NEET - Strength of Materials 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The atomic mass of oxygen is
A. 12
B. 14
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : C
A. 12
B. 14
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : C
2. The extension of a circular bar tapering uniformly from diameter d? at one end to diameter d? at the other end and subjected to an axial pull of P is given by
A. ?l = 4PE/ ?l²
B. ?l = 4?ld²/PE
C. ?l = 4Pl/?Ed?d?
D. ?l = 4PlE/ ?d?d?
Answer : C
A. ?l = 4PE/ ?l²
B. ?l = 4?ld²/PE
C. ?l = 4Pl/?Ed?d?
D. ?l = 4PlE/ ?d?d?
Answer : C
3. The limit of eccentricity for no tensile conditions for a column of circular section of diameter (D) is
A. d/4
B. d/8
C. d/12
D. d/16
Answer : B
A. d/4
B. d/8
C. d/12
D. d/16
Answer : B
4. The ideal efficiency of a Brayton cycle without regeneration, with increase in pressure ratio will
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain unchanged
D. Increase/decrease depending on application
Answer : A
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain unchanged
D. Increase/decrease depending on application
Answer : A
5. The specific heat of water is
A. 1.817
B. 2512
C. 4.187
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. 1.817
B. 2512
C. 4.187
D. None of these
Answer : C
6. The maximum diameter of the hole that can be punched from a plate of maximum shear stress 1/4th of its maximum crushing stress of punch, is equal to (where t = Thickness of the plate)
A. t
B. 2t
C. 4t
D. 8t
Answer : C
A. t
B. 2t
C. 4t
D. 8t
Answer : C
7. When a body is subjected to a direct tensile stress (?x) in one plane accompanied by a simple shear stress (?xy), the maximum normal stress i
A. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
B. (?x/2) - (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
C. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² - 4 ?²xy)
D. (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
Answer : A
A. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
B. (?x/2) - (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
C. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² - 4 ?²xy)
D. (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
Answer : A
8. For the same compression ratio, the efficiency of Diesel cycle is __________ Otto cycle.
A. Greater than
B. Less than
C. Equal to
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Greater than
B. Less than
C. Equal to
D. None of these
Answer : B
9. Kelvin-Planck's law deals with
A. Conservation of work
B. Conservation of heat
C. Conversion of heat into work
D. Conversion of work into heat
Answer : C
A. Conservation of work
B. Conservation of heat
C. Conversion of heat into work
D. Conversion of work into heat
Answer : C
10. According to Kelvin-Planck's statement of second law of thermodynamics,
A. It is impossible to construct an engine working on a cyclic process, whose sole purpose is to convert heat energy into work
B. It is possible to construct an engine working on a cyclic process, whose sole purpose is to convert heat energy into work
C. It is impossible to construct a device which operates in a cyclic process and produces no effect other than the transfer of heat from a cold body to a hot body
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. It is impossible to construct an engine working on a cyclic process, whose sole purpose is to convert heat energy into work
B. It is possible to construct an engine working on a cyclic process, whose sole purpose is to convert heat energy into work
C. It is impossible to construct a device which operates in a cyclic process and produces no effect other than the transfer of heat from a cold body to a hot body
