SSC CPO - Strength of Materials 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. When the gas is heated at constant pressure, the heat supplied
A. Increases the internal energy of the gas
B. Increases the temperature of the gas
C. Does some external work during expansion
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Increases the internal energy of the gas
B. Increases the temperature of the gas
C. Does some external work during expansion
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
2. When a gas is heated at constant pressure
A. Its temperature will increase
B. Its volume will increase
C. Both temperature and volume will increase
D. Neither temperature not volume will increase
Answer : C
A. Its temperature will increase
B. Its volume will increase
C. Both temperature and volume will increase
D. Neither temperature not volume will increase
Answer : C
3. The hyperbolic process is governed by
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. Avogadro's law
Answer : A
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. Avogadro's law
Answer : A
4. The thermodynamic difference between a Rankine cycle working with saturated steam and the Carnot cycle is that
A. Carnot cycle can't work with saturated steam
B. Heat is supplied to water at temperature below the maximum temperature of the cycle
C. A Rankine cycle receives heat at two places
D. Rankine cycle is hypothetical
Answer : B
A. Carnot cycle can't work with saturated steam
B. Heat is supplied to water at temperature below the maximum temperature of the cycle
C. A Rankine cycle receives heat at two places
D. Rankine cycle is hypothetical
Answer : B
5. The efficiency of the Carnot cycle may be increased by
A. Increasing the highest temperature
B. Decreasing the highest temperature
C. Increasing the lowest temperature
D. Keeping the lowest temperature constant
Answer : A
A. Increasing the highest temperature
B. Decreasing the highest temperature
C. Increasing the lowest temperature
D. Keeping the lowest temperature constant
Answer : A
6. The section modulus of a circular section about an axis through its C.G., is
A. ?d²/4
B. ?d²/16
C. ?d3/16
D. ?d3/32
Answer : D
A. ?d²/4
B. ?d²/16
C. ?d3/16
D. ?d3/32
Answer : D
7. When gas is heated at constant pressure, the heat supplied is utilised in
A. Increasing the internal energy of gas
B. Doing some external work
C. Increasing the internal energy of gas and also for doing some external work
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Increasing the internal energy of gas
B. Doing some external work
C. Increasing the internal energy of gas and also for doing some external work
D. None of the above
Answer : C
8. Diesel cycle consists of __________ processes.
A. Two constant volume and two isentropic
B. Two constant pressure and two isentropic
C. Two constant volume and two isothermal
D. One constant pressure, one constant volume and two isentropic
Answer : D
A. Two constant volume and two isentropic
B. Two constant pressure and two isentropic
C. Two constant volume and two isothermal
D. One constant pressure, one constant volume and two isentropic
Answer : D
9. For same compression ratio and for same heat added
A. Otto cycle is more efficient than Diesel cycle
B. Diesel cycle is more efficient than Otto cycle
C. Efficiency depends on other factors
D. Both Otto and Diesel cycles are equally efficient
Answer : A
A. Otto cycle is more efficient than Diesel cycle
B. Diesel cycle is more efficient than Otto cycle
C. Efficiency depends on other factors
D. Both Otto and Diesel cycles are equally efficient
Answer : A
10. Stirling and Ericsson cycles are
A. Reversible cycles
B. Irreversible cycles
C. Semi-reversible cycles
D. Quasi-static cycles
Answer : A
A. Reversible cycles
B. Irreversible cycles
C. Semi-reversible cycles
D. Quasi-static cycles
Answer : A
11. The efficiency of Diesel cycle with decrease in cut-off
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. First increases and then decreases
D. First decreases and then increases
Answer : A
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. First increases and then decreases
D. First decreases and then increases
Answer : A
12. The total elongation produced in a bar of uniform section hanging vertically downwards due to its own weight is equal to that produced by a weight
