Basics of Economics 1000+ MCQ with answer for IBPS Clerk
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. LMC represents change in LTC (long-run total cost) due to producing an additional unit of a good while the fixed and variable factors:
A. Cannot be changed
B. Can be changed
C. Can partially be changed
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Cannot be changed
B. Can be changed
C. Can partially be changed
D. None of the above
Answer : B
2. Increasing returns imply:
A. Constant average cost
B. Diminishing cost per unit of output
C. Optimum use of capital and factor
D. External economies
Answer : B
A. Constant average cost
B. Diminishing cost per unit of output
C. Optimum use of capital and factor
D. External economies
Answer : B
3. The supply curve would probably shift to the right if:
A. Resource( factors of production) used in production became more costly
B. The technology of production improves
C. Consumers income increased
D. Some sellers left the market
Answer : B
A. Resource( factors of production) used in production became more costly
B. The technology of production improves
C. Consumers income increased
D. Some sellers left the market
Answer : B
4. Indifference curve approach (ordinal approach) is superior to utility approach (cardinal approach) because:
A. In ordinal approach we can separate the income effect from the substitution effect of a price change
B. In ordinal approach we can study the consumer behavior more closely
C. In ordinal approach the consumer is assumed more rational
D. In ordinal approach the consumer has more income
Answer : A
A. In ordinal approach we can separate the income effect from the substitution effect of a price change
B. In ordinal approach we can study the consumer behavior more closely
C. In ordinal approach the consumer is assumed more rational
D. In ordinal approach the consumer has more income
Answer : A
5. Which is not a central problem of an economy?
A. What to produce
B. How to produce
C. How to maximize private profit
D. For whom to produce
Answer : C
A. What to produce
B. How to produce
C. How to maximize private profit
D. For whom to produce
Answer : C
6. Other things remaining the same, when a consumers income increases his equilibrium point moves to:
A. A lower indifference curve
B. A lower PPC curve
C. Remains on same indifference curve
D. A higher indifference curve
Answer : D
A. A lower indifference curve
B. A lower PPC curve
C. Remains on same indifference curve
D. A higher indifference curve
Answer : D
7. When in a market, the number of buyers is very large and the number of sellers is very small, it is known as:
A. Monopoly
B. Oligopoly
C. Imperfect competition
D. Perfect competition
Answer : B
A. Monopoly
B. Oligopoly
C. Imperfect competition
D. Perfect competition
Answer : B
8. The difference between laws of return and laws of return to scale is:
A. In case of laws of return, one factor of production is constant and other is variable while in laws of return to scale both factors of production are variable
B. In case of laws of return to scale, one factor of production is constant and other is variable while in laws of return, both factors of production are variable
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. In case of laws of return, one factor of production is constant and other is variable while in laws of return to scale both factors of production are variable
B. In case of laws of return to scale, one factor of production is constant and other is variable while in laws of return, both factors of production are variable
