1000+ Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics MCQ for DRDO [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Which of the following is not an extensive property?
A. Free energy
B. Entropy
C. Refractive index
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Free energy
B. Entropy
C. Refractive index
D. None of these
Answer : C
2. A gas can be liquefied by pressure alone only, when its temperature is __________ its critical temperature.
A. Less than
B. More than
C. Equal to or higher than
D. Less than or equal to
Answer : D
A. Less than
B. More than
C. Equal to or higher than
D. Less than or equal to
Answer : D
3. In case of vapour compression refrigeration system, elevating the evaporator temperature (keeping the condenser temperature constant) results in
A. Enhanced COP
B. Decreased COP
C. No change in the value of COP
D. Increased or decreased COP; depending upon the type of refrigerant
Answer : A
A. Enhanced COP
B. Decreased COP
C. No change in the value of COP
D. Increased or decreased COP; depending upon the type of refrigerant
Answer : A
4. Law of corresponding states says that
A. Two different gases behave similarly, if their reduced properties (i.e. P, V and T) are same
B. The surface of separation (i. e. the meniscus) between liquid and vapour phase disappears at the critical temperature
C. No gas can be liquefied above the critical temperature, howsoever high the pressure may be.
D. The molar heat of energy of gas at constant volume should be nearly constant (about 3 calories)
Answer : A
A. Two different gases behave similarly, if their reduced properties (i.e. P, V and T) are same
B. The surface of separation (i. e. the meniscus) between liquid and vapour phase disappears at the critical temperature
C. No gas can be liquefied above the critical temperature, howsoever high the pressure may be.
D. The molar heat of energy of gas at constant volume should be nearly constant (about 3 calories)
Answer : A
5. Maximum work that could be secured by expanding the gas over a given pressure range is the __________ work.
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isentropic
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isentropic
D. None of these
Answer : A
6. In case of the decomposition of hydroiodic acid (2HI ? H2 + I2), addition of H2 (at equilibrium condition) will
A. Increase the partial pressure of I2
B. Decrease the partial pressure of HI
C. Diminish the degree of dissociation of HI
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Increase the partial pressure of I2
B. Decrease the partial pressure of HI
C. Diminish the degree of dissociation of HI
D. None of these
Answer : C
7. The unity of Planck's constant 'h' in the equation, E = hv is
A. J/s
B. J.S
C. J/kmol
D. kmol/J
Answer : B
A. J/s
B. J.S
C. J/kmol
D. kmol/J
Answer : B
8. After throttling, gas temperature
A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. Remain same
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : A
A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. Remain same
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : A
9. Which one is true for a throttling process?
A. A gas may have more than one inversion temperatures
B. The inversion temperature is different for different gases
C. The inversion temperature is same for all gases
D. The inversion temperature is the temperature at which Joule-Thomson co-efficient is infinity
Answer : B
A. A gas may have more than one inversion temperatures
B. The inversion temperature is different for different gases
C. The inversion temperature is same for all gases
D. The inversion temperature is the temperature at which Joule-Thomson co-efficient is infinity
Answer : B
10. Entropy change of the reaction, H2O (liquid) ? H2O (gas), is termed as the enthalpy of
A. Solution
B. Vaporisation
C. Formation
D. Sublimation
Answer : B
A. Solution
B. Vaporisation
C. Formation
D. Sublimation
Answer : B
11. (?T/?P)H is the mathematical expression for
A. Specific heat at constant pressure (Cp)
B. Specific heat at constant volume (Cv)
C. Joule-Thompson co-efficient
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Specific heat at constant pressure (Cp)
