1000+ Strength of Materials Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The temperature at which the volume of a gas becomes zero is called
A. Absolute scale of temperature
B. Absolute zero temperature
C. Absolute temperature
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Absolute scale of temperature
B. Absolute zero temperature
C. Absolute temperature
D. None of these
Answer : B
2. Stirling and Ericsson cycles are
A. Reversible cycles
B. Irreversible cycles
C. Semi-reversible cycles
D. Quasi-static cycles
Answer : A
A. Reversible cycles
B. Irreversible cycles
C. Semi-reversible cycles
D. Quasi-static cycles
Answer : A
3. The ratio of specific heat at constant pressure (cp) and specific heat at constant volume (cv) is always __________ one.
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : C
4. The shear force diagram of a cantilever beam of length l and carrying a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length will be
A. A right angled triangle
B. An isosceles triangle
C. An equilateral triangle
D. A rectangle
Answer : A
A. A right angled triangle
B. An isosceles triangle
C. An equilateral triangle
D. A rectangle
Answer : A
5. When it is indicated that a member is elastic, it means that when force is applied, it will
A. Not deform
B. Be safest
C. Stretch
D. Not stretch
Answer : C
A. Not deform
B. Be safest
C. Stretch
D. Not stretch
Answer : C
6. Which of the following is an intensive property of a thermodynamic system?
A. Volume
B. Temperature
C. Mass
D. Energy
Answer : B
A. Volume
B. Temperature
C. Mass
D. Energy
Answer : B
7. For riveting, the size of hole drilled in plates is __________ shank diameter of rivet.
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : C
8. The thermal efficiency of an ideal gas turbine plant is given by (where r = Pressure ratio)
A. r? - 1
B. 1 - r? - 1
C. 1 - (1/r) ?/? - 1
D. 1 - (1/r) ? - 1/ ?
Answer : D
A. r? - 1
B. 1 - r? - 1
C. 1 - (1/r) ?/? - 1
D. 1 - (1/r) ? - 1/ ?
Answer : D
9. In case of an under-reinforced beam, the depth of actual neutral axis is __________ that of the critical neutral axis.
A. Same as
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Same as
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : B
10. The pull required to tear off the plate per pitch length is (where p = Pitch of rivets, t = Thickness of plates, and ?t, ? and ?c = Permissible tensile, shearing and crushing stresses respectively)
A. (p - 2d) t × ?c
B. (p - d) t × ?
C. (p - d) t × ?t
D. (2p - d) t × ?t
Answer : C
A. (p - 2d) t × ?c
B. (p - d) t × ?
C. (p - d) t × ?t
D. (2p - d) t × ?t
Answer : C
11. According to Avogadro's law, the density of any two gases is __________ their molecular masses, if the gases are at the same temperature and pressure.
A. Equal to
B. Directly proportional to
C. Inversely proportional to
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Equal to
B. Directly proportional to
C. Inversely proportional to
D. None of these
Answer : B
12. Charles' law states that all perfect gases change in volume by __________ of its original volume at 0°C for every 1°C change in temperature, when pressure remains constant.
A. 1/27th
B. 1/93th
C. 1/173th
D. 1/273th
Answer : D
A. 1/27th
B. 1/93th
C. 1/173th
D. 1/273th
Answer : D
13. Elasticity of Mild Steel specimen is defined by
A. Hookes law
B. Yield point
C. Plastic flow
D. Proof stress
Answer : C
A. Hookes law
B. Yield point
C. Plastic flow
D. Proof stress
Answer : C
14. The fuel mostly used in cement industry and in metallurgical processes is
A. Wood charcoal
B. Bituminous coke
C. Pulverised coal
D. Coke
Answer : C
A. Wood charcoal
B. Bituminous coke
C. Pulverised coal
D. Coke
Answer : C
15. Which of the following statement is correct?
A. The increase in entropy is obtained from a given quantity of heat at a low temperature.
B. The change in entropy may be regarded as a measure of the rate of the availability or unavailability of heat for transformation into work.
C. The entropy represents the maximum amount of work obtainable per degree drop in temperature.
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. The increase in entropy is obtained from a given quantity of heat at a low temperature.
