1000+ Basics of Neurology Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Topic: Alzheimer's Disease
Subject: Medicine
Which one of the following is associated with an increased risk of developing Alzheimers disease?
A. A positive homozygous genotype for apolipoprotein E4
B. Elevated serum aluminum
C. Elevated serum alpha-tocopherol
D. Decreased serum Beta-carotene
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
Which one of the following is associated with an increased risk of developing Alzheimers disease?
A. A positive homozygous genotype for apolipoprotein E4
B. Elevated serum aluminum
C. Elevated serum alpha-tocopherol
D. Decreased serum Beta-carotene
Answer : A
2. Topic: Peripheral Neuropathy
Subject: Medicine
A 68-year-old male presents to your department complaining of a very horrible sensation in his legs that started out 4 weeks ago as pins and needles tickling him but now has progressed and feels like being stabbed in his feet. He has started to use a walker because he feels that when he walks it feels like stepping on eggshells. The pain has not been responsive to acetaminophen and ibuprofen. The patients past medical history is significant for diabetes type II treated with metformin and glimepiride. The patient has not been very compliant with medications, especially metformin because he feels it causes him an upset stomach. His most recent HbA1C level was 9.8%. He also has hypercholesterolemia treated with lovastatin and hypertension treated with Lisinopril and amlodipine. His vital signs are temperature 37.4°C, BP is 125/70 mmHg, pulse 85/min, and respirations 15/min. The dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses are +2 bilaterally. No distal muscles weakness or atrophy is observed. Manual esthesiometer with monofilaments is used and reveals decreased sensation from the midfoot distally on both feet. There is no evidence of erythema, edema, or any wounds on either foot. He has tenderness to light touch on both feet. Labs reveal normal Vitamin B12 and thyroid function.
Which of the following would be the most appropriate treatment for this patients pain?
A. Daily metformin compliance
B. Metoclopramide
C. Pregabalin
D. Alpha lipoic acid
Answer : C
Subject: Medicine
A 68-year-old male presents to your department complaining of a very horrible sensation in his legs that started out 4 weeks ago as pins and needles tickling him but now has progressed and feels like being stabbed in his feet. He has started to use a walker because he feels that when he walks it feels like stepping on eggshells. The pain has not been responsive to acetaminophen and ibuprofen. The patients past medical history is significant for diabetes type II treated with metformin and glimepiride. The patient has not been very compliant with medications, especially metformin because he feels it causes him an upset stomach. His most recent HbA1C level was 9.8%. He also has hypercholesterolemia treated with lovastatin and hypertension treated with Lisinopril and amlodipine. His vital signs are temperature 37.4°C, BP is 125/70 mmHg, pulse 85/min, and respirations 15/min. The dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses are +2 bilaterally. No distal muscles weakness or atrophy is observed. Manual esthesiometer with monofilaments is used and reveals decreased sensation from the midfoot distally on both feet. There is no evidence of erythema, edema, or any wounds on either foot. He has tenderness to light touch on both feet. Labs reveal normal Vitamin B12 and thyroid function.
Which of the following would be the most appropriate treatment for this patients pain?
A. Daily metformin compliance
B. Metoclopramide
C. Pregabalin
D. Alpha lipoic acid
Answer : C
3. Topic: Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Subject: Medicine
A previously alert, otherwise healthy 74-year-old black male has a history of slowly developing progressive memory loss and dementia associated with urinary incontinence and gait disturbance resembling ataxia.
This presentation is most consistent with:
A. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
B. Alzheimers disease
C. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
D. Multiple sclerosis
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
A previously alert, otherwise healthy 74-year-old black male has a history of slowly developing progressive memory loss and dementia associated with urinary incontinence and gait disturbance resembling ataxia.
This presentation is most consistent with:
A. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
B. Alzheimers disease
C. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
D. Multiple sclerosis
Answer : A
4. Topic: Postherpetic Neuralgia
Subject: Medicine
When given during acute herpes zoster (varicella) infection, which one of the following drugs has been shown to reduce the incidence of postherpetic neuralgia?
A. Imipramine (Tofranil)
B. Capsaicin (Zostrix)
C. Amitriptyline
D. Acyclovir (Zovirax)
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
When given during acute herpes zoster (varicella) infection, which one of the following drugs has been shown to reduce the incidence of postherpetic neuralgia?
A. Imipramine (Tofranil)
B. Capsaicin (Zostrix)
C. Amitriptyline
D. Acyclovir (Zovirax)
Answer : D
5. Topic: Dementia
Subject: Medicine
Clinical features of multi-infarct dementia may include all of the following, except:
A. Parkinsonism
B. Deteriorating course
C. Evidence of cerebrovascular disease
D. Focal neurologic signs
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
Clinical features of multi-infarct dementia may include all of the following, except:
A. Parkinsonism
B. Deteriorating course
C. Evidence of cerebrovascular disease
D. Focal neurologic signs
Answer : A
6. Topic: Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Subject: Medicine
A 76-year-old male is brought to your office by his son. The patient complains of dizziness that has slowly been worsening over the past year. His description is vague, but he says that he notices the dizziness when he tries to walk. The review of systems is normal, except for increasing problems with his prostate in the last 6 months, with dribbling and accidents at times. The patient admits to going more often, and sometimes without warning. The son states that his father seems more forgetful, slower of speech, and not as full of life as he used to be. A neurologic examination reveals the patient to be oriented x 3, with a somewhat flat affect and a wide-based, slow, shuffling gate. The examination is otherwise normal. His Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score is 22 out of 30. No tremor is noted. A CBC, creatinine level, TSH level, vitamin B12 level and VDRL are all normal.
