Anatomy of flowering plant 1000+ MCQ with answer for SBI Clerk
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Match the terms given in column I with their funciton given in column II and choose the correct option.
A. A I, B III, C V, D II, E IV
B. A III, B I, C II, D V, E IV
C. A II, B IV, C V, D I, E III
D. A V, B IV, C III, D II, E I
Answer : B
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| (Term) | (Functions) |
| A. Meristem | I. Photosynthesis, storage |
| B. Parenchyma | II. Mechanical support |
| C. Collenchyma | III. Actively dividing cells |
| D. Sclerenchyma | IV. Stomata |
| E. Epidermal tissue | V. Sclereids |
A. A I, B III, C V, D II, E IV
B. A III, B I, C II, D V, E IV
C. A II, B IV, C V, D I, E III
D. A V, B IV, C III, D II, E I
Answer : B
2. Match the terms given in column I with their features given in column II and choose the correct option.
A. A - (i), B - (ii), C - (iii), D - (iv), E - (v)
B. A - (iii), B - (v), C - (ii), D - (iv), E - (i)
C. A - (iii), B - (i), C - (v), D - (ii), E - (iv)
D. A - (v), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (i), E - (ii)
Answer : B
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| (Terms) | (Features) |
| A. Fibres | (i) Cells are living and thin walled with cellulosic cell wall, store food materials in the form of starch or fat |
| B. Sclereids | (ii) Main water conductive cells of the pteridophytes and the gymnosperms |
| C. Tracheids | (iii) Thick walled, elongated and pointed cells, generally occurring in groups |
| D. Vessels | (iv) Long cylindrical tube like structure and cells are devoid of protoplasm. Characteristic feature of angiosperms |
| E. Xylem parenchyma | (v) Reduced form of sclerenchyma cells with highly thickened lignified cellular walls that form small bundles of durable layers of tissue in most plants. |
A. A - (i), B - (ii), C - (iii), D - (iv), E - (v)
B. A - (iii), B - (v), C - (ii), D - (iv), E - (i)
C. A - (iii), B - (i), C - (v), D - (ii), E - (iv)
D. A - (v), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (i), E - (ii)
Answer : B
3. The vessel elements of angiosperms differ from other elements of xylem in having
A. simple pits on their radial walls.
B. bordered pits on their lateral walls.
C. simple and bordered pits on their end walls.
D. simple perforation on their end walls.
Answer : D
A. simple pits on their radial walls.
B. bordered pits on their lateral walls.
C. simple and bordered pits on their end walls.
D. simple perforation on their end walls.
Answer : D
4. The given figure shows the secondary growth in a dicot stem. Their parts are marked as A, B, C, D, E & F. Choose the correct labelling of the parts marked as A to F.
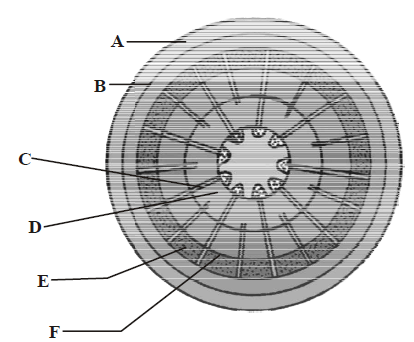
A. A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Medullary rays, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Cambium ring
B. A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Medullary rays, D Secondary phloem, E Secondary xylem, F Cambium ring
C. A Phellogen, B Phellem, C Medullary rays, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Cambium ring
D. A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Cambium ring, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Medullary rays
Answer : A

