1000+ Basics of Economics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. According to the principle of substitution?
A. Many goods have no effective substitutes
B. Nearly all goods have substitutes
C. The prices of substitute goods must be the same
D. Buyers will stop buying a good if its price rises
Answer : B
A. Many goods have no effective substitutes
B. Nearly all goods have substitutes
C. The prices of substitute goods must be the same
D. Buyers will stop buying a good if its price rises
Answer : B
2. The Cambridge School of Thought refers to the group of English economists who came under the influence of:
A. Alfred Marshal
B. J.M.Keynes
C. Paul A.Samuelson
D. A.C.Pigou
Answer : A
A. Alfred Marshal
B. J.M.Keynes
C. Paul A.Samuelson
D. A.C.Pigou
Answer : A
3. A significant property of the Cobb-Douglas production function is that the elasticity of substitution between inputs is:
A. Greater than one
B. Less than one
C. Zero
D. Equal to one
Answer : D
A. Greater than one
B. Less than one
C. Zero
D. Equal to one
Answer : D
4. Total fixed costs are:
A.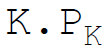
B.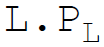
C.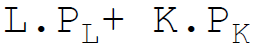
D.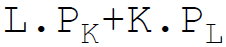
Answer : A
A.
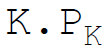
B.
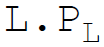
C.
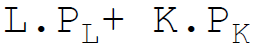
D.
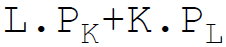
Answer : A
5. In non-collusive oligopoly firms enter into:
A. Secret agreements
B. No secret agreements
C. Bad habits
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Secret agreements
B. No secret agreements
C. Bad habits
D. None of the above
Answer : B
6. At the point where the straight line from the origin is tangent to the TC curve, AC is:
A. Maximum
B. Minimum
C. Equal
D. Lower
Answer : B
A. Maximum
B. Minimum
C. Equal
D. Lower
Answer : B
7. Income-elasticity of demand is expressed as:
A. % change in quantity demanded % change in income
B. % change in income % change in quantity demanded
C. Change in income Change in quantity demanded
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. % change in quantity demanded % change in income