D. None of the above
Answer : A
11. One molecule of oxygen consists of __________ atoms of oxygen.
A. 2
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
Answer : A
A. 2
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
Answer : A
12. An isothermal process is governed by
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. Avogadro's law
Answer : A
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. Avogadro's law
Answer : A
13. The unit of energy is S. I. units is
A. Joule (J)
B. Joule metre (Jm)
C. Watt (W)
D. Joule/metre (J/m)
Answer : A
A. Joule (J)
B. Joule metre (Jm)
C. Watt (W)
D. Joule/metre (J/m)
Answer : A
14. A cylindrical section having no joint is known as
A. Joint less section
B. Homogeneous section
C. Perfect section
D. Seamless section
Answer : D
A. Joint less section
B. Homogeneous section
C. Perfect section
D. Seamless section
Answer : D
15. The columns whose slenderness ratio is less than 80, are known as
A. Short columns
B. Long columns
C. Weak columns
D. Medium columns
Answer : A
A. Short columns
B. Long columns
C. Weak columns
D. Medium columns
Answer : A
16. Otto cycle consists of following four processes
A. Two isothermals and two isentropic
B. Two isentropic and two constant volumes
C. Two isentropic, one constant volume and one constant pressure
D. Two isentropic and two constant pressures
Answer : B
A. Two isothermals and two isentropic
B. Two isentropic and two constant volumes
C. Two isentropic, one constant volume and one constant pressure
D. Two isentropic and two constant pressures
Answer : B
17. The heating of a gas at constant pressure is governed by
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. Avogadro's law
Answer : B
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. Avogadro's law
Answer : B
18. In an irreversible process, there is a
A. Loss of heat
B. No loss of heat
C. Gain of heat
D. No gain of heat
Answer : A
A. Loss of heat
B. No loss of heat
C. Gain of heat
D. No gain of heat
Answer : A
19. The pressure exerted by an ideal gas is ________ of the kinetic energy of all the molecules contained in a unit volume of gas.
A. One-half
B. One-third
C. Two-third
D. Three-fourth
Answer : C
A. One-half
B. One-third
C. Two-third
D. Three-fourth
Answer : C
20. Reversed joule cycle is called
A. Carnot cycle
B. Rankine cycle
C. Brayton cycle
D. Bell Coleman cycle
Answer : C
A. Carnot cycle
B. Rankine cycle
C. Brayton cycle
D. Bell Coleman cycle
Answer : C
21. The sum of internal energy (U) and the product of pressure and volume (p.v) is known as
A. Workdone
B. Entropy
C. Enthalpy
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Workdone
B. Entropy
C. Enthalpy
D. None of these
Answer : C
22. The root mean square velocity of the gas molecules is given by (where k = Boltzmann's constant, T = Absolute temperature, and m = Mass of one molecule of a gas)
A. ?(KT/m)
B. ?(2KT/m)
C. ?(3KT/m)
D. ?(5KT/m)
Answer : C
A. ?(KT/m)
B. ?(2KT/m)
C. ?(3KT/m)
D. ?(5KT/m)
Answer : C
23. True stress strain-curve for materials is plotted between
A. Load/original cross-sectional area and change in length/original length
B. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and loge (original area/ instantaneous area)
C. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and change in length/ original length
D. Load/ instantaneous area and instantaneous area/original area
Answer : B
A. Load/original cross-sectional area and change in length/original length
B. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and loge (original area/ instantaneous area)
C. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and change in length/ original length
D. Load/ instantaneous area and instantaneous area/original area
Answer : B
24. The buckling load for a given material depends on
A. Slenderness ratio and area of cross-section
B. Poisson's ratio and modulus of elasticity
C. Slenderness ratio and modulus of elasticity
D. Slenderness ratio, area of cross-section and modulus of elasticity
Answer : D
A. Slenderness ratio and area of cross-section
B. Poisson's ratio and modulus of elasticity
C. Slenderness ratio and modulus of elasticity
D. Slenderness ratio, area of cross-section and modulus of elasticity
Answer : D
25. A composite shaft consisting of two stepped portions having spring constants K? and K? is held between two rigid supports at the ends. Its equivalent spring constant is
