CTET - Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. While dissolving a gas into a liquid at a constant temperature, the ratio of the concentration of the gas in the solution phase and in the gaseous phase is
A. Infinity
B. Unity
C. Constant
D. Negative
Answer : C
A. Infinity
B. Unity
C. Constant
D. Negative
Answer : C
2. A system undergoes a change from a given initial state to a given final state either by an irreversible process or by a reversible process, then (where, ? S1 and ? SR are the entropy changes of the system for the irreversible and reversible processes respectively)
A. ? S1 is always < ? SR
B. ? S1 is sometimes > ? SR
C. ? S1 is always > ? SR
D. ? S1 is always = ? SR
Answer : C
A. ? S1 is always < ? SR
B. ? S1 is sometimes > ? SR
C. ? S1 is always > ? SR
D. ? S1 is always = ? SR
Answer : C
3. Pick out the correct statement.
A. Like internal energy and enthalpy, the absolute value of standard entropy for elementary substances is zero
B. Melting of ice involves increase in enthalpy and a decrease in randomness
C. The internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on its pressure
D. Maximum work is done under reversible conditions
Answer : D
A. Like internal energy and enthalpy, the absolute value of standard entropy for elementary substances is zero
B. Melting of ice involves increase in enthalpy and a decrease in randomness
C. The internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on its pressure
D. Maximum work is done under reversible conditions
Answer : D
4. Filling of gas from a high pressure cylinder into small bottles is an example of a/an __________ process.
A. Equilibrium
B. Adiabatic
C. Steady
D. Unsteady
Answer : D
A. Equilibrium
B. Adiabatic
C. Steady
D. Unsteady
Answer : D
5. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. The conversion for a gas phase reaction increases with decrease in pressure, if there is an increase in volume accompanying the reaction
B. With increase in temperature, the equilibrium constant increases for an exothermic reaction
C. The equilibrium constant of a reaction depends upon temperature only
D. The conversion for a gas phase reaction increases with increase in pressure, if there is a decrease in volume accompanying the reaction
Answer : B
A. The conversion for a gas phase reaction increases with decrease in pressure, if there is an increase in volume accompanying the reaction
B. With increase in temperature, the equilibrium constant increases for an exothermic reaction
C. The equilibrium constant of a reaction depends upon temperature only
D. The conversion for a gas phase reaction increases with increase in pressure, if there is a decrease in volume accompanying the reaction
Answer : B
6. Which is an example of closed system?
A. Air compressor
B. Liquid cooling system of an automobile
C. Boiler
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Air compressor
B. Liquid cooling system of an automobile
C. Boiler
D. None of these
Answer : B
7. Internal energy change of a system over one complete cycle in a cyclic process is
A. Zero
B. +ve
C. -ve
D. Dependent on the path
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. +ve
C. -ve
D. Dependent on the path
Answer : A
8. Specific __________ does not change during a phase change (e.g. sublimation, melting, vaporisation etc.).
A. Entropy
B. Internal energy
C. Enthalpy
D. Gibbs free energy
Answer : D
A. Entropy
B. Internal energy
C. Enthalpy
D. Gibbs free energy
Answer : D
9. The activity of an ideal gas is numerically __________ its pressure.
A. More than
B. Less than
C. Equal to
D. Data insufficient, can't be predicted
Answer : C
A. More than
B. Less than
C. Equal to
D. Data insufficient, can't be predicted
Answer : C
10. Pressure-enthalpy chart is useful in refrigeration. The change in internal energy of an ideal fluid used in ideal refrigeration cycle is
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. Infinity
Answer : C
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. Infinity
Answer : C
11. Which of the following diagrams does not represent an Otto cycle?
A.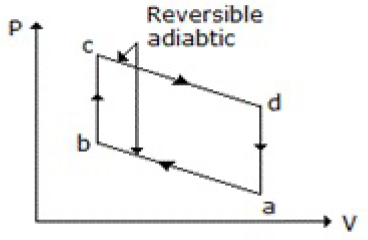
B.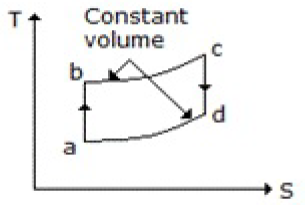
C.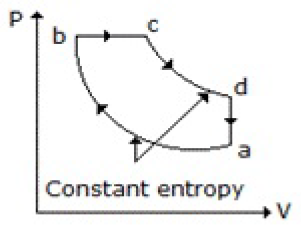
D. None of these
Answer : C
A.