B. % change in income % change in quantity demanded
C. Change in income Change in quantity demanded
D. None of the above
Answer : A
8. Law of Substitution in production was presented by:
A. Classical economists
B. Keynes
C. Neo-classical economists
D. Karl Marx
Answer : A
A. Classical economists
B. Keynes
C. Neo-classical economists
D. Karl Marx
Answer : A
9. If less is demanded at the same price or same quantity demanded at a lower price, it is a case of:
A. Contraction of demand
B. Decrease in demand
C. Increase in demand
D. Extension of demand
Answer : B
A. Contraction of demand
B. Decrease in demand
C. Increase in demand
D. Extension of demand
Answer : B
10. Under monopolistic competition, in long-run there is:
A. Ban on exit
B. Ban on entry
C. Free entry
D. Free entry and exit
Answer : D
A. Ban on exit
B. Ban on entry
C. Free entry
D. Free entry and exit
Answer : D
11. The concept of period refers to:
A. A specific duration of time
B. A varying duration of time
C. A duration of time which permits necessary adjustments
D. A period with calculated intervals
Answer : B
A. A specific duration of time
B. A varying duration of time
C. A duration of time which permits necessary adjustments
D. A period with calculated intervals
Answer : B
12. Who is the founder of classical school of thought?
A. David Ricardo
B. Adam Smith
C. T.R.Malthus
D. J.S.Mill
Answer : B
A. David Ricardo
B. Adam Smith
C. T.R.Malthus
D. J.S.Mill
Answer : B
13. The long run total cost is attained by:
A. LMC.Q
B. AC.Q
C. LC.Q
D. LAC.Q
Answer : D
A. LMC.Q
B. AC.Q
C. LC.Q
D. LAC.Q
Answer : D
14. Law of Variable Proportions is regarding in:
A. Short-Run
B. Long-Run
C. Medium-Run
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Short-Run
B. Long-Run
C. Medium-Run
D. None of the above
Answer : A
15. Price leadership is associated with:
A. Collusive oligopoly
B. Non-collusive oligopoly
C. Cartel
D. Perfect competition
Answer : A
A. Collusive oligopoly
B. Non-collusive oligopoly
C. Cartel
D. Perfect competition
Answer : A
16. The point where the supply and demand curves intersect on a graph determines:
A. Market price
B. Equilibrium price
C. Long-term price
D. Short-term price
Answer : B
A. Market price
B. Equilibrium price
C. Long-term price
D. Short-term price
Answer : B
17. All the firms with identical costs under perfect competition well, in the long-run, earn only:
A. Normal profits
B. Abnormal profits
C. Differential profits
D. No profits
Answer : A
A. Normal profits
B. Abnormal profits
C. Differential profits
D. No profits
Answer : A
18. Economics define technology as:
A. Societys knowledge of production
B. Applied science
C. Knowledge of science and mathematics
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Societys knowledge of production
B. Applied science
C. Knowledge of science and mathematics
D. None of the above
Answer : A
19. Production function relates:
A. Cost to input
B. Wages to profits
C. Cost to output
D. Inputs to output
Answer : D
A. Cost to input
B. Wages to profits
C. Cost to output
D. Inputs to output
Answer : D
20. When elasticity of demand is greater than one (e >1), then following the formula MR=P[1-1/e], the MR will:
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. None of the above
Answer : A
21. Given a U shaped average cost curve, the relationship between average cost and marginal cost is such that marginal cost must always be:
A. Falling when average cost is falling
B. Rising when average cost is falling
C. Falling when average cost is rising
D. Rising when average cost is rising
Answer : D
A. Falling when average cost is falling
B. Rising when average cost is falling
C. Falling when average cost is rising
D. Rising when average cost is rising
Answer : D
22. A decrease in demand lowers the price the most:
A. In the immediate run
B. In the short run
C. When the supply is perfectly elastic
D. When producers have sufficient time to fuly adjust to the demand change
Answer : A
A. In the immediate run
B. In the short run
C. When the supply is perfectly elastic
D. When producers have sufficient time to fuly adjust to the demand change
Answer : A
23. The maximization of output subject to cost requires equilibrium at the:
A. Lowest isoquant
B. Lowest isocost line
C. Highest isoquant
D. Highest isocost line
Answer : C
A. Lowest isoquant
B. Lowest isocost line
C. Highest isoquant
D. Highest isocost line
Answer : C
24. When AC curve falls, MC curve falls:
A. More than AC curve
B. Less than AC curve
C. Equal to AC curve
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. More than AC curve
B. Less than AC curve
C. Equal to AC curve
D. None of the above
Answer : A
25. In monopolistic competition, the cost curves of all firms are:
A. Uniform
B. Different
C. Dependent
D. Independent
Answer : A
A. Uniform
B. Different
C. Dependent
D. Independent
Answer : A
26. If as a result of an increase in prices, total outlay (expenditures) on a commodity decreases, its price-elasticity of demand is:
A. Perfect elastic (infinitely elastic)
B. Relatively elastic (greater than one elasticity)
C. Unit elastic
D. Relatively inelastic (less than one elasticity)
Answer : B
A. Perfect elastic (infinitely elastic)
B. Relatively elastic (greater than one elasticity)
C. Unit elastic
D. Relatively inelastic (less than one elasticity)
Answer : B
27. The combination of labor and capital where the cost of a given output is minimized is known as:
A. Least cost factor combination
B. Optimum factor combination
C. Both a and b
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. Least cost factor combination
B. Optimum factor combination
C. Both a and b
D. None of them
Answer : C
28. According to Chamberlin, the activity of a monopolistic competitive firm:
A. Get noticed by the rival firms
B. Get unnoticed by the rival firms
C. Get noticed by the employees of the rival firms
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Get noticed by the rival firms
B. Get unnoticed by the rival firms
C. Get noticed by the employees of the rival firms
D. None of the above
Answer : B
29. The products, under monopolistic competition are differentiated, yet they are:
A. Complements
B. Close substitutes
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Complements
B. Close substitutes
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : B
30. In monopolistic competition, the customers are attached with one product because of:
A. Product similarity
B. Product differentiations
C. Product inferiority
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Product similarity
B. Product differentiations
C. Product inferiority
D. None of the above
Answer : B
31. In monopolistic competition (also in kinked demand curve model), a firm sells the amount where:
A. Individual demand curve (IDC) is equal to proportional demand curve (PDC)
B. Individual demand curve (IDC) is greater than proportional demand curve (PDC)
C. Individual demand curve (IDC) is less than proportional demand curve (PDC)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Individual demand curve (IDC) is equal to proportional demand curve (PDC)
B. Individual demand curve (IDC) is greater than proportional demand curve (PDC)
C. Individual demand curve (IDC) is less than proportional demand curve (PDC)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