Which one of the following should you do next?
A. Order a brain MRI
B. Prescribe sertraline (Zoloft)
C. Prescribe carbidopa/levodopa (Sinemet)
D. Order physical therapy
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
A 76-year-old male is brought to your office by his son. The patient complains of dizziness that has slowly been worsening over the past year. His description is vague, but he says that he notices the dizziness when he tries to walk. The review of systems is normal, except for increasing problems with his prostate in the last 6 months, with dribbling and accidents at times. The patient admits to going more often, and sometimes without warning. The son states that his father seems more forgetful, slower of speech, and not as full of life as he used to be. A neurologic examination reveals the patient to be oriented x 3, with a somewhat flat affect and a wide-based, slow, shuffling gate. The examination is otherwise normal. His Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score is 22 out of 30. No tremor is noted. A CBC, creatinine level, TSH level, vitamin B12 level and VDRL are all normal.
Which one of the following should you do next?
A. Order a brain MRI
B. Prescribe sertraline (Zoloft)
C. Prescribe carbidopa/levodopa (Sinemet)
D. Order physical therapy
Answer : A
7. Topic: Fragile X Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
You are asked to see a mentally challenged 45-yearold male from a nearby group home who has groin pain. On examination you notice that he has large ears, a prominent jaw, and large symmetric testicles.
These findings are consistent with:
A. A variant form of Down syndrome
B. Aspergers syndrome
C. Klinefelters syndrome
D. Fragile X syndrome
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
You are asked to see a mentally challenged 45-yearold male from a nearby group home who has groin pain. On examination you notice that he has large ears, a prominent jaw, and large symmetric testicles.
These findings are consistent with:
A. A variant form of Down syndrome
B. Aspergers syndrome
C. Klinefelters syndrome
D. Fragile X syndrome
Answer : D
8. Topic: Horner's Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
A 54-year-old white male presents with drooping of his right eyelid for 3 weeks. On examination, he has ptosis of the right upper lid, miosis of the right pupil, and decreased sweating on the right side of his face. Extraocular muscle movements are intact. In addition to a complete history and physical examination, which one of the following would be most appropriate at this point?
A. A chest radiograph
B. MRI of the brain and orbits
C. 131 Iodine thyroid scanning
D. A fasting blood glucose level
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
A 54-year-old white male presents with drooping of his right eyelid for 3 weeks. On examination, he has ptosis of the right upper lid, miosis of the right pupil, and decreased sweating on the right side of his face. Extraocular muscle movements are intact. In addition to a complete history and physical examination, which one of the following would be most appropriate at this point?
A. A chest radiograph
B. MRI of the brain and orbits
C. 131 Iodine thyroid scanning
D. A fasting blood glucose level
Answer : A
9. Topic: Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Subject: Medicine
A 36-year-old female presents with the sudden onset of severe headache, nausea, and photophobia. Her level of consciousness is progressively diminishing. Which one of the following would be the most appropriate next step?
A. Head CT without contrast
B. Head CT with contrast
C. Head MRI
D. Lumbar puncture
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
A 36-year-old female presents with the sudden onset of severe headache, nausea, and photophobia. Her level of consciousness is progressively diminishing. Which one of the following would be the most appropriate next step?
A. Head CT without contrast
B. Head CT with contrast
C. Head MRI
D. Lumbar puncture
Answer : A
10. Topic: Status Epilepticus
Subject: Medicine
A 58-year-old male with a history of seizure attacks suffered from a 30 min loss of consciousness with repetitive seizures with no recovery of consciousness between attacks. What is the disorder this patient is suffering from?
A. Tonic-clonic seizure
B. Absence seizure
C. Atonic seizure
D. Status epilepticus
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
A 58-year-old male with a history of seizure attacks suffered from a 30 min loss of consciousness with repetitive seizures with no recovery of consciousness between attacks. What is the disorder this patient is suffering from?
A. Tonic-clonic seizure
B. Absence seizure
C. Atonic seizure
D. Status epilepticus
Answer : D
11. Topic: Dementia
Subject: Medicine
An 85 year old white male is brought to you for the first time by his son. The father has recently seen a neurologist who performed a workup for dementia and diagnosed moderate Alzheimers disease. Which one of the following is true regarding the use of a cholinesterase inhibitor in this patient?
