Anatomy of flowering plant MCQ Solved Paper for SSC CPO
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. During the formation of leaves and elongation of stem, some cells left behind from the shoot apical meristem, constitute the
A. lateral meristem
B. axillary bud
C. cork cambium
D. fascicular cambium
Answer : B
A. lateral meristem
B. axillary bud
C. cork cambium
D. fascicular cambium
Answer : B
2. The given figures are types of elements (A and B) which constitute one type of complex tissue (c) of a plant . Identify A, B and C.
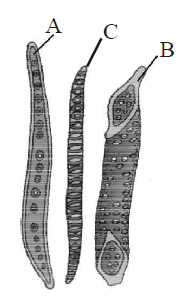
A. A Tracheid, B Vessel, C Xylem
B. A Vessel, B Tracheild, C Phloem
C. A Fibre, B Tracheid, C Bark
D. A Fibre, B Sclereid, C Casparian strips
Answer : A

A. A Tracheid, B Vessel, C Xylem
B. A Vessel, B Tracheild, C Phloem
C. A Fibre, B Tracheid, C Bark
D. A Fibre, B Sclereid, C Casparian strips
Answer : A
3. In land plants, the guard cells differ from other epidermal cells in having
A. cytoskeleton.
B. mitochondria.
C. endoplasmic reticulum.
D. chloroplasts.
Answer : D
A. cytoskeleton.
B. mitochondria.
C. endoplasmic reticulum.
D. chloroplasts.
Answer : D
4. Match the names of the structures given in column-I with the functions given in column-II, choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the two columns :
A. A V, B III, C I, D IV
B. A I, B IV, C V, D III
C. A II, B IV, C I, D III
D. A IV, B I, C III, D V
Answer : D
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| (Structure) | (Function) |
| A. Stomata | I. Protection of stem |
| B. Bark | II. Plant movement |
| C. Cambium | III. Secondary growth |
| D. Cuticle | IV. Transpiration |
| V. Prevent the loss of water | ... |
A. A V, B III, C I, D IV
B. A I, B IV, C V, D III
C. A II, B IV, C I, D III
D. A IV, B I, C III, D V
Answer : D
5. The given figure shows apical meristem of root apex with few part marked as A, B and C. Identify the correct labelling of A, B and C.
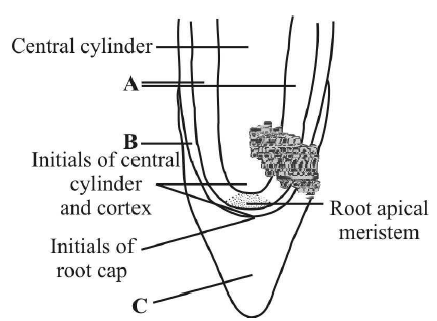
A. A Vascular structure, B Protoderm, C Root cap
B. A Cortex, B Endodermis, C Root cap
C. A Cortex, B Protoderm, C Root cap
D. A Tunica, B Protoderm, C Root cap
Answer : C

A. A Vascular structure, B Protoderm, C Root cap
B. A Cortex, B Endodermis, C Root cap
C. A Cortex, B Protoderm, C Root cap
D. A Tunica, B Protoderm, C Root cap
Answer : C
6. Which one of the following option shows the correct labelling of the parts marked as A, B, C and D in the given figure of a typical dicot root?
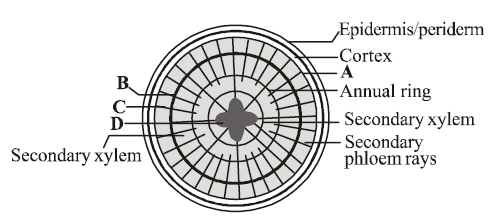
A. A Primary phloem, B Vascular cambium, C Secondary phloem, D Primary xylem
B. A Secondary phloem, B Vascular cambium, C Primary phloem, D Primary xylem
C. A Primary phloem, B Primary xylem, C Secondary phloem, D Vascular cambium
D. A Secondary phloem, B Primary xylem, C Primary phloem, D Vascular cambium
Answer : A

