A. Maximum weight
B. Minimum weight
C. No weight
D. No effect on its weight
Answer : C
3. One Newton is equivalent to
A. 105 dyne
B. 106 dyne
C. 107 dyne
D. 108 dyne
Answer : A
A. 105 dyne
B. 106 dyne
C. 107 dyne
D. 108 dyne
Answer : A
4. A bullet weighing 10 gm moves with a velocity of l km/sec. Its kinetic energy is (i) 5000 Nm (ii) 5000 kg.m (iii) 5000 J The correct answer is
A. Only (ii)
B. Both (i) and (iii)
C. Both (ii) and (iii)
D. All (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer : B
A. Only (ii)
B. Both (i) and (iii)
C. Both (ii) and (iii)
D. All (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer : B
5. The intrinsic equation of catenary is
A. S = c tan ?
B. y = c cosh x/c
C. y = c cosh ?
D. y = c sinh ?
Answer : A
A. S = c tan ?
B. y = c cosh x/c
C. y = c cosh ?
D. y = c sinh ?
Answer : A
6. In a simple harmonic motion, the position of equilibrium is always
A. Stable
B. Unstable
C. Neutral
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Stable
B. Unstable
C. Neutral
D. None of the above
Answer : A
7. Periodic time of body moving with simple harmonic motion, is
A. Directly proportional to its angular velocity
B. Directly proportional to the square of its angular velocity
C. Inversely proportional to the square of its angular velocity
D. Inversely proportional to its angular velocity
Answer : D
A. Directly proportional to its angular velocity
B. Directly proportional to the square of its angular velocity
C. Inversely proportional to the square of its angular velocity
D. Inversely proportional to its angular velocity
Answer : D
8. A number of forces acting simultaneously on a particle of a body
A. May not be replaced by a single force
B. May be replaced by a single force
C. May be replaced by a single force through C.G. of the body
D. May be replaced by a couple
Answer : B
A. May not be replaced by a single force
B. May be replaced by a single force
C. May be replaced by a single force through C.G. of the body
D. May be replaced by a couple
Answer : B
9. The following factor affects the orbit of a satellite up to an altitude of 720 km from the earth's surface
A. Uneven distribution of the gravitational field
B. Gravity of the sun and the moon
C. Aerodynamic forces
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Uneven distribution of the gravitational field
B. Gravity of the sun and the moon
C. Aerodynamic forces
D. None of these
Answer : D
10. For a simple pendulum, time period for a beat, is
A. ? ?(l/g)
B. ? ?(2l/g)
C. ? ?(g/2l)
D. ? ?(l/2g)
Answer : A
A. ? ?(l/g)
B. ? ?(2l/g)
C. ? ?(g/2l)
D. ? ?(l/2g)
Answer : A
11. Pick up the incorrect statement from the following:
A. The C.G. of a circle is at its centre
B. The C.G. of a triangle is at the intersection of its medians
C. The C.G. of a rectangle is at the intersection of its diagonals
D. The C.G. of a semicircle is at a distance of r/2 from the centre
Answer : D
A. The C.G. of a circle is at its centre
B. The C.G. of a triangle is at the intersection of its medians
C. The C.G. of a rectangle is at the intersection of its diagonals
D. The C.G. of a semicircle is at a distance of r/2 from the centre
Answer : D
12. For perfectly elastic bodies, the value of coefficient of restitution is
A. Zero
B. 0.5
C. 1.0
D. Between 0 and 1
Answer : C
A. Zero
B. 0.5
C. 1.0
D. Between 0 and 1
Answer : C
13. The rate of change of displacement of a body with respect to its surrounding, is known
A. Velocity
B. Acceleration
C. Speed
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Velocity
B. Acceleration
C. Speed
D. None of these
Answer : C
14. A ball moving on a smooth horizontal table hits a rough vertical wall, the coefficient of restitution between ball and wall being 1/3. The ball rebounds at the same angle. The fraction of its kinetic energy lost is
A. 1/3
B. 2/3
C. 1/9
D. 8/9
Answer : D
A. 1/3
B. 2/3
C. 1/9
D. 8/9
Answer : D
15. A square hole is made in a circular lamina, the diagonal of the square is equal to the radius of the circle as shown in below figure the shift in the centre of gravity is 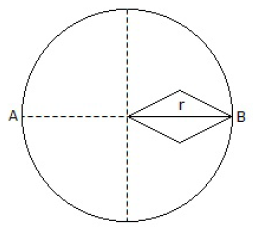
A. r (? - 0.75)/(? - 0.5)
B. r (? - 0.25)/(? - 0.75)
C. r (? - 0.5)/(? - 0.75)
D. r (? - 0.5)/(? - 0.25)
Answer : A

A. r (? - 0.75)/(? - 0.5)
B. r (? - 0.25)/(? - 0.75)
C. r (? - 0.5)/(? - 0.75)
D. r (? - 0.5)/(? - 0.25)