A. K? K?
B. (K? + K?)/ 2
C. (K? + K?)/ K? K?
D. K? K?/ (K? + K?)
Answer : A
A. K? K?
B. (K? + K?)/ 2
C. (K? + K?)/ K? K?
D. K? K?/ (K? + K?)
Answer : A
26. The layer at the centre of gravity of the beam as shown in the below figure, will be

A. In tension
B. In compression
C. Neither in tension nor in compression
D. None of these
Answer : C

A. In tension
B. In compression
C. Neither in tension nor in compression
D. None of these
Answer : C
27. The percentage reduction in area of a cast iron specimen during tensile test would be of the order of
A. More than 50 %
B. 25-50 %
C. 10-25 %
D. Negligible
Answer : D
A. More than 50 %
B. 25-50 %
C. 10-25 %
D. Negligible
Answer : D
28. The compression ratio is the ratio of
A. Swept volume to total volume
B. Total volume to swept volume
C. Swept volume to clearance volume
D. Total volume to clearance volume
Answer : D
A. Swept volume to total volume
B. Total volume to swept volume
C. Swept volume to clearance volume
D. Total volume to clearance volume
Answer : D
29. The ultimate tensile stress of mild steel compared to ultimate compressive stress is
A. Same
B. More
C. Less
D. Unpredictable
Answer : B
A. Same
B. More
C. Less
D. Unpredictable
Answer : B
30. A tri-atomic molecule consists of __________ atoms.
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
Answer : C
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
Answer : C
31. A series of operations, which takes place in a certain order and restore the initial conditions at the end, is known as
A. Reversible cycle
B. Irreversible cycle
C. Thermodynamic cycle
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Reversible cycle
B. Irreversible cycle
C. Thermodynamic cycle
D. None of these
Answer : C
32. The materials which exhibit the same elastic properties in all directions are called
A. Homogeneous
B. Inelastic
C. Isotropic
D. Isentropic
Answer : C
A. Homogeneous
B. Inelastic
C. Isotropic
D. Isentropic
Answer : C
33. A riveted joint in which every rivet of a row is opposite to other rivet of the outer row, is known as
A. Chain riveted joint
B. Diamond riveted joint
C. Crisscross riveted joint
D. Zigzag riveted joint
Answer : A
A. Chain riveted joint
B. Diamond riveted joint
C. Crisscross riveted joint
D. Zigzag riveted joint
Answer : A
34. In an extensive property of a thermodynamic system
A. Extensive heat is transferred
B. Extensive work is done
C. Extensive energy is utilised
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Extensive heat is transferred
B. Extensive work is done
C. Extensive energy is utilised
D. None of these
Answer : D
35. Within elastic limit, stress is
A. Inversely proportional to strain
B. Directly proportional to strain
C. Square root of strain
D. Equal to strain
Answer : B
A. Inversely proportional to strain
B. Directly proportional to strain
C. Square root of strain
D. Equal to strain
Answer : B
36. Kerosene is distilled at
A. 65° to 220°C
B. 220° to 345°C
C. 345° to 470°C
D. 470° to 550°C
Answer : B
A. 65° to 220°C
B. 220° to 345°C
C. 345° to 470°C
D. 470° to 550°C
Answer : B
37. The gas constant (R) is equal to the
A. Sum of two specific heats
B. Difference of two specific heats
C. Product of two specific heats
D. Ratio of two specific heats
Answer : B
A. Sum of two specific heats
B. Difference of two specific heats
C. Product of two specific heats
D. Ratio of two specific heats
Answer : B
38. The pull required to tear off the plate per pitch length is (where p = Pitch of rivets, t = Thickness of plates, and ?t, ? and ?c = Permissible tensile, shearing and crushing stresses respectively)
A. (p - 2d) t × ?c
B. (p - d) t × ?
C. (p - d) t × ?t
D. (2p - d) t × ?t
Answer : C
A. (p - 2d) t × ?c
B. (p - d) t × ?
C. (p - d) t × ?t
D. (2p - d) t × ?t
Answer : C
39. The property of a material by virtue of which a body returns to its original, shape after removal of the load is called
