IBPS RRB - Applied Mechanics and Graphic Statics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Moment of inertia of a squares of side b about an axis through its centre of gravity, is
A. b3/4
B. b4/12
C. b4/3
D. b4/8
Answer : B
A. b3/4
B. b4/12
C. b4/3
D. b4/8
Answer : B
2. The horizontal reaction at the support A of the structure shown in below figure, is
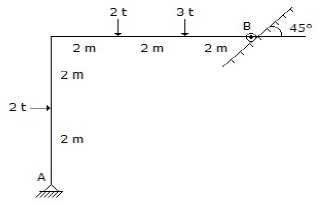
A. Zero
B. 2 t
C. 3 t
D. 1 t
Answer : A

A. Zero
B. 2 t
C. 3 t
D. 1 t
Answer : A
3. The unit of rotational inertia of a body in C.G.S system is
A. cm4
B. kg.cm²
C. gm.cm²
D. gm.cm3
Answer : C
A. cm4
B. kg.cm²
C. gm.cm²
D. gm.cm3
Answer : C
4. Two parallel forces 20 kg and 15 kg act. In order that the distance of the resultant from 20 kg force may be the same as that of the former resultant was from 15 kg, the 20 kg force is diminished by
A. 5.5 kg
B. 6.25 kg
C. 8.75 kg
D. 10.5 kg
Answer : C
A. 5.5 kg
B. 6.25 kg
C. 8.75 kg
D. 10.5 kg
Answer : C
5. The C.G. of a thin hollow cone of height h, above its base lies on the axis, at a height of
A. h/3
B. h/4
C. 2h/3
D. 3h/4
Answer : C
A. h/3
B. h/4
C. 2h/3
D. 3h/4
Answer : C
6. The resultant of two forces acting at right angles is ?34 kg and acting at 60° is 70 kg. The forces are
A. 1 kg and 4 kg
B. 2 kg and 3 kg
C. ?3 kg and ?5 kg
D. 3 kg and 5 kg
Answer : D
A. 1 kg and 4 kg
B. 2 kg and 3 kg
C. ?3 kg and ?5 kg
D. 3 kg and 5 kg
Answer : D
7. Periodic time of body moving with simple harmonic motion, is
A. Directly proportional to its angular velocity
B. Directly proportional to the square of its angular velocity
C. Inversely proportional to the square of its angular velocity
D. Inversely proportional to its angular velocity
Answer : D
A. Directly proportional to its angular velocity
B. Directly proportional to the square of its angular velocity
C. Inversely proportional to the square of its angular velocity
D. Inversely proportional to its angular velocity
Answer : D
8. A system of coplanar forces is in equilibrium when
A. Force polygon closes
B. Funicular polygon closes
C. Both force polygon and funicular polygon close
D. All the forces are concurrent
Answer : C
A. Force polygon closes
B. Funicular polygon closes
C. Both force polygon and funicular polygon close
D. All the forces are concurrent
Answer : C
9. Coefficient of friction depends on
A. Nature of surfaces only
B. Area of contact only
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Nature of surfaces only
B. Area of contact only
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
10. The centre of gravity of the trapezium as shown in below figure from the side is at a distance of
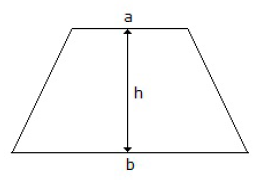
A. (h/3) × [(b + 2a)/(b + a)]
B. (h/3) × [(2b + a)/(b + a)]
C. (h/2) × [(b + 2a)/(b + a)]
D. (h/2) × [(2b + a)/(b + a)]
Answer : A

