1000+ Strength of Materials Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The distillation carried out in such a way that the liquid with the lowest boiling point is first evaporated and recondensed, then the liquid with the next higher boiling point is then evaporated and recondensed, and so on until all the available liquid fuels are separately recovered in the sequence of their boiling points. Such a process is called
A. Cracking
B. Carbonisation
C. Fractional distillation
D. Full distillation
Answer : C
A. Cracking
B. Carbonisation
C. Fractional distillation
D. Full distillation
Answer : C
2. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water through one Kelvin is called
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. kilo-Joule
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. kilo-Joule
D. None of these
Answer : C
3. Strain energy is the
A. Energy stored in a body when strained within elastic limits
B. Energy stored in a body when strained up to the breaking of a specimen
C. Maximum strain energy which can be stored in a body
D. Proof resilience per unit volume of a material
Answer : A
A. Energy stored in a body when strained within elastic limits
B. Energy stored in a body when strained up to the breaking of a specimen
C. Maximum strain energy which can be stored in a body
D. Proof resilience per unit volume of a material
Answer : A
4. Resilience is the
A. Energy stored in a body when strained within elastic limits
B. Energy stored in a body when strained up to the breaking of the specimen maximum strain
C. Energy which can be stored in a body
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. Energy stored in a body when strained within elastic limits
B. Energy stored in a body when strained up to the breaking of the specimen maximum strain
C. Energy which can be stored in a body
D. None of the above
Answer : D
5. Modular ratio of two materials is the ratio of
A. Strains
B. Stress and strain
C. Shear stress and shear strain
D. Moduli and elasticity
Answer : D
A. Strains
B. Stress and strain
C. Shear stress and shear strain
D. Moduli and elasticity
Answer : D
6. The efficiency of Diesel cycle approaches to Otto cycle efficiency when
A. Cut-off is increased
B. Cut-off is decreased
C. Cut-off is zero
D. Cut-off is constant
Answer : C
A. Cut-off is increased
B. Cut-off is decreased
C. Cut-off is zero
D. Cut-off is constant
Answer : C
7. The relation between equivalent length (L) and actual length (l) of a column for both ends fixed is
A. L = l/2
B. L = l/?2
C. L = l
D. L = 2l
Answer : A
A. L = l/2
B. L = l/?2
C. L = l
D. L = 2l
Answer : A
8. The value of specific heat at constant pressure (cp) is __________ that of at constant volume (cv).
A. Less than
B. Equal to
C. More than
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Less than
B. Equal to
C. More than
D. None of these
Answer : C
9. The assumption made in Euler's column theory is that
A. The failure of column occurs due to buckling alone
B. The length of column is very large as compared to its cross-sectional dimensions
C. The column material obeys Hooke's law
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. The failure of column occurs due to buckling alone