A. A Primary phloem, B Vascular cambium, C Secondary phloem, D Primary xylem
B. A Secondary phloem, B Vascular cambium, C Primary phloem, D Primary xylem
C. A Primary phloem, B Primary xylem, C Secondary phloem, D Vascular cambium
D. A Secondary phloem, B Primary xylem, C Primary phloem, D Vascular cambium
Answer : A
7. Apical, intercalary and lateral meristems are differentiated on the basis of
A. origin
B. function
C. position
D. development
Answer : C
A. origin
B. function
C. position
D. development
Answer : C
8. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct ?
A. (i) and (iv) only
B. (ii) and (v) only
C. (iii) and (iv) only
D. (ii), (iii) and (v) only
Answer : D
- Uneven thickening of cell wall is characteristic of sclerenchyma.
- Periblem forms cortex of the stem and the root.
- Tracheids are the chief water transporting elements in gymnosperms.
- Companion cell is devoid of nucleus at maturity.
- The commercial cork is obtained from Quercus suber.
A. (i) and (iv) only
B. (ii) and (v) only
C. (iii) and (iv) only
D. (ii), (iii) and (v) only
Answer : D
9. Read the following statements and answer the question.
Which plant anatomy is being described by the above statements?
A. Dicotyledonous root
B. Monocotyledonous root
C. Dicotyledonous stem
D. Monocotyledonous stem
Answer : D
- It has a sclerenchymatous hypodermis, a large number of scattered vascular bundles and a large parenchymatous ground tissue.
- Vascular bundles are conjoint and closed.
- Peripheral vascular bundles are generally smaller than the centrally located ones.
- Phloem parenchyma is absent, and water- containing cavities are present within the vascular bundles.
Which plant anatomy is being described by the above statements?
A. Dicotyledonous root
B. Monocotyledonous root
C. Dicotyledonous stem
D. Monocotyledonous stem
Answer : D
10. Which of the following pair of match is not correct?
A. Pith - Large and well developed in monocotyledonous root.
B. Root hairs - Helps in preventing water loss due to transpiration
C. Sieve tube elements - Its functions are controlled by the nucleus of companion cells.
D. Stomatal apparatus - Consists of stomatal aperture, guard cells and surrounding subsidiary cells
Answer : A
A. Pith - Large and well developed in monocotyledonous root.
B. Root hairs - Helps in preventing water loss due to transpiration
C. Sieve tube elements - Its functions are controlled by the nucleus of companion cells.
D. Stomatal apparatus - Consists of stomatal aperture, guard cells and surrounding subsidiary cells
Answer : A
11. The apical meristem of the root is present
A. in all the roots.
B. only in radicals.
C. only in tap roots.
D. only in adventitious roots.
Answer : A
A. in all the roots.
B. only in radicals.
C. only in tap roots.
D. only in adventitious roots.
Answer : A
12. Match the followings and choose the correct option
A. A III, B IV, C I, D II
B. A I, B II, C III, D IV
C. A III, B II, C IV, D I
D. A III, B II, C I, D IV
Answer : A
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| A. Cuticle | I. Guard cells |
| B. Bulliform cells | II. Outer layer |
| C. Stomata | III. Waxy layer |
| D. Epidermis | IV. Empty colourless cell |
A. A III, B IV, C I, D II
B. A I, B II, C III, D IV
C. A III, B II, C IV, D I
D. A III, B II, C I, D IV
Answer : A
13. Match column-I with column-II and choose the correct option.
A. A III, B V, C IV, D I, E II
B. A II, B V, C I, D III, E IV
C. A II, B IV, C I, D III, E V
D. A III, B I, C V, D II, E IV
Answer : D
| Column -I | Column -II |
|---|---|
| A. Bulliform cells | I. Initiation of lateral roots |
| B. Pericycle | II. Root |
| C. Endarch xylem | III. Grasses |
| D. Exarch xylem | IV. Dicot leaf |
| E. Bundle sheath cells | V. Stem |
A. A III, B V, C IV, D I, E II
B. A II, B V, C I, D III, E IV
C. A II, B IV, C I, D III, E V
D. A III, B I, C V, D II, E IV
Answer : D
14. Apical and intercalary meristems are primary meristems because
A. they occur in the mature region of roots and shoots of many plants.
B. they made up of different kinds of tissues.
C. they involved in secondary growth.
D. they appear early in life of a plant and contribute to the formation of the primary plant body.
Answer : D
A. they occur in the mature region of roots and shoots of many plants.