32. Under conditions of perfect competition, price in the long-run is equal to:
A. Minimum of average variable cost
B. Minimum of marginal cost
C. Minimum of average fixed cost
D. Minimum of average cost
Answer : D
A. Minimum of average variable cost
B. Minimum of marginal cost
C. Minimum of average fixed cost
D. Minimum of average cost
Answer : D
33. Which of the following would be least likely to cause a consumer to eat less beef?
A. An increase in the price of beef
B. An increase in the price of lamb
C. A reduction in the consumers income
D. A reduction in the price of lamb
Answer : B
A. An increase in the price of beef
B. An increase in the price of lamb
C. A reduction in the consumers income
D. A reduction in the price of lamb
Answer : B
34. Indifference curve represents:
A. Only two commodities
B. Only three commodities
C. More than three commodities
D. Any number of commodities
Answer : A
A. Only two commodities
B. Only three commodities
C. More than three commodities
D. Any number of commodities
Answer : A
35. In Prisoner Dilemma, the best choice of strategy is:
A. Stable
B. Unstable
C. Negative
D. Neutral
Answer : B
A. Stable
B. Unstable
C. Negative
D. Neutral
Answer : B
36. The average fixed cost (AFC) curve is asymptote to:
A. X-axis
B. Y-axis
C. Z-axis
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. X-axis
B. Y-axis
C. Z-axis
D. None of the above
Answer : A
37. In case of monopoly, when total revenue is maximum:
A. MR is positive
B. MR falls
C. MR rises
D. MR is zero
Answer : D
A. MR is positive
B. MR falls
C. MR rises
D. MR is zero
Answer : D
38. To get more revenue, a Finance Minister impose tax on that commodity which has:
A. Inelastic demand
B. Elastic demand
C. Unit elasticity
D. Zero elasticity
Answer : A
A. Inelastic demand
B. Elastic demand
C. Unit elasticity
D. Zero elasticity
Answer : A
39. Moving along the indifference curve leaves the consumer:
A. Better off
B. Worse off
C. In equilibrium
D. Neither better off nor Worse off
Answer : D
A. Better off
B. Worse off
C. In equilibrium
D. Neither better off nor Worse off
Answer : D
40. Indifference curves reflect:
A. Preferences
B. Income
C. Prices
D. Consumption
Answer : A
A. Preferences
B. Income
C. Prices
D. Consumption
Answer : A
41. Which is not an essential feature of a socialist economy?
A. Social ownership of the means of production
B. Freedom of enterprise
C. Use of centralized planning
D. Government decisions
Answer : B
A. Social ownership of the means of production
B. Freedom of enterprise
C. Use of centralized planning
D. Government decisions
Answer : B
42. If the commodity is inferior then the increase in income of the consumer results in:
A. More purchase
B. Less purchase
C. Same purchase
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. More purchase
B. Less purchase
C. Same purchase
D. None of the above
Answer : B
43. When price decreases and with it the total outlay on a commodity also decreases, it is a case of:
A. Perfect elasticity (infinitely elastic)
B. Relative elasticity (greater than one elasticity)
C. Perfect inelasticity (zero elasticity)
D. Relative inelasticity (less than one elasticity)
Answer : D
A. Perfect elasticity (infinitely elastic)
B. Relative elasticity (greater than one elasticity)
C. Perfect inelasticity (zero elasticity)
D. Relative inelasticity (less than one elasticity)
Answer : D
44. A price is a ratio of exchange between:
A. Money and exchange
B. Quantity and production
C. Production and consumption
D. Money and quantity
Answer : D
A. Money and exchange
B. Quantity and production
C. Production and consumption
D. Money and quantity
Answer : D
45. In cournot model, during the process of adjustment, the number of firms:
A. Donot change
B. Change
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Donot change
B. Change
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : A
46. In case of monopoly, both AR and MR fall, but MR falls:
A. Double to that of AR
B. 1/2 to that of AR
C. 2/3 to that of AR
D. Four times to that of AR
Answer : A
A. Double to that of AR
B. 1/2 to that of AR
C. 2/3 to that of AR
D. Four times to that of AR
Answer : A
47. The situation in between the extremes of the govt. controlled, planned economy and the perfectly free, unplanned economy is known as:
A. Developed economy
B. Laissez-fair economy
C. Mixed economy
D. Capitalistic economy
Answer : C
A. Developed economy
B. Laissez-fair economy
C. Mixed economy
D. Capitalistic economy
Answer : C
48. Perfect competition assumes:
A. All buyers and sellers have perfect knowledge of the market
B. Freedom of entry of firms into the industry
C. Homogeneous product
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. All buyers and sellers have perfect knowledge of the market
B. Freedom of entry of firms into the industry
C. Homogeneous product
D. All of the above
Answer : D
49. Which of the following is not characteristic of perfect competition?
A. Freedom of entry and exit
B. Each seller is a price taker
C. Perfect information about prices
D. Heterogeneous products
Answer : D
A. Freedom of entry and exit
B. Each seller is a price taker
C. Perfect information about prices
D. Heterogeneous products
Answer : D
50. Total utility and price are:
A. Directly related
B. Unrelated
C. Closely related
D. Negatively related
Answer : B
A. Directly related
B. Unrelated
C. Closely related
D. Negatively related
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
IBPS PO - Auto CAD 2D 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
CAT - Basics of Economics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Current Affairs August 2017 Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Current Affairs August 2017 1000+ MCQ with answer for GATE
WAN MCQ Solved Paper for FCI Recruitment
1000+ Automobile Engineering Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]