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : A
9. In the case where two commodities are good substitutes then cross elasticity will be:
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : A
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : A
10. External economies are witnessed in:
A. A rising supply curve
B. A rising demand curve
C. A falling supply curve
D. A falling demand curve
Answer : D
A. A rising supply curve
B. A rising demand curve
C. A falling supply curve
D. A falling demand curve
Answer : D
11. A decrease in demand lowers the price the most:
A. In the immediate run
B. In the short run
C. When the supply is perfectly elastic
D. When producers have sufficient time to fully adjust to the demand change
Answer : A
A. In the immediate run
B. In the short run
C. When the supply is perfectly elastic
D. When producers have sufficient time to fully adjust to the demand change
Answer : A
12. An increase in the price of the good measured on the horizontal axis causes:
A. The budget line to get steeper
B. The budget line to shift parallel to the right
C. The indifference curve to shift up
D. The budget line to get flatter
Answer : A
A. The budget line to get steeper
B. The budget line to shift parallel to the right
C. The indifference curve to shift up
D. The budget line to get flatter
Answer : A
13. We can measure consumers surplus with the help of
A. TU curve
B. MU curve
C. Supply curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. TU curve
B. MU curve
C. Supply curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
14. The marshallian demand curve includes:
A. Substitution Effect
B. Income Effect
C. Both substitution and income effect
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. Substitution Effect
B. Income Effect
C. Both substitution and income effect
D. None of them
Answer : C
15. When AC curve falls, MC curve falls:
A. More than AC curve
B. Less than AC curve
C. Equal to AC curve
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. More than AC curve
B. Less than AC curve
C. Equal to AC curve
D. None of the above
Answer : A
16. Which is the first-order condition for the profit of a firm to be maximum?
A. AC=MR
B. MC=MR
C. MR=AR
D. AC=AR
Answer : B
A. AC=MR
B. MC=MR
C. MR=AR
D. AC=AR
Answer : B
17. Production function shows:
A. Technical relationship between inputs and output
B. Profitability production
C. Relation between MR and MC
D. Relation between AR and AC
Answer : A
A. Technical relationship between inputs and output
B. Profitability production
C. Relation between MR and MC
D. Relation between AR and AC
Answer : A
18. The firms in non-cooperative games:
A. Enforce contracts
B. Make contracts
C. Make negotiations
D. Do not make negotiations
Answer : D
A. Enforce contracts
B. Make contracts
C. Make negotiations
D. Do not make negotiations
Answer : D
19. We can write ordinal utility function as:
A. U = x1 x2
B. U = x1 + x2
C. U = y1 +x1
D. U = x1.x2
Answer : D
A. U = x1 x2
B. U = x1 + x2
C. U = y1 +x1
D. U = x1.x2
Answer : D
20. The optimum level of output in long run takes place where:
A. LAC = LMC
B. SAC = LMC
C. SAC =MC
D. SAC =LAC
Answer : D
A. LAC = LMC
B. SAC = LMC
C. SAC =MC
D. SAC =LAC
Answer : D
21. The demand curve in monopolistic competition (also in kinked demand curve model), which shows the share of a firm in market is called:
A. Relative demand curve
B. Proportional demand curve
C. Productive demand curve
D. Differential demand curve
Answer : B
A. Relative demand curve
B. Proportional demand curve
C. Productive demand curve
D. Differential demand curve
Answer : B
22. In non-constant sum game (non-zero sum game), if there are two parties then:
A. Both parties make better-off
B. Both parties make worse-off
C. Both parties become Neutral
D. Both parties can become better off or worse off
Answer : D
A. Both parties make better-off
B. Both parties make worse-off
C. Both parties become Neutral
D. Both parties can become better off or worse off
Answer : D
23. A budget line shows:
A. Price of commodity X in terms of Y
B. Price of commodity Y in term of X
C. Income of the consumer
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Price of commodity X in terms of Y
B. Price of commodity Y in term of X
C. Income of the consumer
D. All of the above
Answer : D
24. In the long-run competitive equilibrium:
A. There is tendency for firms to enter but not leave the industry
B. Firms have no tendency either to enter or to leave the industry
C. Some firms may enter while the others may leave the market even after the equilibrium of the industry
D. Entry or exit of the firms cannot be predicted
Answer : C
A. There is tendency for firms to enter but not leave the industry
B. Firms have no tendency either to enter or to leave the industry
C. Some firms may enter while the others may leave the market even after the equilibrium of the industry
D. Entry or exit of the firms cannot be predicted
Answer : C
25. An indifference curve normally slopes downward from:
A. Left to right
B. Right to left
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : A
A. Left to right
B. Right to left
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : A
26. Total variable costs in equation form are:
A.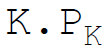
B.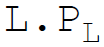
C.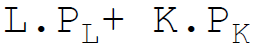
D.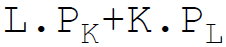
Answer : B
A.
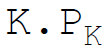
B.