A. (h/3) × [(b + 2a)/(b + a)]
B. (h/3) × [(2b + a)/(b + a)]
C. (h/2) × [(b + 2a)/(b + a)]
D. (h/2) × [(2b + a)/(b + a)]
Answer : A
11. Which of the following represents the state of neutral equilibrium?
A. A cube resting on one edge
B. A smooth cylinder lying on a curved surface
C. A smooth cylinder lying on a convex surface
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. A cube resting on one edge
B. A smooth cylinder lying on a curved surface
C. A smooth cylinder lying on a convex surface
D. None of the above
Answer : D
12. A ball of mass 250 g moving on a smooth horizontal table with a velocity of 10 m/sec hits an identical stationary ball B on the table. If the impact is perfectly plastic, the velocity of the ball B just after impact would be
A. Zero
B. 5 m/sec
C. 10 m/sec
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. 5 m/sec
C. 10 m/sec
D. None of these
Answer : A
13. The acceleration of a train starting from rest at any instant is 1/6(V + 1) m/sec² where V is the velocity of the train in m/sec. The train will attain a velocity of 36 km/hour after travelling a distance of
A. 2000 m
B. 2100 m
C. 2200 m
D. 2300 m
Answer : D
A. 2000 m
B. 2100 m
C. 2200 m
D. 2300 m
Answer : D
14. The maximum frictional force which comes into play, when a body just begins to slide over the surface of a another body, is known
A. Sliding friction
B. Rolling friction
C. Limiting friction
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Sliding friction
B. Rolling friction
C. Limiting friction
D. None of these
Answer : C
15. At the instantaneous center, the velocity of the moving lamina at any instant is
A. Zero
B. Maximum
C. Minimum
D. Varying
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Maximum
C. Minimum
D. Varying
Answer : A
16. The mechanical advantage of an ideal machine is 100. For moving the local through 2 m, the effort moves through
A. 0.02 m
B. 2 m
C. 2.5 m
D. 20 m
Answer : A
A. 0.02 m
B. 2 m
C. 2.5 m
D. 20 m
Answer : A
17. A satellite moves in its orbit around the earth due to
A. Gravitational force
B. Centripetal force
C. Centrifugal force
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Gravitational force
B. Centripetal force
C. Centrifugal force
D. None of these
Answer : B
18. Two circular discs of same weight and thickness are made from metals having different densities. Which disc will have the larger rotational inertia about its central axis?
A. Disc with larger density
B. Disc with smaller density
C. Both discs will have same rotational inertia
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Disc with larger density
B. Disc with smaller density
C. Both discs will have same rotational inertia
D. None of the above
Answer : B
19. When a body slides down an inclined surface, the acceleration (f) of the body, is given by
A. f = g
B. f = g sin ?
C. f = g cos ?
D. f = g tan ?
Answer : B
A. f = g
B. f = g sin ?
C. f = g cos ?
D. f = g tan ?
Answer : B
20. Centre of gravity of a thin hollow cone lies on the axis of symmetry at a height of
A. One-half of the total height above base
B. One-third of the total height above base
C. One-fourth of the total height above base
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. One-half of the total height above base
B. One-third of the total height above base
C. One-fourth of the total height above base
D. None of these
Answer : B
div class="panel-body">21. The moment of inertia of a hollow circular section whose external diameter is 8 cm and internal diameter is 6 cm, about centroidal axis, is
A. 437.5 cm4
B. 337.5 cm4
C. 237.5 cm4
D. 137.5 cm4
Answer : D
A. 437.5 cm4
B. 337.5 cm4
C. 237.5 cm4
D. 137.5 cm4
Answer : D
22. The necessary condition of equilibrium of a body is:
A. Algebraic sum of horizontal components of all the forces must be zero
B. Algebraic sum of vertical components of all the forces must be zero
C. Algebraic sum of the moments of the forces about a point must be zero
D. All (a), (b) and (c)
Answer : D
A. Algebraic sum of horizontal components of all the forces must be zero
B. Algebraic sum of vertical components of all the forces must be zero
C. Algebraic sum of the moments of the forces about a point must be zero
D. All (a), (b) and (c)