A. It istoo late to initiate cholinesterase therapy
B. Agitation is often intensified by these agents
C. Memory is likely to improve significantly
D. Nursing-home placement may be delayed a year or longer
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
An 85 year old white male is brought to you for the first time by his son. The father has recently seen a neurologist who performed a workup for dementia and diagnosed moderate Alzheimers disease. Which one of the following is true regarding the use of a cholinesterase inhibitor in this patient?
A. It istoo late to initiate cholinesterase therapy
B. Agitation is often intensified by these agents
C. Memory is likely to improve significantly
D. Nursing-home placement may be delayed a year or longer
Answer : D
12. Topic: Brown-Sequard Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
Which of the following would not be expected in a right-sided Brown-S�quard syndrome?
A. Right-sided hemi-paresis
B. Right-sided loss of proprioception
C. Left-sided decreased sensitivity to pinprick
D. Left-sided decreased vibration sense
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
Which of the following would not be expected in a right-sided Brown-S�quard syndrome?
A. Right-sided hemi-paresis
B. Right-sided loss of proprioception
C. Left-sided decreased sensitivity to pinprick
D. Left-sided decreased vibration sense
Answer : D
13. Topic: Essential Tremor
Subject: Medicine
Which one of the following is most likely to be of benefit in patients with essential tremor of the hand?
A. Isoniazid
B. Diazepam
C. Primidone
D. Clonidine
Answer : C
Subject: Medicine
Which one of the following is most likely to be of benefit in patients with essential tremor of the hand?
A. Isoniazid
B. Diazepam
C. Primidone
D. Clonidine
Answer : C
14. Topic: Delirium Tremens
Subject: Medicine
A patient with delirium tremens manifests all of the following, except:
A. Clouded consciousness
B. Hypothermia
C. Coarse tremor
D. Tachypnea
Answer : B
Subject: Medicine
A patient with delirium tremens manifests all of the following, except:
A. Clouded consciousness
B. Hypothermia
C. Coarse tremor
D. Tachypnea
Answer : B
15. Topic: Essential Tremor
Subject: Medicine
A 75 year old white male complains of a tremor which has been progressive over the past 2 years. The tremor interferes with writing, pouring liquids, and eating soup. He has no other medical problems. He abstains from alcohol and tobacco products. Physical examination is remarkable for an action tremor of the upper extremities and a head tremor. No rigidity or gait disorder is noted. Of the following agents, which one is most appropriate as initial drug therapy for this problem?
A. Alprazolam (Xanax)
B. Clonazepam (Klonopin)
C. Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
D. Propranolol (Inderal)
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
A 75 year old white male complains of a tremor which has been progressive over the past 2 years. The tremor interferes with writing, pouring liquids, and eating soup. He has no other medical problems. He abstains from alcohol and tobacco products. Physical examination is remarkable for an action tremor of the upper extremities and a head tremor. No rigidity or gait disorder is noted. Of the following agents, which one is most appropriate as initial drug therapy for this problem?
A. Alprazolam (Xanax)
B. Clonazepam (Klonopin)
C. Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
D. Propranolol (Inderal)
Answer : D
16. Topic: Adverse Drug Effect
Subject: Medicine
A 68-year-old man with a history of urolithiasis, suffered from a seizure attack which involved loss of consciousness with tonic and clonic muscular contractions. His tongue fell back into his throat and he choked. He is treated with valproic acid.
What are the most common side effects caused by this medication?
A. Weight gain
B. Rash
C. Nausea and headache
D. Tardive dyskinesia
Answer : C
Subject: Medicine
A 68-year-old man with a history of urolithiasis, suffered from a seizure attack which involved loss of consciousness with tonic and clonic muscular contractions. His tongue fell back into his throat and he choked. He is treated with valproic acid.
What are the most common side effects caused by this medication?
A. Weight gain
B. Rash
C. Nausea and headache
D. Tardive dyskinesia
Answer : C
17. Topic: Huntington Chorea
Subject: Medicine
A patient previously diagnosed with Huntington chorea (HC) comes for a family planning consult with his wife. He states that his father had the disease and his mother was unaffected. They ask you what is the likelihood having a son with this condition?
A. Zero
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
Answer : B
Subject: Medicine
A patient previously diagnosed with Huntington chorea (HC) comes for a family planning consult with his wife. He states that his father had the disease and his mother was unaffected. They ask you what is the likelihood having a son with this condition?
A. Zero
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
Answer : B
18. Topic: Cholinergic Toxidrome
Subject: Medicine
A 37 year old male arrives at the Emergency Department unconscious. He is warm and sweaty. His heart rate is 52 bpm, his BP is 90/60. His pupils are constricted, his eyes are teary, and he is drooling. You assume he is suffering from a toxidrome.
What antidote will you give him?
A. Flumazenil
B. Naloxone
C. Glucagon
D. Atropine
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
A 37 year old male arrives at the Emergency Department unconscious. He is warm and sweaty. His heart rate is 52 bpm, his BP is 90/60. His pupils are constricted, his eyes are teary, and he is drooling. You assume he is suffering from a toxidrome.
What antidote will you give him?
