Basics of Economics 1000+ MCQ with answer for RRB Group D
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. General equilibrium is concerned with simultaneous equilibrium of:
A. Few economic agents
B. All the economic agents
C. Two economic agents
D. Many economic agents
Answer : B
A. Few economic agents
B. All the economic agents
C. Two economic agents
D. Many economic agents
Answer : B
2. Under monopolistic competition, the products sold by the firms are:
A. Economic substitutes
B. Technical substitutes
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Economic substitutes
B. Technical substitutes
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : C
3. Each firm in cournot model starts selling:
A. 1/2 of the total market demand
B. 1/4 of the total market demand
C. 1/3 of the total market demand
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. 1/2 of the total market demand
B. 1/4 of the total market demand
C. 1/3 of the total market demand
D. None of the above
Answer : A
4. Variable costs refer to:
A. Capital cost plus operating costs
B. Capital costs alone
C. Capital costs plus spill-over costs
D. Operating costs alone
Answer : D
A. Capital cost plus operating costs
B. Capital costs alone
C. Capital costs plus spill-over costs
D. Operating costs alone
Answer : D
5. In monopoly, when average revenue curve falls:
A. MR constant
B. MR rises
C. MR falls
D. MR is zero
Answer : C
A. MR constant
B. MR rises
C. MR falls
D. MR is zero
Answer : C
6. At the point where the straight line from the origin is tangent to the TC curve, AC is:
A. Maximum
B. Minimum
C. Equal
D. Lower
Answer : B
A. Maximum
B. Minimum
C. Equal
D. Lower
Answer : B
7. Suppose income increases by 10% and demand for commodity increases by 5% then the income elasticity of demand is:
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Zero
D. Infinity
Answer : B
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Zero
D. Infinity
Answer : B
8. By reducing the prices of its products below those of its competitors, a perfectly competitive seller:
A. Reduces its revenues
B. Increases its revenues
C. Can sell nothing
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Reduces its revenues
B. Increases its revenues
C. Can sell nothing
D. None of the above
Answer : A
9. The long run average cost curve is the envelope of:
A. SACs
B. LACs
C. SMCs
D. LMCs
Answer : A
A. SACs
B. LACs
C. SMCs
D. LMCs
Answer : A
10. Whish of the following represents the average revenue curve of a firm?
A. The curve representing the cost per unit of output
B. The demand curve of consumers for the firms product
C. Total receipts realized by the firm
D. All of the above
Answer : B
A. The curve representing the cost per unit of output
B. The demand curve of consumers for the firms product
C. Total receipts realized by the firm
D. All of the above
Answer : B
11. The Law of Equi-Marginal Utility refers to:
A. Marginal utility of commodity X
B. Marginal utility of commodity Y
C. Marginal utility per rupee spent on X and Y commodities
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Marginal utility of commodity X
B. Marginal utility of commodity Y
C. Marginal utility per rupee spent on X and Y commodities
D. None of the above
Answer : C
12. Elasticity of demand is equal to unity while marginal revenue is:
A. Positive
B. Zero
C. Negative
D. Indeterminate
Answer : B
A. Positive
B. Zero
C. Negative
D. Indeterminate
Answer : B
13. Which is not an essential feature of a socialist economy?
A. Social ownership of the means of production
B. Freedom of enterprise
C. Use of centralized planning
D. Government decisions
Answer : B
A. Social ownership of the means of production
B. Freedom of enterprise
C. Use of centralized planning
D. Government decisions
Answer : B
14. An effective price ceiling usually results in:
A. Excess demand
B. Qd > Qs
C. Shortage of supply
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Excess demand
B. Qd > Qs
C. Shortage of supply
D. All of the above
Answer : D
15. If the commodity is inferior then Income Effect (I.E) is:
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Zero
D. Infinite
Answer : A
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Zero
D. Infinite
Answer : A
16. Which of the following is assumed to be constant when a supply curve is drawn:
A. Technology
B. Number of buyers in the market
C. Consumer income
D. Household tastes
Answer : A
A. Technology
B. Number of buyers in the market
C. Consumer income
D. Household tastes
Answer : A
17. In the immediate run:
A. Supply curves are inelastic
B. Supply curves are perfectly elastic
C. Demand curves are elastic
D. Supply curves are elastic
Answer : A
A. Supply curves are inelastic
B. Supply curves are perfectly elastic
C. Demand curves are elastic
D. Supply curves are elastic
Answer : A
18. In case the two commodities are complements, cross elasticity will be:
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : C
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : C
19. The main objective of the firm is to:
A. Face losses
B. Avoid losses
C. Bear losses
D. Make economic decisions
Answer : D
A. Face losses
B. Avoid losses
C. Bear losses
D. Make economic decisions
Answer : D
20. A high value of cross-elasticity indicates that the two commodities are:
A. Very good substitutes
B. Poor substitutes
C. Good complements
D. Poor complements
Answer : A
A. Very good substitutes
B. Poor substitutes
C. Good complements
D. Poor complements
Answer : A
21. The main contribution of Prof. Lord Keynes is in the field of:
A. Determination of the rate of interest
B. Determination of the market price
C. Determination of the wage rate
D. Determination of production of firm
Answer : A
A. Determination of the rate of interest
B. Determination of the market price
C. Determination of the wage rate
D. Determination of production of firm
Answer : A
22. According to Saint Thomas Aquinas value is determined by God, but prices by:
A. Consumers
B. Employees
C. People
D. Labor
Answer : C
A. Consumers
B. Employees
C. People
D. Labor
Answer : C
23. In the case of a normal goods, the income effect:
A. Is always equal to the substitution effect
B. Completely offsets the substitution effect
C. Partially offsets the substitution effect
D. Reinforces the substitution effect
Answer : D
A. Is always equal to the substitution effect
B. Completely offsets the substitution effect
C. Partially offsets the substitution effect
D. Reinforces the substitution effect
Answer : D
24. When total product falls:
A. MP is positive
B. MP is negative
C. MP is falling
D. MP is rising
Answer : B
A. MP is positive
B. MP is negative
C. MP is falling
D. MP is rising
Answer : B
25. Opportunity costs are also known as:
A. Spill-over costs
B. Money costs
C. Alternative costs
D. External costs
Answer : C
A. Spill-over costs
B. Money costs
C. Alternative costs
D. External costs
Answer : C
26. Whenever a group of monopolistic competitors attains equilibrium, the firms in this group usually:
A. Charge different prices, but produce identical outputs
B. Produce different outputs, but charge identical prices
C. Charge different prices, and produce different outputs
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Charge different prices, but produce identical outputs
B. Produce different outputs, but charge identical prices
C. Charge different prices, and produce different outputs
D. None of the above
Answer : C
27. In the case of substitutes, the cross demand curve slopes
A. Downwards to the right
B. Upwards to the right
C. Backwards to the right
D. Inwards at the bottom
Answer : B
A. Downwards to the right
B. Upwards to the right
C. Backwards to the right
D. Inwards at the bottom
Answer : B
28. When the level of optimal factor combination is over and more labor is employed with the fixed plant, the efficiency of labor:
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains constant
D. Becomes zero
Answer : B
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains constant
D. Becomes zero
Answer : B
29. A demand schedule is shown as:
A. A function of price alone
B. A result of change in tastes
C. A result of increase in the size of the family
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. A function of price alone
B. A result of change in tastes
C. A result of increase in the size of the family
D. None of the above
Answer : A
30. Who finalized the model of monopolistic competition?
A. Ricardo
B. Marshal
C. Chamberlin
D. Mrs. Robinson
Answer : C
A. Ricardo
B. Marshal
C. Chamberlin
D. Mrs. Robinson
Answer : C
31. Which is the other name that is given to the average revenue curve?
A. Profit curve
B. Demand curve
C. Average cost curve
D. Indifference curve
Answer : B
A. Profit curve
B. Demand curve
C. Average cost curve
D. Indifference curve
Answer : B
32. In discriminating monopoly (price discrimination), the elasticity of demand of product in two markets are:
A. Different
B. Same
C. Zero
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Different
B. Same
C. Zero
D. None of the above
Answer : A
33. Identify the author of The Principles of political Economy and Taxation:
A. Alfred Marshal
B. J.S.Mill
C. David Ricardo
D. A.C.Pigou
Answer : C
A. Alfred Marshal
B. J.S.Mill
C. David Ricardo
D. A.C.Pigou
Answer : C
34. Marginal revenue from a given output:
A. The price at which the marginal unit sells
B. Total revenue sale of all units divided by volume of sales
C. Average revenue of total output average revenue of last unit
D. The change in total revenue resulting from the sale of one unit more of output
Answer : D
A. The price at which the marginal unit sells
B. Total revenue sale of all units divided by volume of sales
C. Average revenue of total output average revenue of last unit
D. The change in total revenue resulting from the sale of one unit more of output
Answer : D
35. Consumer surplus is the difference between
A. Price demanded and price paid
B. Price quoted and price actually paid
C. Price that a consumer is willing to pay and the price actually paid
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Price demanded and price paid
B. Price quoted and price actually paid
C. Price that a consumer is willing to pay and the price actually paid
D. None of the above
Answer : C
36. Necessary condition for consumer equilibrium is:
A.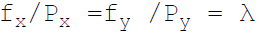
B.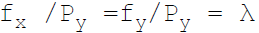
C.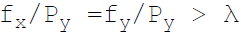
D.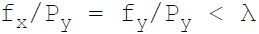
Answer : A
A.
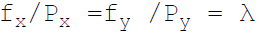
B.
