Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics MCQ Solved Paper for LSAT
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. A two stage compressor is used to compress an ideal gas. The gas is cooled to the initial temperature after each stage. The intermediate pressure for the minimum total work requirement should be equal to the __________ mean of P1 and P2. (where, P1 and P2 are initial and final pressures respectively)
A. Logarithmic
B. Arithmetic
C. Geometric
D. Harmonic
Answer : C
A. Logarithmic
B. Arithmetic
C. Geometric
D. Harmonic
Answer : C
2. The thermodynamic law, PVy = constant, is not applicable in case of
A. Ideal compression of air
B. Free expansion of an ideal gas
C. Adiabatic expansion of steam in a turbine
D. Adiabatic compression of a perfect gas
Answer : B
A. Ideal compression of air
B. Free expansion of an ideal gas
C. Adiabatic expansion of steam in a turbine
D. Adiabatic compression of a perfect gas
Answer : B
3. For an ideal liquid solution, which of the following is unity?
A. Activity
B. Fugacity
C. Activity co-efficient
D. Fugacity co-efficient
Answer : C
A. Activity
B. Fugacity
C. Activity co-efficient
D. Fugacity co-efficient
Answer : C
4. With increase in reduced temperature, the fugacity co-efficient of a gas at constant reduced pressure
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remain same
D. Decreases linearly
Answer : A
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remain same
D. Decreases linearly
Answer : A
5. The minimum number of phases that can exist in a system is
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : B
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : B
6. A thermodynamic system is taken from state A to B along ACB and is brought back to A along BDA as shown below in the P-V diagram. The net work done during the complete cycle is given by the area covered by
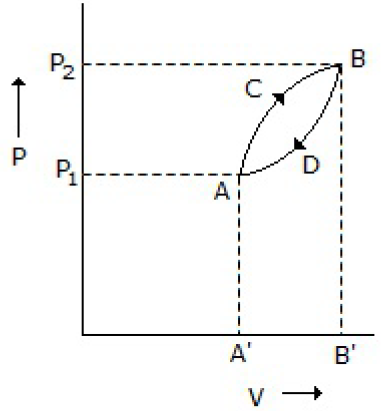
A. P1ACBP2P1
B. ACBB1A1A
C. ACBDA
D. ADBB1A1A
Answer : C

A. P1ACBP2P1
B. ACBB1A1A
C. ACBDA
D. ADBB1A1A
Answer : C
7. Entropy of a substance remains constant during a/an __________ change.
A. Reversible isothermal
B. Irreversible isothermal
C. Reversible adiabatic
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Reversible isothermal
B. Irreversible isothermal
C. Reversible adiabatic
D. None of these
Answer : C
8. At absolute zero temperature, the __________ of the gas is zero.
A. Pressure
B. Volume
C. Mass
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Pressure
B. Volume
C. Mass
D. None of these
Answer : B
9. Fugacity is most helpful in
A. Representing actual behaviour of real gases
B. Representing actual behaviour of ideal gases
C. The study of chemical equilibria involving gases at atmospheric pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Representing actual behaviour of real gases
B. Representing actual behaviour of ideal gases
C. The study of chemical equilibria involving gases at atmospheric pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
10. In the reaction, represented by, 2SO2 + O2 ? 2SO3; ?H = - 42 kcal; the forward reaction will be favoured by
A. Low temperature
B. High pressure
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Low temperature
B. High pressure
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
11. Air enters an adiabatic compressor at 300K. The exit temperature for a compression ratio of 3, assuming air to be an ideal gas (Y = Cp/Cv = 7/5) and the process to be reversible, is
A. 300 × (32/7)
B. 300 × (33/5)
C. 300 × (333/7)
D. 300 × (35/7)
Answer : A
A. 300 × (32/7)
B. 300 × (33/5)
C. 300 × (333/7)
D. 300 × (35/7)
Answer : A
12. The value of gas constant 'R' is
A. 1.987 cal/gm mole °K
B. 1.987 BTU/lb. mole °R
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. 1.987 cal/gm mole °K
B. 1.987 BTU/lb. mole °R
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
13. The equation, (d loge PA/d loge xA) = (d loge PA/d loge xB) applicable to a binary solution of components. A and B in equilibrium with their vapors at constant temperature and pressure is called the __________ equation.
A. Van Laar
B. Margules
C. Gibbs-Duhem
D. Gibbs-Duhem-Margules
Answer : D
A. Van Laar
B. Margules
C. Gibbs-Duhem
D. Gibbs-Duhem-Margules
Answer : D
14. A cylinder contains 640 gm of liquid oxygen. The volume occupied (in litres) by the oxygen, when it is released and brought to standard conditions (0°C, 760 mm Hg) will be __________ litres.
A. 448
B. 224
C. 22.4
D. Data insufficient; can't be computed
Answer : A
A. 448
B. 224
C. 22.4
D. Data insufficient; can't be computed
Answer : A
15. In the decomposition of PCl5 represented by, PCl5 ? PCl3 + Cl2, decrease in the pressure of the system will __________ the degree of dissociation of PCl5.
