1000+ Basics of Economics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. If cross-elasticity of one commodity for another turns out to be zero, it means they are:
A. Close substitutes
B. Good complements
C. Completely unrelated (independent goods)
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Close substitutes
B. Good complements
C. Completely unrelated (independent goods)
D. None of the above
Answer : C
2. Cross-elasticity of demand is measured as:
A. Percentage change in the quantity of a commodity demanded divided by the percentage change in the price of that commodity
B. Percentage change in the quantity of commodity X divided by percentage change in the price of commodity Y
C. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X
D. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X divided by percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity Y
Answer : B
A. Percentage change in the quantity of a commodity demanded divided by the percentage change in the price of that commodity
B. Percentage change in the quantity of commodity X divided by percentage change in the price of commodity Y
C. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X
D. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X divided by percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity Y
Answer : B
3. The basic subject matter of economics is:
A. Money
B. Capital resources
C. Scarcity
D. Inflation
Answer : B
A. Money
B. Capital resources
C. Scarcity
D. Inflation
Answer : B
4. Duopoly is a market where there are:
A. Two sellers
B. A few sellers
C. Five sellers
D. Many sellers
Answer : A
A. Two sellers
B. A few sellers
C. Five sellers
D. Many sellers
Answer : A
5. Elasticity of demand is equal to unity while marginal revenue is:
A. Positive
B. Zero
C. Negative
D. Indeterminate
Answer : B
A. Positive
B. Zero
C. Negative
D. Indeterminate
Answer : B
6. In market sharing cartel model, cartel determines the shares of:
A. the individuals
B. industry
C. firms
D. associations
Answer : C
A. the individuals
B. industry
C. firms
D. associations
Answer : C
7. In collusive olligopoly, the firms may make:
A. Open agreements
B. Secret agreements
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Open agreements
B. Secret agreements
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : C
8. Moving along the indifference curve leaves the consumer:
A. Better off
B. Worse off
C. In equilibrium
D. Neither better off nor Worse off
Answer : D
A. Better off
B. Worse off
C. In equilibrium
D. Neither better off nor Worse off
Answer : D
9. Dumping is international discriminating:
A. Monopoly
B. Oligopoly
C. Duopoly
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Monopoly
B. Oligopoly
C. Duopoly
D. None of the above
Answer : A
10. Which of the following has more elastic demand curve?
A. A commodity without substitutes
B. A commodity with substitutes
C. A commodity on which a small fraction of income is spent
D. A commodity the use of which cannot be postponed
Answer : B
A. A commodity without substitutes
B. A commodity with substitutes
C. A commodity on which a small fraction of income is spent
D. A commodity the use of which cannot be postponed
Answer : B
11. To get more revenue, a Finance Minister impose tax on that commodity which has:
A. Inelastic demand
B. Elastic demand
C. Unit elasticity
D. Zero elasticity
Answer : A
A. Inelastic demand
B. Elastic demand
C. Unit elasticity
D. Zero elasticity
Answer : A
12. In monopolistic competition, the firm compete on the basis of:
A. Price
B. Entry
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Price
B. Entry
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : C
13. The consumer is in equilibrium at the where:
A. Budget line and indifference curve intersect each other
B. Budget line and indifference curve are tangent to each other
C. Budget line and indifference curve are opposite to each other
D. Budget line and indifference curve are parallel to each other
Answer : B
A. Budget line and indifference curve intersect each other
B. Budget line and indifference curve are tangent to each other
C. Budget line and indifference curve are opposite to each other
D. Budget line and indifference curve are parallel to each other
Answer : B
14. In terms of price, the indirect utility function may be:
A. Concave
B. Quasi-convex
C. Straight line
D. Convex
Answer : B
A. Concave
B. Quasi-convex
C. Straight line
D. Convex
Answer : B
15. Engel curves shows that:
A. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of price
B. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of satisfaction
C. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of income
D. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of taxes
Answer : C
A. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of price
B. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of satisfaction
C. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of income
D. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of taxes
Answer : C
16. The number of sellers in oligopoly are:
A. Two
B. Many
C. Four
D. Very few
Answer : D
A. Two
B. Many
C. Four
D. Very few
Answer : D
17. The game theory is concerned with:
A. Perfect competition
B. Imperfect competition
C. Price discrimination
D. Duopoly and oligopoly
Answer : D
A. Perfect competition
B. Imperfect competition
C. Price discrimination
D. Duopoly and oligopoly
Answer : D
18. MC = MR = AC = AR shows the long run equilibrium position of the:
A. Competitive firm
B. Oligopolistic firm
C. Monopolist firm
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Competitive firm
B. Oligopolistic firm
C. Monopolist firm
D. None of the above
Answer : A
19. Demand for a commodity is elastic when it has
A. Only one use
B. Many uses
C. Uses which cannot be postponed
D. Uses very essential for the consumer
Answer : B
A. Only one use
B. Many uses
C. Uses which cannot be postponed
D. Uses very essential for the consumer
Answer : B
20. In microeconomics, we study:
A. Aggregates of the economy
B. Few units of the economy
C. Large units of the economy
D. Individual units of the economy
Answer : D
A. Aggregates of the economy
B. Few units of the economy
C. Large units of the economy
D. Individual units of the economy
Answer : D
21. Slope of a demand curve is:
A. Not relevant to elasticity
B. The only factor determining elasticity
C. Only one of the factors influencing elasticity
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Not relevant to elasticity