Answer : D
23. If two forces acting at a point are in equilibrium, they must be equal in magnitude and their line of action must be along
A. The same line in the same sense
B. The same line in opposite sense
C. The perpendicular to both the lines
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. The same line in the same sense
B. The same line in opposite sense
C. The perpendicular to both the lines
D. None of these
Answer : B
24. An ordinate in a funicular polygon represents
A. Shear force
B. Resultant force
C. Bending moment
D. Equilibrium
Answer : C
A. Shear force
B. Resultant force
C. Bending moment
D. Equilibrium
Answer : C
25. Instantaneous center is at infinity when the angular velocity is
A. Constant
B. Zero
C. Maximum
D. Minimum
Answer : B
A. Constant
B. Zero
C. Maximum
D. Minimum
Answer : B
26. Varingons theorem of moments states
A. Arithmetical sum of the moments of two forces about any point, is equal to the moments of their resultant about that point
B. Algebraic sum of the moments of two forces about any point, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
C. Arithmetical sum of the moments of the forces about any point in their plane, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
D. Algebraic sum of the moments of the forces about any point in their plane, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
Answer : D
A. Arithmetical sum of the moments of two forces about any point, is equal to the moments of their resultant about that point
B. Algebraic sum of the moments of two forces about any point, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
C. Arithmetical sum of the moments of the forces about any point in their plane, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
D. Algebraic sum of the moments of the forces about any point in their plane, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
Answer : D
27. u1 and u2 are the velocities of approach of two moving bodies in the same direction and their corresponding velocities of separation are v1 and v2. As per Newton's law of collision of elastic bodies, the coefficient of restitution (e) is given by
A. e = v1 - v2/u2 - u1
B. e = u2 - u1/v1 - v2
C. e = v2 - v1/u1 - u2
D. e = v1 - v2/u2 + u1
Answer : C
A. e = v1 - v2/u2 - u1
B. e = u2 - u1/v1 - v2
C. e = v2 - v1/u1 - u2
D. e = v1 - v2/u2 + u1
Answer : C
28. Joule is the unit of
A. Power
B. Impulse
C. Work
D. Momentum
Answer : C
A. Power
B. Impulse
C. Work
D. Momentum
Answer : C
29. The reaction at the support A of the beam shown in below figure is 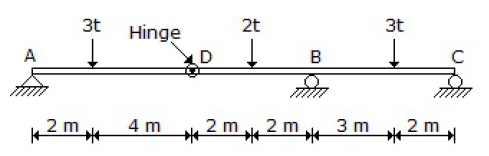
A. 2 t
B. 5.8 t
C. 0.2 t
D. 3.5 t
Answer : A

A. 2 t
B. 5.8 t
C. 0.2 t
D. 3.5 t
Answer : A
30. The reaction at the support B of the beam shown in below figure is 
A. 1.6 t
B. 9.6 t
C. 8.5 t
D. 0.5 t
Answer : C

A. 1.6 t
B. 9.6 t
C. 8.5 t
D. 0.5 t
Answer : C
31. Rate of change of angular momentum is equal to
A. Force
B. Torque
C. Linear momentum
D. Impulse
Answer : B
A. Force
B. Torque
C. Linear momentum
D. Impulse
Answer : B
32. A retarding force on a body does not
A. Change the motion of the body
B. Retard the motion of the body
C. Introduce the motion of the body
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Change the motion of the body
B. Retard the motion of the body
C. Introduce the motion of the body
D. None of these
Answer : B
33. A Second's pendulum gains 2 minutes a day. To make it to keep correct time its length
A. Must be decreased
B. Must be increased
C. Is not changed but weight of the bob is increased
D. Is not changed but weight of the bob is decreased
Answer : B
A. Must be decreased
B. Must be increased
C. Is not changed but weight of the bob is increased
D. Is not changed but weight of the bob is decreased
Answer : B
34. The ratio of kinetic energy and potential energy of a simple harmonic oscillator, at a displacement equal to half its amplitude is given by
A. 1 : 2
B. 1 : 1
C. 2 : 1
D. 3 : 1
Answer : D
A. 1 : 2
B. 1 : 1
C. 2 : 1
D. 3 : 1
Answer : D
35. A weight W is suspended at the free end of a light member hinged to a vertical wall. If the angle of inclination of the member with the upper wall is ?°, the force introduced in the member, is
