1000+ Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Sound waves propagation in air exemplifies an __________ process.
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : A
2. For an isothermal reversible compression of an ideal gas
A. Only ?E = 0
B. Only ?H =0
C. ?E = ?H = 0
D. dQ = dE
Answer : C
A. Only ?E = 0
B. Only ?H =0
C. ?E = ?H = 0
D. dQ = dE
Answer : C
3. Which of the following is Virial equation of state?
A. (p + a/V2)(V - b) = nRT
B. PV = nRT
C. PV = A + B/V + C/V2 + D/V3 + ...
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. (p + a/V2)(V - b) = nRT
B. PV = nRT
C. PV = A + B/V + C/V2 + D/V3 + ...
D. None of these
Answer : C
4. All gases above its inversion temperature, in a throttling process will show
A. A heating effect
B. No change in temperature
C. A cooling effect
D. Either (A) or (C)
Answer : A
A. A heating effect
B. No change in temperature
C. A cooling effect
D. Either (A) or (C)
Answer : A
5. Domestic refrigerator usually works on the __________ refrigeration cycle.
A. Carnot
B. Air
C. Absorption
D. vapour-ejection
Answer : C
A. Carnot
B. Air
C. Absorption
D. vapour-ejection
Answer : C
6. As the temperature is lowered towards the absolute zero, the value of the quantity (??F/?T) approaches
A. Zero
B. Unity
C. Infinity
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Unity
C. Infinity
D. None of these
Answer : A
7. In a P-V diagram (for an ideal gas), an isothermal curve will coincide within adiabatic curve (through a point), when
A. Cp < Cv
B. Cp = Cv
C. Cp > Cv
D. C ? Cv
Answer : B
A. Cp < Cv
B. Cp = Cv
C. Cp > Cv
D. C ? Cv
Answer : B
8. For the gaseous phase chemical reaction, C2H4(g) + H2O(g) ? C2H5OH(g), the equilibrium conversion does not depend on the
A. Steam to ethylene ratio
B. Temperature
C. Pressure
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Steam to ethylene ratio
B. Temperature
C. Pressure
D. None of these
Answer : D
9. Critical solution temperature (or the consolute temperature) for partially miscible liquids (e.g., phenol-water) is the minimum temperature at which
A. A homogeneous solution (say of phenol water) is formed
B. Mutual solubility of the two liquids shows a decreasing trend
C. Two liquids are completely separated into two layers
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. A homogeneous solution (say of phenol water) is formed
B. Mutual solubility of the two liquids shows a decreasing trend
C. Two liquids are completely separated into two layers
D. None of these
Answer : A
10. What is the degree of freedom for two miscible (non-reacting) substances in vapor-liquid equilibrium forming an azeotrope?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : C
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : C
11. Any substance above its critical temperature exists as
A. Saturated vapour
B. Solid
C. Gas
D. Liquid
Answer : C
A. Saturated vapour
B. Solid
C. Gas
D. Liquid
Answer : C
12. In a working refrigerator, the value of COP is always
A. 0
B. < 0
C. < 1
D. > 1
Answer : D
A. 0
B. < 0
C. < 1
D. > 1
Answer : D
13. Pick out the correct statement:
A. In an isothermal system, irreversible work is more than reversible work
B. Under reversible conditions, the adiabatic work is less than isothermal work
C. Heat, work, enthalpy and entropy are all 'state functions'
D. Matter and energy cannot be exchanged with the surroundings in a closed system
Answer : B
A. In an isothermal system, irreversible work is more than reversible work
B. Under reversible conditions, the adiabatic work is less than isothermal work
C. Heat, work, enthalpy and entropy are all 'state functions'
D. Matter and energy cannot be exchanged with the surroundings in a closed system
Answer : B
14. For organic compounds, group contribution method can be used for the estimation of
A. Critical properties
B. Specific gravity
C. Specific volume
D. Thermal conductivity
Answer : A
A. Critical properties
B. Specific gravity
C. Specific volume
D. Thermal conductivity
Answer : A
15. If the internal energy of an ideal gas decreases by the same amount as the work done by the system, then the
A. Process must be isobaric
B. Temperature must decrease
C. Process must be adiabatic
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Process must be isobaric
B. Temperature must decrease
C. Process must be adiabatic
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
16. Number of degrees of freedom for a three phase system in equilibrium comprising of three nonreacting chemical species is
A. 2
B. 0
C. 1
D. 3
Answer : A
A. 2
B. 0
C. 1
D. 3
Answer : A
17. The relation connecting the fugacities of various components in a solution with one another and to composition at constant temperature and pressure is called the __________ equation.