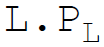
C.
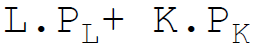
D.
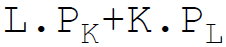
Answer : B
27. If a straight line supply curve makes an intercept on the Y-axis, elasticity of supply is:
A. Equal to unity
B. Less than unity
C. More than unity
D. Zero
Answer : C
A. Equal to unity
B. Less than unity
C. More than unity
D. Zero
Answer : C
28. A firm under perfect competition has:
A. An AR curve which is a horizontal straight line
B. An AR curve which slopes downward
C. An AR curve which has a kink
D. An AR curve shape of which cannot be predicted
Answer : A
A. An AR curve which is a horizontal straight line
B. An AR curve which slopes downward
C. An AR curve which has a kink
D. An AR curve shape of which cannot be predicted
Answer : A
29. In substitution effect, we:
A. Move to another indifference curve
B. Move along given indifference curve
C. Move to a higher indifference curve
D. Move to a lower indifference curve
Answer : B
A. Move to another indifference curve
B. Move along given indifference curve
C. Move to a higher indifference curve
D. Move to a lower indifference curve
Answer : B
30. Total costs in the short-term (short-run) are classified into fixed costs and variable costs. Which one of the following is a variable cost?
A. Cost of raw materials
B. Cost of equipment
C. Interest payment on past borrowing
D. Payment of rent on buildings
Answer : A
A. Cost of raw materials
B. Cost of equipment
C. Interest payment on past borrowing
D. Payment of rent on buildings
Answer : A
31. The equilibrium level of output for the pure monopolist is where:
A. MR = MC
B. MR > MC
C. MR < MC
D. P < AC
Answer : A
A. MR = MC
B. MR > MC
C. MR < MC
D. P < AC
Answer : A
32. In repeated game, the Prisoners Dillemma can have a:
A. Non-cooperative outcome
B. Cooperative outcome
C. Dominant behavior
D. Recessive behavior
Answer : B
A. Non-cooperative outcome
B. Cooperative outcome
C. Dominant behavior
D. Recessive behavior
Answer : B
33. Who developed the concept of Representative Firm?
A. A.C.Pigou
B. Alfred Marshal
C. J.M.Keynes
D. D.H.Robertson
Answer : B
A. A.C.Pigou
B. Alfred Marshal
C. J.M.Keynes
D. D.H.Robertson
Answer : B
34. When the slope of a demand curve is zero (also known as vertical demand curve) then elasticity will be:
A. Zero (perfectly inelastic)
B. Equal to one (unitary elastic)
C. Infinite (perfectly elastic)
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Zero (perfectly inelastic)
B. Equal to one (unitary elastic)
C. Infinite (perfectly elastic)
D. None of the above
Answer : C
35. Under pure monopoly, there will be:
A. No distinction between firm and industry
B. One firm and no industry
C. No firm and no industry
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. No distinction between firm and industry
