GATE - Basics of Economics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Supply and demand changes have their most rapid impact in:
A. Auction market
B. Contract markets
C. Market for commercial office space
D. Natural gas market
Answer : A
A. Auction market
B. Contract markets
C. Market for commercial office space
D. Natural gas market
Answer : A
2. The expansion point is attained by joining:
A. Similar optimal combinations
B. Different optimal combinations
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : B
A. Similar optimal combinations
B. Different optimal combinations
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : B
3. If the commodity is inferior then the increase in income of the consumer results in:
A. More purchase
B. Less purchase
C. Same purchase
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. More purchase
B. Less purchase
C. Same purchase
D. None of the above
Answer : B
4. Along an isoquant, output remains same, and capital labor ratio:
A. Is also same
B. Is different
C. Is constant
D. Is zero
Answer : B
A. Is also same
B. Is different
C. Is constant
D. Is zero
Answer : B
5. Extension (expansion) of demand means:
A. More quantity demanded at a lower price
B. More quantity demanded at a higher price
C. More quantity demanded at the same price
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. More quantity demanded at a lower price
B. More quantity demanded at a higher price
C. More quantity demanded at the same price
D. None of the above
Answer : A
6. The normal long-run average cost curve is influenced by the:
A. Principle of diminishing returns
B. Economies and diseconomies of large scale production
C. Principle of constant return to scale
D. All of the above
Answer : B
A. Principle of diminishing returns
B. Economies and diseconomies of large scale production
C. Principle of constant return to scale
D. All of the above
Answer : B
7. Total utility and price are:
A. Directly related
B. Unrelated
C. Closely related
D. Negatively related
Answer : B
A. Directly related
B. Unrelated
C. Closely related
D. Negatively related
Answer : B
8. Least cost combination of two factor inputs is achieved at a point where:
A. Budget line cuts the isoquant
B. Budget line is below the isoquant
C. Budget line is tangent with isoquant
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Budget line cuts the isoquant
B. Budget line is below the isoquant
C. Budget line is tangent with isoquant
D. None of the above
Answer : C
9. Who is the author of Choice of Technique?
A. K.N.Raj
B. Amartiya Sen
C. A.C.Pigou
D. Alfred Marshal
Answer : B
A. K.N.Raj
B. Amartiya Sen
C. A.C.Pigou
D. Alfred Marshal
Answer : B
10. For monopolistic competitive firm:
A. P=AR and P>MR
B. P
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. P=AR and P>MR
B. P
D. None of the above
Answer : A
11. The general markets results from the imposition of price ceilings has been:
A. Higher prices
B. Increased prices
C. Increased consumption
D. Shortage of products
Answer : D
A. Higher prices
B. Increased prices
C. Increased consumption
D. Shortage of products
Answer : D
12. In case of monopoly, the price charged against the additional unit is:
A. Not different
B. Same
C. Not same
D. Zero
Answer : C
A. Not different
B. Same
C. Not same
D. Zero
Answer : C
13. Price elasticity of demand can be measured in the following way:
A. Percentage change in quantity demanded of a commodity divided by percentage change in price of that commodity
B. Change in quantity demanded of a commodity divided by change in price of that commodity
C. Percentage change in price of a commodity divided by percentage change in quantity demanded of that commodity
D. None of that commodity
Answer : A
A. Percentage change in quantity demanded of a commodity divided by percentage change in price of that commodity
B. Change in quantity demanded of a commodity divided by change in price of that commodity
C. Percentage change in price of a commodity divided by percentage change in quantity demanded of that commodity
D. None of that commodity
Answer : A
14. Firms average and marginal revenues are equal under:
A. Monopoly
B. Perfect competition
C. Oligopoly
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : B
A. Monopoly
B. Perfect competition
C. Oligopoly
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : B
15. A normal profit is:
A. A zero economic profit
B. Revenues less explicit cost
C. About 10% for most industries
D. A zero accounting profit
Answer : A
A. A zero economic profit
B. Revenues less explicit cost
C. About 10% for most industries
D. A zero accounting profit
Answer : A
16. To calculate the elasticity of demand, which of the following formula is used?:
A. Percentage change in demand Original demand
B. Proportionate change in demand Proportionate change in price
C. Change in demand Change in price
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Percentage change in demand Original demand