B. The length of column is very large as compared to its cross-sectional dimensions
C. The column material obeys Hooke's law
D. All of the above
Answer : D
10. The compression ratio is the ratio of
A. Swept volume to total volume
B. Total volume to swept volume
C. Swept volume to clearance volume
D. Total volume to clearance volume
Answer : D
A. Swept volume to total volume
B. Total volume to swept volume
C. Swept volume to clearance volume
D. Total volume to clearance volume
Answer : D
11. Which of the following is correct?
A. Absolute pressure = Gauge pressure + Atmospheric pressure
B. Gauge pressure = Absolute pressure + Atmospheric pressure
C. Atmospheric pressure = Absolute pressure + Gauge pressure
D. Absolute pressure = Gauge pressure - Atmospheric pressure
Answer : A
A. Absolute pressure = Gauge pressure + Atmospheric pressure
B. Gauge pressure = Absolute pressure + Atmospheric pressure
C. Atmospheric pressure = Absolute pressure + Gauge pressure
D. Absolute pressure = Gauge pressure - Atmospheric pressure
Answer : A
12. The sum of internal energy (U) and the product of pressure and volume (p.v) is known as
A. Workdone
B. Entropy
C. Enthalpy
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Workdone
B. Entropy
C. Enthalpy
D. None of these
Answer : C
13. The extremeties of any diameter on Mohr's circle represent
A. Principal stresses
B. Normal stresses on planes at 45°
C. Shear stresses on planes at 45°
D. Normal and shear stresses on a plane
Answer : B
A. Principal stresses
B. Normal stresses on planes at 45°
C. Shear stresses on planes at 45°
D. Normal and shear stresses on a plane
Answer : B
14. The efficiency of Diesel cycle with decrease in cut-off
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. First increases and then decreases
D. First decreases and then increases
Answer : A
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. First increases and then decreases
D. First decreases and then increases
Answer : A
15. If the rivets in adjacent rows are staggered and the outermost row has only one rivets, the arrangement of the rivets is called
A. Chain riveting
B. Zigzag riveting
C. Diamond riveting
D. Crisscross riveting
Answer : C
A. Chain riveting
B. Zigzag riveting
C. Diamond riveting
D. Crisscross riveting
Answer : C
16. A composite bar made up of steel and copper bars of equal lengths are heated through 100°C. The stresses developed shall be
A. Tensile in both the material
B. Tensile in steel and compressive in copper
C. Compressive in steel and tensile in copper
D. Compressive in both the materials
Answer : D
A. Tensile in both the material
B. Tensile in steel and compressive in copper
C. Compressive in steel and tensile in copper
D. Compressive in both the materials
Answer : D
17. One kilowatt is equal to
A. 1 N-m/s
B. 100 N-m
C. 1000 N-m/s
D. 1 × 106 N-m/s
Answer : C
A. 1 N-m/s
B. 100 N-m
C. 1000 N-m/s
D. 1 × 106 N-m/s
Answer : C
18. One Joule (J) is equal to
A. 1 N-m
B. 1 kN-m
C. 10 N-m/s
D. 10 kN-m/s
Answer : A
A. 1 N-m
B. 1 kN-m
C. 10 N-m/s
D. 10 kN-m/s
Answer : A
19. Carbonisation of coal consists of
A. Drying and crushing the coal to a fine powder
B. Moulding the finely ground coal under pressure with or without a binding material
C. Heating the wood with a limited supply of air to temperature not less than 280°C
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. Drying and crushing the coal to a fine powder
B. Moulding the finely ground coal under pressure with or without a binding material
C. Heating the wood with a limited supply of air to temperature not less than 280°C
D. None of the above
Answer : D
20. The entropy may be expressed as a function of
A. Pressure and temperature
B. Temperature and volume
C. Heat and work
D. All of these
Answer : A
A. Pressure and temperature
B. Temperature and volume
C. Heat and work
D. All of these
Answer : A
21. The atomic mass of oxygen is
A. 12
B. 14
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : C
A. 12
B. 14
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : C
22. The unit of Young's modulus is
A. mm/mm
B. kg/cm
C. Kg
D. kg/cm²
Answer : D
A. mm/mm
B. kg/cm
C. Kg
D. kg/cm²
Answer : D
23. When both ends of a column are fixed, the effective length is
A. Its own length
B. Twice its length
C. Half its length
D. 1/?2 × its length
Answer : C
A. Its own length
B. Twice its length
C. Half its length
D. 1/?2 × its length
Answer : C
24. The strain energy stored in a body due to suddenly applied load compared to when it is applied gradually is
A. Same
B. Twice
C. Four times
D. Eight times
Answer : C
A. Same
B. Twice
C. Four times
D. Eight times
Answer : C
25. The efficiency of Carnot cycle depends upon
A. Temperature limits
B. Pressure ratio
C. Volume compression ratio
D. Cut-off ratio and compression ratio
Answer : A
A. Temperature limits
B. Pressure ratio
C. Volume compression ratio
D. Cut-off ratio and compression ratio
Answer : A
26. According to kinetic theory of gases, the velocity of molecules __________ with the increase in temperature.
A. Remains constant
B. Increases
C. Decreases
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Remains constant
B. Increases
C. Decreases
D. None of these
Answer : B
27. The change in the unit volume of a material under tension with increase in its Poisson's ratio will
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain same
D. Increase initially and then decrease
Answer : B
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain same
D. Increase initially and then decrease
Answer : B
28. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of __________ water through one degree is called kilojoules.