A. W sec ?
B. W cos ?
C. W sin ?
D. W cosec ?
Answer : A
A. W sec ?
B. W cos ?
C. W sin ?
D. W cosec ?
Answer : A
36. A projectile has maximum range of 40 m on a horizontal plane. If angle of projection is a and the time of flight is 1 second, then sin a must be about (Assume g = 10 m/sec²)
A. 1/4
B. 1/3
C. 1/2
D. 1/5
Answer : A
A. 1/4
B. 1/3
C. 1/2
D. 1/5
Answer : A
37. If the angle between the applied force and the direction of motion of a body, is between 90° and 180°, the work done, is called
A. Virtual work
B. Imaginary work
C. Zero work
D. Negative work
Answer : D
A. Virtual work
B. Imaginary work
C. Zero work
D. Negative work
Answer : D
38. Joule is the unit of
A. Work
B. Force
C. Power
D. Torque
Answer : A
A. Work
B. Force
C. Power
D. Torque
Answer : A
39. If the tension in a cable supporting a lift moving upwards is twice the tension when the lift is moving downwards, the acceleration of the lift, is
A. g/2
B. g/3
C. g/4
D. g/5
Answer : B
A. g/2
B. g/3
C. g/4
D. g/5
Answer : B
40. If ? and u are the angle of projection and initial velocity of a projectile respectively, the horizontal range of the projectile, is
A. u² sin ?/g
B. u² sin² ?/g
C. u² sin ?/2g
D. u² sin² ?/2g
Answer : A
A. u² sin ?/g
B. u² sin² ?/g
C. u² sin ?/2g
D. u² sin² ?/2g
Answer : A
41. The forces which meet at one point and have their lines of action in different planes are called
A. Coplanar non-concurrent forces
B. Non-coplanar concurrent forces
C. Non-coplanar non-current forces
D. Intersecting forces
Answer : B
A. Coplanar non-concurrent forces
B. Non-coplanar concurrent forces
C. Non-coplanar non-current forces
D. Intersecting forces
Answer : B
42. The acceleration of a particle moving along the circumference of a circle with a uniform speed, is directed
A. Radially
B. Tangentially at that point
C. Away from the centre
D. Towards the centre
Answer : B
A. Radially
B. Tangentially at that point
C. Away from the centre
D. Towards the centre
Answer : B
43. A particle moves along a straight line such that distance x traversed in t seconds is given by x = t2(t + 1), the acceleration of the particle, will be
A. 3t3 - 2t
B. 3t2 + 2t
C. 6t - 2
D. 6t + 2
Answer : D
A. 3t3 - 2t
B. 3t2 + 2t
C. 6t - 2
D. 6t + 2
Answer : D
44. The velocity ratio of an inclined plane of inclination ? with horizontal for lifting a load is
A. sin ?
B. cos ?
C. tan ?
D. cosec ?
Answer : D
A. sin ?
B. cos ?
C. tan ?
D. cosec ?
Answer : D
45. Time period and length of a seconds pendulum respectively are
A. 1 sec and 99.4 cm
B. 1 sec and 92.7 cm
C. 2 sec and 99.4 cm
D. 2 sec and 92.7 cm
Answer : C
A. 1 sec and 99.4 cm
B. 1 sec and 92.7 cm
C. 2 sec and 99.4 cm
D. 2 sec and 92.7 cm
Answer : C
46. A particle is dropped from the top of a tower 60 m high and another is projected upwards from the foot of the tower to meet the first particle at a height of 15.9 m. The velocity of projection of the second particle is
A. 16 m/sec
B. 18 m/sec
C. 20 m/sec
D. 22 m/sec
Answer : C
A. 16 m/sec
B. 18 m/sec
C. 20 m/sec
D. 22 m/sec
Answer : C
47. The Law of Polygon of Forces states that
A. If a polygon representing the forces acting at point in a body is closed, the forces are in equilibrium
B. If forces acting on a point can be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a polygon taken in order, then the resultant of the forces will be represented in magnitude and direction by the closing side of the polygon
C. If forces acting on a point can be represented of a polygon taken in order, their sides of a polygon taken in order, their resultant will be represented in magnitude and direction by the closing side of the polygon, taken in opposite order
D. If forces acting on a point can be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a polygon in order, the forces are in equilibrium
Answer : C
A. If a polygon representing the forces acting at point in a body is closed, the forces are in equilibrium
B. If forces acting on a point can be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a polygon taken in order, then the resultant of the forces will be represented in magnitude and direction by the closing side of the polygon
C. If forces acting on a point can be represented of a polygon taken in order, their sides of a polygon taken in order, their resultant will be represented in magnitude and direction by the closing side of the polygon, taken in opposite order
D. If forces acting on a point can be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a polygon in order, the forces are in equilibrium
Answer : C
48. The resultant of two forces P and Q is R. If Q is doubled, the new resultant is perpendicular to P. Then,
A. P = R
B. Q = R
C. P = Q
D. None of the above is correct
Answer : B
A. P = R
B. Q = R
C. P = Q
D. None of the above is correct
Answer : B
49. In simple harmonic motion, acceleration of a particle is proportional to
A. Rate of change of velocity
B. Displacement
C. Velocity
D. Direction
Answer : B
A. Rate of change of velocity
B. Displacement
C. Velocity
D. Direction
Answer : B
50. A ball which is thrown upwards, returns to the ground describing a parabolic path during its flight
A. Vertical component of velocity remains constant
B. Horizontal component of velocity remains constant
C. Speed of the ball remains constant
D. Kinetic energy of the ball remains constant
Answer : B
A. Vertical component of velocity remains constant
B. Horizontal component of velocity remains constant
C. Speed of the ball remains constant
D. Kinetic energy of the ball remains constant
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Biological Classification Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ The Living World Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
SSC JE - CorelDraw 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Urologic infections and inflammations 1000+ MCQ with answer for ESIC
Tumors of the prostate MCQ Solved Paper for SSC CGL
Theory of Machines 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC GD