B.

C.

D. None of these
Answer : C
12. Enthalpy changes over a constant pressure path are always zero for __________ gas.
A. Any
B. A perfect
C. An easily liquefiable
D. A real
Answer : B
A. Any
B. A perfect
C. An easily liquefiable
D. A real
Answer : B
13. In case of vapour compression refrigeration system, elevating the evaporator temperature (keeping the condenser temperature constant) results in
A. Enhanced COP
B. Decreased COP
C. No change in the value of COP
D. Increased or decreased COP; depending upon the type of refrigerant
Answer : A
A. Enhanced COP
B. Decreased COP
C. No change in the value of COP
D. Increased or decreased COP; depending upon the type of refrigerant
Answer : A
14. Ideal gas law is applicable at
A. Low T, low P
B. High T, high P
C. Low T, high P
D. High T, low P
Answer : D
A. Low T, low P
B. High T, high P
C. Low T, high P
D. High T, low P
Answer : D
15. Van Laar equation deals with the activity coefficients in
A. Binary solutions
B. Ternary solutions
C. Azeotropic mixture only
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Binary solutions
B. Ternary solutions
C. Azeotropic mixture only
D. None of these
Answer : A
16. Clausius-Clapeyron equation is applicable to __________ equilibrium processes.
A. Solid-vapor
B. Solid-liquid
C. Liquid-vapor
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Solid-vapor
B. Solid-liquid
C. Liquid-vapor
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
17. Specific volume of an ideal gas is
A. Equal to its density
B. The reciprocal of its density
C. Proportional to pressure
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Equal to its density
B. The reciprocal of its density
C. Proportional to pressure
D. None of these
Answer : B
18. In an irreversible process
A. Tds = dE - dW = 0
B. dE - dW - Tds = 0
C. Tds - dE + dW < 0
D. Tds - dT + dW < 0
Answer : C
A. Tds = dE - dW = 0
B. dE - dW - Tds = 0
C. Tds - dE + dW < 0
D. Tds - dT + dW < 0
Answer : C
19. Which of the following is a thermodynamic property of a system?
A. Concentration
B. Mass
C. Temperature
D. Entropy
Answer : D
A. Concentration
B. Mass
C. Temperature
D. Entropy
Answer : D
20. 1st law of thermodynamics is nothing but the law of conservation of
A. Momentum
B. Mass
C. Energy
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Momentum
B. Mass
C. Energy
D. None of these
Answer : C
21. Boyle's law for gases states that
A. P ? 1/V, when temperature is constant
B. P ? 1/V, when temperature & mass of the gas remain constant
C. P ? V, at constant temperature & mass of the gas
D. P/V = constant, for any gas
Answer : B
A. P ? 1/V, when temperature is constant
B. P ? 1/V, when temperature & mass of the gas remain constant
C. P ? V, at constant temperature & mass of the gas
D. P/V = constant, for any gas
Answer : B
22. When a system in equilibrium is subjected to a change in temperature, pressure or concentration, the equilibrium is displaced in a direction which tends to undo the effect of the change. This is called the
