Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics MCQ Solved Paper for NEET
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The most important application of distribution law is in
A. Evaporation
B. Liquid extraction
C. Drying
D. Distillation
Answer : B
A. Evaporation
B. Liquid extraction
C. Drying
D. Distillation
Answer : B
2. Work done in an adiabatic process between two states depends on the
A. Rate of heat transmission
B. Initial state only
C. End states only
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Rate of heat transmission
B. Initial state only
C. End states only
D. None of these
Answer : C
3. A cylinder contains 640 gm of liquid oxygen. The volume occupied (in litres) by the oxygen, when it is released and brought to standard conditions (0°C, 760 mm Hg) will be __________ litres.
A. 448
B. 224
C. 22.4
D. Data insufficient; can't be computed
Answer : A
A. 448
B. 224
C. 22.4
D. Data insufficient; can't be computed
Answer : A
4. The root mean square speed of molecules of a gas is equal to (where, m = mass of the molecule K = Boltzmanns constant, T = absolute temperature)
A. ?(2KT/m)
B. ?(3KT/m)
C. ?(6KT/m)
D. 3KT/m
Answer : B
A. ?(2KT/m)
B. ?(3KT/m)
C. ?(6KT/m)
D. 3KT/m
Answer : B
5. Which of the following is not an extensive property?
A. Free energy
B. Entropy
C. Refractive index
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Free energy
B. Entropy
C. Refractive index
D. None of these
Answer : C
6. On opening the door of an operating refrigerator kept in a closed room, the temperature of the room will
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain same
D. Increase in summer and will decrease in winter
Answer : A
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain same
D. Increase in summer and will decrease in winter
Answer : A
7. Which of the following is true for Virial equation of state?
A. Virial co-efficients are universal constants
B. Virial co-efficients 'B' represents three body interactions
C. Virial co-efficients are function of temperature only
D. For some gases, Virial equations and ideal gas equations are the same
Answer : C
A. Virial co-efficients are universal constants
B. Virial co-efficients 'B' represents three body interactions
C. Virial co-efficients are function of temperature only
D. For some gases, Virial equations and ideal gas equations are the same
Answer : C
8. Chemical potential of ith component of a system is given by
A. ?i = (?F/?ni)T, P, ni
B. ?i = (?A/?ni)T, P, ni
C. ?i = (?F/?ni)T, P
D. ?i = (?A/?ni)T, P
Answer : A
A. ?i = (?F/?ni)T, P, ni
B. ?i = (?A/?ni)T, P, ni
C. ?i = (?F/?ni)T, P
D. ?i = (?A/?ni)T, P
Answer : A
9. For multi-component multiple phases to be in equilibrium at the same pressure and temperature, the __________ of each component must be same in all phases.
A. Chemical potential
B. Fugacity
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Chemical potential
B. Fugacity
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
10. Which law of the thermodynamics provides basis for measuring the thermodynamic property?
A. First law
B. Zeroth law
C. Third law
D. Second law
Answer : B
A. First law
B. Zeroth law
C. Third law
D. Second law
Answer : B
11. The compressibility factor of a gas is given by (where, V1 = actual volume of the gas V2 = gas volume predicted by ideal gas law)
A. V1/V2
B. V2/V1
C. V1 - V2
D. V1.V2
Answer : A
A. V1/V2
B. V2/V1
C. V1 - V2
D. V1.V2
Answer : A
12. Dryness fraction of wet steam is defined as the ratio of mass of vapour in the mixture to the mass of mixture __________ calorimeter is not used for measuring the dryness fraction of steam.
A. Bomb
B. Separating
C. Bucket
D. Throttling
Answer : A
A. Bomb
B. Separating
C. Bucket
D. Throttling
Answer : A
13. Which of the following is not an intensive property?
A. Molar heat capacity
B. Internal energy
C. Viscosity
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Molar heat capacity
B. Internal energy
C. Viscosity
D. None of these
Answer : B
14. In an ideal refrigeration cycle, the change in internal energy of the fluid is
A. +ve
B. -ve
C. 0
D. Either of the above three; depends on the nature of refrigerant
Answer : C
A. +ve
B. -ve
C. 0
D. Either of the above three; depends on the nature of refrigerant
Answer : C
15. Gibbs free energy (G) is represented by, G = H - TS, whereas Helmholtz free energy, (A) is given by, A = E - TS. Which of the following is the Gibbs-Helmholtz equation?