B. The only factor determining elasticity
C. Only one of the factors influencing elasticity
D. None of the above
Answer : B
22. Average cost curve contains in it:
A. Normal profits
B. No normal profits
C. Sometimes normal profits and sometimes no normal profits
D. Super normal profits
Answer : A
A. Normal profits
B. No normal profits
C. Sometimes normal profits and sometimes no normal profits
D. Super normal profits
Answer : A
A. Productive resources such as labor and capital equipment that firms use to manufacture goods and services are called inputs or factors of production
B. Unproductive resources that do not take part in production process are called inputs or factors of production
C. Firms own resources are called inputs or factors of production
D. None of the above
Answer : A
24. The MC curve cuts the AVC and ATC curves:
A. At different points
B. At the falling parts of each
C. At their respective minimums
D. At the rising parts of each
Answer : C
A. At different points
B. At the falling parts of each
C. At their respective minimums
D. At the rising parts of each
Answer : C
25. The partial equilibrium model keeps other things:
A. Variable
B. Constant
C. Increasing
D. Decreasing
Answer : B
A. Variable
B. Constant
C. Increasing
D. Decreasing
Answer : B
26. The cobweb model will convergent when the slope of:
A. Demand curve is more than supply curve
B. Supply curve is more than demand curve
C. Supply curve is equal to demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Demand curve is more than supply curve
B. Supply curve is more than demand curve
C. Supply curve is equal to demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : A
27. In long run, a firm can change:
A. Fixed factors
B. Variable factors
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. Fixed factors
B. Variable factors
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
28. Substitution effect means a consumer
A. Shifts away from the commodity the price of which has fallen
B. Shifts in favour of a commodity the price of which has risen
C. Shifts away from a commodity the price of which has risen, in favour of a commodity the price of which has fallen
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Shifts away from the commodity the price of which has fallen
B. Shifts in favour of a commodity the price of which has risen
C. Shifts away from a commodity the price of which has risen, in favour of a commodity the price of which has fallen
D. None of the above
Answer : C
29. In monopoly and perfect competition, TC curves are:
A. Different
B. Similar
C. Opposite
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Different
B. Similar
C. Opposite
D. None of the above
Answer : B
30. The spending of money by the producer to influence consumers is an example of:
A. Derived demand
B. Joint demand
C. Demand creation
D. Compressed demand
Answer : C
A. Derived demand
B. Joint demand
C. Demand creation
D. Compressed demand
Answer : C
31. At high prices, demand is likely to be:
A. More elastic
B. Less elastic
C. Unit elastic
D. Perfectly inelastic
Answer : A
A. More elastic
B. Less elastic
C. Unit elastic
D. Perfectly inelastic
Answer : A
32. Increasing return to scales can be explained in terms of:
A. Optimal factor proportions
B. Fixed scale of plant
C. External and internal economies
D. Labor productivity
Answer : C
A. Optimal factor proportions
B. Fixed scale of plant
C. External and internal economies
D. Labor productivity
Answer : C
33. The average product is given as:
A. Q.L
B. Q- L
C. Q+ L
D. Q/L
Answer : D
A. Q.L
B. Q- L
C. Q+ L
D. Q/L
Answer : D
34. MRSxy measures:
A. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and still remain on the same indifference curve
B. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and still remain on the same indifference curve
C. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and move to a higher indifference curve
D. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and move to a higher indifference curve
Answer : B
A. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and still remain on the same indifference curve
B. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and still remain on the same indifference curve
C. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and move to a higher indifference curve
D. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and move to a higher indifference curve
Answer : B
35. In monopolistic competition (also in kinked demand curve model), a firm sells the amount where:
A. Individual demand curve (IDC) is equal to proportional demand curve (PDC)
B. Individual demand curve (IDC) is greater than proportional demand curve (PDC)
C. Individual demand curve (IDC) is less than proportional demand curve (PDC)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Individual demand curve (IDC) is equal to proportional demand curve (PDC)
B. Individual demand curve (IDC) is greater than proportional demand curve (PDC)
C. Individual demand curve (IDC) is less than proportional demand curve (PDC)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
36. Which of the following formula determine the income elasticity of demand?:
A. Proportionate change in demand Proportionate change in price
B. Proportional change in the purchase of Y Proportional change in the price of X
C. Proportionate change in demand Proportionate change in income
D. Proportionate change in demand Proportionate change in price
Answer : C
A. Proportionate change in demand Proportionate change in price
B. Proportional change in the purchase of Y Proportional change in the price of X
C. Proportionate change in demand Proportionate change in income
D. Proportionate change in demand Proportionate change in price
Answer : C
37. If a commodity sold under monopoly is got free of cost, then MC will be:
A. Zero
B. Identical with the MR
C. A horizontal straight line
D. Infinite
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Identical with the MR
C. A horizontal straight line
D. Infinite
Answer : A
38. Other things remaining the same, when a consumers income increases his equilibrium point moves to:
A. A lower indifference curve
B. A lower PPC curve
C. Remains on same indifference curve
D. A higher indifference curve
Answer : D
A. A lower indifference curve
B. A lower PPC curve
C. Remains on same indifference curve
D. A higher indifference curve
Answer : D
39. If the commodities X and Y are perfect substitutes then:
A.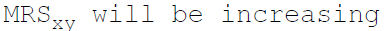 B.