Answer : A
16. Lami's theorem states that
A. Three forces acting at a point are always in equilibrium
B. If three forces acting on a point can be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a triangle, the point will be in the state of equilibrium
C. Three coplanar forces acting at a point will be in equilibrium, if each force is proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two
D. Three coplanar forces acting at a point will be in equilibrium if each force is inversely proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two
Answer : C
A. Three forces acting at a point are always in equilibrium
B. If three forces acting on a point can be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a triangle, the point will be in the state of equilibrium
C. Three coplanar forces acting at a point will be in equilibrium, if each force is proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two
D. Three coplanar forces acting at a point will be in equilibrium if each force is inversely proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two
Answer : C
17. If a body is lying on a plane whose inclination with the horizontal is less than the angle of friction, then? (i) A force is required to move the body upwards (ii) A force is required to move the body downward (iii) The body will not be in equilibrium The correct answer is
A. Only (i)
B. Only (ii)
C. Both (i) and (ii)
D. Both (i) and (iii)
Answer : C
A. Only (i)
B. Only (ii)
C. Both (i) and (ii)
D. Both (i) and (iii)
Answer : C
18. To attain the synchronous orbit, the launch of a satellite, is done from a place
A. On equator
B. On 30° latitude
C. On 45° latitude
D. On the poles
Answer : A
A. On equator
B. On 30° latitude
C. On 45° latitude
D. On the poles
Answer : A
19. If ? and u are the angle of projection and initial velocity of a projectile respectively, the horizontal range of the projectile, is
A. u² sin ?/g
B. u² sin² ?/g
C. u² sin ?/2g
D. u² sin² ?/2g
Answer : A
A. u² sin ?/g
B. u² sin² ?/g
C. u² sin ?/2g
D. u² sin² ?/2g
Answer : A
div class="panel-body">20. Impulse can be obtained from a
A. Force-displacement diagram
B. Force-time diagram
C. Velocity-time diagram
D. Velocity-displacement diagram
Answer : B
A. Force-displacement diagram
B. Force-time diagram
C. Velocity-time diagram
D. Velocity-displacement diagram
Answer : B
21. A smooth cylinder lying on its convex surface remains
A. In stable equilibrium
B. In unstable equilibrium
C. In neutral equilibrium
D. Out of equilibrium
Answer : B
A. In stable equilibrium
B. In unstable equilibrium
C. In neutral equilibrium
D. Out of equilibrium
Answer : B
22. The motion of a particle moving with S.H.M. from an extremity to the other, constitutes
A. Half an oscillation
B. One full oscillation
C. Two oscillations
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Half an oscillation
B. One full oscillation
C. Two oscillations
D. None of these
Answer : A
23. A marble ball is rolled on a smooth floor of a room to hit a wall. If the time taken by the ball in returning to the point of projection is twice the time taken in reaching the wall, the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the wall, is
A. 0.25
B. 0.50
C. 0.75
D. 1.0
Answer : B
A. 0.25
B. 0.50
C. 0.75
D. 1.0
Answer : B
24. Two shots fired simultaneously from the top and bottom of a vertical tower with elevations of 30° and 45° respectively strike a target simultaneously. If horizontal distance of the target from the tower is 1000 m, the height of the tower is
A. 350 m
B. 375 m
C. 400 m
D. 425 m
Answer : D
A. 350 m
B. 375 m
C. 400 m
D. 425 m
Answer : D
25. A rigid body suspended vertically at a point and oscillating with a small amplitude under the action of the force of gravity, is called
A. Simple pendulum
B. Compound pendulum
C. Second's pendulum
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Simple pendulum
B. Compound pendulum
C. Second's pendulum
D. None of these
Answer : B
26. The mechanical advantage of an ideal machine is 100. For moving the local through 2 m, the effort moves through
A. 0.02 m
B. 2 m
C. 2.5 m
D. 20 m
Answer : A
A. 0.02 m
B. 2 m
C. 2.5 m
D. 20 m
Answer : A
27. If a particle moves with a uniform angular velocity ? radians/sec along the circumference of a circle of radius r, the equation for the velocity of the particle, is
