1000+ Basics of Economics MCQ for RRB JE [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Which industries spend a relatively large share of their revenue on research and development in order to keep up with their competitors?
A. Grocery stores
B. High-Tech industries
C. Automobiles
D. Construction
Answer : B
A. Grocery stores
B. High-Tech industries
C. Automobiles
D. Construction
Answer : B
2. The average fixed cost (AFC) curve is asymptote to:
A. X-axis
B. Y-axis
C. Z-axis
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. X-axis
B. Y-axis
C. Z-axis
D. None of the above
Answer : A
3. If X and Y are close substitutes, a rise in the price of X will lead to:
A. Increase in demand for Y
B. Decrease in demand for Y
C. Decrease in demand for both X and Y
D. No change in demand for Y
Answer : A
A. Increase in demand for Y
B. Decrease in demand for Y
C. Decrease in demand for both X and Y
D. No change in demand for Y
Answer : A
4. The budget constraint equation of the firm is:
A.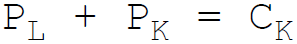
B.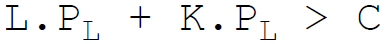
C.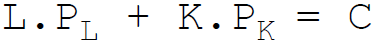
D.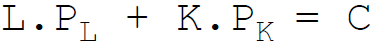
Answer : C
A.
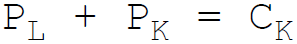
B.
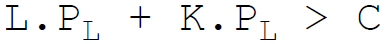
C.
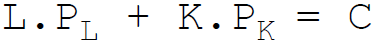
D.
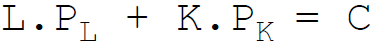
Answer : C
5. The average cost curve is a geometrical illustration of:
A. Hydraulic function
B. Cubic function
C. Pentagonic function
D. Quadratic function
Answer : D
A. Hydraulic function
B. Cubic function
C. Pentagonic function
D. Quadratic function
Answer : D
6. The least cost combination of factors x , y and z will generally be the point at which:
A. Price of x = Price of z Price of y Price of x
B. MP of x = MP of y Price of x Price of x
C. MP of x = MP of y = MP of z Price of x Price of y Price of z
D. MP of x = MP of y = MP of z
Answer : C
A. Price of x = Price of z Price of y Price of x
B. MP of x = MP of y Price of x Price of x
C. MP of x = MP of y = MP of z Price of x Price of y Price of z
D. MP of x = MP of y = MP of z
Answer : C
7. Microeconomics is also known as:
A. Price theory
B. Demand theory
C. Supply theory
D. Income theory
Answer : A
A. Price theory
B. Demand theory
C. Supply theory
D. Income theory
Answer : A
8. Variable costs refer to:
A. Capital cost plus operating costs
B. Capital costs alone
C. Capital costs plus spill-over costs
D. Operating costs alone
Answer : D
A. Capital cost plus operating costs
B. Capital costs alone
C. Capital costs plus spill-over costs
D. Operating costs alone
Answer : D
9. Supply of a commodity refers to:
A. Total stock of a commodity in the market
B. Total production of a commodity during the year
C. Total production plus total stock of a commodity
D. Amount of commodity offered for sale at some price at a particular place and time
Answer : D
A. Total stock of a commodity in the market
B. Total production of a commodity during the year
C. Total production plus total stock of a commodity
D. Amount of commodity offered for sale at some price at a particular place and time
Answer : D
10. The number of sellers in duopoly is:
A. A few
B. Four
C. Two
D. Very large
Answer : C
A. A few
B. Four
C. Two
D. Very large
Answer : C
11. The situation in between the extremes of the govt. controlled, planned economy and the perfectly free, unplanned economy is known as:
