SSC Scientific Assistant - Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. For a reversible process involving only pressure-volume work
A. (dF)T, p < 0
B. (dF)T, p > 0
C. (dF)T, p = 0
D. (dA)T, v < 0
Answer : C
A. (dF)T, p < 0
B. (dF)T, p > 0
C. (dF)T, p = 0
D. (dA)T, v < 0
Answer : C
2. Joule-Thomson experiment is
A. Isobaric
B. Adiabatic
C. Isenthalpic
D. Both (B) & (C)
Answer : D
A. Isobaric
B. Adiabatic
C. Isenthalpic
D. Both (B) & (C)
Answer : D
3. (?E/?T)V is the mathematical expression for
A. CV
B. Enthalpy change
C. Free energy change
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. CV
B. Enthalpy change
C. Free energy change
D. None of these
Answer : D
4. Efficiency of a heat engine working on Carnot cycle between two temperature levels depends upon the
A. Two temperatures only
B. Pressure of working fluid
C. Mass of the working fluid
D. Mass and pressure both of the working fluid
Answer : A
A. Two temperatures only
B. Pressure of working fluid
C. Mass of the working fluid
D. Mass and pressure both of the working fluid
Answer : A
5. The most important application of distribution law is in
A. Evaporation
B. Liquid extraction
C. Drying
D. Distillation
Answer : B
A. Evaporation
B. Liquid extraction
C. Drying
D. Distillation
Answer : B
6. Entropy of the system decreases, when
A. Snow melts into water
B. A gas expands spontaneously from high pressure to low pressure
C. Water is converted into ice
D. Both (B) & (C)
Answer : D
A. Snow melts into water
B. A gas expands spontaneously from high pressure to low pressure
C. Water is converted into ice
D. Both (B) & (C)
Answer : D
7. It is desired to bring about a certain change in the state of a system by performing work on the system under adiabatic conditions.
A. The amount of work needed is path dependent
B. Work alone cannot bring out such a change of state
C. The amount of work needed is independent of path
D. More information is needed to conclude anything about the path dependence or otherwise of the work needed
Answer : A
A. The amount of work needed is path dependent
B. Work alone cannot bring out such a change of state
C. The amount of work needed is independent of path
D. More information is needed to conclude anything about the path dependence or otherwise of the work needed
Answer : A
8. For any system, what is the minimum number of degrees of freedom?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
9. Solid and liquid phases of a substance are in equilibrium at the
A. Critical temperature
B. Melting point
C. Freezing point
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Critical temperature
B. Melting point
C. Freezing point
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
10. In an isothermal process on an ideal gas, the pressure increases by 0.5 percent. The volume decreases by about __________ percent.
A. 0.25
B. 0.5
C. 0.75
D. 1
Answer : B
A. 0.25
B. 0.5
C. 0.75
D. 1
Answer : B
11. A solid is transformed into vapour without going to the liquid phase at
A. Triple point
B. Boiling point
C. Below triple point
D. Always
Answer : A
A. Triple point
B. Boiling point
C. Below triple point
D. Always
Answer : A
12. The acentric factor of a materical, '?', is defined as ? = -log10(Prsat)Tr-1 = 0.7, where, Prsat = reduced vapor pressure, Tr = reduced temperature. The value of acentric factor is always
A. > 2
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. < 3
Answer : B
A. > 2
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. < 3
Answer : B
13. At 60° C, vapour pressure of methanol and water are 84.562 kPa and 19.953 kPa respectively. An aqueous solution of methanol at 60° C exerts a pressure of 39.223 kPa; the liquid phase and vapour phase mole fractions of methanol are 0.1686 and 0.5714 respectively. Activity co-efficient of methanol is
A. 1.572
B. 1.9398
C. 3.389
D. 4.238
Answer : A
A. 1.572
B. 1.9398
C. 3.389
D. 4.238
Answer : A
14. For a given substance at a specified temperature, activity is __________ to fugacity.
A. Directly proportional
B. Inversely proportional
C. Equal
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Directly proportional
B. Inversely proportional
C. Equal
D. None of these
Answer : A
15. The third law of thermodynamics states that the
A. Heat capacity of a crystalline solid is zero at absolute zero temperature
B. Heat transfer from low temperature to high temperature source is not possible without external work
C. Gases having same reduced properties behaves similarly
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Heat capacity of a crystalline solid is zero at absolute zero temperature
B. Heat transfer from low temperature to high temperature source is not possible without external work
C. Gases having same reduced properties behaves similarly
D. None of these
Answer : A
16. What is the degree of freedom for a system comprising liquid water equilibrium with its vapour?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : B
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : B
17. Heat of formation of an element in its standard state is
A. 0
B. < 0
C. > 0
D. A function of pressure
Answer : A
A. 0
B. < 0
C. > 0
D. A function of pressure
Answer : A
18. The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of conservation of
A. Heat
B. Momentum
C. Energy
D. Work
Answer : C
A. Heat
B. Momentum
C. Energy
D. Work
Answer : C
19. Translational kinetic energy of molecules of an ideal gas is proportional to (where, T = absolute temperature of the gas)