A. v = ? ?(y² - r²)
B. y = ? ?(y - r)
C. v = ? ?(r² + y²)
D. v = ? ?(r² - y²)
Answer : D
A. v = ? ?(y² - r²)
B. y = ? ?(y - r)
C. v = ? ?(r² + y²)
D. v = ? ?(r² - y²)
Answer : D
28. The centre of gravity of a plane lamina will not be at its geometrical centre if it is a
A. Circle
B. Equilateral triangle
C. Rectangle
D. Right angled triangle
Answer : D
A. Circle
B. Equilateral triangle
C. Rectangle
D. Right angled triangle
Answer : D
29. The velocity ratio of an inclined plane of inclination ? with horizontal for lifting a load is
A. sin ?
B. cos ?
C. tan ?
D. cosec ?
Answer : D
A. sin ?
B. cos ?
C. tan ?
D. cosec ?
Answer : D
30. The resultant of the forces acting on a body will be zero if the body
A. Rotates
B. Moves with variable velocity in a straight line
C. Moves along a curved path
D. Does not move at all
Answer : D
A. Rotates
B. Moves with variable velocity in a straight line
C. Moves along a curved path
D. Does not move at all
Answer : D
31. Time period and length of a seconds pendulum respectively are
A. 1 sec and 99.4 cm
B. 1 sec and 92.7 cm
C. 2 sec and 99.4 cm
D. 2 sec and 92.7 cm
Answer : C
A. 1 sec and 99.4 cm
B. 1 sec and 92.7 cm
C. 2 sec and 99.4 cm
D. 2 sec and 92.7 cm
Answer : C
32. At a given instant ship A is travelling at 6 km/h due east and ship B is travelling at 8 km/h due north. The velocity of B relative to A is
A. 7 km/hrs
B. 2 km/hrs
C. 1 km/hrs
D. 10 km/hrs
Answer : D
A. 7 km/hrs
B. 2 km/hrs
C. 1 km/hrs
D. 10 km/hrs
Answer : D
33. The velocity ratio of the differential wheel and axle is
A. R/r1 - r2
B. 2R/r1
C. 3R/r1 - r2
D. 2R/r1 + r2
Answer : B
A. R/r1 - r2
B. 2R/r1
C. 3R/r1 - r2
D. 2R/r1 + r2
Answer : B
34. A ball moving with a velocity of 5 m/sec impinges a fixed plane at an angle of 45° and its direction after impact is equally inclined to the line of impact. If the coefficient of restitution is 0.5, the velocity of the ball after impact will be
A. 0.5 m/sec
B. 1.5 m/sec
C. 2.5 m/sec
D. 3.5 m/sec
Answer : C
A. 0.5 m/sec
B. 1.5 m/sec
C. 2.5 m/sec
D. 3.5 m/sec
Answer : C
35. A Second's pendulum gains 2 minutes a day. To make it to keep correct time its length
A. Must be decreased
B. Must be increased
C. Is not changed but weight of the bob is increased
D. Is not changed but weight of the bob is decreased
Answer : B
A. Must be decreased
B. Must be increased
C. Is not changed but weight of the bob is increased
D. Is not changed but weight of the bob is decreased
Answer : B
36. A body of weight 14 g appears to weight 13 g when weighed by a spring balance in a moving lift. The acceleration of the lift at that moment was
A. 0.5 m/sec2
B. 0.7 m/sec2
C. 1 m/sec2
D. 1 cm/sec2
Answer : B
A. 0.5 m/sec2
B. 0.7 m/sec2
C. 1 m/sec2
D. 1 cm/sec2
Answer : B
37. If two forces acting at a point are in equilibrium, they must be equal in magnitude and their line of action must be along
A. The same line in the same sense
B. The same line in opposite sense
C. The perpendicular to both the lines
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. The same line in the same sense
B. The same line in opposite sense
C. The perpendicular to both the lines
D. None of these
Answer : B
38. A pilot flies a small plane in a vertical loop of radius r. At the top of its trajectory he experiences weightlessness. If the acceleration due to gravity is g, the speed of the plane at the top of its trajectory would be
A. Zero
B. Infinite
C. gr
D. 2gr
Answer : C
A. Zero
B. Infinite
C. gr
D. 2gr
Answer : C
39. In which of the following trusses, the method of substitution is required for determining the forces in all the members of the truss by graphic statics?