A. Developed economy
B. Laissez-fair economy
C. Mixed economy
D. Capitalistic economy
Answer : C
A. Developed economy
B. Laissez-fair economy
C. Mixed economy
D. Capitalistic economy
Answer : C
12. Consumers Surplus can also be defined as:
A. Extra price benefits
B. Shortage of quantity
C. Surplus of quantity
D. Difference between actual price and potential price
Answer : D
A. Extra price benefits
B. Shortage of quantity
C. Surplus of quantity
D. Difference between actual price and potential price
Answer : D
13. Most of the supply curves with which the average consumer deals are:
A. Vertical
B. Horizontal
C. Controlled by the largest producers
D. Unaffected by inflation
Answer : B
A. Vertical
B. Horizontal
C. Controlled by the largest producers
D. Unaffected by inflation
Answer : B
14. When total product increases at a decreasing rate:
A. MP = AP
B. MP < AP
C. MP > AP =0
D. MP > AP
Answer : D
A. MP = AP
B. MP < AP
C. MP > AP =0
D. MP > AP
Answer : D
15. Any straight line supply which cuts the x-axis will have:
A. Zero elasticity
B. An elasticity greater than one
C. Unitary elasticity of supply
D. An elasticity less than one
Answer : B
A. Zero elasticity
B. An elasticity greater than one
C. Unitary elasticity of supply
D. An elasticity less than one
Answer : B
16. The non-price competition cartel is a:
A. stable cartel
B. unstable cartel
C. prominent cartel
D. special cartel
Answer : B
A. stable cartel
B. unstable cartel
C. prominent cartel
D. special cartel
Answer : B
17. The law of variable proportions comes into being when:
A. All factors are variable
B. There is a fixed factor and variable factor
C. All factors are non-variable
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. All factors are variable
B. There is a fixed factor and variable factor
C. All factors are non-variable
D. None of the above
Answer : B
18. The slope of budget line shows the price ratios of:
A. Many goods
B. Few goods
C. Two goods
D. Three goods
Answer : C
A. Many goods
B. Few goods
C. Two goods
D. Three goods
Answer : C
19. Marginal cost is the cost:
A. Of the last unit of production
B. Of marginal unit
C. Of marginal efficient units
D. Of the average units of production
Answer : A
A. Of the last unit of production
B. Of marginal unit
C. Of marginal efficient units
D. Of the average units of production
Answer : A
20. Airlines that try to lower fares in order to increase revenues believe that demand for airline services is:
A. Price elastic
B. Price inelastic
C. Income elastic
D. Income inelastic
Answer : A
A. Price elastic
B. Price inelastic
C. Income elastic
D. Income inelastic
Answer : A
21. The long run average cost curve is the envelope of:
A. SACs
B. LACs
C. SMCs
D. LMCs
Answer : A
A. SACs
B. LACs
C. SMCs
D. LMCs
Answer : A
22. Of the following, which one corresponds to fixed cost?
A. Payments for raw materials
B. Labor cost
C. Transportation charges
D. Insurance premium on property
Answer : D
A. Payments for raw materials
B. Labor cost
C. Transportation charges
D. Insurance premium on property
Answer : D
23. The partial equilibrium model keeps other things:
A. Variable
B. Constant
C. Increasing
D. Decreasing
Answer : B
A. Variable
B. Constant
C. Increasing
D. Decreasing
Answer : B
24. All the firms with identical costs under perfect competition well, in the long-run, earn only:
A. Normal profits
B. Abnormal profits
C. Differential profits
D. No profits
Answer : A
A. Normal profits
B. Abnormal profits
C. Differential profits
D. No profits
Answer : A
25. Price elasticity of demand can be measured in the following way:
A. Percentage change in quantity demanded of a commodity divided by percentage change in price of that commodity
B. Change in quantity demanded of a commodity divided by change in price of that commodity
C. Percentage change in price of a commodity divided by percentage change in quantity demanded of that commodity
D. None of that commodity
Answer : A