B. The change in entropy may be regarded as a measure of the rate of the availability or unavailability of heat for transformation into work.
C. The entropy represents the maximum amount of work obtainable per degree drop in temperature.
D. All of the above
Answer : D
16. The limit of eccentricity for no tensile conditions for a column of circular section of diameter (D) is
A. d/4
B. d/8
C. d/12
D. d/16
Answer : B
A. d/4
B. d/8
C. d/12
D. d/16
Answer : B
17. Kerosene is distilled at
A. 65° to 220°C
B. 220° to 345°C
C. 345° to 470°C
D. 470° to 550°C
Answer : B
A. 65° to 220°C
B. 220° to 345°C
C. 345° to 470°C
D. 470° to 550°C
Answer : B
18. The maximum diameter of the hole that can be punched from a plate of maximum shear stress 1/4th of its maximum crushing stress of punch, is equal to (where t = Thickness of the plate)
A. t
B. 2t
C. 4t
D. 8t
Answer : C
A. t
B. 2t
C. 4t
D. 8t
Answer : C
19. When a bar is cooled to - 5°C, it will develop
A. No stress
B. Shear stress
C. Tensile stress
D. Compressive stress
Answer : C
A. No stress
B. Shear stress
C. Tensile stress
D. Compressive stress
Answer : C
20. A bar of copper and steel form a composite system, which is heated to a temperature of 40°C. The stress induced in the copper bar will be
A. Tensile
B. Compressive
C. Shear
D. Zero
Answer : B
A. Tensile
B. Compressive
C. Shear
D. Zero
Answer : B
21. A molecule consisting of one atom is known as
A. Mono-atomic
B. Di-atomic
C. Tri-atomic
D. Poly-atomic
Answer : A
A. Mono-atomic
B. Di-atomic
C. Tri-atomic
D. Poly-atomic
Answer : A
22. Workdone during adiabatic expansion is given by (where p v1, T1 = Pressure, volume and temperature for the initial condition of gas, p2, v2, T2 = Corresponding values for the final condition of gas, R = Gas constant, and ? = Ratio of specific heats)
A. (p1 v1 - p2 v2)/(? - 1)
B. [m R (T1 - T2)] /(? - 1)
C. [m R T1/(? - 1)][1 - (p2 v2 /p1 v1)]
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. (p1 v1 - p2 v2)/(? - 1)
B. [m R (T1 - T2)] /(? - 1)
C. [m R T1/(? - 1)][1 - (p2 v2 /p1 v1)]
D. All of these
Answer : D
23. In the below figure, the plastic range occurs
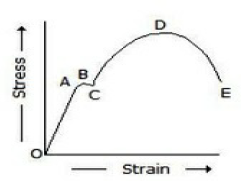
A. Before point A
B. Beyond point A
C. Between points A and D
D. Between points D and E
Answer : B

A. Before point A
B. Beyond point A
C. Between points A and D
D. Between points D and E
Answer : B
24. When gas is heated at constant pressure, the heat supplied is utilised in
A. Increasing the internal energy of gas
B. Doing some external work
C. Increasing the internal energy of gas and also for doing some external work
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Increasing the internal energy of gas
B. Doing some external work
C. Increasing the internal energy of gas and also for doing some external work
D. None of the above
Answer : C
25. True stress strain-curve for materials is plotted between
A. Load/original cross-sectional area and change in length/original length
B. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and loge (original area/ instantaneous area)
C. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and change in length/ original length
D. Load/ instantaneous area and instantaneous area/original area
Answer : B
A. Load/original cross-sectional area and change in length/original length
B. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and loge (original area/ instantaneous area)
C. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and change in length/ original length