A. Of same magnitude as that of bar and applied at the lower end
B. Half the weight of bar applied at lower end
C. Half of the square of weight of bar applied at lower end
D. One fourth of weight of bar applied at lower end
Answer : B
A. Of same magnitude as that of bar and applied at the lower end
B. Half the weight of bar applied at lower end
C. Half of the square of weight of bar applied at lower end
D. One fourth of weight of bar applied at lower end
Answer : B
13. Workdone in a free expansion process is
A. Zero
B. Minimum
C. Maximum
D. Positive
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Minimum
C. Maximum
D. Positive
Answer : A
14. The compression ratio for petrol engines is
A. 3 to 6
B. 5 to 8
C. 10 to 20
D. 15 to 30
Answer : B
A. 3 to 6
B. 5 to 8
C. 10 to 20
D. 15 to 30
Answer : B
15. One kg of carbon monoxide requires _______kg of oxygen to produce 11/7 kg of carbon dioxide gas.
A. 11/7
B. 9/7
C. 4/7
D. All of the above
Answer : C
A. 11/7
B. 9/7
C. 4/7
D. All of the above
Answer : C
16. In an isothermal process,
A. There is no change in temperature
B. There is no change in enthalpy
C. There is no change in internal energy
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. There is no change in temperature
B. There is no change in enthalpy
C. There is no change in internal energy
D. All of these
Answer : D
17. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of the unit mass of gas through one degree at constant volume, is called
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. Kilo Joule
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. Kilo Joule
D. None of these
Answer : A
18. A molecule consisting of one atom is known as
A. Mono-atomic
B. Di-atomic
C. Tri-atomic
D. Poly-atomic
Answer : A
A. Mono-atomic
B. Di-atomic
C. Tri-atomic
D. Poly-atomic
Answer : A
19. Which of the following gas is mostly used in town for street and domestic lighting and heating?
A. Producer gas
B. Coal gas
C. Mond gas
D. Coke oven gas
Answer : B
A. Producer gas
B. Coal gas
C. Mond gas
D. Coke oven gas
Answer : B
20. If the value of n = 0 in the equation pvn = C, then the process is called
A. Constant volume process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Constant pressure process
D. Isothermal process
Answer : C
A. Constant volume process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Constant pressure process
D. Isothermal process
Answer : C
21. Which of the following has the highest calorific value?
A. Peat
B. Lignite
C. Bituminous coal
D. Anthracite coal
Answer : D
A. Peat
B. Lignite
C. Bituminous coal
D. Anthracite coal
Answer : D
22. The bending moment of a cantilever beam of length l and carrying a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length is __________ at the fixed end.
A. wl/4
B. wl/2
C. wl
D. wl²/2
Answer : D
A. wl/4
B. wl/2
C. wl
D. wl²/2
Answer : D
23. In a free expansion process,
A. W1 - 2 = 0
B. Q1 - 2 = 0
C. dU = 0
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. W1 - 2 = 0
B. Q1 - 2 = 0
C. dU = 0
D. All of these
Answer : D
24. The heat and work are mutually convertible. This statement is called __________ law of thermodynamics.
A. Zeroth
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
Answer : B
A. Zeroth
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
Answer : B
25. If the slenderness ratio for a column is 100, then it is said to be a _________ column.
A. Long
B. Medium
C. Short
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Long
B. Medium
C. Short
D. None of these
Answer : A
26. For a beam, as shown in the below figure, the deflection at C is (where E = Young's modulus for the beam material, and I = Moment of inertia of the beam section.
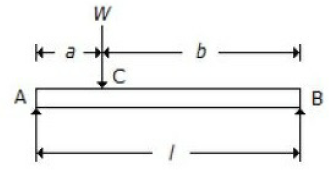
A. Wl3/48 EI
B. Wa²b²/3EIl
C. [Wa/(a?3) x EIl] x (l² - a²)3/2
D. 5Wl3/384 EI
Answer : B

A. Wl3/48 EI
B. Wa²b²/3EIl
C. [Wa/(a?3) x EIl] x (l² - a²)3/2
D. 5Wl3/384 EI
Answer : B
27. When a body is subjected to biaxial stress i.e. direct stresses (?x) and (?y) in two mutually perpendicular planes accompanied by a simple shear stress (?xy), then maximum normal stress is