A. Gibbs-Duhem
B. Van Laar
C. Gibbs-Helmholtz
D. Margules
Answer : A
A. Gibbs-Duhem
B. Van Laar
C. Gibbs-Helmholtz
D. Margules
Answer : A
18. Out of the following refrigeration cycles, which one has the minimum COP (Co-efficient of performance)?
A. Air cycle
B. Carnot cycle
C. Ordinary vapour compression cycle
D. Vapour compression with a reversible expansion engine
Answer : A
A. Air cycle
B. Carnot cycle
C. Ordinary vapour compression cycle
D. Vapour compression with a reversible expansion engine
Answer : A
19. On opening the door of an operating refrigerator kept in a closed room, the temperature of the room will
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain same
D. Increase in summer and will decrease in winter
Answer : A
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain same
D. Increase in summer and will decrease in winter
Answer : A
20. Entropy change of the reaction, H2O (liquid) ? H2O (gas), is termed as the enthalpy of
A. Solution
B. Vaporisation
C. Formation
D. Sublimation
Answer : B
A. Solution
B. Vaporisation
C. Formation
D. Sublimation
Answer : B
21. Claude's liquefaction process employs the cooling of gases by
A. Expansion in an engine
B. Following a constant pressure cycle
C. Throttling
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Expansion in an engine
B. Following a constant pressure cycle
C. Throttling
D. None of these
Answer : A
22. Variation of equilibrium pressure with temperature for any two phases of a given substances is given by the __________ equation.
A. Gibbs-Duhem
B. Maxwell's
C. Clapeyron
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Gibbs-Duhem
B. Maxwell's
C. Clapeyron
D. None of these
Answer : C
23. A thermodynamic system is taken from state A to B along ACB and is brought back to A along BDA as shown below in the P-V diagram. The net work done during the complete cycle is given by the area covered by
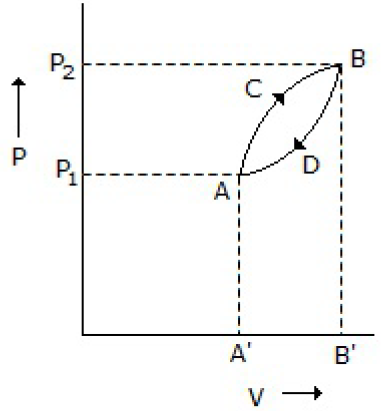
A. P1ACBP2P1
B. ACBB1A1A
C. ACBDA
D. ADBB1A1A
Answer : C

A. P1ACBP2P1
B. ACBB1A1A
C. ACBDA
D. ADBB1A1A
Answer : C
24. In case of a reversible process (following pvn = constant), work obtained for trebling the volume (v1 = 1 m3 and v23 m3) is maximum, when the value of 'n' is
A. 0
B. 1
C. y = 1.44
D. 1.66
Answer : A
A. 0
B. 1
C. y = 1.44
D. 1.66
Answer : A
25. One ton of refrigeration capacity is equivalent to the heat removal rate of
A. 50 kcal/hr
B. 200 BTU/hr
C. 200 BTU/minute
D. 200 BTU/day
Answer : C
A. 50 kcal/hr
B. 200 BTU/hr
C. 200 BTU/minute
D. 200 BTU/day
Answer : C
26. The total change in the enthalpy of a system is independent of the
A. Number of intermediate chemical reactions involved
B. Pressure and temperature
C. State of combination and aggregation in the beginning and at the end of the reaction
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Number of intermediate chemical reactions involved