A. 1 g
B. 10 g
C. 100 g
D. 1000 g
Answer : D
A. 1 g
B. 10 g
C. 100 g
D. 1000 g
Answer : D
29. In the below figure, the plastic range occurs
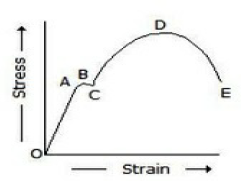
A. Before point A
B. Beyond point A
C. Between points A and D
D. Between points D and E
Answer : B

A. Before point A
B. Beyond point A
C. Between points A and D
D. Between points D and E
Answer : B
30. A molecule consisting of one atom is known as
A. Mono-atomic
B. Di-atomic
C. Tri-atomic
D. Poly-atomic
Answer : A
A. Mono-atomic
B. Di-atomic
C. Tri-atomic
D. Poly-atomic
Answer : A
31. A cylindrical section having no joint is known as
A. Joint less section
B. Homogeneous section
C. Perfect section
D. Seamless section
Answer : D
A. Joint less section
B. Homogeneous section
C. Perfect section
D. Seamless section
Answer : D
32. Modulus of rigidity is defined as the ratio of
A. Longitudinal stress to longitudinal strain
B. Volumetric stress to volumetric strain
C. Lateral stress to Lateral strain
D. Shear stress to shear strain
Answer : D
A. Longitudinal stress to longitudinal strain
B. Volumetric stress to volumetric strain
C. Lateral stress to Lateral strain
D. Shear stress to shear strain
Answer : D
33. Young's modulus is defined as the ratio of
A. Volumetric stress and volumetric strain
B. Lateral stress and lateral strain
C. Longitudinal stress and longitudinal strain
D. Shear stress to shear strain
Answer : C
A. Volumetric stress and volumetric strain
B. Lateral stress and lateral strain
C. Longitudinal stress and longitudinal strain
D. Shear stress to shear strain
Answer : C
34. Which of the following gas has a minimum molecular mass?
A. Oxygen
B. Nitrogen
C. Hydrogen
D. Methane
Answer : C
A. Oxygen
B. Nitrogen
C. Hydrogen
D. Methane
Answer : C
35. For the constant pressure and heat input, the air standard efficiency of gas power cycle is in the order
A. Dual cycle, Diesel cycle, Otto cycle
B. Otto cycle, Diesel cycle, Dual cycle
C. Dual cycle, Otto cycle, Diesel cycle
D. Diesel cycle, Otto cycle, Dual cycle
Answer : A
A. Dual cycle, Diesel cycle, Otto cycle
B. Otto cycle, Diesel cycle, Dual cycle
C. Dual cycle, Otto cycle, Diesel cycle
D. Diesel cycle, Otto cycle, Dual cycle
Answer : A
36. Volumetric strain for a rectangular specimen of length l, breadth b and thickness t subjected to a pull of P is given by
A. e (1 - 2m)
B. e (1 - 2/m)
C. e (m - 2)
D. e (2/m - 1)
Answer : B
A. e (1 - 2m)
B. e (1 - 2/m)
C. e (m - 2)
D. e (2/m - 1)
Answer : B
37. A material obeys hooks law up to
A. Plastic limit
B. Elastic limit
C. Yield point
D. Limit of proportionality
Answer : B
A. Plastic limit
B. Elastic limit
C. Yield point
D. Limit of proportionality
Answer : B
38. Which of the following is a proper sequence?
A. Proportional limit, elastic limit, yielding, failure
B. Elastic limit, proportional limit, yielding, failure
C. Yielding, proportional limit, elastic limit, failure
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Proportional limit, elastic limit, yielding, failure