A. Flumazenil
B. Naloxone
C. Glucagon
D. Atropine
Answer : D
19. Topic: Mini Mental Status Exam (or MMSE)
Subject: Medicine
A 63-year-old retired teacher shared with his primary care physician (PCP) during a routine office visit that he has noticed increasing difficulty with his memory. Otherwise he is in good health and requiring no medication.
Which one of the following psychological tests is a valuable screening device to be used by primary care physicians in this type of situation?
A. MMPI
B. WAIS
C. Thematic Apperception Test
D. Mini-Mental State Exam
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
A 63-year-old retired teacher shared with his primary care physician (PCP) during a routine office visit that he has noticed increasing difficulty with his memory. Otherwise he is in good health and requiring no medication.
Which one of the following psychological tests is a valuable screening device to be used by primary care physicians in this type of situation?
A. MMPI
B. WAIS
C. Thematic Apperception Test
D. Mini-Mental State Exam
Answer : D
20. Topic: Foot Drop
Subject: Medicine
During the physical exam of a patients foot, you notice an inability to dorsiflex. What nerve root(s) is most likely affected?
A. T12
B. L1
C. L2
D. L4 - L5
Answer : E
Subject: Medicine
During the physical exam of a patients foot, you notice an inability to dorsiflex. What nerve root(s) is most likely affected?
A. T12
B. L1
C. L2
D. L4 - L5
Answer : E
21. Topic: Seizure
Subject: Medicine
Of the following, which is the most frequent cause of seizures in the elderly?
A. Alcohol withdrawal
B. Stroke
C. Head trauma
D. Hypoglycemia
Answer : B
Subject: Medicine
Of the following, which is the most frequent cause of seizures in the elderly?
A. Alcohol withdrawal
B. Stroke
C. Head trauma
D. Hypoglycemia
Answer : B
22. Topic: Trigeminal Neuralgia
Subject: Medicine
A man complains that recently when he shaves he has a shooting type of pain in his face. It happens once in a while and then goes away. You suspect trigeminal neuralgia.
What is the treatment of choice?
A. Fluoxetine
B. Prednisone
C. Acyclovir
D. Carbamazepine
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
A man complains that recently when he shaves he has a shooting type of pain in his face. It happens once in a while and then goes away. You suspect trigeminal neuralgia.
What is the treatment of choice?
A. Fluoxetine
B. Prednisone
C. Acyclovir
D. Carbamazepine
Answer : D
23. Topic: Seizure
Subject: Medicine
A 68-year-old man with a history of urolithiasis, suffered from a seizure attack which involved loss of consciousness with tonic and clonic muscular contractions. His tongue fell back into his throat and he choked.
Which of the following medications is contraindicated in this patient's treatment?
A. Levetiracetam
B. Phenytoin
C. Topiramate
D. Carbamazepine
Answer : C
Subject: Medicine
A 68-year-old man with a history of urolithiasis, suffered from a seizure attack which involved loss of consciousness with tonic and clonic muscular contractions. His tongue fell back into his throat and he choked.
Which of the following medications is contraindicated in this patient's treatment?
A. Levetiracetam
B. Phenytoin
C. Topiramate
D. Carbamazepine
Answer : C
24. Topic: Temporal Arteritis
Subject: Medicine
A 75-year-old female presents with a 2-month history of bilateral headache, diffuse myalgias, and diplopia. On examination she has substantially diminished vision in her left eye, but no other neurologic findings. A moderately tender, cordlike structure is palpable just anterior to her ear and extending up to her lateral scalp. Blood tests show a markedly elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Which one of the following would be most appropriate at this point?
A. Clopidogrel (Plavix)
B. High-dose corticosteroids
C. NSAIDs
D. Dipyridamole/aspirin (Aggrenox)
Answer : B
Subject: Medicine
A 75-year-old female presents with a 2-month history of bilateral headache, diffuse myalgias, and diplopia. On examination she has substantially diminished vision in her left eye, but no other neurologic findings. A moderately tender, cordlike structure is palpable just anterior to her ear and extending up to her lateral scalp. Blood tests show a markedly elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Which one of the following would be most appropriate at this point?
A. Clopidogrel (Plavix)
B. High-dose corticosteroids
C. NSAIDs
D. Dipyridamole/aspirin (Aggrenox)
Answer : B
25. Topic: Status Epilepticus
Subject: Medicine
A 58-year-old male with a history of seizure attacks suffered from a 30min loss of consciousness with repetitive seizures with no recovery of consciousness between attacks. What is the best initial treatment for his condition?
A. Lorazepam
B. Phenytoin
C. Phenobarbital
D. Carbamazepine
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
A 58-year-old male with a history of seizure attacks suffered from a 30min loss of consciousness with repetitive seizures with no recovery of consciousness between attacks. What is the best initial treatment for his condition?
A. Lorazepam
B. Phenytoin
C. Phenobarbital
D. Carbamazepine
Answer : A
26. Topic: Temporal Arteritis
Subject: Medicine
A 70-year-old wman returns to the office because of aching and weakness in her arms to the point where she cannot lift her arm to brush her hair. Physical examination shows no muscle tenderness or other evidence of joint disease in both arms. The aching improves when she takes the prescribed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). She also describes tenderness over the right temporal area of her scalp. Physical examination of the scalp shows no lesions.