A. [?(G/T)/?T] = - (H/T2)
B. [?(A/T)/?T]V = - E/T2
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. [?(G/T)/?T] = - (H/T2)
B. [?(A/T)/?T]V = - E/T2
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
16. All gases above its inversion temperature, in a throttling process will show
A. A heating effect
B. No change in temperature
C. A cooling effect
D. Either (A) or (C)
Answer : A
A. A heating effect
B. No change in temperature
C. A cooling effect
D. Either (A) or (C)
Answer : A
17. Melting of wax is accompanied with __________ in entropy.
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. No change
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. No change
D. None of these
Answer : A
18. The internal energy of an ideal gas does not change in a reversible __________ process.
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isobaric
D. Isometric
Answer : A
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isobaric
D. Isometric
Answer : A
19. In case of steady flow compression polytropic process (PVn = constant), the work done on air is the lowest, when
A. n = y = 1.4
B. n = 0
C. n = 1
D. n = 1.66
Answer : C
A. n = y = 1.4
B. n = 0
C. n = 1
D. n = 1.66
Answer : C
20. In the equation, PVn = constant, if the value of n = 1, then it represents a reversible __________ process.
A. Isothermal
B. Isobaric
C. Polytropic
D. Adiabatic
Answer : A
A. Isothermal
B. Isobaric
C. Polytropic
D. Adiabatic
Answer : A
21. The intensive properties are
A. Molar volume, density, viscosity and boiling point
B. Refractive index and surfae tension
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Molar volume, density, viscosity and boiling point
B. Refractive index and surfae tension
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
22. Sound waves propagation in air exemplifies an __________ process.
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : A
23. Claude's liquefaction process employs the cooling of gases by
A. Expansion in an engine
B. Following a constant pressure cycle
C. Throttling
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Expansion in an engine
B. Following a constant pressure cycle
C. Throttling
D. None of these
Answer : A
24. Charles' law for gases states that
A. V/T = Constant
B. V ? 1/T
C. V ? 1/P
D. PV/T = Constant
Answer : A
A. V/T = Constant
B. V ? 1/T
C. V ? 1/P
D. PV/T = Constant
Answer : A
25. During the phase transition, __________ changes.
A. Pressure
B. Volume
C. Temperature
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : B
A. Pressure
B. Volume
C. Temperature
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : B
26. An ideal gas is taken around the cycle ABCA as shown in P-V diagram below: The work done by the gas during the cycle is equal to
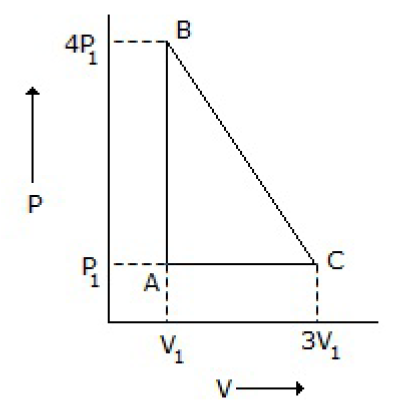
A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C

A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C
27. Thermal efficiency of a Carnot engine can approach 100%, only when the temperature of the
A. Cold reservoir approaches zero
B. Hot reservoir approaches infinity
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Cold reservoir approaches zero
B. Hot reservoir approaches infinity
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
28. Joule-Thomson co-efficient for a perfect gas is
A. Zero
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : A
29. Pick out the extensive property out of the following.
A. Surface tension
B. Free energy
C. Specific heat
D. Refractive index
Answer : B
A. Surface tension
B. Free energy
C. Specific heat
D. Refractive index
Answer : B
30. In which of the following reaction equilibrium, the value of equilibrium constant Kp will be more than is Kc?
A. 2HI ? H2 + I2
B. N2O4 ? 2NO2
C. 2SO2 + O2 ? 2SO3
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. 2HI ? H2 + I2
B. N2O4 ? 2NO2
C. 2SO2 + O2 ? 2SO3
D. None of these
Answer : B
31. Work done in case of free expansion is
A. Indeterminate
B. Zero
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Indeterminate
B. Zero
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : B
32. Internal energy change of a system over one complete cycle in a cyclic process is
A. Zero
B. +ve
C. -ve
D. Dependent on the path
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. +ve
C. -ve
D. Dependent on the path
Answer : A
33. A gas can be liquefied by pressure alone only, when its temperature is __________ its critical temperature.
A. Less than
B. More than
C. Equal to or higher than
D. Less than or equal to
Answer : D
A. Less than
B. More than
C. Equal to or higher than
D. Less than or equal to
Answer : D
34. One ton of refrigeration is defined as the heat rate corresponding to melting of one ton of ice in one
A. Hour
B. Day
C. Minute
D. Second
Answer : B
A. Hour
B. Day
C. Minute
D. Second
Answer : B
35. The freezing point of a liquid decreases when the pressure is increased, if the liquid __________ while freezing.
A. Contracts
B. Expands
C. Does not change in volume
D. Either (A), (B) or (C)
Answer : A
A. Contracts
B. Expands
C. Does not change in volume
D. Either (A), (B) or (C)
Answer : A
36. If the heat of solution of an ideal gas in a liquid is negative, then its solubility at a given partial pressure varies with the temperature as