B. Elastic limit, proportional limit, yielding, failure
C. Yielding, proportional limit, elastic limit, failure
D. None of the above
Answer : A
39. The thermal efficiency of an ideal gas turbine plant is given by (where r = Pressure ratio)
A. r? - 1
B. 1 - r? - 1
C. 1 - (1/r) ?/? - 1
D. 1 - (1/r) ? - 1/ ?
Answer : D
A. r? - 1
B. 1 - r? - 1
C. 1 - (1/r) ?/? - 1
D. 1 - (1/r) ? - 1/ ?
Answer : D
40. The ratio of molar specific heats for mono-atomic gas is
A. 1
B. 1.4
C. 1.67
D. 1.87
Answer : C
A. 1
B. 1.4
C. 1.67
D. 1.87
Answer : C
41. The maximum shear stress, in the given figure, is equal to __________ of the Mohr's circle.
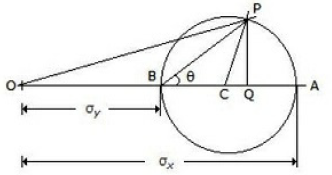
A. Radius
B. Diameter
C. Circumference
D. Area
Answer : A

A. Radius
B. Diameter
C. Circumference
D. Area
Answer : A
42. The heat and work are mutually convertible. This statement is called __________ law of thermodynamics.
A. Zeroth
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
Answer : B
A. Zeroth
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
Answer : B
43. The absolute zero pressure can be attained at a temperature of
A. 0°C
B. 273°C
C. 273 K
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. 0°C
B. 273°C
C. 273 K
D. None of these
Answer : D
44. Which of the following statement is correct?
A. The increase in entropy is obtained from agiven quantity of heat at a low temperature.
B. The change in entropy may be regarded as a measure of the rate of the availability or unavailability of heat for transformation into work.
C. The entropy represents the maximum amount of work obtainable per degree drop in temperature.
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. The increase in entropy is obtained from agiven quantity of heat at a low temperature.
B. The change in entropy may be regarded as a measure of the rate of the availability or unavailability of heat for transformation into work.
C. The entropy represents the maximum amount of work obtainable per degree drop in temperature.
D. All of the above
Answer : D
45. In a belt drive, the pulley diameter is doubled, the belt tension and pulley width remaining same. The changes required in key will be
A. Increase key length
B. Increase key depth
C. Increase key width
D. Double all the dimensions
Answer : C
A. Increase key length
B. Increase key depth
C. Increase key width
D. Double all the dimensions
Answer : C
46. The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress is
A. Zero
B. Minimum
C. Maximum
D. Infinity
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Minimum
C. Maximum
D. Infinity
Answer : A
47. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of the unit mass of gas through one degree at constant volume, is called
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. Kilo Joule
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. Kilo Joule
D. None of these
Answer : A
48. The relation between Young's modulus (E), shear modulus (C) and bulk modulus (K) is given by
A. E = 3K.C/(3K + C)
B. E = 6K.C/(3K + C)
C. E = 9K.C/(3K + C)
D. E = 12K.C/(3K + C)
Answer : C
A. E = 3K.C/(3K + C)
B. E = 6K.C/(3K + C)
C. E = 9K.C/(3K + C)
D. E = 12K.C/(3K + C)
Answer : C
49. The limit of eccentricity for no tensile conditions for a column of circular section of diameter (D) is
A. d/4
B. d/8
C. d/12
D. d/16
Answer : B
A. d/4
B. d/8
C. d/12
D. d/16
Answer : B
50. When a body is subjected to biaxial stress i.e. direct stresses (?x) and (?y) in two mutually perpendicular planes accompanied by a simple shear stress (?xy), then minimum normal stress is
A. (?x + ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
B. (?x + ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
C. (?x - ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
D. (?x - ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
Answer : B
A. (?x + ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
B. (?x + ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
C. (?x - ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
D. (?x - ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Urinary Calculus Disease Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Building Construction MCQ for IBPS PO [Solved]
1000+ Current Affairs February 2023 Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Steam Boilers, Engines, Nozzles & Turbines Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
SSC MTS - Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download