B. Pressure and temperature
C. State of combination and aggregation in the beginning and at the end of the reaction
D. None of these
Answer : A
27. Which of the following liquid metals has the highest thermal conductivity?
A. Molten sodium
B. Molten lead
C. Mercury
D. Molten potassium
Answer : A
A. Molten sodium
B. Molten lead
C. Mercury
D. Molten potassium
Answer : A
28. The extensive properties are
A. Volume, mass and number of moles
B. Free energy, entropy and enthalpy
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Volume, mass and number of moles
B. Free energy, entropy and enthalpy
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
29. The thermodynamic law, PVy = constant, is not applicable in case of
A. Ideal compression of air
B. Free expansion of an ideal gas
C. Adiabatic expansion of steam in a turbine
D. Adiabatic compression of a perfect gas
Answer : B
A. Ideal compression of air
B. Free expansion of an ideal gas
C. Adiabatic expansion of steam in a turbine
D. Adiabatic compression of a perfect gas
Answer : B
30. Which of the following will increase the volume of a real gas by four times?
A. Doubling the absolute temperature as well as pressure of the gas
B. Reducing pressure to one fourth at constant temperature
C. Reducing temperature to one fourth at constant pressure
D. Reducing the temperature to half and doubling the pressure
Answer : B
A. Doubling the absolute temperature as well as pressure of the gas
B. Reducing pressure to one fourth at constant temperature
C. Reducing temperature to one fourth at constant pressure
D. Reducing the temperature to half and doubling the pressure
Answer : B
31. Which of the following is Clausius-Clapeyron Equation for vaporisation of an ideal gas under the condition that the molar volume of liquid is negligible compared to that of the vapor?
A. d ln p/dt = Hvap/RT2
B. d ln p/dt = RT2/Hvap
C. dp/dt = RT2/Hvap
D. dp/dt = Hvap/RT2
Answer : A
A. d ln p/dt = Hvap/RT2
B. d ln p/dt = RT2/Hvap
C. dp/dt = RT2/Hvap
D. dp/dt = Hvap/RT2
Answer : A
32. A cyclic engine exchanges heat with two reservoirs maintained at 100 and 300°C respectively. The maximum work (in J) that can be obtained from 1000 J of heat extracted from the hot reservoir is