B. they made up of different kinds of tissues.
C. they involved in secondary growth.
D. they appear early in life of a plant and contribute to the formation of the primary plant body.
Answer : D
15. Which of the following statements are correct ?
A. (i) and (iii)
B. (i) and (ii)
C. (iii) and (iv)
D. (i) and (iv)
Answer : B
- Xylem transports water and minerals.
- Gymnosperms lack sieve tubes and companion cells in phloem.
- The first formed primary xylem is called metaxylem.
- Phloem fibres (bast fibres) are made up of collenchymatous cells.
A. (i) and (iii)
B. (i) and (ii)
C. (iii) and (iv)
D. (i) and (iv)
Answer : B
16. A tissue is a group of cells which are
A. similar in origin, but dissimilar in form and function.
B. dissimilar in origin, form and function.
C. dissimilar in origin, but similar in form and function.
D. similar in origin, form and function.
Answer : D
A. similar in origin, but dissimilar in form and function.
B. dissimilar in origin, form and function.
C. dissimilar in origin, but similar in form and function.
D. similar in origin, form and function.
Answer : D
17. Main function of lenticel is
A. transpiration
B. guttation
C. gaseous exchange
D. both (a) & (c)
Answer : A
A. transpiration
B. guttation
C. gaseous exchange
D. both (a) & (c)
Answer : A
18. Tissue(s) present in an annual ring is/are
A. secondary xylem and phloem.
B. primary xylem and phloem.
C. secondary xylem only.
D. primary phloem and secondary xylem.
Answer : C
A. secondary xylem and phloem.
B. primary xylem and phloem.
C. secondary xylem only.
D. primary phloem and secondary xylem.
Answer : C
19. Which of the following process helps the trichomes in preventing water loss?
A. Where companion cells helps in maintaining the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.
B. Where plants absorb water through the roots and then give off water vapor through pores in their leaves.
C. Where activity of cork cambium builds pressure on the remaining layers peripheral to phellogen and ultimately these layers dies and slough off.
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Where companion cells helps in maintaining the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.
B. Where plants absorb water through the roots and then give off water vapor through pores in their leaves.
C. Where activity of cork cambium builds pressure on the remaining layers peripheral to phellogen and ultimately these layers dies and slough off.
D. None of the above
Answer : B
20. An organised and differentiated cellular structure having cytoplasm but no nucleus is called _________.
A. vessels
B. xylem parenchyma
C. sieve tubes
D. tracheids
Answer : C
A. vessels
B. xylem parenchyma
C. sieve tubes
D. tracheids
Answer : C
21. Match column-I with column-II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
A. A IV, B I, C II, D III
B. A III, B II, C I, D IV
C. A I, B II, C III, D IV
D. A IV, B II, C I, D III
Answer : A
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| A. Stele | I. Innermost layer of cortex |
| B. Endodermis | II. Suberin |
| C. Casparian strips | III. All the tissues exterior to vascular cambium |
| D. Bark | IV. All the tissues inner to endodermis |
A. A IV, B I, C II, D III
B. A III, B II, C I, D IV
C. A I, B II, C III, D IV
D. A IV, B II, C I, D III
Answer : A
22. Cork is formed from
A. phellogen
B. vascular cambium
C. phloem
D. xylem
Answer : A
A. phellogen
B. vascular cambium
C. phloem
D. xylem
Answer : A
23. A narrow layer of thin walled cells found between phloem/ bark and wood of a dicot is
A. cork cambium
B. vascular cambium
C. endodermis
D. both (a) & (c)
Answer : B
A. cork cambium
B. vascular cambium
C. endodermis
D. both (a) & (c)
Answer : B
24. T.S. of dicot leaf passing through the midrib is given below. Certain parts have been marked by alphabets (A to H). Choose the option showing their correct labelling.
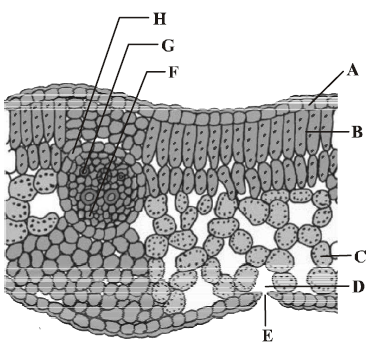
A. A Epidermis, B Spongy mesophyll, C Palisade mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
B. A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Stoma, F Phloem, G Xylem, H Bundle sheath
C. A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Epidermis, G Xylem, H Phloem
D. A Epidermis, C Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
Answer : B