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
A. Increase the dose of the NSAID
B. Order determination of erythrocyte sedimentation rate
C. Order determination of serum rheumatoid factor
D. Order x-ray films of the cervical spine
Answer : B
Subject: Medicine
A 70-year-old wman returns to the office because of aching and weakness in her arms to the point where she cannot lift her arm to brush her hair. Physical examination shows no muscle tenderness or other evidence of joint disease in both arms. The aching improves when she takes the prescribed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). She also describes tenderness over the right temporal area of her scalp. Physical examination of the scalp shows no lesions.
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
A. Increase the dose of the NSAID
B. Order determination of erythrocyte sedimentation rate
C. Order determination of serum rheumatoid factor
D. Order x-ray films of the cervical spine
Answer : B
27. Topic: Status Epilepticus
Subject: Medicine
Which one of the following should be given intravenously in the initial treatment of status epilepticus?
A. Propofol (Diprivan)
B. Phenobarbital
C. Lorazepam (Ativan)
D. Midazolam (Versed)
Answer : C
Subject: Medicine
Which one of the following should be given intravenously in the initial treatment of status epilepticus?
A. Propofol (Diprivan)
B. Phenobarbital
C. Lorazepam (Ativan)
D. Midazolam (Versed)
Answer : C
28. Topic: Seizure
Subject: Medicine
A 52-year-old male with a history of seizure attacks suffered from loss of consciousness and tonic and clonic muscular contractions. His tongue fell back into the throat and he choked. What is the most likely diagnosis of this presentation?
A. Petit mal seizure
B. Grand mal seizure
C. Myoclonic seizure
D. Atonic seizure
Answer : B
Subject: Medicine
A 52-year-old male with a history of seizure attacks suffered from loss of consciousness and tonic and clonic muscular contractions. His tongue fell back into the throat and he choked. What is the most likely diagnosis of this presentation?
A. Petit mal seizure
B. Grand mal seizure
C. Myoclonic seizure
D. Atonic seizure
Answer : B
29. Topic: Seizure
Subject: Medicine
A 36-year-old male with a history of a seizure disorder is brought to the emergency department with generalized tonic-clonic activity. Emergency medical personnel report this has been ongoing for 20 minutes.
After initial resuscitative measures, the preferred medication in this situation is:
A. Phenytoin (Dilantin)
B. Fosphenytoin (Cerebyx)
C. Naloxone
D. Lorazepam (Ativan)
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
A 36-year-old male with a history of a seizure disorder is brought to the emergency department with generalized tonic-clonic activity. Emergency medical personnel report this has been ongoing for 20 minutes.
After initial resuscitative measures, the preferred medication in this situation is:
A. Phenytoin (Dilantin)
B. Fosphenytoin (Cerebyx)
C. Naloxone
D. Lorazepam (Ativan)
Answer : D
30. Topic: Horner's Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
A 70-year-old man presented with ptosis, myosis and anhydrosis on the left side. Which one of the following is the most likely cause of this condition?
A. Tumour induced exophthalmos
B. Fourth cranial nerve palsy
C. Apical pulmonary carcinoma
D. Enlarged thyroid gland
Answer : C
Subject: Medicine
A 70-year-old man presented with ptosis, myosis and anhydrosis on the left side. Which one of the following is the most likely cause of this condition?
A. Tumour induced exophthalmos
B. Fourth cranial nerve palsy
C. Apical pulmonary carcinoma
D. Enlarged thyroid gland
Answer : C
31. Topic: Horner's Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
A 70-year-old man presented with ptosis, myosis and anhydrosis on the left side. Which one of the following is the most likely cause of this condition?
A. Tumour induced exophthalmos
B. Fourth cranial nerve palsy
C. Apical pulmonary carcinoma
D. Enlarged thyroid gland
Answer : C
Subject: Medicine
A 70-year-old man presented with ptosis, myosis and anhydrosis on the left side. Which one of the following is the most likely cause of this condition?
A. Tumour induced exophthalmos
B. Fourth cranial nerve palsy
C. Apical pulmonary carcinoma
D. Enlarged thyroid gland
Answer : C
32. Topic: Analgesics
Subject: Medicine
A 74-year-old black female has moderately severe pain due to osteoarthritis. However, she is also on medication for a seizure disorder. When choosing medications to manage her chronic pain, which one of the following should be used with caution because of her history of seizures?
A. Salsalate (Disalcid)
B. Celecoxib (Celebrex)
C. Hydrocodone (Lortab)
D. Tramadol (Ultram)
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
A 74-year-old black female has moderately severe pain due to osteoarthritis. However, she is also on medication for a seizure disorder. When choosing medications to manage her chronic pain, which one of the following should be used with caution because of her history of seizures?