A. Howe truss
B. King post truss
C. Fink truss
D. Warren truss
Answer : C
A. Howe truss
B. King post truss
C. Fink truss
D. Warren truss
Answer : C
40. The equation of motion of a particle starting from rest along a straight line is x = t3 - 3l2 + 5. The ratio of the velocities after 5 sec and sec will be
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Answer : D
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Answer : D
41. Instantaneous center is at infinity when the angular velocity is
A. Constant
B. Zero
C. Maximum
D. Minimum
Answer : B
A. Constant
B. Zero
C. Maximum
D. Minimum
Answer : B
42. A stone is thrown up a slope of inclination 60° to the horizontal. At what angle to the slope must the stone be thrown so as to land as far as possible from the point of projection?
A. 15°
B. 30°
C. 45°
D. 75°
Answer : A
A. 15°
B. 30°
C. 45°
D. 75°
Answer : A
43. The ends of a string weighing w/metre are attached to two points at the same horizontal level. If the central dip is very small, the horizontal tension of the string throughout is
A. wl/4d
B. wl²/4d
C. wl²/8d
D. wl²/16d
Answer : C
A. wl/4d
B. wl²/4d
C. wl²/8d
D. wl²/16d
Answer : C
44. The Centre of gravity of a 10 × 15 × 5 cm T-section from its bottom, is
A. 7.5 cm
B. 5.0 cm
C. 8.75 cm
D. 7.85 cm
Answer : C
A. 7.5 cm
B. 5.0 cm
C. 8.75 cm
D. 7.85 cm
Answer : C
45. A projectile has maximum range of 40 m on a horizontal plane. If angle of projection is a and the time of flight is 1 second, then sin a must be about (Assume g = 10 m/sec²)
A. 1/4
B. 1/3
C. 1/2
D. 1/5
Answer : A
A. 1/4
B. 1/3
C. 1/2
D. 1/5
Answer : A
46. Work may be defined as
A. Force × distance
B. Force × velocity
C. Force × acceleration
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Force × distance
B. Force × velocity
C. Force × acceleration
D. None of these
Answer : A
47. One end of a light string 4 m in length is fixed to a point on a smooth wall and the other end fastened to a point on the surface of a smooth sphere of diameter 2.25 m and of weight 100 kg. The tension in the string is
A. 17.5 kg
B. 19.5 kg
C. 22.5 kg
D. 25 kg
Answer : C
A. 17.5 kg
B. 19.5 kg
C. 22.5 kg
D. 25 kg
Answer : C
48. Minimum potential energy of a system will be in the position of
A. Stable equilibrium
B. Unstable equilibrium
C. Neutral equilibrium
D. All of the above
Answer : A
A. Stable equilibrium
B. Unstable equilibrium
C. Neutral equilibrium
D. All of the above
Answer : A
49. The shape of a suspended cable for a uniformly distributed load over it is
A. Circular
B. Parabolic
C. Catenary
D. Cubic parabola
Answer : B
A. Circular
B. Parabolic
C. Catenary
D. Cubic parabola
Answer : B
50. For a non-concurrent force system to be in equilibrium
A. Only the closure of force polygon is sufficient
B. Only the closure of funicular polygon is sufficient
C. Both force polygon and funicular polygon must close
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Only the closure of force polygon is sufficient
B. Only the closure of funicular polygon is sufficient
C. Both force polygon and funicular polygon must close
D. None of the above
Answer : C
Sharing is caring
Related Post
General Physics MCQ Solved Paper for SSC JHT
XAT - Building Materials 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ CorelDraw Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Theory of Machines Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
SSC CPO - General knowledge 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
GMAT - PageMaker 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download