A. T
B. ?T
C. T2
D. 1/?T
Answer : A
A. T
B. ?T
C. T2
D. 1/?T
Answer : A
20. The number of degrees of freedom at the triple point of water is
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
21. Measurement of thermodynamic property of temperature is facilitated by __________ law of thermodynamics.
A. 1st
B. Zeroth
C. 3rd
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. 1st
B. Zeroth
C. 3rd
D. None of these
Answer : B
22. A solute distributes itself between two nonmiscible solvents in contact with each other in such a way that, at a constant temperature, the ratio of its concentrations in two layers is constant, irrespective of its total amount. This is
A. The distribution law
B. Followed from Margules equation
C. A corollary of Henry's law
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. The distribution law
B. Followed from Margules equation
C. A corollary of Henry's law
D. None of these
Answer : A
23. Entropy of an ideal gas depends upon its
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
24. A chemical reaction will occur spontaneously at constant pressure and temperature, if the free energy is
A. Zero
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Zero
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : C
25. For a constant volume process
A. dE = CpdT
B. dE = CvdT
C. dQ = dE + pdV
D. dW = pdV
Answer : B
A. dE = CpdT
B. dE = CvdT
C. dQ = dE + pdV
D. dW = pdV
Answer : B
26. Critical compressibility factor for all substances
A. Are more or less constant (vary from 0.2 to 0.3)
B. Vary as square of the absolute temperature
C. Vary as square of the absolute pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Are more or less constant (vary from 0.2 to 0.3)
B. Vary as square of the absolute temperature
C. Vary as square of the absolute pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
27. Molar heat capacity of water in equilibrium with ice at constant pressure is __________ Kcal/kg mole. °K
A. 0
B. ?
C. 50
D. 100
Answer : B
A. 0
B. ?
C. 50
D. 100
Answer : B
28. The intensive properties are
A. Molar volume, density, viscosity and boiling point
B. Refractive index and surface tension
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Molar volume, density, viscosity and boiling point
B. Refractive index and surface tension
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
29. Henry's law is closely obeyed by a gas, when its __________ is extremely high.
A. Pressure
B. Solubility
C. Temperature
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Pressure
B. Solubility
C. Temperature
D. None of these
Answer : D
30. A system in which there is exchange of energy but not of mass, is called a/an __________ system.
A. Isolated
B. Open
C. Insulated
D. Closed
Answer : D
A. Isolated
B. Open
C. Insulated
D. Closed
Answer : D
31. Gibbs free energy at constant pressure and temperature under equilibrium conditions is
A. ?
B. 0
C. Maximum
D. Minimum
Answer : D
A. ?
B. 0
C. Maximum
D. Minimum
Answer : D
32. What is the value of maximum COP in case of absorption refrigeration, if refrigeration provided is at temperature, TR (where, T1 and T2 are source & surrounding temperatures respectively.)?
A. TR/(T2 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
B. TR/(T2 - TR) × T1/(T1 - T2)
C. TR/(T1 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. TR/(T2 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
B. TR/(T2 - TR) × T1/(T1 - T2)
C. TR/(T1 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
D. None of these
Answer : A
33. Internal energy is equal to the heat absorbed in case of a/an __________ process.
A. Constant volume
B. Polytropic
C. Adiabatic
D. Constant pressure
Answer : A
A. Constant volume
B. Polytropic
C. Adiabatic
D. Constant pressure
Answer : A
34. Compressibility factor (i.e., the ratio of actual volume of gas to the volume predicted by ideal gas law) for all gases are