B. One firm and no industry
C. No firm and no industry
D. None of the above
Answer : A
36. From analysis, it is clear that both Marshal and Walras market models are:
A. Unstable
B. Stable
C. Variable
D. Fluctuating
Answer : B
A. Unstable
B. Stable
C. Variable
D. Fluctuating
Answer : B
37. In monopolistic competition, the individual demand curve is also known as:
A. Planned products curve
B. Planned material curve
C. Planned costs curve
D. Planned sales curve
Answer : D
A. Planned products curve
B. Planned material curve
C. Planned costs curve
D. Planned sales curve
Answer : D
38. When total revenues equal to total opportunity cost then the firm will earn:
A. Abnormal profit
B. Zero profit
C. Normal profit
D. Negative profit
Answer : C
A. Abnormal profit
B. Zero profit
C. Normal profit
D. Negative profit
Answer : C
39. Economic laws are:
A. Conditional
B. Moral by nature
C. Predicted
D. Like laws of sports
Answer : A
A. Conditional
B. Moral by nature
C. Predicted
D. Like laws of sports
Answer : A
40. According to the principle of substitution?
A. Many goods have no effective substitutes
B. Nearly all goods have substitutes
C. The prices of substitute goods must be the same
D. Buyers will stop buying a good if its price rises
Answer : B
A. Many goods have no effective substitutes
B. Nearly all goods have substitutes
C. The prices of substitute goods must be the same
D. Buyers will stop buying a good if its price rises
Answer : B
41. The Tit for Tat strategy means cooperation by the 2nd firm if:
A. 1st firm does not cooperate
B. 1st firm cooperates
C. 1st firm collapses
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. 1st firm does not cooperate
B. 1st firm cooperates
C. 1st firm collapses
D. None of the above
Answer : B
42. Price discrimination is possible:
A. When elasticities of demand in different markets are the same at the ruling price
B. When elasticities of demand are different in different markets at the ruling price
C. When elasticities cannot be known
D. When elasticities of demands are zero in different markets at the rulling price
Answer : B
A. When elasticities of demand in different markets are the same at the ruling price
B. When elasticities of demand are different in different markets at the ruling price
C. When elasticities cannot be known
D. When elasticities of demands are zero in different markets at the rulling price
Answer : B
43. Neutral Technological Progress can be defined as:
A. Technological progress that causes to raise the marginal product of capital and labor in the same proportion
B. Technological progress that causes the marginal product of capital to increase relative to the marginal product of labor
C. Technological progress that causes the marginal product of labor to increase relative to the marginal product of capital
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Technological progress that causes to raise the marginal product of capital and labor in the same proportion
B. Technological progress that causes the marginal product of capital to increase relative to the marginal product of labor
C. Technological progress that causes the marginal product of labor to increase relative to the marginal product of capital
D. None of the above
Answer : A
44. Excess capacity is concerned with the:
A. V-shaped traditional cost curves
B. S-shaped traditional cost curves
C. Modern cost curves
D. U-shaped traditional cost curves
Answer : D
A. V-shaped traditional cost curves
B. S-shaped traditional cost curves
C. Modern cost curves
D. U-shaped traditional cost curves
Answer : D
45. The marginal revenues are derivatives of:
A. TR function
B. AR function
C. MR function
D. AP function
Answer : A
A. TR function
B. AR function
C. MR function
D. AP function
Answer : A
46. Normal profits are considered as:
A. Explicit costs
B. Implicit costs
C. Social costs
D. Private cost
Answer : B
A. Explicit costs
B. Implicit costs
C. Social costs
D. Private cost
Answer : B
47. Law of Variable Proportions is regarding in:
A. Short-Run
B. Long-Run
C. Medium-Run
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Short-Run
B. Long-Run
C. Medium-Run
D. None of the above
Answer : A
48. Supply and demand changes have their most rapid impact in:
A. Auction market
B. Contract markets
C. Market for commercial office space
D. Natural gas market
Answer : A
A. Auction market
B. Contract markets
C. Market for commercial office space
D. Natural gas market
Answer : A
49. According to law of Equi-Marginal Utility when price of commodity falls then we bought:
A. More units
B. Less units
C. Same units
D. Zero units
Answer : A
A. More units
B. Less units
C. Same units
D. Zero units
Answer : A
50. On an indifference map higher indifference curves show:
A. The same level of price
B. The same level of satisfaction
C. The higher level of satisfaction
D. The lower level of satisfaction
Answer : C
A. The same level of price
B. The same level of satisfaction
C. The higher level of satisfaction
D. The lower level of satisfaction
Answer : C
Sharing is caring
Related Post
SSC MTS - Java Programming 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Compressors, Gas Turbines & Jet Engines MCQ for XAT [Solved]
Clause Analysis MCQ Solved Paper for LSAT
Sentence Correction 1000+ MCQ with answer for CEED
IBPS Clerk - Advance DBMS 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
WAN MCQ Solved Paper for FCI Recruitment