B. Specific heat at constant volume (Cv)
C. Joule-Thompson co-efficient
D. None of these
Answer : C
12. Third law of thermodynamics is concerned with the
A. Value of absolute entropy
B. Energy transfer
C. Direction of energy transfer
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Value of absolute entropy
B. Energy transfer
C. Direction of energy transfer
D. None of these
Answer : A
13. Heat of reaction at constant volume is identified with __________ change.
A. Enthalpy
B. Internal energy
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
A. Enthalpy
B. Internal energy
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
14. Isobaric process means a constant process.
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. Entropy
Answer : B
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. Entropy
Answer : B
15. Translational kinetic energy of molecules of an ideal gas is proportional to (where, T = absolute temperature of the gas)
A. T
B. ?T
C. T2
D. 1/?T
Answer : A
A. T
B. ?T
C. T2
D. 1/?T
Answer : A
16. PV? = Constant (where, ? = Cp/Cv) is valid for a/an __________ process.
A. Isothermal
B. Isentropic
C. Isobaric
D. Adiabatic
Answer : D
A. Isothermal
B. Isentropic
C. Isobaric
D. Adiabatic
Answer : D
17. In which of the following reaction equilibrium, the value of equilibrium constant Kp will be more than is Kc?
A. 2HI ? H2 + I2
B. N2O4 ? 2NO2
C. 2SO2 + O2 ? 2SO3
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. 2HI ? H2 + I2
B. N2O4 ? 2NO2
C. 2SO2 + O2 ? 2SO3
D. None of these
Answer : B
18. A closed system is cooled reversibly from 100°C to 50°C. If no work is done on the system
A. its internal energy (U) decreases and its entropy (S) increases
B. U and S both decreases
C. U decreases but S is constant
D. U is constant but S decreases
Answer : B
A. its internal energy (U) decreases and its entropy (S) increases
B. U and S both decreases
C. U decreases but S is constant
D. U is constant but S decreases
Answer : B
19. In the equation, PVn = constant, if the value of n = ± ?, then it represents a reversible __________ process.
A. Adiabatic
B. Isometric
C. Isentropic
D. Isothermal
Answer : B
A. Adiabatic
B. Isometric
C. Isentropic
D. Isothermal
Answer : B
20. When a gas is subjected to adiabatic expansion, it gets cooled due to
A. Decrease in velocity
B. Decrease in temperature
C. Decrease in kinetic energy
D. Energy spent in doing work
Answer : D
A. Decrease in velocity
B. Decrease in temperature
C. Decrease in kinetic energy
D. Energy spent in doing work
Answer : D
21. __________ decreases during adiabatic throttling of a perfect gas.
A. Entropy
B. Temperature
C. Enthalpy
D. Pressure
Answer : D
A. Entropy
B. Temperature
C. Enthalpy
D. Pressure
Answer : D
22. In any spontaneous process,
A. Only F decreases
B. Only A decreases
C. Both F and A decreases
D. Both F and A increase
Answer : C
A. Only F decreases
B. Only A decreases
C. Both F and A decreases
D. Both F and A increase
Answer : C
23. For a multi-component system, the term chemical potential is equivalent to the
A. Molal concentration difference
B. Molar free energy
C. Partial molar free energy
D. Molar free energy change
Answer : C
A. Molal concentration difference
B. Molar free energy
C. Partial molar free energy
D. Molar free energy change
Answer : C
24. A system is said to be isopiestic, if there is no __________ change.
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. None of these
Answer : B
25. Gibbs phase rule finds application, when heat transfer occurs by
A. Conduction
B. Convection
C. Radiation
D. Condensation
Answer : D
A. Conduction
B. Convection
C. Radiation
D. Condensation
Answer : D
26. At __________ point, all the three phases (i.e. solid, liquid and gas) co-exist.
A. Eutectic
B. Triple
C. Plait
D. Critical
Answer : B
A. Eutectic
B. Triple
C. Plait
D. Critical
Answer : B
27. A system undergoes a change from a given initial state to a given final state either by an irreversible process or by a reversible process, then (where, ? S1 and ? SR are the entropy changes of the system for the irreversible and reversible processes respectively)