A. 349
B. 651
C. 667
D. 1000
Answer : A
A. 349
B. 651
C. 667
D. 1000
Answer : A
33. Isentropic process means a constant __________ process.
A. Enthalpy
B. Pressure
C. Entropy
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Enthalpy
B. Pressure
C. Entropy
D. None of these
Answer : C
34. Sublimation temperature of dry ice (solid CO2) is __________ °C.
A. -273
B. 0
C. -78
D. 5
Answer : C
A. -273
B. 0
C. -78
D. 5
Answer : C
35. In a reversible process
A. Tds = dE + dW
B. dE - dW = Tds
C. dW - dE = Tds
D. Tds - dW + dE >0
Answer : A
A. Tds = dE + dW
B. dE - dW = Tds
C. dW - dE = Tds
D. Tds - dW + dE >0
Answer : A
36. The ammonia synthesis reaction represented by N2 + 3H2 ? 2NH3; ?H = - 22.4 kcal, is
A. Endothermic
B. Exothermic
C. Isothermal
D. Adiabatic
Answer : B
A. Endothermic
B. Exothermic
C. Isothermal
D. Adiabatic
Answer : B
37. Which of the following is not an equation of state?
A. Bertholet equation
B. Clausius-Clapeyron equation
C. Beattie-Bridgeman equation
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Bertholet equation
B. Clausius-Clapeyron equation
C. Beattie-Bridgeman equation
D. None of these
Answer : B
38. Pick out the undesirable property for a good refrigerant.
A. High thermal conductivity
B. Low freezing point
C. Large latent heat of vaporisation
D. High viscosity
Answer : D
A. High thermal conductivity
B. Low freezing point
C. Large latent heat of vaporisation
D. High viscosity
Answer : D
39. Internal energy of an element at 1 atm and 25° C is __________ kcal/kg.mole.
A. 0
B. 273
C. 25
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. 0
B. 273
C. 25
D. None of these
Answer : A
40. For a thermodynamic system containing 'x' chemical species, the maximum number of phases that can co-exist at equilibrium is
A. x
B. x + 1
C. x + 2
D. x + 3
Answer : C
A. x
B. x + 1
C. x + 2
D. x + 3
Answer : C
41. Mollier chart is a __________ plot.
A. Pressure vs. enthalpy
B. Pressure vs. volume
C. Enthalpy vs. entropy
D. Temperature vs. entropy
Answer : C
A. Pressure vs. enthalpy
B. Pressure vs. volume
C. Enthalpy vs. entropy
D. Temperature vs. entropy
Answer : C
42. What is the ratio of adiabatic compressibility to isothermal compressibility?
A. 1
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. >> 1
Answer : B
A. 1
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. >> 1
Answer : B
43. The expression for entropy change given by, ?S = - nR ln (P2/P1), holds good for
A. Expansion of a real gas
B. Reversible isothermal volume change
C. Heating of an ideal gas
D. Cooling of a real gas
Answer : B
A. Expansion of a real gas
B. Reversible isothermal volume change
C. Heating of an ideal gas
D. Cooling of a real gas
Answer : B
44. Melting of ice exemplifies a/an
A. Adiabatic process
B. Endothermic reaction
C. Exothermic reaction
D. Process involving a chemical reaction
Answer : B
A. Adiabatic process
B. Endothermic reaction
C. Exothermic reaction
D. Process involving a chemical reaction
Answer : B
45. Which of the following is a thermodynamic property of a system?
A. Concentration
B. Mass
C. Temperature
D. Entropy
Answer : D
A. Concentration
B. Mass
C. Temperature
D. Entropy
Answer : D
46. If we increase the pressure on a substance (which is at its triple point), then the triple point
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains unchanged
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the substance
Answer : C
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains unchanged
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the substance
Answer : C
47. If an ideal solution is formed by mixing two pure liquids in any proportion, then the __________ of mixing is zero
A. Enthalpy
B. Volume
C. Both 'a' & 'b'
D. Neither 'a' nor 'b'
Answer : C
A. Enthalpy
B. Volume
C. Both 'a' & 'b'
D. Neither 'a' nor 'b'
Answer : C
48. __________ law of thermodynamics ascertains the direction of a particular spontaneous process.
A. Zeroth
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
Answer : C
A. Zeroth
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
Answer : C
49. Specific __________ does not change during a phase change (e.g. sublimation, melting, vaporisation etc.).
A. Entropy
B. Internal energy
C. Enthalpy
D. Gibbs free energy
Answer : D
A. Entropy
B. Internal energy
C. Enthalpy
D. Gibbs free energy
Answer : D
50. For a real gas, the chemical potential is given by
A. RT d ln P
B. RT d ln f
C. R d ln f
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. RT d ln P
B. RT d ln f
C. R d ln f
D. None of these
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Building Construction MCQ Solved Paper for RRB ALP
1000+ The Living World Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Compressors, Gas Turbines & Jet Engines Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
C Programming MCQ Solved Paper for RRB NTPC
Urothelial tumors of the upper & lower urinary tracts 1000+ MCQ with answer for SBI PO
Steam Boilers, Engines, Nozzles & Turbines 1000+ MCQ with answer for NMAT