A. (?x + ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
B. (?x + ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
C. (?x - ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
D. (?x - ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
Answer : A
A. (?x + ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
B. (?x + ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
C. (?x - ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
D. (?x - ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
Answer : A
28. The rivets are used for __________ fastenings.
A. Permanent
B. Temporary
C. Semi-permanent
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Permanent
B. Temporary
C. Semi-permanent
D. None of these
Answer : A
29. If the radius of wire stretched by a load is doubled, then its Youngs modulus will be
A. Doubled
B. Halved
C. Becomes four times
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. Doubled
B. Halved
C. Becomes four times
D. None of the above
Answer : D
30. One kg of carbon produces __________ kg of carbon dioxide.
A. 3/7
B. 7/3
C. 11/3
D. 3/11
Answer : C
A. 3/7
B. 7/3
C. 11/3
D. 3/11
Answer : C
31. When a thin cylindrical shell is subjected to an internal pressure, the volumetric strain is (where ?? = Hoop strain, and ?? = Longitudinal strain)
A. 2?? - ??
B. 2?? + ??
C. 2?? - ??
D. 2?? + ??
Answer : B
A. 2?? - ??
B. 2?? + ??
C. 2?? - ??
D. 2?? + ??
Answer : B
32. Diamond riveted joint can be adopted in the case of following type of joint
A. Butt joint
B. Lap joint
C. Double riveted lap joints
D. All types of joints
Answer : A
A. Butt joint
B. Lap joint
C. Double riveted lap joints
D. All types of joints
Answer : A
33. The mass of flue gas per kg of fuel is the ratio of the
A. Mass of oxygen in 1 kg of flue gas to the mass of oxygen in 1 kg of fuel
B. Mass of oxygen in 1 kg of fuel to the mass of oxygen in 1 kg of flue gas
C. Mass of carbon in 1 kg of flue gas to the mass of carbon in 1 kg of fuel
D. Mass of carbon in 1 kg of fuel to the mass of carbon in 1 kg of flue gas
Answer : C
A. Mass of oxygen in 1 kg of flue gas to the mass of oxygen in 1 kg of fuel
B. Mass of oxygen in 1 kg of fuel to the mass of oxygen in 1 kg of flue gas
C. Mass of carbon in 1 kg of flue gas to the mass of carbon in 1 kg of fuel
D. Mass of carbon in 1 kg of fuel to the mass of carbon in 1 kg of flue gas
Answer : C
34. The value of gas constant (R) in S. I. units is
A. 0.287 J/kgK
B. 2.87 J/kgK
C. 28.7 J/kgK
D. 287 J/kgK
Answer : D
A. 0.287 J/kgK
B. 2.87 J/kgK
C. 28.7 J/kgK
D. 287 J/kgK
Answer : D
35. The efficiency and work ratio of a simple gas turbine cycle are
A. Low
B. Very low
C. High
D. Very high
Answer : B
A. Low
B. Very low
C. High
D. Very high
Answer : B
36. The ultimate tensile stress of mild steel compared to ultimate compressive stress is
A. Same
B. More
C. Less
D. Unpredictable
Answer : B
A. Same
B. More
C. Less
D. Unpredictable
Answer : B
37. Formula based on IS codes is based on
A. Straight line formula
B. Eulers formula
C. Rankines formula
D. Secant formula
Answer : D
A. Straight line formula
B. Eulers formula
C. Rankines formula
D. Secant formula
Answer : D
38. The deformation of a bar under its own weight is _________ the deformation, if the same body is subjected to a direct load equal to weight of the body.