A. Percentage change in quantity demanded of a commodity divided by percentage change in price of that commodity
B. Change in quantity demanded of a commodity divided by change in price of that commodity
C. Percentage change in price of a commodity divided by percentage change in quantity demanded of that commodity
D. None of that commodity
Answer : A
26. The firm in cournot model:
A. face costs
B. face taxes
C. donot face taxes
D. donot face costs
Answer : D
A. face costs
B. face taxes
C. donot face taxes
D. donot face costs
Answer : D
27. Under monopolistic competition, in long-run there is:
A. Ban on exit
B. Ban on entry
C. Free entry
D. Free entry and exit
Answer : D
A. Ban on exit
B. Ban on entry
C. Free entry
D. Free entry and exit
Answer : D
28. If the supply and demand increases equally, the price will:
A. Rise
B. Fall
C. Remain unchanged
D. Change depending on respective elasticities
Answer : C
A. Rise
B. Fall
C. Remain unchanged
D. Change depending on respective elasticities
Answer : C
29. If the price of product increases and in the result the demand for product B also increases then:
A. A and B are substitute goods
B. A and B are complementary goods
C. A is inferior to B
D. A is superior to B
Answer : A
A. A and B are substitute goods
B. A and B are complementary goods
C. A is inferior to B
D. A is superior to B
Answer : A
30. In respect of which of the following category of goods is consumers surplus highest?
A. Giffen goods
B. Necessities
C. Luxuries
D. Prestige goods
Answer : B
A. Giffen goods
B. Necessities
C. Luxuries
D. Prestige goods
Answer : B
31. While buying two goods X and Y with unequal prices, to maximize total utility from his income, a consumer should get:
A. Equal MU from both commodities X and Y
B. More MU from commodity X than from commodity Y
C. More MU from commodity Y than from commodity X
D. Equal marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity X and commodity Y
Answer : D
A. Equal MU from both commodities X and Y
B. More MU from commodity X than from commodity Y
C. More MU from commodity Y than from commodity X
D. Equal marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity X and commodity Y
Answer : D
32. The elliptical isoquant represents the:
A. Economic combinations of labor and capital
B. Uneconomic combinations of labor and capital
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Economic combinations of labor and capital
B. Uneconomic combinations of labor and capital
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : C
33. Under monopolistic competition, the products sold by the firms are:
A. Economic substitutes
B. Technical substitutes
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Economic substitutes
B. Technical substitutes
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : C
34. Neutral Technological Progress can be defined as:
A. Technological progress that causes to raise the marginal product of capital and labor in the same proportion
B. Technological progress that causes the marginal product of capital to increase relative to the marginal product of labor
C. Technological progress that causes the marginal product of labor to increase relative to the marginal product of capital
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Technological progress that causes to raise the marginal product of capital and labor in the same proportion
B. Technological progress that causes the marginal product of capital to increase relative to the marginal product of labor
C. Technological progress that causes the marginal product of labor to increase relative to the marginal product of capital
D. None of the above
Answer : A
35. In the long run:
A. All factors can be used in different proportions
B. Management can be re-organized
C. A firm can experience returns to scale
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. All factors can be used in different proportions