A. A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Medullary rays, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Cambium ring
B. A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Medullary rays, D Secondary phloem, E Secondary xylem, F Cambium ring
C. A Phellogen, B Phellem, C Medullary rays, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Cambium ring
D. A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Cambium ring, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Medullary rays
Answer : A
5. In stems, the protoxylem lies towards the _____________ and the metaxylem lies towards the ____________ of the organ.
A. centre; periphery
B. periphery; centre
C. periphery; periphery
D. centre; centre
Answer : A
A. centre; periphery
B. periphery; centre
C. periphery; periphery
D. centre; centre
Answer : A
6. Match the names of the structures given in column-I with the functions given in column-II, choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the two columns :
A. A V, B III, C I, D IV
B. A I, B IV, C V, D III
C. A II, B IV, C I, D III
D. A IV, B I, C III, D V
Answer : D
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| (Structure) | (Function) |
| A. Stomata | I. Protection of stem |
| B. Bark | II. Plant movement |
| C. Cambium | III. Secondary growth |
| D. Cuticle | IV. Transpiration |
| V. Prevent the loss of water | ... |
A. A V, B III, C I, D IV
B. A I, B IV, C V, D III
C. A II, B IV, C I, D III
D. A IV, B I, C III, D V
Answer : D
7. A narrow layer of thin walled cells found between phloem/ bark and wood of a dicot is
A. cork cambium
B. vascular cambium
C. endodermis
D. both (a) & (c)
Answer : B
A. cork cambium
B. vascular cambium
C. endodermis
D. both (a) & (c)
Answer : B
8. The given diagrams show stomatal apparatus in dicots and monocots. Which one is correct option for A, B and C?
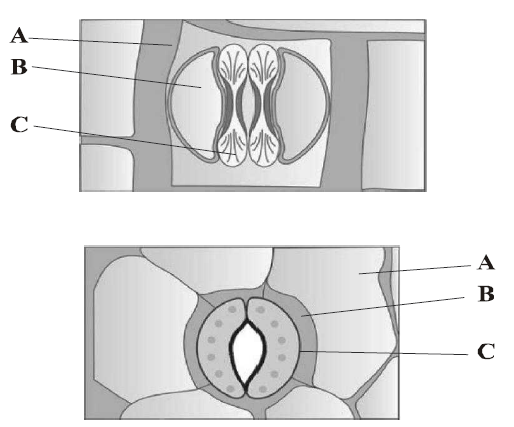
A. A Epidermal cells; B Subsidiary cells; C chloroplast
B. A Guard cells; B Subsidiary cells; C Stomatal pore
C. A Guard cells; B Epidermal cells; C Guard cells
D. A Epidermal cells; B Subsidiary cells; C Guard cells
Answer : D

A. A Epidermal cells; B Subsidiary cells; C chloroplast
B. A Guard cells; B Subsidiary cells; C Stomatal pore
C. A Guard cells; B Epidermal cells; C Guard cells
D. A Epidermal cells; B Subsidiary cells; C Guard cells
Answer : D
9. Which meristem helps in increasing girth?
A. Lateral meristem
B. Intercalary meristem
C. Primary meristem
D. Apical meristem
Answer : A
A. Lateral meristem
B. Intercalary meristem
C. Primary meristem
D. Apical meristem
Answer : A
10. Which of following helps bamboo and grasses to elongate ?
A. Apical meristems
B. Lateral meristems
C. Secondary meristems
D. Intercalary meristems
Answer : D
A. Apical meristems
B. Lateral meristems
C. Secondary meristems
D. Intercalary meristems
Answer : D
11. The given figures are types of elements (A and B) which constitute one type of complex tissue (c) of a plant . Identify A, B and C.
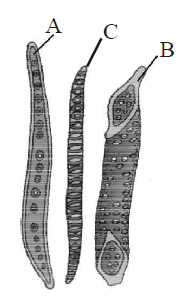
A. A Tracheid, B Vessel, C Xylem
B. A Vessel, B Tracheild, C Phloem
C. A Fibre, B Tracheid, C Bark
D. A Fibre, B Sclereid, C Casparian strips
Answer : A