B. Proportionate change in demand Proportionate change in price
C. Change in demand Change in price
D. None of the above
Answer : B
17. Which is the first-order condition for the profit of a firm to be maximum?
A. AC=MR
B. MC=MR
C. MR=AR
D. AC=AR
Answer : B
A. AC=MR
B. MC=MR
C. MR=AR
D. AC=AR
Answer : B
18. Who finalized the model of monopolistic competition?
A. Ricardo
B. Marshal
C. Chamberlin
D. Mrs. Robinson
Answer : C
A. Ricardo
B. Marshal
C. Chamberlin
D. Mrs. Robinson
Answer : C
19. The basic subject matter of economics is:
A. Money
B. Capital resources
C. Scarcity
D. Inflation
Answer : B
A. Money
B. Capital resources
C. Scarcity
D. Inflation
Answer : B
20. The budget line is described by each of the following except:
A. Prices of products are assumed to be fixed
B. The consumer need not to spend all his income
C. Consumer income is assumed to be fixed
D. The slope represents relative prices
Answer : B
A. Prices of products are assumed to be fixed
B. The consumer need not to spend all his income
C. Consumer income is assumed to be fixed
D. The slope represents relative prices
Answer : B
21. Equilibrium of a firm represents maximization of profits as well as:
A. Maximization of losses
B. Minimization of losses
C. Minimization of profits
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Maximization of losses
B. Minimization of losses
C. Minimization of profits
D. None of the above
Answer : B
22. If the commodity is inferior then Income Effect (I.E) is:
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Zero
D. Infinite
Answer : A
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Zero
D. Infinite
Answer : A
23. The production process is:
A. Consuming goods and services
B. Transforming inputsinto outputs
C. Wasting goods and services
D. Buying goods and services
Answer : B
A. Consuming goods and services
B. Transforming inputsinto outputs
C. Wasting goods and services
D. Buying goods and services
Answer : B
24. In a socialist (communist) economy the invisible hand:
A. Guides most resource allocation decisions
B. Operates effectively only in the labor market
C. Operates effectively only in the market for capital
D. Is prevented from operating effectively
Answer : D
A. Guides most resource allocation decisions
B. Operates effectively only in the labor market
C. Operates effectively only in the market for capital
D. Is prevented from operating effectively
Answer : D
25. According to marginalistic rule, the profit maximization hypothesis requires:
A. MC
C. MC=AP
D. MC=MR
Answer : D
A. MC
C. MC=AP
D. MC=MR
Answer : D
26. In modern theory of costs, a firm normally utilizes:
A. 2/3 of capacity of its plants
B. 3/4 of capacity of its plants
C. 1/3 of capacity of its plants
D. 1/2 of capacity of its plants
Answer : A
A. 2/3 of capacity of its plants
B. 3/4 of capacity of its plants
C. 1/3 of capacity of its plants
D. 1/2 of capacity of its plants
Answer : A
27. The demand curve of ostentation goods (Veblen goods) will be:
A. Negatively sloped
B. Positively sloped
C. Parallel to X-axis
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Negatively sloped
B. Positively sloped
C. Parallel to X-axis
D. None of the above
Answer : B
28. In case the two commodities are complements, cross elasticity will be:
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : C
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : C
29. Isocost line shows the combinations of labor and capital where a firms budget is:
A. Fully spent
B. Half spent
C. Partially spent
D. Nearly spent
Answer : A
A. Fully spent
B. Half spent
C. Partially spent
D. Nearly spent
Answer : A
30. In dominant price leadership model, the dominant firm set the:
A. price
B. output
C. both a and b
D. none of the above
Answer : A
A. price
B. output
C. both a and b
D. none of the above
Answer : A
31. A monopolist has control over the price he charges for his product. He will be able to maximize his profit by:
A. Lowering the price, if the demand curve is elastic
B. Lowering the price, if the demand curve is inelastic
C. Rising the price, if the demand curve is elastic
D. None of the above is applicable
Answer : A
A. Lowering the price, if the demand curve is elastic
B. Lowering the price, if the demand curve is inelastic
C. Rising the price, if the demand curve is elastic
D. None of the above is applicable
Answer : A
32. The Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) Theory is presented by:
A. J.M.Keynes
B. E.D.Domar
C. Adam Smith
D. Gustav Cassel
Answer : D
A. J.M.Keynes
B. E.D.Domar
C. Adam Smith
D. Gustav Cassel
Answer : D
33. The budget-line is also known as the:
A. Iso-utility curve
B. Production possibility line
C. Isoquant
D. Consumption possibility line
Answer : D
A. Iso-utility curve
B. Production possibility line
C. Isoquant
D. Consumption possibility line
Answer : D
34. The marginal revenue of a perfectly competitive firm is:
A. Equal to the prices of its products
B. Positively related to output
C. Negatively related to output
D. Always higher than marginal cost
Answer : A
A. Equal to the prices of its products
B. Positively related to output
C. Negatively related to output
D. Always higher than marginal cost
Answer : A
35. In case of monopoly, both AR and MR fall, but MR falls:
A. Double to that of AR
B. 1/2 to that of AR
C. 2/3 to that of AR
D. Four times to that of AR
Answer : A
A. Double to that of AR
B. 1/2 to that of AR
C. 2/3 to that of AR
D. Four times to that of AR
Answer : A
36. The slope of the iso-cost line (budget line) is determined by:
A. Pricing of two factors
B. Productivity of the two factors
C. Degree of substitutability of two factors
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Pricing of two factors
B. Productivity of the two factors
C. Degree of substitutability of two factors
D. None of the above
Answer : A
37. The number of sellers in oligopoly are:
A. Two
B. Many
C. Four
D. Very few
Answer : D
A. Two
B. Many
C. Four
D. Very few
Answer : D
38. Necessary condition for consumer equilibrium is:
A.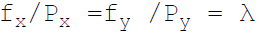
B.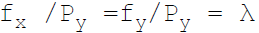
C.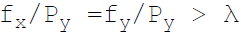
D.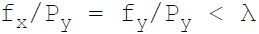
Answer : A
A.