A. Equal to
B. Half
C. Double
D. Quadruple
Answer : B
A. Equal to
B. Half
C. Double
D. Quadruple
Answer : B
39. The work ratio of a gas turbine plant is given by
A. (Net work output)/(Workdone by the turbine)
B. (Net work output)/(Heat supplied)
C. (Actual temperature drop)/(Isentropic temperature drop)
D. (Isentropic increase in temperature)/(Actual increase in temperature)
Answer : A
A. (Net work output)/(Workdone by the turbine)
B. (Net work output)/(Heat supplied)
C. (Actual temperature drop)/(Isentropic temperature drop)
D. (Isentropic increase in temperature)/(Actual increase in temperature)
Answer : A
40. The smallest quantity of a substance, which can exist by itself in a chemically recognizable form is known as
A. Element
B. Compound
C. Atom
D. Molecule
Answer : D
A. Element
B. Compound
C. Atom
D. Molecule
Answer : D
41. One kg of carbon monoxide requires 4/7 kg of oxygen and produces
A. 11/3 kg of carbon dioxide gas
B. 7/3 kg of carbon monoxide gas
C. 11/7 kg of carbon dioxide gas
D. 8/3 kg of carbon monoxide gas
Answer : C
A. 11/3 kg of carbon dioxide gas
B. 7/3 kg of carbon monoxide gas
C. 11/7 kg of carbon dioxide gas
D. 8/3 kg of carbon monoxide gas
Answer : C
42. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
A. The liquid fuels have higher calorific value than solid fuels
B. The solid fuels have higher calorific value than liquid fuels
C. A good fuel should have low ignition point
D. The liquid fuels consist of hydrocarbons
Answer : /strong> B
A. The liquid fuels have higher calorific value than solid fuels
B. The solid fuels have higher calorific value than liquid fuels
C. A good fuel should have low ignition point
D. The liquid fuels consist of hydrocarbons
Answer : /strong> B
43. A circular shaft fixed at, A has diameter D for half of its length and diameter D/2 over the other half, as shown in the below figure. If the rotation of B relative to A is 0.1 radian, the rotation of C relative to B will be
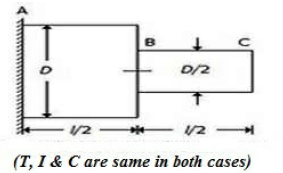
A. 0.4 radian
B. 0.8 radian
C. 1.6 radian
D. 3.2 radian
Answer : C

A. 0.4 radian
B. 0.8 radian
C. 1.6 radian
D. 3.2 radian
Answer : C
44. The given figure shows the Mohr's circle of stress for two unequal and like principal stresses (?x and ?y) acting at a body across two mutually perpendicular planes. The normal stress on an oblique section making an angle ? with the minor principle plane is given by
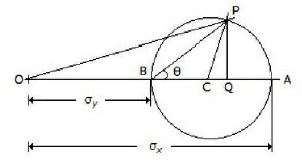
A. OC
B. OP
C. OQ
D. PQ
Answer : C

A. OC
B. OP
C. OQ
D. PQ
Answer : C
45. Producer gas is obtained by
A. Partial combustion of coal, coke, anthracite coal or charcoal in a mixed air steam blast
B. Carbonisation of bituminous coal
C. Passing steam over incandescent coke
D. Passing air and a large amount of steam over waste coal at about 650°C
Answer : A
A. Partial combustion of coal, coke, anthracite coal or charcoal in a mixed air steam blast
B. Carbonisation of bituminous coal
C. Passing steam over incandescent coke
D. Passing air and a large amount of steam over waste coal at about 650°C
Answer : A
46. The efficiency of Stirling cycle is __________ Carnot cycle.
A. Greater than
B. Less than
C. Equal to
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Greater than
B. Less than
C. Equal to
D. None of these
Answer : C
47. When a perfect gas is expanded through an aperture of minute dimensions, the process is known as
A. Isothermal process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Free expansion process
D. Throttling process
Answer : D
A. Isothermal process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Free expansion process
D. Throttling process
Answer : D
48. The following cycle is used for air craft refrigeration
A. Brayton cycle
B. Joule cycle
C. Carnot cycle
D. Reversed Brayton cycle
Answer : D
A. Brayton cycle
B. Joule cycle
C. Carnot cycle
D. Reversed Brayton cycle
Answer : D
49. A cycle consisting of two constant pressure and two isentropic processes is known as
A. Carnot cycle
B. Stirling cycle
C. Otto cycle
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Carnot cycle
B. Stirling cycle
C. Otto cycle
D. None of these
Answer : D
50. The temperature at which the volume of a gas becomes zero is called
A. Absolute scale of temperature
B. Absolute zero temperature
C. Absolute temperature
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Absolute scale of temperature
B. Absolute zero temperature
C. Absolute temperature
D. None of these
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
LIC ADO - Cell - the unit of life 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Current Affairs July 2017 1000+ MCQ with answer for GMAT
Line Graph 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC Scientific Assistant
1000+ Astronomy Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Classifications of Animal Kindom MCQ for IBPS SO [Solved]
Computer Fundamental 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC Scientific Assistant