A. A Tracheid, B Vessel, C Xylem
B. A Vessel, B Tracheild, C Phloem
C. A Fibre, B Tracheid, C Bark
D. A Fibre, B Sclereid, C Casparian strips
Answer : A
12. In an experiment, a student cut a transverse section of young stem of a plant which he has taken from his school garden.
After observing it under the microscope how would he ascertain whether it is a monocot stem or a dicot stem?
A. With the help of bulliform cells.
B. With the help of casparian strips.
C. With the help of vascular bundles.
D. With the help of stomatal apparatus.
Answer : C
After observing it under the microscope how would he ascertain whether it is a monocot stem or a dicot stem?
A. With the help of bulliform cells.
B. With the help of casparian strips.
C. With the help of vascular bundles.
D. With the help of stomatal apparatus.
Answer : C
13. Which one of the following have vessels as their characteristic feature?
A. Angiosperms
B. Gymnosperms
C. Pteridophytes
D. Bryophytes
Answer : A
A. Angiosperms
B. Gymnosperms
C. Pteridophytes
D. Bryophytes
Answer : A
14. As secondary growth proceeds, in a dicot stem, the thickness of
A. sapwood increases.
B. heartwood increase.
C. both sapwood and heartwood increases.
D. both sapwood and heartwood remains the same.
Answer : C
A. sapwood increases.
B. heartwood increase.
C. both sapwood and heartwood increases.
D. both sapwood and heartwood remains the same.
Answer : C
15. T.S. of dicot stem is given below, certain parts have been marked by alphabets (A I). Choose the option which shows their correct labelling.
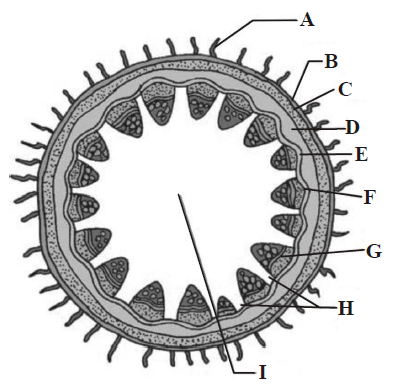
A. A Epidermis, B Epidermal hair, C Parenchyma, D Starch sheath, E Hypodermis (collenchyma), F Vascular bundle, G Bundle cap, H Medulla or pith, I Medullary rays
B. A Epidermal hair, B Epidermis, C Hypodermis (collenchyma), D Parenchyma, E Endoderm is (Starch Sheath), F Pericycle, G Vascular bundle, H Medullary rays, I Medulla or pith
C. A Epidermal hair, B Epidermis, C Hypodermis (collenchyma), D Starch sheath, E Parenchyma, F Vascular bundle, G Bundle cap, H Medulla or pith, I Medullary rays
D. A Epidermal hair, B Epidermis, C Parenchyma, D Hypodermis (collenchyma), E Starch sheath, F Vascular bundle, G Bundle cap, H Medulla or pith, I Medullary rays
Answer : B

A. A Epidermis, B Epidermal hair, C Parenchyma, D Starch sheath, E Hypodermis (collenchyma), F Vascular bundle, G Bundle cap, H Medulla or pith, I Medullary rays
B. A Epidermal hair, B Epidermis, C Hypodermis (collenchyma), D Parenchyma, E Endoderm is (Starch Sheath), F Pericycle, G Vascular bundle, H Medullary rays, I Medulla or pith
C. A Epidermal hair, B Epidermis, C Hypodermis (collenchyma), D Starch sheath, E Parenchyma, F Vascular bundle, G Bundle cap, H Medulla or pith, I Medullary rays
D. A Epidermal hair, B Epidermis, C Parenchyma, D Hypodermis (collenchyma), E Starch sheath, F Vascular bundle, G Bundle cap, H Medulla or pith, I Medullary rays
Answer : B
16. In land plants, the guard cells differ from other epidermal cells in having
A. cytoskeleton.
B. mitochondria.
C. endoplasmic reticulum.
D. chloroplasts.
Answer : D
A. cytoskeleton.
B. mitochondria.
C. endoplasmic reticulum.
D. chloroplasts.
Answer : D
17. Tissues are classified into two main groups, namely meristematic and permanent tissues on the basis of
A. whether the cells being able to divide or not.
B. position of the cells.
C. whether they are living or dead.
D. none of the above
Answer : A
A. whether the cells being able to divide or not.
B. position of the cells.
C. whether they are living or dead.
D. none of the above
Answer : A
18. Which of the following figure is a type of permanent tissue having many different types of cell?
A.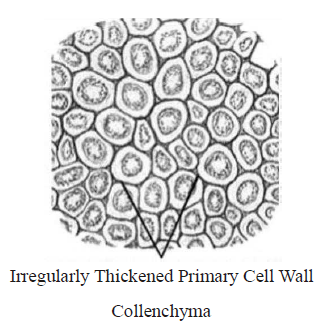
B.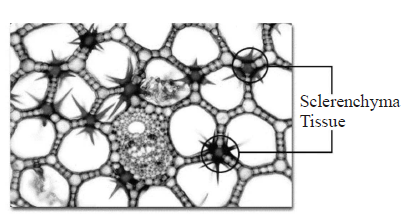
C.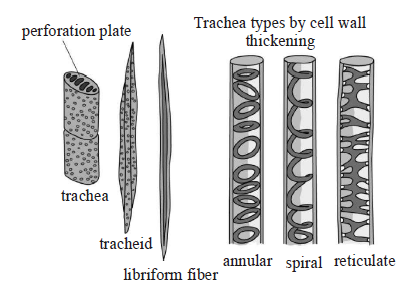
D.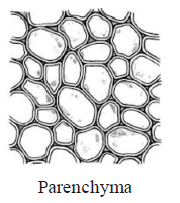
Answer : C
A.