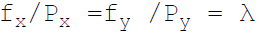
B.
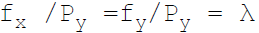
C.
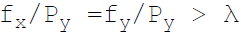
D.
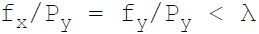
Answer : A
39. In the theory of firm, Chamberline presented the idea of:
A. Rising cost
B. Falling cost
C. Rising input
D. Falling input
Answer : B
A. Rising cost
B. Falling cost
C. Rising input
D. Falling input
Answer : B
40. Under the perfect competition, the transportation cost:
A. Is considered to be negligible and thus ignored
B. Is considered to be vital for the calculation of total cost
C. Is charged along with the price of the commodity
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Is considered to be negligible and thus ignored
B. Is considered to be vital for the calculation of total cost
C. Is charged along with the price of the commodity
D. None of the above
Answer : A
41. Competitors in monopolistic competition have full control over:
A. The price of their product
B. Product quality
C. The shape of the market demand curve
D. The elasticity of product substitution
Answer : B
A. The price of their product
B. Product quality
C. The shape of the market demand curve
D. The elasticity of product substitution
Answer : B
42. Price discrimination is possible:
A. Only under monopoly situation
B. Under any market form
C. Only under monopolistic competition
D. Only under perfect competition
Answer : A
A. Only under monopoly situation
B. Under any market form
C. Only under monopolistic competition
D. Only under perfect competition
Answer : A
43. Law of Variable Proportions is regarding in:
A. Short-Run
B. Long-Run
C. Medium-Run
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Short-Run
B. Long-Run
C. Medium-Run
D. None of the above
Answer : A
44. In cournot model, each firm expects a reaction from his rival but the expected reaction is not:
A. important
B. materialized
C. accepted
D. rejected
Answer : B
A. important
B. materialized
C. accepted
D. rejected
Answer : B
45. The Latin term citeris paribus means:
A. Other things being equal
B. Because of this
C. Due to this
D. All the factors changes at the same rate
Answer : A
A. Other things being equal
B. Because of this
C. Due to this
Answer : A
46. Law of variable proportions is based on the assumption of:
A. Short period of time
B. Long period of time
C. Timeless production relationship
D. All of the above
Answer : A
A. Short period of time
B. Long period of time
C. Timeless production relationship
D. All of the above
Answer : A
47. If the consumers expect that the price of computers will decrease in next year then:
A. Current demand for computers will fall
B. Current demand for computers will rise
C. Current demand will change unpredictably
D. Current supply of computers will rise
Answer : A
A. Current demand for computers will fall
B. Current demand for computers will rise
C. Current demand will change unpredictably
D. Current supply of computers will rise
Answer : A
48. Which of the following conditions is met in the long-run equilibrium in monopolistic competition, where the firm is earning only normal profits?
A. MC =AC and P
C. P =MC and P
Answer : D
A. MC =AC and P
C. P =MC and P
Answer : D
49. The spending of money by the producer to influence consumers is an example of:
A. Derived demand
B. Joint demand
C. Demand creation
D. Compressed demand
Answer : C
A. Derived demand
B. Joint demand
C. Demand creation
D. Compressed demand
Answer : C
50. If two households have identical preferences but different incomes then:
A. They must consume the same amounts of all goods
B. The wealthier one will have lower marginal utility for most goods
C. The wealthier one will have higher marginal utility for most goods
D. They will enjoy the same level of utility
Answer : B
A. They must consume the same amounts of all goods
B. The wealthier one will have lower marginal utility for most goods
C. The wealthier one will have higher marginal utility for most goods
D. They will enjoy the same level of utility
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ WAN MCQ for SSC CHSL [Solved]
1000+ Human reproductive system MCQ for CLAT PG [Solved]
1000+ Compressors, Gas Turbines & Jet Engines Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Auto CAD 2D Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
SSC Scientific Assistant - Urinary Calculus Disease 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
ESIC - Machine Design 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download