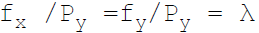
C.
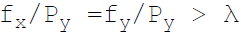
D.
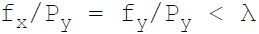
Answer : A
37. Contraction in demand occurs when:
A. Price increases and demand decreases
B. Price increases but demand also increases
C. Price remains constant but demand falls down
D. Price falls down but demand remains constant
Answer : A
A. Price increases and demand decreases
B. Price increases but demand also increases
C. Price remains constant but demand falls down
D. Price falls down but demand remains constant
Answer : A
38. The vertical distance between TVC and TC is equal to:
A. MC
B. AVC
C. TFC
D. AC
Answer : C
A. MC
B. AVC
C. TFC
D. AC
Answer : C
39. We get constant returns to scale when:
A. a = ½
B. � = ½
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. a = ½
B. � = ½
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
40. For the given production function, technical efficiency is defined as:
A. Sets of points relating production function that maximizes output given input (labor) i.e. Q = f(L, K)
B. Sets of points relating production function that produces less output than possible for a given set of input (labor) i.e. Q < f(L, K)
C. Use of imported technology
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Sets of points relating production function that maximizes output given input (labor) i.e. Q = f(L, K)
B. Sets of points relating production function that produces less output than possible for a given set of input (labor) i.e. Q < f(L, K)
C. Use of imported technology
D. None of the above
Answer : A
41. A firm considering what type of new plant to build is involved in a:
A. Immediate-run decision
B. Market period decision
C. Short-run decision
D. Long-run decision
Answer : D
A. Immediate-run decision
B. Market period decision
C. Short-run decision
D. Long-run decision
Answer : D
42. The arc elasticity is the measure of average elasticity at the mid-point of the chord and connects:
A. Two points on demand curve
B. Two points on supply curve
C. Many points on demand curve
D. Many points on demand curve
Answer : A
A. Two points on demand curve
B. Two points on supply curve
C. Many points on demand curve
D. Many points on demand curve
Answer : A
43. Government planners play a central role in allocating resources:
A. Only under socialism(communism)
B. Only under capitalism
C. Under both (a) and (b)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Only under socialism(communism)
B. Only under capitalism
C. Under both (a) and (b)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
44. In second degree price discrimination, monopolist takes away :
A. All of the consumer surplus
B. All of the producer surplus
C. Some part of the consumer surplus
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. All of the consumer surplus
B. All of the producer surplus
C. Some part of the consumer surplus
D. None of them
Answer : C
45. If, at the prevailin price, more of a good is desired than is available for sale:
A. The price is below equilibrium
B. The price is at equilibrium
C. The price must fall
D. We cannot tell anything about the price
Answer : A
A. The price is below equilibrium
B. The price is at equilibrium
C. The price must fall
D. We cannot tell anything about the price
Answer : A
46. Technological Progress (Invention) can be defined as:
A. Technological progress shifts the production function by allowing the firm to achieve more output from a given combination of inputs (or the same output with fewer inputs)
B. Technological progress shifts the production function by allowing the firm to achieve less output from a given combination of inputs (or the same output with more inputs)
C. Technological progress shifts the import function to the right
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Technological progress shifts the production function by allowing the firm to achieve more output from a given combination of inputs (or the same output with fewer inputs)
B. Technological progress shifts the production function by allowing the firm to achieve less output from a given combination of inputs (or the same output with more inputs)
C. Technological progress shifts the import function to the right
D. None of the above
Answer : A
47. The combination of labor and capital where the cost of a given output is minimized is known as:
A. Least cost factor combination
B. Optimum factor combination
C. Both a and b
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. Least cost factor combination
B. Optimum factor combination
C. Both a and b
D. None of them
Answer : C
48. Moving along an indifference curve leaves the consumer:
A. Better off
B. Worse off
C. Neither better nor worse off
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Better off
B. Worse off
C. Neither better nor worse off
D. None of the above
Answer : C
49. Under monopolistic competition, in long-run there is:
A. Ban on exit
B. Ban on entry
C. Free entry
D. Free entry and exit
Answer : D
A. Ban on exit
B. Ban on entry
C. Free entry
D. Free entry and exit
Answer : D
50. AR curve under perfect competition:
A. Slopes downwards to the right
B. Slopes upward to the right
C. Is vertical to the x-axis
D. Is horizontal to the x-axis
Answer : D
A. Slopes downwards to the right
B. Slopes upward to the right
C. Is vertical to the x-axis
D. Is horizontal to the x-axis
Answer : D
Sharing is caring
Related Post
ISRO Recruitment - Error Detection 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
IBPS PO - Synthesis of Sentences 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
DBMS 1000+ MCQ with answer for DRDO
1000+ Human reproductive system MCQ for LSAT [Solved]
1000+ Atomic Structure Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
NEET - Power Plant Engineering 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download