A. Le-Chatelier principle
B. Kopp's rule
C. Law of corresponding state
D. Arrhenius hypothesis
Answer : A
A. Le-Chatelier principle
B. Kopp's rule
C. Law of corresponding state
D. Arrhenius hypothesis
Answer : A
23. With increase in temperature, the atomic heat capacities of all solid elements
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains unchanged
D. Decreases linearly
Answer : A
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains unchanged
D. Decreases linearly
Answer : A
24. A gas has a volume of 27.3 c.c. at 0°C. Its volume at 10°C (if pressure remains unchanged) will be __________ c.c.
A. 2.73
B. 28.3
C. 273
D. 283
Answer : B
A. 2.73
B. 28.3
C. 273
D. 283
Answer : B
25. The Joule-Thomson co-efficient is defined as (?T/?P)H. Its value at the inversion point is
A. ?
B. 1
C. 0
D. -ve
Answer : C
A. ?
B. 1
C. 0
D. -ve
Answer : C
26. After throttling, gas temperature
A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. Remain same
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : A
A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. Remain same
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : A
27. The heat capacities for the ideal gas state depend upon the
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
28. Work done may be calculated by the expression ? p dA for __________ processes.
A. Non-flow reversible
B. Adiabatic
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Non-flow reversible
B. Adiabatic
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
29. What is the number of degree of freedom for a system of two miscible non-reacting species in vapor-liquid equilibrium forming an azeotrope?
A. 0
B. 2
C. 1
D. 3
Answer : C
A. 0
B. 2
C. 1
D. 3
Answer : C
30. (?T/?P)H is the mathematical expression for
A. Specific heat at constant pressure (Cp)
B. Specific heat at constant volume (Cv)
C. Joule-Thompson co-efficient
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Specific heat at constant pressure (Cp)
B. Specific heat at constant volume (Cv)
C. Joule-Thompson co-efficient
D. None of these
Answer : C
31. A system in which there is exchange of energy but not of mass, is called a/an __________ system.
A. Isolated
B. Open
C. Insulated
D. Closed
Answer : D
A. Isolated
B. Open
C. Insulated
D. Closed
Answer : D
32. __________ decreases during adiabatic throttling of a perfect gas.
A. Entropy
B. Temperature
C. Enthalpy
D. Pressure
Answer : D
A. Entropy
B. Temperature
C. Enthalpy
D. Pressure
Answer : D
33. Generation of heat by friction is an example of a/an __________ change.
A. Isothermal
B. Irreversible
C. Adiabatic
D. Reversible
Answer : B
A. Isothermal
B. Irreversible
C. Adiabatic
D. Reversible
Answer : B
34. In the equation, PVn = constant, if the value of n is in between 1 and y (i.e. Cp/Cv), then it represents a reversible __________ process.
A. Isometric
B. Polytropic
C. Isentropic
D. Isobaric
Answer : B
A. Isometric
B. Polytropic
C. Isentropic
D. Isobaric
Answer : B
35. When a gas in a vessel expands, its internal energy decreases. The process involved is
A. Reversible
B. Irreversible
C. Isothermal
D. Adiabatic
Answer : A
A. Reversible
B. Irreversible
C. Isothermal
D. Adiabatic
Answer : A
36. At __________ point, all the three phases (i.e. solid, liquid and gas) co-exist.
A. Eutectic
B. Triple
C. Plait
D. Critical
Answer : B
A. Eutectic
B. Triple
C. Plait
D. Critical
Answer : B
37. A cyclic engine exchanges heat with two reservoirs maintained at 100 and 300°C respectively. The maximum work (in J) that can be obtained from 1000 J of heat extracted from the hot reservoir is