A. A Epidermis, B Spongy mesophyll, C Palisade mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
B. A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Stoma, F Phloem, G Xylem, H Bundle sheath
C. A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Epidermis, G Xylem, H Phloem
D. A Epidermis, C Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
Answer : B
25. Cells of permanent tissues are specialized
A. functionally.
B. only structurally.
C. both structurally and functionally.
D. for mitosis.
Answer : C
A. functionally.
B. only structurally.
C. both structurally and functionally.
D. for mitosis.
Answer : C
26. When we peel the skin of a potato tuber, we remove
A. periderm
B. epidermis
C. cuticle
D. leaves
Answer : A
A. periderm
B. epidermis
C. cuticle
D. leaves
Answer : A
27. Match the elements of xylem given in column I with their character given in the column II and choose the correct option.
A. A IV; B III; C II; D I
B. A III; B II; C I; D IV
C. A II; B I; C IV; D III
D. A III; B IV; C II; D I
Answer : D
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| A. Xylem vessels | I. Store food materials |
| B. Xylem tracheids | II. Obliterated lumen |
| C. Xylem fibres | III. Perforated plates |
| D. Xylem parenchyma | IV. Chisel-like ends |
A. A IV; B III; C II; D I
B. A III; B II; C I; D IV
C. A II; B I; C IV; D III
D. A III; B IV; C II; D I
Answer : D
28. Which one of the following have vessels as their characteristic feature?
A. Angiosperms
B. Gymnosperms
C. Pteridophytes
D. Bryophytes
Answer : A
A. Angiosperms
B. Gymnosperms
C. Pteridophytes
D. Bryophytes
Answer : A
29. Choose the correct labelling of (A J) in the given figure of T.S. of monocot root.

A. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pericycle, G Pith, H Phloem, I Metaxylem.
B. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pith, G Pericycle, H Metaxylem, I Phloem.
C. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Pericycle, F Phloem, G Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
D. A Root hair, B Cortex, C Epiblema, D Pericycle, E Endodermis, F Pith, G Phlem, H Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
Answer : C

A. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pericycle, G Pith, H Phloem, I Metaxylem.
B. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pith, G Pericycle, H Metaxylem, I Phloem.
C. A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Pericycle, F Phloem, G Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
D. A Root hair, B Cortex, C Epiblema, D Pericycle, E Endodermis, F Pith, G Phlem, H Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
Answer : C
30. Some vascular bundles are described as open because these
A. are surrounded by pericycle but not endodermis.
B. are capable of producing secondary xylem and phloem.
C. possess conjunctive tissue between xylem and phloem.
D. are not surrounded by pericycle.
Answer : B
A. are surrounded by pericycle but not endodermis.
B. are capable of producing secondary xylem and phloem.
C. possess conjunctive tissue between xylem and phloem.
D. are not surrounded by pericycle.
Answer : B
31. Phellogen and phellem respectively denote
A. cork and cork cambium,
B. cork cambium and cork,
C. secondary cortex and cork,
D. cork and secondary cortex,
Answer : B
A. cork and cork cambium,
B. cork cambium and cork,
C. secondary cortex and cork,
D. cork and secondary cortex,
Answer : B
32. The given figure shows the T.S of dicot root. Some parts are marked as A, B, C, D, E, & F. Choose the option which shows the correct labelling of marked part.
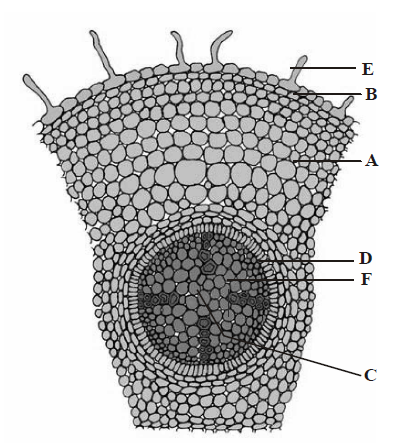
A. A Epiblema, B Root hair, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Pith, F Pericycle
B. A Cortex, B Pith, C Epiblema, D Endodermis, E Root hair, F Pericycle
C. A Epiblema, B Endodermis, C Cortex, D Root hair, E Pith, F Pericycle
D. A Cortex, B Epiblema, C Pith, D Endodermis, E Root hair, F Pericycle
Answer : D

A. A Epiblema, B Root hair, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Pith, F Pericycle
B. A Cortex, B Pith, C Epiblema, D Endodermis, E Root hair, F Pericycle
C. A Epiblema, B Endodermis, C Cortex, D Root hair, E Pith, F Pericycle
D. A Cortex, B Epiblema, C Pith, D Endodermis, E Root hair, F Pericycle
Answer : D
33. A vascular bundle in which the protoxylem is pointing to the periphery is called __________.
A. endarch
B. exarch
C. radial
D. closed
Answer : B
A. endarch
B. exarch
C. radial
D. closed
Answer : B
34. Which meristem helps in increasing girth?
A. Lateral meristem
B. Intercalary meristem
C. Primary meristem
D. Apical meristem
Answer : A
A. Lateral meristem
B. Intercalary meristem
C. Primary meristem
D. Apical meristem
Answer : A
35. The __________ occurs in layers below the epidermis in dicotyledonous plants.
A. parenchyma
B. sclerenchyma
C. collenchyma
D. aerenchyma
Answer : C
A. parenchyma
B. sclerenchyma
C. collenchyma
D. aerenchyma
Answer : C
36. Cork cambium and vascular cambium are
A. the parts of secondary xylem and phloem.
B. the parts of pericycle.
C. lateral meristems.
D. apical meristems.
Answer : C
A. the parts of secondary xylem and phloem.
B. the parts of pericycle.
C. lateral meristems.
D. apical meristems.
Answer : C
37. Which one of the following statement is incorrect ?
A. Only (i)
B. Only (iv)
C. Only (iii)
D. Only (v)
Answer : D
- Epidermal cell has small amount of cytoplasm and a large vacuole.
- Waxy cuticle layer is absent in roots.
- Root hairs are unicellular, while stem hairs / trichomes are multicellular.
- Trichomes may be branched or unbranched, soft or stiff and prevent transpiration.
- Guard cells are dumbell shaped in dicots and beanshaped in monocots (e.g. grass).
A. Only (i)
B. Only (iv)
C. Only (iii)
D. Only (v)
Answer : D
38. Xylem functions as a conducting tissue for water and minerals from _________to the ______and__________.
A. roots, stems, leaves
B. stems, roots, leaves
C. leaves, stems, roots
D. leaves, stems, leaves
Answer : A
A. roots, stems, leaves
B. stems, roots, leaves
C. leaves, stems, roots
D. leaves, stems, leaves
Answer : A
39. Identify types of vascular bundles in given figures A, B and C.
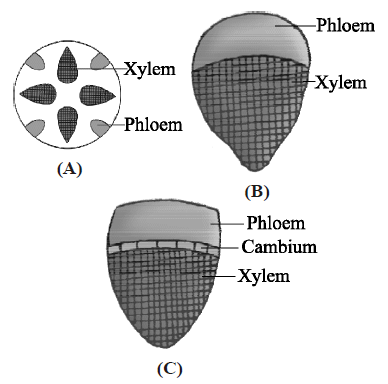
A. Radial; Conjoint closed; Conjoint open
B. Conjoint closed; Conjoint open; Radial
C. Conjoint open; Conjoint closed; Radial
D. Bicollateral; Concentric; Radial
Answer : A