D. Load/ instantaneous area and instantaneous area/original area
Answer : B
26. Which of the following cycles is not a reversible cycle?
A. Carnot
B. Ericsson
C. Stirling
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. Carnot
B. Ericsson
C. Stirling
D. None of the above
Answer : D
27. In the tensile test, the phenomenon of slow extension of the material, i. e. stress increasing with the time at a constant load is called
A. Creeping
B. Yielding
C. Breaking
D. Plasticity
Answer : A
A. Creeping
B. Yielding
C. Breaking
D. Plasticity
Answer : A
28. For the same compression ratio, the efficiency of dual combustion cycle is
A. Greater than Diesel cycle and less than Otto cycle
B. Less than Diesel cycle and greater than Otto cycle
C. Greater than Diesel cycle
D. Less than Diesel cycle
Answer : A
A. Greater than Diesel cycle and less than Otto cycle
B. Less than Diesel cycle and greater than Otto cycle
C. Greater than Diesel cycle
D. Less than Diesel cycle
Answer : A
29. The general gas energy equation is (where Q1 - 2 = Heat supplied, dU = Change in internal energy, and W1 - 2 = Work done in heat units)
A. Q1 - 2 = dU + W1 - 2
B. Q1 - 2 = dU - W1 - 2
C. Q1 - 2 = dU/W1 - 2
D. Q1 - 2 = dU × W1 - 2
Answer : A
A. Q1 - 2 = dU + W1 - 2
B. Q1 - 2 = dU - W1 - 2
C. Q1 - 2 = dU/W1 - 2
D. Q1 - 2 = dU × W1 - 2
Answer : A
30. The absolute zero temperature is taken as
A. -273°C
B. 73°C
C. 237°C
D. -237°C
Answer : A
A. -273°C
B. 73°C
C. 237°C
D. -237°C
Answer : A
31. The ratio of specific heat at constant pressure (cp) and specific heat at constant volume (cv) is
A. Equal to one
B. Less than one
C. Greater than one
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Equal to one
B. Less than one
C. Greater than one
D. None of these
Answer : C
32. In compression test, the fracture in cast iron specimen would occur along
A. The axis of load
B. An oblique plane
C. At right angles to the axis of specimen
D. Would not occur
Answer : B
A. The axis of load
B. An oblique plane
C. At right angles to the axis of specimen
D. Would not occur
Answer : B
33. The given figure shows the Mohr's circle of stress for two unequal and like principal stresses (?x and ?y) acting at a body across two mutually perpendicular planes. The normal stress on an oblique section making an angle ? with the minor principle plane is given by
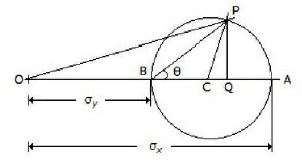
A. OC
B. OP
C. OQ
D. PQ
Answer : C

A. OC
B. OP
C. OQ
D. PQ
Answer : C
34. The ideal efficiency of a Brayton cycle without regeneration, with increase in pressure ratio will
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain unchanged
D. Increase/decrease depending on application
Answer : A
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain unchanged
D. Increase/decrease depending on application
Answer : A
35. The entropy may be expressed as a function of
A. Pressure and temperature
B. Temperature and volume
C. Heat and work
D. All of these
Answer : A
A. Pressure and temperature
B. Temperature and volume
C. Heat and work
D. All of these
Answer : A
36. A body is subjected to a tensile stress of 1200 MPa on one plane and another tensile stress of 600 MPa on a plane at right angles to the former. It is also subjected to a shear stress of 400 MPa on the same planes. The maximum normal stress will be
A. 400 MPa
B. 500 MPa
C. 900 MPa
D. 1400 MPa
Answer : D
A. 400 MPa
B. 500 MPa
C. 900 MPa
D. 1400 MPa
Answer : D
37. A masonry dam may fail due to
A. Tension in the masonry of the dam and its base
B. Overturning of the dam
C. Crushing of masonry at the base of the dam
D. Any one of the above
Answer : D
A. Tension in the masonry of the dam and its base
B. Overturning of the dam
C. Crushing of masonry at the base of the dam
D. Any one of the above
Answer : D
38. Which of the following statement is correct according to Clausis statement of second law of thermodynamics?
A. It is possible to transfer heat from a body at a lower temperature to a body at a higher temperature.
B. It is impossible to transfer heat from a body at a lower temperature to a body at a higher temperature, without the aid of an external source.
C. It is possible to transfer heat from a body at a lower temperature to a body at a higher temperature by using refrigeration cycle.
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. It is possible to transfer heat from a body at a lower temperature to a body at a higher temperature.
B. It is impossible to transfer heat from a body at a lower temperature to a body at a higher temperature, without the aid of an external source.