B. 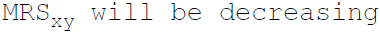
C.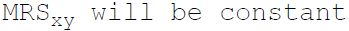 >
>
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A.
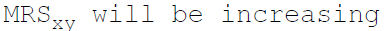 B.
B. 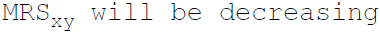
C.
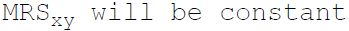 >
> D. None of the above
Answer : C
40. The demand curve of giffen goods will be:
A. Negatively sloped
B. Positively sloped
C. Parallel to X-axis
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Negatively sloped
B. Positively sloped
C. Parallel to X-axis
D. None of the above
Answer : B
41. Which one of the following is also known as Plant Curves:
A. Long-run average cost (LAC) curves
B. Short-run average cost (SAC) curves
C. Average variable cost (AVC) curves
D. Average total cost (ATC) curves
Answer : B
A. Long-run average cost (LAC) curves
B. Short-run average cost (SAC) curves
C. Average variable cost (AVC) curves
D. Average total cost (ATC) curves
Answer : B
42. 7.In an economy based on the price system the decision on what shall be produced is made by:
A. Government
B. Consumer
C. Producer
D. Stock holder
Answer: B
A. Government
B. Consumer
C. Producer
D. Stock holder
Answer: B
43. The name of the system of direct exchange is:
A. Price system
B. Barter system
C. Islamic economic system
D. Socialistic system
Answer : B
A. Price system
B. Barter system
C. Islamic economic system
D. Socialistic system
Answer : B
44. For a few products such as insulin for diabetics,:
A. The demand curve can be upward sloping
B. The price elasticity of demand could be zero
C. The price elasticity of demand could be greater than one
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. The demand curve can be upward sloping
B. The price elasticity of demand could be zero
C. The price elasticity of demand could be greater than one
D. None of the above
Answer : B
45. Total profits are maximized at the point where:
A. TR equals TC
B. The TR curve and the TC curve intersect such that TR and TC lie at the same point
C. The TR curve and the TC curve are parallel and TC exceeds TR
D. The TR curve and the TC curve are parallel and TR exceeds TC
Answer : D
A. TR equals TC
B. The TR curve and the TC curve intersect such that TR and TC lie at the same point
C. The TR curve and the TC curve are parallel and TC exceeds TR
D. The TR curve and the TC curve are parallel and TR exceeds TC
Answer : D
46. The elasticity of demand is equal to slope of demand function divided by:
A. Average demand function
B. Qualified demand function
C. Constructive demand function
D. Relative demand function
Answer : A
A. Average demand function
B. Qualified demand function
C. Constructive demand function
D. Relative demand function
Answer : A
47. A maximin strategy:
A. Maximizes the minimum gain that can be earned
B. Maximizes the gain of one player, but minimizes the gain of the opponent
C. Minimizes the maximum gain that can be earned
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Maximizes the minimum gain that can be earned
B. Maximizes the gain of one player, but minimizes the gain of the opponent
C. Minimizes the maximum gain that can be earned
D. None of the above
Answer : A
48. In short run, a firm can change its:
A. Total production
B. Fixed production
C. Variable production
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Total production
B. Fixed production
C. Variable production
D. None of the above
Answer : C
49. The substitution effect works to encourage a consumer to purchase more of a product when the price of that good is falling because:
A. The consumers real income has increased
B. The consumers real income has decreased
C. The product is now relatively less expensive than before
D. Other products are now less expensive than before
Answer : C
A. The consumers real income has increased
B. The consumers real income has decreased
C. The product is now relatively less expensive than before
D. Other products are now less expensive than before
Answer : C
50. The utility function u = f(x) is based upon :
A. Two goods
B. Few goods
C. One good
D. Zero goods
Answer : C
A. Two goods
B. Few goods
C. One good
D. Zero goods
Answer : C
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Urothelial tumors of the upper & lower urinary tracts MCQ for IBPS SO [Solved]
Urologic infections and inflammations MCQ Solved Paper for RRB Group D
1000+ Compressors, Gas Turbines & Jet Engines Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
SSC GD - Anatomy of flowering plant 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Software Engineering 1000+ MCQ with answer for LSAT
Multimedia and Graphics 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC Scientific Assistant