A. Radial; Conjoint closed; Conjoint open
B. Conjoint closed; Conjoint open; Radial
C. Conjoint open; Conjoint closed; Radial
D. Bicollateral; Concentric; Radial
Answer : A
40. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Lenticels occur in most woody trees.
B. Sclerenchymatous cells are usually present in cortex.
C. The vascular tissue system is divided into three main zones- cortex, pericycle and pith.
D. The conjoint vascular bundles usually have the xylem located only on the outer side of the phloem.
Answer : A
A. Lenticels occur in most woody trees.
B. Sclerenchymatous cells are usually present in cortex.
C. The vascular tissue system is divided into three main zones- cortex, pericycle and pith.
D. The conjoint vascular bundles usually have the xylem located only on the outer side of the phloem.
Answer : A
41. A piece of wood having no vessels (trachea) must be belonged to
A. teak
B. mango
C. pine
D. palm
Answer : C
A. teak
B. mango
C. pine
D. palm
Answer : C
42. The vessel elements of angiosperms differ from other elements of xylem in having
A. simple pits on their radial walls.
B. bordered pits on their lateral walls.
C. simple and bordered pits on their end walls.
D. simple perforation on their end walls.
Answer : D
A. simple pits on their radial walls.
B. bordered pits on their lateral walls.
C. simple and bordered pits on their end walls.
D. simple perforation on their end walls.
Answer : D
43. As secondary growth proceeds, in a dicot stem, the thickness of
A. sapwood increases.
B. heartwood increase.
C. both sapwood and heartwood increases.
D. both sapwood and heartwood remains the same.
Answer : C
A. sapwood increases.
B. heartwood increase.
C. both sapwood and heartwood increases.
D. both sapwood and heartwood remains the same.
Answer : C
44. A plant tissue when stained showed the presence of hemicellulose and pectin in cells wall of its cells. The tissue is called
A. collenchyma
B. sclerenchyma
C. xylem
D. meristem
Answer : A
A. collenchyma
B. sclerenchyma
C. xylem
D. meristem
Answer : A
45. T.S. of monocot leaf is given below, certain parts have been marked by alphabets (A G). Which one is the option showing there correct labelling?
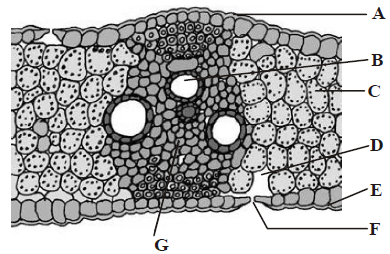
A. A Adaxial epidermis, B Xylem, C Mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Stoma, G Phloem
B. A Adaxial epidermis, B Abaxial epidermis, C Xylem, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Stoma, F Mesophyll, G Phloem
C. A Adaxial epidermis, B Phloem, C Mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Xylem, G Stoma
D. A Adaxial epidermis, B Xylem, C Stoma, D Substomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Phloem, G Mesophyll
Answer : A