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Not alter
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Not alter
D. None of these
Answer : A
16. y = specific heat ratio of an ideal gas is equal to
A. Cp/Cv
B. Cp/(CP-R)
C. 1 + (R/CV)
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Cp/Cv
B. Cp/(CP-R)
C. 1 + (R/CV)
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
17. With increase in pressure (above atmospheric pressure), the Cp of a gas
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains unchanged
D. First decreases and then increases
Answer : A
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains unchanged
D. First decreases and then increases
Answer : A
18. Melting of ice is an example of an __________ process.
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : B
19. Which of the following processes cannot be made reversible even under ideal condition of operation?
A. Free expansion of a gas
B. Compression of air in a compressor
C. Expansion of steam in a turbine
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : A
A. Free expansion of a gas
B. Compression of air in a compressor
C. Expansion of steam in a turbine
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : A
20. What is the value of maximum COP in case of absorption refrigeration, if refrigeration provided is at temperature, TR (where, T1 and T2 are source & surrounding temperatures respectively.)?
A. TR/(T2 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
B. TR/(T2 - TR) × T1/(T1 - T2)
C. TR/(T1 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. TR/(T2 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
B. TR/(T2 - TR) × T1/(T1 - T2)
C. TR/(T1 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
D. None of these
Answer : A
21. Which of the following liquid metals has the highest thermal conductivity?
A. Molten sodium
B. Molten lead
C. Mercury
D. Molten potassium
Answer : A
A. Molten sodium
B. Molten lead
C. Mercury
D. Molten potassium
Answer : A
22. Entropy of an ideal gas depends upon its
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
23. Partial molar free energy of an element A in solution is same as its
A. Chemical potential
B. Activity
C. Fugacity
D. Activity co-efficient
Answer : A
A. Chemical potential
B. Activity
C. Fugacity
D. Activity co-efficient
Answer : A
24. Trouton's ratio of __________ liquids is calculated using Kistyakowsky equation.
A. Polar
B. Non-polar
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
A. Polar
B. Non-polar
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
25. Joule-Thomson co-efficient is defined as
A. ? = (?P/?T)H
B. ? = (?T/?P)H
C. ? = (?E/?T)H
D. ? = (?E/?P)H
Answer : B
A. ? = (?P/?T)H
B. ? = (?T/?P)H
C. ? = (?E/?T)H
D. ? = (?E/?P)H
Answer : B
26. Which of the following is not an intensive property?
A. Volume
B. Density
C. Temperature
D. Pressure
Answer : A
A. Volume
B. Density
C. Temperature
D. Pressure
Answer : A
27. What is the degree of freedom for two miscible (non-reacting) substances in vapor-liquid equilibrium forming an azeotrope?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : C
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : C
28. An isolated system can exchange __________ with its surroundings.
A. Matter
B. Energy
C. Neither matter nor energy
D. Both matter and energy
Answer : C
A. Matter
B. Energy
C. Neither matter nor energy
D. Both matter and energy
Answer : C
29. Which is not constant for an ideal gas?
A. (?P/?V)T
B. (?V/?T)P
C. (?P/?V)V
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : A
A. (?P/?V)T
B. (?V/?T)P
C. (?P/?V)V
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : A
30. The specific heat of saturated water vapour at 100°C is
A. ?
B. -ve
C. 0
D. +ve
Answer : B
A. ?
B. -ve
C. 0
D. +ve
Answer : B
31. What is the number of degrees of freedom for liquid water in equilibrium with a mixture of nitrogen and water vapor?
A. 2
B. 0
C. 3
D. 1
Answer : A
A. 2
B. 0
C. 3
D. 1
Answer : A
32. Which of the following is not an equation of state?
A. Bertholet equation
B. Clausius-Clapeyron equation
C. Beattie-Bridgeman equation
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Bertholet equation
B. Clausius-Clapeyron equation
C. Beattie-Bridgeman equation
D. None of these
Answer : B
33. If different processes are used to bring about the same chemical reaction, the enthalpy change is same for all of them. This is __________ law.
A. Hess's
B. Kirchoff's
C. Lavoisier and Laplace
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Hess's
B. Kirchoff's
C. Lavoisier and Laplace
D. None of these
Answer : A
34. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. A closed system does not permit exchange of mass with its surroundings but may permit exchange of energy.
B. An open system permits exchange of both mass and energy with its surroundings
C. The term microstate is used to characterise an individual, whereas macro-state is used to designate a group of micro-states with common characteristics
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. A closed system does not permit exchange of mass with its surroundings but may permit exchange of energy.