A. Plasticity
B. Elasticity
C. Ductility
D. Malleability
Answer : B
A. Plasticity
B. Elasticity
C. Ductility
D. Malleability
Answer : B
40. Which of the following statement is correct?
A. The stress is the pressure per unit area
B. The strain is expressed in mm
C. Hook's law holds good upto the breaking point
D. Stress is directly proportional to strain within elastic limit
Answer : D
A. The stress is the pressure per unit area
B. The strain is expressed in mm
C. Hook's law holds good upto the breaking point
D. Stress is directly proportional to strain within elastic limit
Answer : D
41. The hard coke is obtained when carbonisation of coal is carried out at
A. 300° to 500°C
B. 500° to 700°C
C. 700° to 900°C
D. 900° to 1100°C
Answer : D
A. 300° to 500°C
B. 500° to 700°C
C. 700° to 900°C
D. 900° to 1100°C
Answer : D
42. The deformation of a bar under its own weight is _________ the deformation, if the same body is subjected to a direct load equal to weight of the body.
A. Equal to
B. Half
C. Double
D. Quadruple
Answer : B
A. Equal to
B. Half
C. Double
D. Quadruple
Answer : B
43. Which of the following gas is mostly used in town for street and domestic lighting and heating?
A. Producer gas
B. Coal gas
C. Mond gas
D. Coke oven gas
Answer : B
A. Producer gas
B. Coal gas
C. Mond gas
D. Coke oven gas
Answer : B
44. The __________ states that change of internal energy of a perfect gas is directly proportional to the change of temperature.
A. Boyle's law
B. Charle's law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. Joule's law
Answer : D
A. Boyle's law
B. Charle's law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. Joule's law
Answer : D
45. The capacity of a strained body for doing work on the removal of the straining force, is called
A. Strain energy
B. Resilience
C. Proof resilience
D. Impact energy
Answer : B
A. Strain energy
B. Resilience
C. Proof resilience
D. Impact energy
Answer : B
46. The property of a material which allows it to be drawn into a smaller section is called
A. Plasticity
B. Ductility
C. Elasticity
D. Malleability
Answer : B
A. Plasticity
B. Ductility
C. Elasticity
D. Malleability
Answer : B
47. In the tensile test, the phenomenon of slow extension of the material, i. e. stress increasing with the time at a constant load is called
A. Creeping
B. Yielding
C. Breaking
D. Plasticity
Answer : A
A. Creeping
B. Yielding
C. Breaking
D. Plasticity
Answer : A
48. The ratio of direct stress to volumetric strain in case of a body subjected to three mutually perpendicular stresses of equal intensity, is equal to
A. Young's modulus
B. Bulk modulus
C. Modulus of rigidity
D. Modulus of elasticity
Answer : B
A. Young's modulus
B. Bulk modulus
C. Modulus of rigidity
D. Modulus of elasticity
Answer : B
49. An adiabatic process is one in which
A. No heat enters or leaves the gas
B. The temperature of the gas changes
C. The change in internal energy is equal to the mechanical workdone
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. No heat enters or leaves the gas
B. The temperature of the gas changes
C. The change in internal energy is equal to the mechanical workdone
D. All of the above
Answer : D
50. The maximum bending moment for the beam shown in the below figure, is
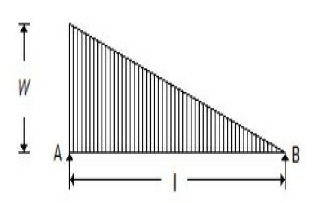
A. wl²/3?3
B. wl²/6?3
C. wl²/9?3
D. wl²/12?3
Answer : C

A. wl²/3?3
B. wl²/6?3
C. wl²/9?3
D. wl²/12?3
Answer : C
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Electrical Circuits MCQ for GRE [Solved]
1000+ Puzzle Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Current Affairs November 2022 MCQ Solved Paper for IBPS PO
Indian Polity & Economy MCQ Solved Paper for SBI Clerk
Synthesis of Sentences MCQ Solved Paper for IBPS Clerk
Data Structure MCQ Solved Paper for CTET