B.

C.

D.

Answer : C
19. Various functions like photosynthesis, storage, excretion performed by _____________.
A. sclerenchyma
B. parenchyma
C. collenchyma
D. aerenchyma
Answer : B
A. sclerenchyma
B. parenchyma
C. collenchyma
D. aerenchyma
Answer : B
20. The given figure shows apical meristem of root apex with few part marked as A, B and C. Identify the correct labelling of A, B and C.
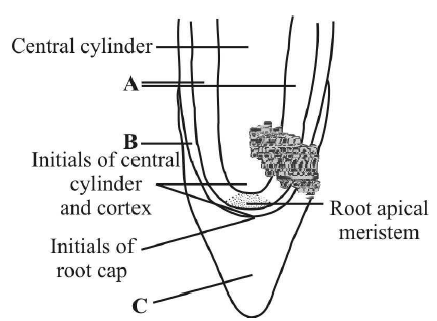
A. A Vascular structure, B Protoderm, C Root cap
B. A Cortex, B Endodermis, C Root cap
C. A Cortex, B Protoderm, C Root cap
D. A Tunica, B Protoderm, C Root cap
Answer : C

A. A Vascular structure, B Protoderm, C Root cap
B. A Cortex, B Endodermis, C Root cap
C. A Cortex, B Protoderm, C Root cap
D. A Tunica, B Protoderm, C Root cap
Answer : C
21. Cells of permanent tissues are specialized
A. functionally.
B. only structurally.
C. both structurally and functionally.
D. for mitosis.
Answer : C
A. functionally.
B. only structurally.
C. both structurally and functionally.
D. for mitosis.
Answer : C
22. Some vascular bundles are described as open because these
A. are surrounded by pericycle but not endodermis.
B. are capable of producing secondary xylem and phloem.
C. possess conjunctive tissue between xylem and phloem.
D. are not surrounded by pericycle.
Answer : B
A. are surrounded by pericycle but not endodermis.
B. are capable of producing secondary xylem and phloem.
C. possess conjunctive tissue between xylem and phloem.
D. are not surrounded by pericycle.
Answer : B
23. Read the following statements and answer the question.
Which plant anatomy is being described by the above statements?
A. Dicotyledonous root
B. Monocotyledonous root
C. Dicotyledonous stem
D. Monocotyledonous stem
Answer : D
- It has a sclerenchymatous hypodermis, a large number of scattered vascular bundles and a large parenchymatous ground tissue.
- Vascular bundles are conjoint and closed.
- Peripheral vascular bundles are generally smaller than the centrally located ones.
- Phloem parenchyma is absent, and water- containing cavities are present within the vascular bundles.
Which plant anatomy is being described by the above statements?
A. Dicotyledonous root
B. Monocotyledonous root
C. Dicotyledonous stem
D. Monocotyledonous stem
Answer : D
24. Trees at sea do not have annual rings because
A. soil is sandy.
B. there is climatic variation.
C. there is no marked climatic variation.
D. there is enough moisture in the atmosphere.
Answer : C
A. soil is sandy.
B. there is climatic variation.
C. there is no marked climatic variation.
D. there is enough moisture in the atmosphere.
Answer : C
25. Which of the following statements are correct ?
A. (i) and (iii)
B. (i) and (ii)
C. (iii) and (iv)
D. (i) and (iv)
Answer : B
- Xylem transports water and minerals.
- Gymnosperms lack sieve tubes and companion cells in phloem.
- The first formed primary xylem is called metaxylem.
- Phloem fibres (bast fibres) are made up of collenchymatous cells.
A. (i) and (iii)
B. (i) and (ii)
C. (iii) and (iv)
D. (i) and (iv)
Answer : B
26. When we peel the skin of a potato tuber, we remove
A. periderm
B. epidermis
C. cuticle
D. leaves
Answer : A
A. periderm
B. epidermis
C. cuticle
D. leaves
Answer : A
27. Choose the correct labelling of (A J) in the given figure of T.S. of monocot root.

A. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pericycle, G Pith, H Phloem, I Metaxylem.
B. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pith, G Pericycle, H Metaxylem, I Phloem.
C. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Pericycle, F Phloem, G Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
D. A Root hair, B Cortex, C Epiblema, D Pericycle, E Endodermis, F Pith, G Phloem, H Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
Answer : C

A. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pericycle, G Pith, H Phloem, I Metaxylem.
B. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pith, G Pericycle, H Metaxylem, I Phloem.
C. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Pericycle, F Phloem, G Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
D. A Root hair, B Cortex, C Epiblema, D Pericycle, E Endodermis, F Pith, G Phloem, H Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
Answer : C
28. T.S. of monocot leaf is given below, certain parts have been marked by alphabets (A G). Which one is the option showing there correct lablling?
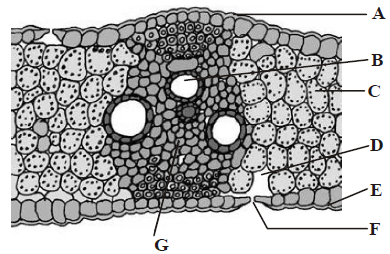
A. A Adaxial epidermis, B Xylem, C Mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Stoma, G Phloem
B. A Adaxial epidermis, B Abaxial epidermis, C Xylem, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Stoma, F Mesophyll, G Phloem
C. A Adaxial epidermis, B Phloem, C Mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Xylem, G Stoma
D. A Adaxial epidermis, B Xylem, C Stoma, D Substomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Phloem, G Mesophyll
Answer : A

A. A Adaxial epidermis, B Xylem, C Mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Stoma, G Phloem
B. A Adaxial epidermis, B Abaxial epidermis, C Xylem, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Stoma, F Mesophyll, G Phloem
C. A Adaxial epidermis, B Phloem, C Mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Xylem, G Stoma
D. A Adaxial epidermis, B Xylem, C Stoma, D Substomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Phloem, G Mesophyll
Answer : A
29. A common structural feature of vessel elements and sieve tube elements are
A. pores on lateral walls.
B. presence of p-protein.
C. enucleate condition.
D. thick secondary walls.
Answer : C
A. pores on lateral walls.
B. presence of p-protein.
C. enucleate condition.
D. thick secondary walls.
Answer : C
30. Which of the following is responsible for the formation of an embryonic shoot called axillary bud?
A. Lateral meristem
B. Apical meristem
C. Intercalary meristem
D. Both
Answer : C
A. Lateral meristem
B. Apical meristem
C. Intercalary meristem
D. Both
Answer : C
31. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Lenticels occur in most woody trees.
B. Sclerenchymatous cells are usually present in cortex.
C. The vascular tissue system is divided into three main zones- cortex, pericycle and pith.
D. The conjoint vascular bundles usually have the xylem located only on the outer side of the phloem.
Answer : A
A. Lenticels occur in most woody trees.
B. Sclerenchymatous cells are usually present in cortex.
C. The vascular tissue system is divided into three main zones- cortex, pericycle and pith.
D. The conjoint vascular bundles usually have the xylem located only on the outer side of the phloem.
Answer : A
32. Cork is formed from
A. phellogen
B. vascular cambium
C. phloem
D. xylem
Answer : A
A. phellogen
B. vascular cambium
C. phloem
D. xylem
Answer : A
33. Identify the types of simple tissue indicated by A, B, C and D and their function.
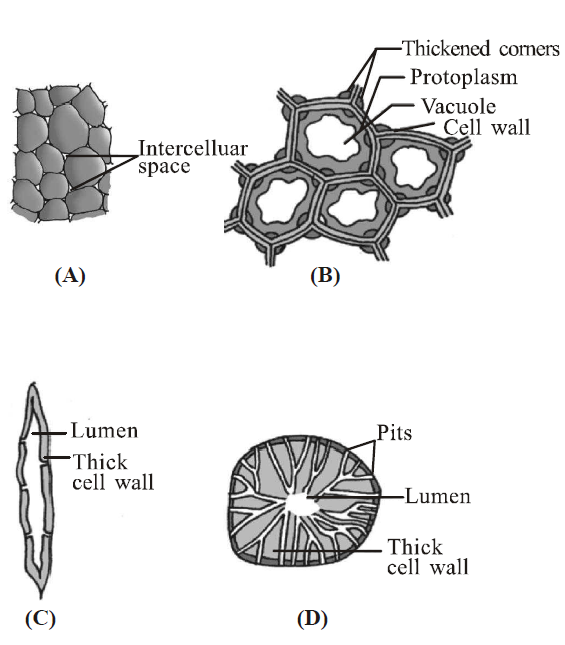
A. A Parenchyma, Photosynthesis, Storage and Secretion.
B. B Sclerenchyma Scleriods; Transport food material
C. C Collenchyma; Provides mechanical support to organs.
D. D Sclerenchyma Fibres; Provide Mechanical support to the growing parts of the plant such as young stem and petiole of a leaf.
Answer : A