B. An open system permits exchange of both mass and energy with its surroundings
C. The term microstate is used to characterise an individual, whereas macro-state is used to designate a group of micro-states with common characteristics
D. None of the above
Answer : D
35. When dilute aqueous solutions of two salts are mixed, the process is associated with
A. Decrease in temperature
B. Increase in temperature
C. No change in temperature
D. Change in temperature which is a function of composition
Answer : B
A. Decrease in temperature
B. Increase in temperature
C. No change in temperature
D. Change in temperature which is a function of composition
Answer : B
36. Which of the following decreases with increase in pressure?
A. Melting point of ice
B. Melting point of wax
C. Boiling point of liquids
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Melting point of ice
B. Melting point of wax
C. Boiling point of liquids
D. None of these
Answer : A
37. Clausius-Clapeyron Equation gives accurate result, when the
A. Vapour pressure is relatively low and the temperature does not vary over wide limits
B. Vapour obeys the ideal gas law and the latent heat of vaporisation is constant
C. Volume in the liquid state is negligible compared with that in the vapour state
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Vapour pressure is relatively low and the temperature does not vary over wide limits
B. Vapour obeys the ideal gas law and the latent heat of vaporisation is constant
C. Volume in the liquid state is negligible compared with that in the vapour state
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
38. A solid metallic block weighing 5 kg has an initial temperature of 500°C. 40 kg of water initially at 25°C is contained in a perfectly insulated tank. The metallic block is brought into contact with water. Both of them come to equilibrium. Specific heat of block material is 0.4 kJ.kg-1. K-1. Ignoring the effect of expansion and contraction and also the heat capacity to tank, the total entropy change in kJ.kg-1, K-1 is
A. -1.87
B. 0
C. 1.26
D. 3.91
Answer : B
A. -1.87
B. 0
C. 1.26
D. 3.91
Answer : B
39. Work done in case of free expansion is
A. Indeterminate
B. Zero
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Indeterminate
B. Zero
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : B
40. The internal energy of an incompressible fluid depends upon its
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
41. The relation connecting the fugacities of various components in a solution with one another and to composition at constant temperature and pressure is called the __________ equation.
A. Gibbs-Duhem
B. Van Laar
C. Gibbs-Helmholtz
D. Margules
Answer : A
A. Gibbs-Duhem
B. Van Laar
C. Gibbs-Helmholtz
D. Margules
Answer : A
42. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. Cp of monatomic gases such as metallic vapor is about 5 kcal/kg.atom
B. The heat capacity of solid inorganic substance is exactly equal to the heat capacity of the substance in the molten state
C. There is an increase in entropy, when a spontaneous change occurs in an isolated system
D. At absolute zero temperature, the heat capacity for many pure crystalline substances is zero
Answer : B
A. Cp of monatomic gases such as metallic vapor is about 5 kcal/kg.atom
B. The heat capacity of solid inorganic substance is exactly equal to the heat capacity of the substance in the molten state
C. There is an increase in entropy, when a spontaneous change occurs in an isolated system
D. At absolute zero temperature, the heat capacity for many pure crystalline substances is zero
Answer : B
43. It is desired to bring about a certain change in the state of a system by performing work on the system under adiabatic conditions.
A. The amount of work needed is path dependent
B. Work alone cannot bring out such a change of state
C. The amount of work needed is independent of path
D. More information is needed to conclude anything about the path dependence or otherwise of the work needed
Answer : A
A. The amount of work needed is path dependent
B. Work alone cannot bring out such a change of state
C. The amount of work needed is independent of path
D. More information is needed to conclude anything about the path dependence or otherwise of the work needed
Answer : A
44. While dissolving a gas into a liquid at a constant temperature, the ratio of the concentration of the gas in the solution phase and in the gaseous phase is
A. Infinity
B. Unity
C. Constant
D. Negative
Answer : C
A. Infinity
B. Unity
C. Constant
D. Negative
Answer : C
45. Entropy change of the reaction, H2O (liquid) ? H2O (gas), is termed as the enthalpy of
A. Solution
B. Vaporisation
C. Formation
D. Sublimation
Answer : B
A. Solution
B. Vaporisation
C. Formation
D. Sublimation
Answer : B
46. A solute distributes itself between two nonmiscible solvents in contact with each other in such a way that, at a constant temperature, the ratio of its concentrations in two layers is constant, irrespective of its total amount. This is
A. The distribution law
B. Followed from Margules equation
C. A corollary of Henry's law
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. The distribution law
B. Followed from Margules equation
C. A corollary of Henry's law
D. None of these
Answer : A
47. The number of degrees of freedom at the triple point of water is
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
48. During Joule-Thomson expansion of gases
A. Enthalpy remains constant
B. Entropy remains constant
C. Temperature remains constant
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Enthalpy remains constant
B. Entropy remains constant
C. Temperature remains constant
D. None of these
Answer : A
49. Pick out the wrong statement pertaining to the decomposition of PCl5 represented by, PCl5 ? PCl3 + Cl2.Degree of dissociation of PCl5 will
A. Decrease on addition of Cl2
B. Increase on addition of an inert gas at constant pressure
C. Decrease on increasing the pressure of the system
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Decrease on addition of Cl2
B. Increase on addition of an inert gas at constant pressure
C. Decrease on increasing the pressure of the system
D. None of these
Answer : D
50. Maximum work that could be secured by expanding the gas over a given pressure range is the __________ work.
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isentropic
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isentropic
D. None of these
Answer : A
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Choosing the correct sentence 1000+ MCQ with answer for UPSC IES
1000+ Engineering Mechanics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Strength of Materials Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Radiologic Examination 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC Stenographer
Biological Classification 1000+ MCQ with answer for CLAT PG
Basics of Economics 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC Scientific Assistant