A. 349
B. 651
C. 667
D. 1000
Answer : A
A. 349
B. 651
C. 667
D. 1000
Answer : A
38. What happens in a reversible adiabatic expansion process?
A. Heating takes place
B. Cooling takes place
C. Pressure is constant
D. Temperature is constant
Answer : B
A. Heating takes place
B. Cooling takes place
C. Pressure is constant
D. Temperature is constant
Answer : B
39. The enthalpy change when ammonia gas is dissolved in water is called the heat of
A. Solution
B. Formation
C. Dilution
D. Combustion
Answer : A
A. Solution
B. Formation
C. Dilution
D. Combustion
Answer : A
40. In the ammonia synthesis reaction, N2 + 3H2 ? 2NH3 + 22.4 kcal, the formation of NH3 will be favoured by
A. High temperature
B. Low pressure
C. Low temperature only
D. Both low temperature and high pressure
Answer : D
A. High temperature
B. Low pressure
C. Low temperature only
D. Both low temperature and high pressure
Answer : D
41. A closed system is cooled reversibly from 100°C to 50°C. If no work is done on the system
A. its internal energy (U) decreases and its entropy (S) increases
B. U and S both decreases
C. U decreases but S is constant
D. U is constant but S decreases
Answer : B
A. its internal energy (U) decreases and its entropy (S) increases
B. U and S both decreases
C. U decreases but S is constant
D. U is constant but S decreases
Answer : B
42. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. A refrigeration cycle violates the second law of thermodynamics
B. Refrigeration cycle is normally represented by a temperature vs. entropy plot
C. In a refrigerator, work required decreases as the temperature of the refrigerator and the temperature at which heat is rejected increases
D. One ton of refrigeration is equivalent to the rate of heat absorption equal to 3.53 kW
Answer : A
A. A refrigeration cycle violates the second law of thermodynamics
B. Refrigeration cycle is normally represented by a temperature vs. entropy plot
C. In a refrigerator, work required decreases as the temperature of the refrigerator and the temperature at which heat is rejected increases
D. One ton of refrigeration is equivalent to the rate of heat absorption equal to 3.53 kW
Answer : A
43. Fugacity co-efficient of a substance is the ratio of its fugacity to
A. Mole fraction
B. Activity
C. Pressure
D. Activity co-efficient
Answer : C
A. Mole fraction
B. Activity
C. Pressure
D. Activity co-efficient
Answer : C
44. A refrigeration cycle is a reversed heat engine. Which of the following has the maximum value of the co-efficient of performance (COP) for a given refrigeration effect?
A. Vapor compression cycle using expansion valve
B. Air refrigeration cycle
C. Vapor compression cycle using expansion engine
D. Carnot refrigeration cycle
Answer : D
A. Vapor compression cycle using expansion valve
B. Air refrigeration cycle
C. Vapor compression cycle using expansion engine
D. Carnot refrigeration cycle
Answer : D
45. The temperature at the eutectic point of the system is the __________ temperature that can be attained in the system.
A. Lowest
B. Highest
C. Average
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Lowest
B. Highest
C. Average
D. None of these
Answer : A
46. Entropy change for an irreversible isolated system is
A. ?
B. 0
C. < 0
D. > 0
Answer : D
A. ?
B. 0
C. < 0
D. > 0
Answer : D
47. The temperature at which a real gas obeys the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is called __________ temperature.
A. Boyle
B. Inversion
C. Critical
D. Reduced
Answer : A
A. Boyle
B. Inversion
C. Critical
D. Reduced
Answer : A
48. The kinetic energy of gas molecule is zero at
A. 0°C
B. 273°C
C. 100°C
D. -273°C
Answer : D
A. 0°C
B. 273°C
C. 100°C
D. -273°C
Answer : D
49. For a multi-component system, the term chemical potential is equivalent to the
A. Molal concentration difference
B. Molar free energy
C. Partial molar free energy
D. Molar free energy change
Answer : C
A. Molal concentration difference
B. Molar free energy
C. Partial molar free energy
D. Molar free energy change
Answer : C
50. Out of the following refrigeration cycles, which one has the minimum COP (Co-efficient of performance)?
A. Air cycle
B. Carnot cycle
C. Ordinary vapour compression cycle
D. Vapour compression with a reversible expansion engine
Answer : A
A. Air cycle
B. Carnot cycle
C. Ordinary vapour compression cycle
D. Vapour compression with a reversible expansion engine
Answer : A
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Concrete Technology and Design MCQ for NDA [Solved]
CAT - Windows 2000 Server 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
SSC CHSL - Indian History 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Planet Kingdom 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC CHSL
1000+ Relationship based problems MCQ for IBPS PO [Solved]
1000+ Urinary Calculus Disease Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]