A. A Parenchyma, Photosynthesis, Storage and Secretion.
B. B Sclerenchyma Scleriods; Transport food material
C. C Collenchyma; Provides mechanical support to organs.
D. D Sclerenchyma Fibres; Provide Mechanical support to the growing parts of the plant such as young stem and petiole of a leaf.
Answer : A
34. Match the elements of xylem given in column I with their character given in the column II and choose the correct option.
A. A IV; B III; C II; D I
B. A III; B II; C I; D IV
C. A II; B I; C IV; D III
D. A III; B IV; C II; D I
Answer : D
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| A. Xylem vessels | I. Store food materials |
| B. Xylem tracheids | II. Obliterated lumen |
| C. Xylem fibres | III. Perforated plates |
| D. Xylem parenchyma | IV. Chisel-like ends |
A. A IV; B III; C II; D I
B. A III; B II; C I; D IV
C. A II; B I; C IV; D III
D. A III; B IV; C II; D I
Answer : D
35. Cambium is considered as a lateral meristem because
A. it gives rise to lateral branches.
B. it causes increase in girth.
C. it increases height and diameter of a plant.
D. it adds bulk to a plant.
Answer : B
A. it gives rise to lateral branches.
B. it causes increase in girth.
C. it increases height and diameter of a plant.
D. it adds bulk to a plant.
Answer : B
36. Cork cambium and vascular cambium are
A. the parts of secondary xylem and phloem.
B. the parts of pericycle.
C. lateral meristems.
D. apical meristems.
Answer : C
A. the parts of secondary xylem and phloem.
B. the parts of pericycle.
C. lateral meristems.
D. apical meristems.
Answer : C
37. Which one of the followings option shows the correct labelling of the parts marked as A, B, C and D in the given figure a lenticel?
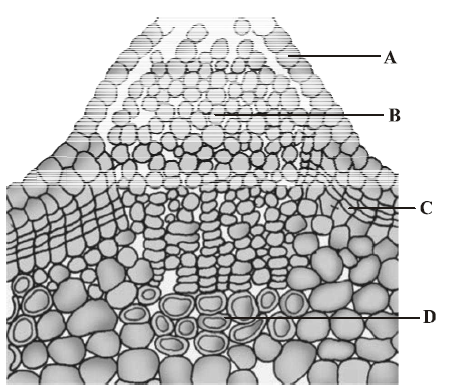
A. A Epidermis, B Secondary cortex, C Cork cambium, D Cork
B. A Pore, B Cork cambium, C Secondary cortex, D Cork
C. A Pore, B Cork, C Complimentary cells, D Cork cambium
D. A Epidermis, B Complimentary cells, C Cork cambium, D Secondary cortex
Answer : D