B. Management can be re-organized
C. A firm can experience returns to scale
D. All of the above
Answer : D
36. Of the following commodities, which has the lowest price-elasticity of demand?
A. Car
B. Salt
C. Tea
D. House
Answer : B
A. Car
B. Salt
C. Tea
D. House
Answer : B
37. Which one of the following has been the most influential work of F.H.Knight?
A. Freedom and Reform
B. The Green Revolution
C. Economic Integration
D. Risk ,Uncertainty and Profit
Answer : D
A. Freedom and Reform
B. The Green Revolution
C. Economic Integration
D. Risk ,Uncertainty and Profit
Answer : D
38. Marginal utility (MU) always:
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains constant
D. None of above
Answer : B
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains constant
D. None of above
Answer : B
39. Other things remaining the same, when a consumers income increases his equilibrium point moves to:
A. A lower indifference curve
B. A lower PPC curve
C. Remains on same indifference curve
D. A higher indifference curve
Answer : D
A. A lower indifference curve
B. A lower PPC curve
C. Remains on same indifference curve
D. A higher indifference curve
Answer : D
40. Income -elasticity of demand will be zero when a given change in income brings about:
A. A less than proportionate change in quantity demanded
B. A more than proportionate change in quantity demanded
C. The same proportionate change in quantity demanded
D. No change in quantity demanded
Answer : D
A. A less than proportionate change in quantity demanded
B. A more than proportionate change in quantity demanded
C. The same proportionate change in quantity demanded
D. No change in quantity demanded
Answer : D
41. The main contribution of Prof.Robbins is in the field of:
A. human welfare
B. national income
C. multiplicity of wants and scarcity of resources
D. theory of production
Answer : C
A. human welfare
B. national income
C. multiplicity of wants and scarcity of resources
D. theory of production
Answer : C
42. The name of the system of direct exchange is:
A. Price system
B. Barter system
C. Islamic economic system
D. Socialistic system
Answer : B
A. Price system
B. Barter system
C. Islamic economic system
D. Socialistic system
Answer : B
43. If as a result of an increase in prices, total outlay (expenditures) on a commodity decreases, its price-elasticity of demand is:
A. Perfect elastic (infinitely elastic)
B. Relatively elastic (greater than one elasticity)
C. Unit elastic
strong>D. Relatively inelastic (less than one elasticity)
Answer : B
A. Perfect elastic (infinitely elastic)
B. Relatively elastic (greater than one elasticity)
C. Unit elastic
strong>D. Relatively inelastic (less than one elasticity)
Answer : B
44. Marginal revenue from a given output:
A. The price at which the marginal unit sells
B. Total revenue sale of all units divided by volume of sales
C. Average revenue of total output average revenue of last unit
D. The change in total revenue resulting from the sale of one unit more of output
Answer : D
A. The price at which the marginal unit sells
B. Total revenue sale of all units divided by volume of sales
C. Average revenue of total output average revenue of last unit
D. The change in total revenue resulting from the sale of one unit more of output
Answer : D
45. A vertical supply curve parallel to the price axis implies that the elasticity of supply is:
A. Zero
B. Infinite
C. Equal to one
D. Greater than zero but less than infinite
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Infinite
C. Equal to one
D. Greater than zero but less than infinite
Answer : A
46. In discriminating monopoly (price discrimination), the elasticity of demand of product in two markets are:
A. Different
B. Same
C. Zero
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Different
B. Same
C. Zero
D. None of the above
Answer : A
47. In the immediate run:
A. Supply curves are inelastic
B. Supply curves are perfectly elastic
C. Demand curves are elastic
D. Supply curves are elastic
Answer : A
A. Supply curves are inelastic
B. Supply curves are perfectly elastic
C. Demand curves are elastic
D. Supply curves are elastic
Answer : A
48. All money costs can be regarded as:
A. Social costs
B. Opportunity costs
C. Explicit costs
D. Implicit costs
Answer : C
A. Social costs
B. Opportunity costs
C. Explicit costs
D. Implicit costs
Answer : C
49. Implicit costs are the costs:
A. Which are not incurred by the firm and may accrue to the community
B. Of resources the cost of factors owned by the firm
C. Of resources supplied by the household
D. Of government externalities
Answer : B
A. Which are not incurred by the firm and may accrue to the community
B. Of resources the cost of factors owned by the firm
C. Of resources supplied by the household
D. Of government externalities
Answer : B
50. Time Preference Theory of Interest was presented by:
A. Adam Smith
B. Carl Menger
C. Ruskin
D. J.B.Say
Answer : B
A. Adam Smith
B. Carl Menger
C. Ruskin
D. J.B.Say
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
LSAT - PageMaker 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Electricity Fundamentals 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC CGL
1000+ Asp Programming MCQ for GATE [Solved]
Animal Kingdom 1000+ MCQ with answer for GRE
UPSC CDS - Indian History 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
RBI Assistant - Sentence Correction 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download