A. A Adaxial epidermis, B Xylem, C Mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Stoma, G Phloem
B. A Adaxial epidermis, B Abaxial epidermis, C Xylem, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Stoma, F Mesophyll, G Phloem
C. A Adaxial epidermis, B Phloem, C Mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Xylem, G Stoma
D. A Adaxial epidermis, B Xylem, C Stoma, D Substomatal cavity, E Abaxial epidermis, F Phloem, G Mesophyll
Answer : A
46. A student was given a tissue to observe under the microscope. He observes the tissue and concludes that the tissue is a type of simple plant tissue and provides mechanical support to young stem and petiole of leaf.
Identify the tissue.
A. Parenchyma
B. Collenchyma
C. Sclerenchyma
D. Xylem parenchyma
Answer : B
Identify the tissue.
A. Parenchyma
B. Collenchyma
C. Sclerenchyma
D. Xylem parenchyma
Answer : B
47. The trees growing in deset will
A. show alternate rings of xylem and sclerenchyma.
B. have only conjunctive tissue and phloem is formed by the activity of cambium.
C. show distinct annual rings.
D. not show distinct annual rings.
Answer : D
A. show alternate rings of xylem and sclerenchyma.
B. have only conjunctive tissue and phloem is formed by the activity of cambium.
C. show distinct annual rings.
D. not show distinct annual rings.
Answer : D
48. Which of the following figure is a type of permanent tissue having many different types of cell?
A.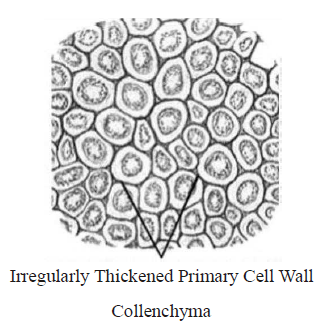
B.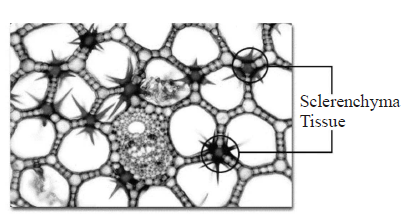
C.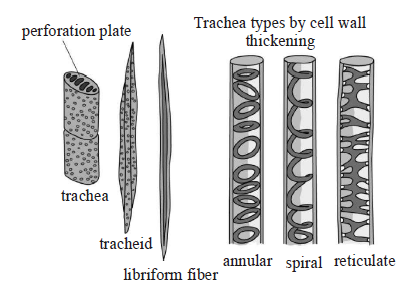
D.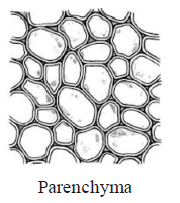
Answer : C
A.

B.

C.

D.

Answer : C
49. Identify A, B and C in the given figure of shoot apical meristem
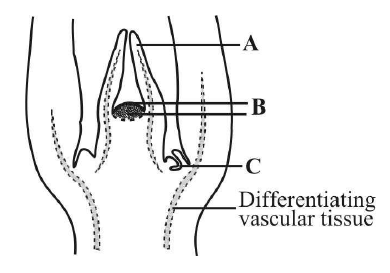
A. A Leaf primordium, B Shoot apical meristem, C Axillary bud
B. A Leaf primordium, B Shoot apical meristem, C Apical bud
C. A Root hair primordium, B Root apical meristem, C Axillary bud
D. A Root hair primordium, B Root apical meristem, C Terminal bud
Answer : A

A. A Leaf primordium, B Shoot apical meristem, C Axillary bud
B. A Leaf primordium, B Shoot apical meristem, C Apical bud
C. A Root hair primordium, B Root apical meristem, C Axillary bud
D. A Root hair primordium, B Root apical meristem, C Terminal bud
Answer : A
50. Bast fibres are made up of _____________cells.
A. sclerenchymatous
B. chlorenchymatous
C. parenchymatous
D. aerenchymatous
Answer : A
A. sclerenchymatous
B. chlorenchymatous
C. parenchymatous
D. aerenchymatous
Answer : A
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ PhotoShop Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Windows 2000 Server Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
SSC JHT - Windows 2000 Server 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Sentence Correction MCQ for IBPS RRB [Solved]
1000+ Chemical Engineering Plant Economics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Urology Basic Science Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]