A. A Epidermis, B Secondary cortex, C Cork cambium, D Cork
B. A Pore, B Cork cambium, C Secondary cortex, D Cork
C. A Pore, B Cork, C Complimentary cells, D Cork cambium
D. A Epidermis, B Complimentary cells, C Cork cambium, D Secondary cortex
Answer : D
38. Read the following statements and answer the question.
Which type of wood is described by the above statements?
A. Sap wood
B. Heart wood
C. Spring wood
D. Autumn wood
Answer : C
- Cambium is very active and produces a large number of xylary elements having vessels with wider cavities.
- It is also called early wood.
- It is lighter in colour and has lower density.
Which type of wood is described by the above statements?
A. Sap wood
B. Heart wood
C. Spring wood
D. Autumn wood
Answer : C
39. Match column-I with column-II and choose the correct option.
A. A III, B V, C IV, D I, E II
B. A II, B V, C I, D III, E IV
C. A II, B IV, C I, D III, E V
D. A III, B I, C V, D II, E IV
Answer : D
| Column -I | Column -II |
|---|---|
| A. Bulliform cells | I. Initiation of lateral roots |
| B. Pericycle | II. Root |
| C. Endarch xylem | III. Grasses |
| D. Exarch xylem | IV. Dicot leaf |
| E. Bundle sheath cells | V. Stem |
A. A III, B V, C IV, D I, E II
B. A II, B V, C I, D III, E IV
C. A II, B IV, C I, D III, E V
D. A III, B I, C V, D II, E IV
Answer : D
40. Which one of the following statement is incorrect ?
A. Only (i)
B. Only (iv)
C. Only (iii)
D. Only (v)
Answer : D
- Epidermal cell has small amount of cytoplasm and a large vacuole.
- Waxy cuticle layer is absent in roots.
- Root hairs are unicellular, while stem hairs / trichomes are multicellular.
- Trichomes may be branched or unbranched, soft or stiff and prevent transpiration.
- Guard cells are dumbell shaped in dicots and beanshaped in monocots (e.g. grass).
A. Only (i)
B. Only (iv)
C. Only (iii)
D. Only (v)
Answer : D
41. A tissue is a group of cells which are
A. similar in origin, but dissimilar in form and function.
B. dissimilar in origin, form and function.
C. dissimilar in origin, but similar in form and function.
D. similar in origin, form and function.
Answer : D
A. similar in origin, but dissimilar in form and function.
B. dissimilar in origin, form and function.
C. dissimilar in origin, but similar in form and function.
D. similar in origin, form and function.
Answer : D
42. T.S. of dicot leaf passing through the midrib is given below. Certain parts have been marked by alphabets (A to H). Choose the option showing their correct labelling.
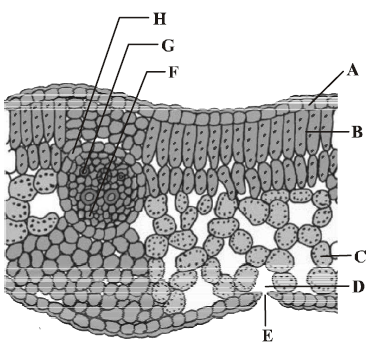
A. A Epidermis,B Spongy mesophyll, C Palisade mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
B. A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Stoma, F Phloem, G Xylem, H Bundle sheath
C. A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Epidermis, G Xylem, H Phloem
D. A Epidermis, C Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
Answer : B