A. ? S1 is always < ? SR
B. ? S1 is sometimes > ? SR
C. ? S1 is always > ? SR
D. ? S1 is always = ? SR
Answer : C
A. ? S1 is always < ? SR
B. ? S1 is sometimes > ? SR
C. ? S1 is always > ? SR
D. ? S1 is always = ? SR
Answer : C
28. Standard temperature and pressure (S.T.P.) is
A. 0°C and 750 mm Hg
B. 15°C and 750 mm Hg
C. 0°C and 1 kgf/cm2
D. 15°C and 1 kgf/cm2
Answer : A
A. 0°C and 750 mm Hg
B. 15°C and 750 mm Hg
C. 0°C and 1 kgf/cm2
D. 15°C and 1 kgf/cm2
Answer : A
29. Refrigerants commonly used for domestic refrigerators are
A. Ethyl chloride or methyl chloride
B. Freon-12
C. Propane
D. NH3 or CO2
Answer : A
A. Ethyl chloride or methyl chloride
B. Freon-12
C. Propane
D. NH3 or CO2
Answer : A
30. Which of the following is not a reversible process?
A. Expansion of an ideal gas against constant pressure
B. Atmospheric pressure vaporisation of water at 100°C
C. Solution of NaCl in water at 50°C
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Expansion of an ideal gas against constant pressure
B. Atmospheric pressure vaporisation of water at 100°C
C. Solution of NaCl in water at 50°C
D. None of these
Answer : C
31. Heat evolved/absorbed during conversion of a substance from one allotropic form to another is termed as the heat of
A. Fusion
B. Vaporisation
C. Transition
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Fusion
B. Vaporisation
C. Transition
D. None of these
Answer : C
32. A refrigeration cycle is a reversed heat engine. Which of the following has the maximum value of the co-efficient of performance (COP) for a given refrigeration effect?
A. Vapor compression cycle using expansion valve
B. Air refrigeration cycle
C. Vapor compression cycle using expansion engine
D. Carnot refrigeration cycle
Answer : D
A. Vapor compression cycle using expansion valve
B. Air refrigeration cycle
C. Vapor compression cycle using expansion engine
D. Carnot refrigeration cycle
Answer : D
33. Free energy, fugacity and activity co-efficient are all affected by change in the temperature. The fugacity co-efficient of a gas at constant pressure ____with the increase of reduced temperature.
A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. Remains constant
D. Decreases logarithmically
Answer : B
A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. Remains constant
D. Decreases logarithmically
Answer : B
34. The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of conservation of
A. Heat
B. Momentum
C. Energy
D. Work
Answer : C
A. Heat
B. Momentum
C. Energy
D. Work
Answer : C
35. The number of degree of freedom for an Azeotropic mixture of ethanol and water in vapourliquid equilibrium, is
A. 3
B. 1
C. 2
D. 0
Answer : B
A. 3
B. 1
C. 2
D. 0
Answer : B
36. Entropy change of mixing two liquid substances depends upon the
A. Molar concentration
B. Quantity (i.e. number of moles)
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Molar concentration
B. Quantity (i.e. number of moles)
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
37. Number of phases in a colloidal system is:
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer : B
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer : B
38. The change in Gibbs free energy for vaporisation of a pure substance is
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. May be positive or negative
Answer : C
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. May be positive or negative
Answer : C
39. A solid metallic block weighing 5 kg has an initial temperature of 500°C. 40 kg of water initially at 25°C is contained in a perfectly insulated tank. The metallic block is brought into contact with water. Both of them come to equilibrium. Specific heat of block material is 0.4 kJ.kg-1. K-1. Ignoring the effect of expansion and contraction and also the heat capacity to tank, the total entropy change in kJ.kg-1, K-1 is
A. -1.87
B. 0
C. 1.26
D. 3.91
Answer : B
A. -1.87
B. 0
C. 1.26
D. 3.91
Answer : B
40. At absolute zero temperature, the __________ of the gas is zero.
A. Pressure
B. Volume
C. Mass
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Pressure
B. Volume
C. Mass
D. None of these
Answer : B
41. It is desired to bring about a certain change in the state of a system by performing work on the system under adiabatic conditions.