A. Salsalate (Disalcid)
B. Celecoxib (Celebrex)
C. Hydrocodone (Lortab)
D. Tramadol (Ultram)
Answer : D
33. Topic: Absence Seizures
Subject: Medicine
The treatment of choice for absence seizures is:
A. Lamotrigine
B. Ethosuximide
C. Phenobarbital
D. Phenytoin
Answer : B
Subject: Medicine
The treatment of choice for absence seizures is:
A. Lamotrigine
B. Ethosuximide
C. Phenobarbital
D. Phenytoin
Answer : B
34. Topic: Hepatic Encephalopathy
Subject: Medicine
A 50-year-old man with a history of hemochromatosis presents to the emergency room vomiting up bright red blood. He had his most recent phlebotomy yesterday. His blood pressure is 110/85 mm Hg, his pulse 115/min; his face is flushed, and he is diaphoretic. During the physical examination splenomegaly and a venous pattern on his chest and abdomen are noted. He seems somewhat drowsy and confused but has no focal neurologic signs.
What is the probable source of this patient's confusion?
A. Severe anemia
B. Hepatic encephalopathy
C. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
D. Vitamin B12 deficiency
Answer : B
Subject: Medicine
A 50-year-old man with a history of hemochromatosis presents to the emergency room vomiting up bright red blood. He had his most recent phlebotomy yesterday. His blood pressure is 110/85 mm Hg, his pulse 115/min; his face is flushed, and he is diaphoretic. During the physical examination splenomegaly and a venous pattern on his chest and abdomen are noted. He seems somewhat drowsy and confused but has no focal neurologic signs.
What is the probable source of this patient's confusion?
A. Severe anemia
B. Hepatic encephalopathy
C. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
D. Vitamin B12 deficiency
Answer : B
35. Topic: DM neuropathy
Subject: Medicine
In which of the following diseases would you see a gloves and stocking neuropathy?
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Lupus
C. Multiple sclerosis
D. ALS
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
In which of the following diseases would you see a gloves and stocking neuropathy?
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Lupus
C. Multiple sclerosis
D. ALS
Answer : A
36. Topic: Temporal Arteritis
Subject: Medicine
A female patient complains of a severe headache and jaw pain when she chews. She also complains of shoulder pain and bilateral wrist weakness. Initial lab tests show an ESR of 75 (normal is less than 30).
What is the most appropriate diagnosis?
A. Rheumatoid Arthritis
B. Temporal Arteritis
C. Polymyositis
D. Sarcoidosis
Answer : B
Subject: Medicine
A female patient complains of a severe headache and jaw pain when she chews. She also complains of shoulder pain and bilateral wrist weakness. Initial lab tests show an ESR of 75 (normal is less than 30).
What is the most appropriate diagnosis?
A. Rheumatoid Arthritis
B. Temporal Arteritis
C. Polymyositis
D. Sarcoidosis
Answer : B
37. Topic: Dementia
Subject: Medicine
All of the following dementias can benefit from specific treatments, except:
A. Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)
B. Alzheimers disease
C. Sarcoidosis
D. Creutzfeldt Jakob disease
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
All of the following dementias can benefit from specific treatments, except:
A. Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)
B. Alzheimers disease
C. Sarcoidosis
D. Creutzfeldt Jakob disease
Answer : D
38. Topic: Mini Mental Status Exam (or MMSE)
Subject: Medicine
While performing the Mini-Mental State Exam the PCP asks her patient to copy the following design. What cognitive function is being assessed by this request?
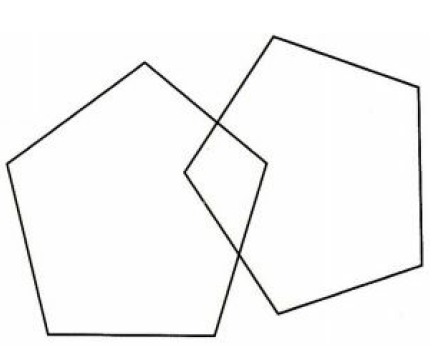
A. Language
B. Orientation
C. Registration
D. Visual-motor integrity
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
While performing the Mini-Mental State Exam the PCP asks her patient to copy the following design. What cognitive function is being assessed by this request?

A. Language
B. Orientation
C. Registration
D. Visual-motor integrity
Answer : D
39. Topic: Osmotic Demyelination
Subject: Medicine
Osmotic demyelination can result when which one of the following is corrected too rapidly?
A. Hypocalcemia
B. Hypoglycemia
C. Hypomagnesemia
D. Hyponatremia
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
Osmotic demyelination can result when which one of the following is corrected too rapidly?
A. Hypocalcemia
B. Hypoglycemia
C. Hypomagnesemia
D. Hyponatremia
Answer : D
40. Topic: Mini Mental Status Exam (or MMSE)
Subject: Medicine
In healthy adults, performance on the Folstein Mini-Mental State Examination is affected by which one of the following?
A. Educational attainment
B. Socioeconomic status
C. Gender
D. Race
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
In healthy adults, performance on the Folstein Mini-Mental State Examination is affected by which one of the following?