A. Solubility increases as temperature increases
B. Solubility increases as temperature decreases
C. Solubility is independent of temperature
D. Solubility increases or decreases with temperature depending on the Gibbs free energy change of solution
Answer : B
A. Solubility increases as temperature increases
B. Solubility increases as temperature decreases
C. Solubility is independent of temperature
D. Solubility increases or decreases with temperature depending on the Gibbs free energy change of solution
Answer : B
37. Filling of gas from a high pressure cylinder into small bottles is an example of a/an __________ process.
A. Equilibrium
B. Adiabatic
C. Steady
D. Unsteady
Answer : D
A. Equilibrium
B. Adiabatic
C. Steady
D. Unsteady
Answer : D
38. A closed system is cooled reversibly from 100°C to 50°C. If no work is done on the system
A. its internal energy (U) decreases and its entropy (S) increases
B. U and S both decreases
C. U decreases but S is constant
D. U is constant but S decreases
Answer : B
A. its internal energy (U) decreases and its entropy (S) increases
B. U and S both decreases
C. U decreases but S is constant
D. U is constant but S decreases
Answer : B
39. While dissolving a gas into a liquid at a constant temperature, the ratio of the concentration of the gas in the solution phase and in the gaseous phase is
A. Infinity
B. Unity
C. Constant
D. Negative
Answer : C
A. Infinity
B. Unity
C. Constant
D. Negative
Answer : C
40. The activity of an ideal gas is numerically __________ its pressure.
A. More than
B. Less than
C. Equal to
D. Data insufficient, can't be predicted
Answer : C
A. More than
B. Less than
C. Equal to
D. Data insufficient, can't be predicted
Answer : C
41. Which of the following identities can be most easily used to verify steam table data for superheated steam?
A. (?T/?V)S = (?p/?S)V
B. (?T/?P)S = (?V/?S)P
C. (?P/?T)V = (?S/?V)T
D. (?V/?T)P = -(?S/?P)T
Answer : D
A. (?T/?V)S = (?p/?S)V
B. (?T/?P)S = (?V/?S)P
C. (?P/?T)V = (?S/?V)T
D. (?V/?T)P = -(?S/?P)T
Answer : D
42. Which of the following represents the Virial equation of state?
A. T = [RT/(V- b)] - [a/?T. V(V + b)]
B. PV/RT = 1 + (B/V) + (C/V2) + ……
C. n1u2 + ?2?1 = 0
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. T = [RT/(V- b)] - [a/?T. V(V + b)]
B. PV/RT = 1 + (B/V) + (C/V2) + ……
C. n1u2 + ?2?1 = 0
D. None of these
Answer : B
43. During adiabatic expansion of gas
A. Pressure remains constant
B. Pressure is increased
C. Temperature remains constant
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Pressure remains constant
B. Pressure is increased
C. Temperature remains constant
D. None of these
Answer : D
44. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. A closed system does not permit exchange of mass with its surroundings but may permit exchange of energy.
B. An open system permits exchange of both mass and energy with its surroundings
C. The term microstate is used to characterise an individual, whereas macro-state is used to designate a group of micro-states with common characteristics
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. A closed system does not permit exchange of mass with its surroundings but may permit exchange of energy.
B. An open system permits exchange of both mass and energy with its surroundings
C. The term microstate is used to characterise an individual, whereas macro-state is used to designate a group of micro-states with common characteristics
D. None of the above
Answer : D
45. The equation, PV = nRT, is best obeyed by gases at
A. Low pressure & high temperature
B. High pressure & low temperature
C. Low pressure & low temperature
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Low pressure & high temperature
B. High pressure & low temperature
C. Low pressure & low temperature
D. None of these
Answer : A
46. For the gaseous phase chemical reaction, C2H4(g) + H2O(g) ? C2H5OH(g), the equilibrium conversion does not depend on the
A. Steam to ethylene ratio
B. Temperature
C. Pressure
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Steam to ethylene ratio
B. Temperature
C. Pressure
D. None of these
Answer : D
47. When a system in equilibrium is subjected to a change in temperature, pressure or concentration, the equilibrium is displaced in a direction which tends to undo the effect of the change. This is called the
A. Le-Chatelier principle
B. Kopp's rule
C. Law of corresponding state
D. Arrhenius hypothesis
Answer : A
A. Le-Chatelier principle
B. Kopp's rule
C. Law of corresponding state
D. Arrhenius hypothesis
Answer : A
48. The equation, Cp - Cv = R, is true for __________ gas.
A. No
B. Any real
C. Only ideal
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : C
A. No
B. Any real
C. Only ideal
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : C
49. Normal temperature and pressure (N.T.P.) corresponds to
A. 0°C and 760 mm Hg
B. 15°C and 760 mm Hg
C. 20°C and 760 mm Hg
D. 0°C and 1 kgf/cm2
Answer : C
A. 0°C and 760 mm Hg
B. 15°C and 760 mm Hg
C. 20°C and 760 mm Hg
D. 0°C and 1 kgf/cm2
Answer : C
50. The temperature at which a real gas obeys the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is called the __________ temperature.
A. Critical
B. Boyle
C. Inversion
D. Reduced
Answer : B
A. Critical
B. Boyle
C. Inversion
D. Reduced
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Current Affairs April 2017 Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Kidney cysts and tumors Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Sentence Correction Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Urology Basic Science MCQ for SSC Stenographer [Solved]
Adobe Flash MCQ Solved Paper for XAT
Indian Polity & Economy 1000+ MCQ with answer for XAT