A. The amount of work needed is path dependent
B. Work alone cannot bring out such a change of state
C. The amount of work needed is independent of path
D. More information is needed to conclude anything about the path dependence or otherwise of the work needed
Answer : A
A. The amount of work needed is path dependent
B. Work alone cannot bring out such a change of state
C. The amount of work needed is independent of path
D. More information is needed to conclude anything about the path dependence or otherwise of the work needed
Answer : A
42. Entropy change for an irreversible isolated system is
A. ?
B. 0
C. < 0
D. > 0
Answer : D
A. ?
B. 0
C. < 0
D. > 0
Answer : D
43. Critical solution temperature (or the consolute temperature) for partially miscible liquids (e.g., phenol-water) is the minimum temperature at which
A. A homogeneous solution (say of phenol water) is formed
B. Mutual solubility of the two liquids shows a decreasing trend
C. Two liquids are completely separated into two layers
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. A homogeneous solution (say of phenol water) is formed
B. Mutual solubility of the two liquids shows a decreasing trend
C. Two liquids are completely separated into two layers
D. None of these
Answer : A
44. Which is an example of closed system?
A. Air compressor
B. Liquid cooling system of an automobile
C. Boiler
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Air compressor
B. Liquid cooling system of an automobile
C. Boiler
D. None of these
Answer : B
45. For multi-component multiple phases to be in equilibrium at the same pressure and temperature, the __________ of each component must be same in all phases.
A. Chemical potential
B. Fugacity
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Chemical potential
B. Fugacity
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
46. Solid and liquid phases of a substance are in equilibrium at the
A. Critical temperature
B. Melting point
C. Freezing point
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Critical temperature
B. Melting point
C. Freezing point
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
47. Which of the following diagrams does not represent an Otto cycle?
A.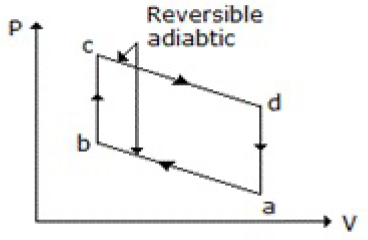
B.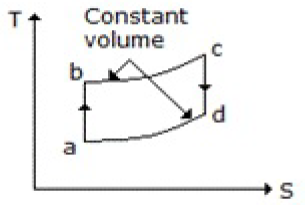
C.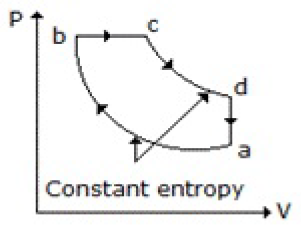
D. None of these
Answer : C
A.

B.

C.

D. None of these
Answer : C
48. To obtain integrated form of Clausius-Clapeyron equation, ln (P2/P1) = (?HV/R) (1/T1 - 1/T2) from the exact Clapeyron equation, it is assumed that the
A. Volume of the liquid phase is negligible compared to that of vapour phase
B. Vapour phase behaves as an ideal gas
C. Heat of vaporisation is independent of temperature
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : D
A. Volume of the liquid phase is negligible compared to that of vapour phase
B. Vapour phase behaves as an ideal gas
C. Heat of vaporisation is independent of temperature
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : D
49. At the absolute zero temperature, the entropy of every perfectly crystalline substance becomes zero. This follows from the
A. Third law of thermodynamics
B. Second law of thermodynamics
C. Nernst heat theorem
D. Maxwell's relations
Answer : A
A. Third law of thermodynamics
B. Second law of thermodynamics
C. Nernst heat theorem
D. Maxwell's relations
Answer : A
50. Number of components (C), phase (P) and degrees of freedom (F) are related by Gibbs phase rule as
A. P + F - C = 2
B. C = P - F + 2
C. F = C - P - 2
D. P = F - C - 2
Answer : A
A. P + F - C = 2
B. C = P - F + 2
C. F = C - P - 2
D. P = F - C - 2
Answer : A
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Current Affairs August 2017 MCQ for IBPS RRB [Solved]
1000+ Direct and Indirect Speech MCQ for NEET [Solved]
Engineering Mechanics MCQ Solved Paper for IBPS RRB
1000+ Antonyms Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Planet Kingdom MCQ for NEET [Solved]
1000+ Steam Boilers, Engines, Nozzles & Turbines Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]