A. Educational attainment
B. Socioeconomic status
C. Gender
D. Race
Answer : A
41. Topic: Trigeminal Neuralgia
Subject: MedicineA 55-year-old man complains of extremely severe, sharp, shooting pain in his face. He describes the episodes as being like a bolt of electricity that are brought about by touching a specific area, last about 60 seconds, and occur many times during the day. Neurologic examination is completely normal, but it is noted that part of his face is unshaven because he fears to touch that area. Gadoliniumenhanced MRI shows no abnormalities of the trigeminal nerve.
Which of the following is the most appropriate initial treatment?
A. Anticonvulsants
B. Aspirin
C. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
D. Vasoconstrictors
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
Which of the following is the most appropriate initial treatment?
A. Anticonvulsants
B. Aspirin
C. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
D. Vasoconstrictors
Answer : A
42. Topic: Adverse Drug Effect
Subject: Medicine
Which one of the following is most associated with falls in older adults?
A. Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
B. Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
C. Metformin (Glucophage)
D. Memantine (Namenda)
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
Which one of the following is most associated with falls in older adults?
A. Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
B. Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
C. Metformin (Glucophage)
D. Memantine (Namenda)
Answer : A
43. Topic: Delirium Tremens
Subject: Medicine
You see a 49-year-old man in the emergency room with a 20-year-history of alcohol abuse. He is agitated and floridly psychotic, with visual hallucinations and persecutory delusions. On examination his blood pressure, heart rate and respiratory rate are all increased. He is disoriented, sweaty, and has abdominal cramps.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Subdural hematoma
B. Alcohol intoxication
C. Hepatic encephalopathy
D. Delirium tremens
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
You see a 49-year-old man in the emergency room with a 20-year-history of alcohol abuse. He is agitated and floridly psychotic, with visual hallucinations and persecutory delusions. On examination his blood pressure, heart rate and respiratory rate are all increased. He is disoriented, sweaty, and has abdominal cramps.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Subdural hematoma
B. Alcohol intoxication
C. Hepatic encephalopathy
D. Delirium tremens
Answer : D
44. Topic: Cauda Equina Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
A 65-year-old male presents with a 1-month history of problems passing urine. He says that his bladder will feel full when he needs to urinate, but the urine stream is weak and his bladder does not feel as if it has emptied completely. The symptoms have become increasingly severe over the past week. Other symptoms include upper respiratory congestion for 3 days which he has treated with an over-thecounter decongestant with some relief, constipation with no passage of stool in the past 9 days, and increasing low back pain incompletely relieved with ibuprofen, with associated weakness in both legs. Examination shows a healthy-appearing male who is moderately overweight. He is afebrile and vital signs are normal. There is no abdominal tenderness and no masses are detected. A rectal examination reveals a large amount of hard stool in the rectum; a markedly enlarged (4+), boggy, tender prostate gland; laxity of the anal sphincter; and numbness in the perianal area. Urinalysis shows trace protein and 10-20 WBCs/hpf. Ultrasonography shows a post-void residual volume of 250 mL (normal for age <100).
Which one of the following must be done urgently in this patient?
A. Foley catheterization
B. Hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics
C. Digital disimpaction of the rectum, and Fleet enemas until clear
D. MRI of the lumbosacral spine
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
A 65-year-old male presents with a 1-month history of problems passing urine. He says that his bladder will feel full when he needs to urinate, but the urine stream is weak and his bladder does not feel as if it has emptied completely. The symptoms have become increasingly severe over the past week. Other symptoms include upper respiratory congestion for 3 days which he has treated with an over-thecounter decongestant with some relief, constipation with no passage of stool in the past 9 days, and increasing low back pain incompletely relieved with ibuprofen, with associated weakness in both legs. Examination shows a healthy-appearing male who is moderately overweight. He is afebrile and vital signs are normal. There is no abdominal tenderness and no masses are detected. A rectal examination reveals a large amount of hard stool in the rectum; a markedly enlarged (4+), boggy, tender prostate gland; laxity of the anal sphincter; and numbness in the perianal area. Urinalysis shows trace protein and 10-20 WBCs/hpf. Ultrasonography shows a post-void residual volume of 250 mL (normal for age <100).
Which one of the following must be done urgently in this patient?
A. Foley catheterization
B. Hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics
C. Digital disimpaction of the rectum, and Fleet enemas until clear
D. MRI of the lumbosacral spine
Answer : D
45. Topic: MMSE
Subject: Medicine
The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) tests for:
A. Mood
B. Behavior
C. Intelligence quotient
D. Cognitive function
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) tests for:
A. Mood
B. Behavior
C. Intelligence quotient
D. Cognitive function
Answer : D
46. Topic: Organophosphate poisoning
Subject: Medicine
What is the mechanism of action in organophosphate poisoning?
A. Cholinesterase inhibition
B. Cholinesterase activation
C. Catecholamine inhibition
D. Catecholamine activation
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
What is the mechanism of action in organophosphate poisoning?