C. It is possible to transfer heat from a body at a lower temperature to a body at a higher temperature by using refrigeration cycle.
D. None of the above
Answer : B
39. For the beam shown in the below figure, the shear force diagram between A and B is
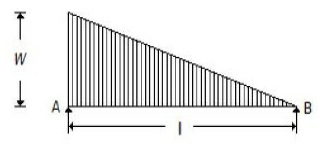
A. A horizontal line
B. A vertical line
C. An inclined line
D. A parabolic curve
Answer : D

A. A horizontal line
B. A vertical line
C. An inclined line
D. A parabolic curve
Answer : D
40. One molecule of oxygen is __________ times heavier than the hydrogen atom.
A. 12
B. 14
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : D
A. 12
B. 14
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : D
41. Which of the following materials is most elastic?
A. Rubber
B. Plastic
C. Brass
D. Steel
Answer : D
A. Rubber
B. Plastic
C. Brass
D. Steel
Answer : D
42. The ratio of the largest load in a test to the original cross-sectional area of the test piece is called
A. Elastic limit
B. Yield stress
C. Ultimate stress
D. Breaking stress
Answer : C
A. Elastic limit
B. Yield stress
C. Ultimate stress
D. Breaking stress
Answer : C
43. The principal constituents of a fuel are
A. Carbon and hydrogen
B. Oxygen and hydrogen
C. Sulphur and oxygen
D. Sulphur and hydrogen
Answer : A
A. Carbon and hydrogen
B. Oxygen and hydrogen
C. Sulphur and oxygen
D. Sulphur and hydrogen
Answer : A
44. If the depth is kept constant for a beam of uniform strength, then its width will vary in proportional to
A. Bending moment (i.e. M)
B. Bending moment² (i.e. M²)
C. Bending moment³ (i.e. M³)
D. Bending moment? (i.e. M?)
Answer : A
A. Bending moment (i.e. M)
B. Bending moment² (i.e. M²)
C. Bending moment³ (i.e. M³)
D. Bending moment? (i.e. M?)
Answer : A
45. When a body is subjected to a direct tensile stress (?x) in one plane accompanied by a simple shear stress (?xy), the maximum normal stress i
A. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
B. (?x/2) - (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
C. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² - 4 ?²xy)
D. (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
Answer : A
A. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
B. (?x/2) - (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
C. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² - 4 ?²xy)
D. (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
Answer : A
46. The oxygen atom is ________ times heavier than the hydrogen atom.
A. 2
B. 8
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : C
A. 2
B. 8
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : C
47. The deformation per unit length is called
A. Tensile stress
B. Compressive stress
C. Shear stress
D. Strain
Answer : D
A. Tensile stress
B. Compressive stress
C. Shear stress
D. Strain
Answer : D
48. A circular shaft fixed at, A has diameter D for half of its length and diameter D/2 over the other half, as shown in the below figure. If the rotation of B relative to A is 0.1 radian, the rotation of C relative to B will be
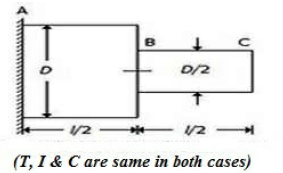
A. 0.4 radian
B. 0.8 radian
C. 1.6 radian
D. 3.2 radian
Answer : C

A. 0.4 radian
B. 0.8 radian
C. 1.6 radian
D. 3.2 radian
Answer : C
49. The layer at the centre of gravity of the beam as shown in the below figure, will be

A. In tension
B. In compression
C. Neither in tension nor in compression
D. None of these
Answer : C

A. In tension
B. In compression
C. Neither in tension nor in compression
D. None of these
Answer : C
50. The property of a material by virtue of which it can be beaten or rolled into plates is called
A. Malleability
B. Ductility
C. Plasticity
D. Elasticity
Answer : A
A. Malleability
B. Ductility
C. Plasticity
D. Elasticity
Answer : A
Sharing is caring
Related Post
CTET - Problems on Trains 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Airport Engineering Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Design of Steel Structures MCQ for JEE Main [Solved]
1000+ Urologic infections and inflammations MCQ for RRB ALP [Solved]
1000+ General Chemistry Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
NEET - Current Affairs June 2017 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download