A. Always greater than one
B. Same at the same reduced temperature
C. Same at the same reduced pressure
D. Both (B) & (C)
Answer : D
A. Always greater than one
B. Same at the same reduced temperature
C. Same at the same reduced pressure
D. Both (B) & (C)
Answer : D
35. Degree of freedom of the system ice-watervapour will be
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
36. The heat capacities for the ideal gas state depend upon the
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
37. A system is said to be at equilibrium, if the entropy of the system has reached __________ value.
A. Minimum
B. Zero
C. Maximum
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Minimum
B. Zero
C. Maximum
D. None of these
Answer : C
38. An ideal monatomic gas is taken round the cycle ABCDA as shown below in the P-V diagram. The work done during the cycle is
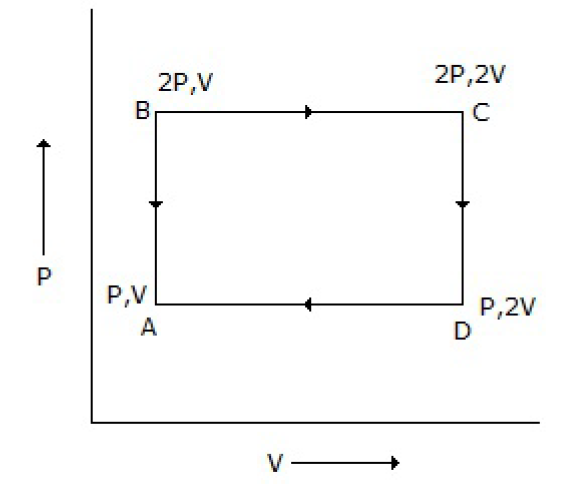
A. PV
B. 2PV
C. PV/2
D. 0
Answer : A

A. PV
B. 2PV
C. PV/2
D. 0
Answer : A
39. An ideal gas is taken around the cycle ABCA as shown in P-V diagram below: The work done by the gas during the cycle is equal to
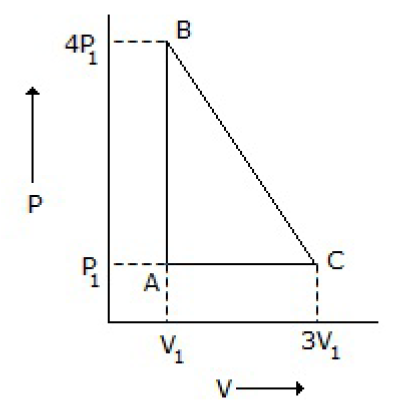
A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C

A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C
40. Free energy change of mixing two liquid substances is a function of the
A. Concentration of the constituents only
B. Quantities of the constituents only
C. Temperature only
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Concentration of the constituents only
B. Quantities of the constituents only
C. Temperature only
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
41. The entropy change in a reversible isothermal process, when an ideal gas expands to four times its initial volume is
A. R loge 4
B. R log10 4
C. Cv log10 4
D. Cv loge 4
Answer : A
A. R loge 4
B. R log10 4
C. Cv log10 4
D. Cv loge 4
Answer : A
42. Isobaric process means a constant process.
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. Entropy
Answer : B
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. Entropy
Answer : B
43. Chemical potential (an intensive property) of a substance is a force that drives the chemical system to equilibrium and is equal to its partial molar properties. The ratio of chemical potential to free energy of a pure substance at constant temperature and pressure is
A. 0
B. 1
C. ?
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. 0
B. 1
C. ?
D. None of these
Answer : B
44. Vapour which is at a pressure smaller than the saturation pressure for the temperature involved is called a __________ vapour.
A. Superheated
B. Desuperheated
C. Non-condensable
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Superheated
B. Desuperheated
C. Non-condensable
D. None of these
Answer : A
45. There is a change in __________ during the phase transition.
A. Volume
B. Pressure
C. Temperature
D. All a, b & c
Answer : A
A. Volume
B. Pressure
C. Temperature
D. All a, b & c
Answer : A
46. Co-efficient of Performance (COP) of a refrigerator is the ratio of the
A. Work required to refrigeration obtained
B. Refrigeration obtained to the work required
C. Lower to higher temperature
D. Higher to lower temperature
Answer : B
A. Work required to refrigeration obtained
B. Refrigeration obtained to the work required
C. Lower to higher temperature
D. Higher to lower temperature
Answer : B
47. Which of the following is not a reversible process?
A. Expansion of an ideal gas against constant pressure
B. Atmospheric pressure vaporisation of water at 100°C
C. Solution of NaCl in water at 50°C
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Expansion of an ideal gas against constant pressure
B. Atmospheric pressure vaporisation of water at 100°C
C. Solution of NaCl in water at 50°C
D. None of these
Answer : C
48. The minimum number of phases that can exist in a system is
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : B
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : B
49. __________ calorimeter is normally used for measuring the dryness fraction of steam, when it is very low.
A. Bucket
B. Throttling
C. Separating
D. A combination of separating & throttling
Answer : D
A. Bucket
B. Throttling
C. Separating
D. A combination of separating & throttling
Answer : D
50. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. Minimum number of degree of freedom of a system is zero
B. Degree of freedom of a system containing a gaseous mixture of helium, carbon dioxide and hydrogen is 4
C. For a two phase system in equilibrium made up of four non-reacting chemical species, the number of degrees of freedom is 4
D. Enthalpy and internal energy change is zero during phase change processes like melting, vaporisation and sublimation
Answer : D
A. Minimum number of degree of freedom of a system is zero
B. Degree of freedom of a system containing a gaseous mixture of helium, carbon dioxide and hydrogen is 4
C. For a two phase system in equilibrium made up of four non-reacting chemical species, the number of degrees of freedom is 4
D. Enthalpy and internal energy change is zero during phase change processes like melting, vaporisation and sublimation
Answer : D
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Current Affairs December 2022 MCQ for IIFT [Solved]
The Living World MCQ Solved Paper for RRB Group D
DBMS 1000+ MCQ with answer for RRB ALP
Current Affairs May 2017 MCQ Solved Paper for LIC ADO
1000+ General Chemistry Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Biological Classification Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]