A. Cholinesterase inhibition
B. Cholinesterase activation
C. Catecholamine inhibition
D. Catecholamine activation
Answer : A
47. Topic: Essential Tremor
Subject: Medicine
A 66 year old white female consults you because she has developed a tremor of her right hand that interferes with her ability to do needlework. She has noticed that the tremor improves when she rests her hands in her lap and gets worse when she holds them up against gravity. She has developed a slight quiver to her voice as well. Her symptoms started gradually over 6 months ago and have progressed slowly. She remembers her mother having similar problems in her later years. She takes no medications, and her physical examination corroborates her history. No other abnormalities are noted. A multiple chemistry screen and TSH level are normal.
Which one of the following is most likely to alleviate her tremor?
A. Propranolol (Inderal)
B. Paroxetine (Paxil)
C. Carbidopa/levodopa (Sinemet)
D. Bromocriptine (Parlodel)
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
A 66 year old white female consults you because she has developed a tremor of her right hand that interferes with her ability to do needlework. She has noticed that the tremor improves when she rests her hands in her lap and gets worse when she holds them up against gravity. She has developed a slight quiver to her voice as well. Her symptoms started gradually over 6 months ago and have progressed slowly. She remembers her mother having similar problems in her later years. She takes no medications, and her physical examination corroborates her history. No other abnormalities are noted. A multiple chemistry screen and TSH level are normal.
Which one of the following is most likely to alleviate her tremor?
A. Propranolol (Inderal)
B. Paroxetine (Paxil)
C. Carbidopa/levodopa (Sinemet)
D. Bromocriptine (Parlodel)
Answer : A
48. Topic: Huntington disease
Subject: Medicine
A 42-year-old white male is brought to your department by his wife because of the progressive loss of his mental abilities, irritability, and some irregular involuntary movements of his hands. She says that she can remember when they were newlyweds, her husbands father had a similar condition at the age of 45 and he died few years later because there was not much doctors could do for him back then. She wants to know if their children may eventually develop a similar condition in the future. None in her family has ever had this type of condition. Which of the following would be the most appropriate answer?
A. Only their male children are at risk
B. If one child develops the disease, siblings are not at risk
C. All their children will inherit the disease
D. Each child has 50% risk of inheriting the disease
Answer : D
Subject: Medicine
A 42-year-old white male is brought to your department by his wife because of the progressive loss of his mental abilities, irritability, and some irregular involuntary movements of his hands. She says that she can remember when they were newlyweds, her husbands father had a similar condition at the age of 45 and he died few years later because there was not much doctors could do for him back then. She wants to know if their children may eventually develop a similar condition in the future. None in her family has ever had this type of condition. Which of the following would be the most appropriate answer?
A. Only their male children are at risk
B. If one child develops the disease, siblings are not at risk
C. All their children will inherit the disease
D. Each child has 50% risk of inheriting the disease
Answer : D
49. Topic: Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Subject: Medicine
A 25-year-old male presents 5 hours after the onset of the worst headache of my life. His temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 140/90 mm Hg, respiratory rate 20/min, and pulse rate 90 beats/min. The patient is lethargic but oriented; there are no focal neurologic findings, but neck stiffness is present. Unenhanced CT of the head is negative. You elect to perform a lumbar puncture. At this time, which one of the following findings in bloody spinal fluid would indicate a diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage?
A. Yellow-orange cerebrospinal fluid supernatant
B. A WBC:RBC ratio of 1/1000
C. A protein (g/L) to RBC (count/L) of 1/1000
D. A glucose level below 2.2 mmol/L
Answer : A
Subject: Medicine
A 25-year-old male presents 5 hours after the onset of the worst headache of my life. His temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 140/90 mm Hg, respiratory rate 20/min, and pulse rate 90 beats/min. The patient is lethargic but oriented; there are no focal neurologic findings, but neck stiffness is present. Unenhanced CT of the head is negative. You elect to perform a lumbar puncture. At this time, which one of the following findings in bloody spinal fluid would indicate a diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage?
A. Yellow-orange cerebrospinal fluid supernatant
B. A WBC:RBC ratio of 1/1000
C. A protein (g/L) to RBC (count/L) of 1/1000
D. A glucose level below 2.2 mmol/L
Answer : A
50. Topic: Horner's Syndrome
Subject: Medicine
A 66-year-old diabetic man presents with constriction of the pupil, drooping of the upper lid, and anhidrosis on the left. Which one of the following nerves is most likely involved?
A. Oculomotor
B. Sympathetic
C. Trochlear
D. Trigeminal
Answer : B
Subject: Medicine
A 66-year-old diabetic man presents with constriction of the pupil, drooping of the upper lid, and anhidrosis on the left. Which one of the following nerves is most likely involved?
A. Oculomotor
B. Sympathetic
C. Trochlear
D. Trigeminal
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Manufacturing & Production Engineering Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Workshop Technology Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Radiologic Examination MCQ for SBI Clerk [Solved]
Microsoft Access MCQ Solved Paper for SBI Clerk
1000+ Manufacturing & Production Engineering MCQ for IBPS RRB [Solved]
Data Structure 1000+ MCQ with answer for JEE Main