A. A Epidermis,B Spongy mesophyll, C Palisade mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
B. A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Stoma, F Phloem, G Xylem, H Bundle sheath
C. A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Epidermis, G Xylem, H Phloem
D. A Epidermis, C Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
Answer : B
43. Tissue(s) present in an annual ring is/are
A. secondary xylem and phloem.
B. primary xylem and phloem.
C. secondary xylem only.
D. primary phloem and secondary xylem.
Answer : C
A. secondary xylem and phloem.
B. primary xylem and phloem.
C. secondary xylem only.
D. primary phloem and secondary xylem.
Answer : C
44. Apical and intercalary meristems are primary meristems because
A. they occur in the mature region of roots and shoots of many plants.
B. they made up of different kinds of tissues.
C. they involved in secondary growth.
D. they appear early in life of a plant and contribute to the formation of the primary plant body.
Answer : D
A. they occur in the mature region of roots and shoots of many plants.
B. they made up of different kinds of tissues.
C. they involved in secondary growth.
D. they appear early in life of a plant and contribute to the formation of the primary plant body.
Answer : D
45. In the given columns, column I contain structures of female reproductive system and column II contain its feature. Select the correct match.
A. A - (i), B - (ii), C - (iii), D - (iv)
B. A - (iii), B - (i), C - (ii), D - (iv)
C. A - (i), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (ii)
D. A - (ii), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (i)
Answer : A
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| A. Lateral meristem | (i) Fascicular vascular cambium, interfascicular cambium and cork cambium. |
| B. Apical meristem | (ii) Produces dermal tissue, ground tissues and vascular tissue. |
| C. Bast fibres | (iii) Generally absent in primary phloem but found in secondary phloem. |
| D. Sap wood | (iv) Involved in the conduction of water and minerals from the root to leaf. |
A. A - (i), B - (ii), C - (iii), D - (iv)
B. A - (iii), B - (i), C - (ii), D - (iv)
C. A - (i), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (ii)
D. A - (ii), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (i)
Answer : A
46. Apical, intercalary and lateral meristems are differentiated on the basis of
A. origin
B. function
C. position
D. development
Answer : C
A. origin
B. function
C. position
D. development
Answer : C
47. In the given figure of phloem tissue, identify the marked part (A, B and C) which help in maintaining the pressure gradient
in the sieve tubes.
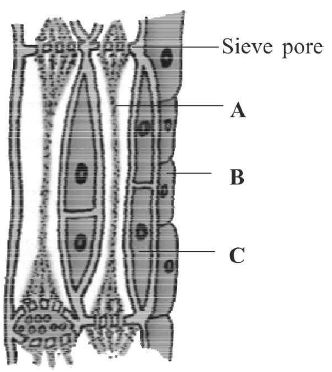
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. None of the above
Answer : C
in the sieve tubes.

A. A
B. B
C. C
D. None of the above
Answer : C
48. Which of the following pair of match is not correct?
A. Pith - Large and well developed in monocotyledonous root.
B. Root hairs - Helps in preventing water loss due to transpiration
C. Sieve tube elements - Its functions are controlled by the nucleus of companion cells.
D. Stomatal apparatus - Consists of stomatal aperture, guard cells and surrounding subsidiary cells
Answer : A
A. Pith - Large and well developed in monocotyledonous root.
B. Root hairs - Helps in preventing water loss due to transpiration
C. Sieve tube elements - Its functions are controlled by the nucleus of companion cells.
D. Stomatal apparatus - Consists of stomatal aperture, guard cells and surrounding subsidiary cells
Answer : A
49. Why grafting is successful in dicots ?
A. In dicots vascular bundles are arranged in a ring.
B. Dicots have cambium for secondary growth.
C. In dicots vessels with elements are arranged end to end.
D. Cork cambium is present in dicots
Answer : B
A. In dicots vascular bundles are arranged in a ring.
B. Dicots have cambium for secondary growth.
C. In dicots vessels with elements are arranged end to end.
D. Cork cambium is present in dicots
Answer : B
50. Phellogen and phellem respectively denote
A. cork and cork cambium,
B. cork cambium and cork,
C. secondary cortex and cork,
D. cork and secondary cortex,
Answer : B
A. cork and cork cambium,
B. cork cambium and cork,
C. secondary cortex and cork,
D. cork and secondary cortex,
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Applied Mechanics and Graphic Statics MCQ Solved Paper for SSC CPO
1000+ Compressors, Gas Turbines & Jet Engines Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Tumors of the prostate 1000+ MCQ with answer for RRB ALP
CTET - Theory of Machines 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
ESIC - Structural Organization In Animals 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Chemical Engineering Basics MCQ Solved Paper for RRB JE