Strength of Materials MCQ Solved Paper for RBI Grade B officer
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The main cause for the irreversibility is
A. Mechanical and fluid friction
B. Unrestricted expansion
C. Heat transfer with a finite temperature difference
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Mechanical and fluid friction
B. Unrestricted expansion
C. Heat transfer with a finite temperature difference
D. All of the above
Answer : D
2. The safe twisting moment for a compound shaft is equal to the
A. Maximum calculated value
B. Minimum calculated value
C. Mean value
D. Extreme value
Answer : B
A. Maximum calculated value
B. Minimum calculated value
C. Mean value
D. Extreme value
Answer : B
3. For a perfect gas, according to Boyle's law (where p = Absolute pressure, v = Volume, and T = Absolute temperature)
A. p v = constant, if T is kept constant
B. v/T = constant, if p is kept constant
C. p/T = constant, if v is kept constant
D. T/p = constant, if v is kept constant
Answer : A
A. p v = constant, if T is kept constant
B. v/T = constant, if p is kept constant
C. p/T = constant, if v is kept constant
D. T/p = constant, if v is kept constant
Answer : A
4. The maximum stress produced in a bar of tapering section is at
A. Smaller end
B. Larger end
C. Middle
D. Anywhere
Answer : A
A. Smaller end
B. Larger end
C. Middle
D. Anywhere
Answer : A
5. The ratio of specific heat at constant pressure (cp) and specific heat at constant volume (cv) is always __________ one.
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : C
6. Principal planes are planes having
A. Maximum shear stress
B. No shear stress
C. Minimum shear stress
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Maximum shear stress
B. No shear stress
C. Minimum shear stress
D. None of the above
Answer : B
7. Resilience is the
A. Energy stored in a body when strained within elastic limits
B. Energy stored in a body when strained up to the breaking of the specimen maximum strain
C. Energy which can be stored in a body
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. Energy stored in a body when strained within elastic limits
B. Energy stored in a body when strained up to the breaking of the specimen maximum strain
C. Energy which can be stored in a body
D. None of the above
Answer : D
8. A process of heating crude oil to a high temperature under a very high pressure to increase the yield of lighter distillates, is known as
A. Cracking
B. Carbonisation
C. Fractional distillation
D. Full distillation
Answer : A
A. Cracking
B. Carbonisation
C. Fractional distillation
D. Full distillation
Answer : A
9. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water through one Kelvin is called
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. kilo-Joule
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. kilo-Joule
D. None of these
Answer : C
10. Modulus of rigidity may be defined as the ratio of
A. Linear stress to lateral strain
B. Lateral strain to linear strain
C. Linear stress to linear strain
D. Shear stress to shear strain
Answer : D
A. Linear stress to lateral strain
B. Lateral strain to linear strain
C. Linear stress to linear strain
D. Shear stress to shear strain
Answer : D
11. The maximum diameter of the hole that can be punched from a plate of maximum shear stress 1/4th of its maximum crushing stress of punch, is equal to (where t = Thickness of the plate)
A. t
B. 2t
C. 4t
D. 8t
Answer : C
A. t
B. 2t
C. 4t
D. 8t
Answer : C
12. In compression test, the fracture in cast iron specimen would occur along
A. The axis of load
B. An oblique plane
C. At right angles to the axis of specimen
D. Would not occur
Answer : B
A. The axis of load
B. An oblique plane
C. At right angles to the axis of specimen
D. Would not occur
Answer : B
13. The bending moment of a cantilever beam of length l and carrying a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length is __________ at the fixed end.
A. wl/4
B. wl/2
C. wl
D. wl²/2
Answer : D
A. wl/4
B. wl/2
C. wl
D. wl²/2
Answer : D
14. A boiler shell 200 cm diameter and plate thickness 1.5 cm is subjected to internal pressure of 1.5 MN/m, and then the hoop stress will be
A. 30 MN/m²
B. 50 MN/m²
C. 100 MN/m²
D. 200 MN/m²
Answer : C
A. 30 MN/m²
B. 50 MN/m²
C. 100 MN/m²
D. 200 MN/m²
Answer : C
15. In a steady flow process, the ratio of
A. Heat transfer is constant
B. Work transfer is constant
C. Mass flow at inlet and outlet is same
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. Heat transfer is constant
B. Work transfer is constant
C. Mass flow at inlet and outlet is same
D. All of these
Answer : D
16. The torque transmitted by a solid shaft of diameter (D) is (where ? = Maximum allowable shear stress)
A. ? /4 × ? × D³
B. ? /16 × ? × D³
C. ? /32 × ? × D³
D. ? /64 × ? × D³
Answer : B
A. ? /4 × ? × D³
B. ? /16 × ? × D³
C. ? /32 × ? × D³
D. ? /64 × ? × D³
Answer : B
17. The shear force diagram of a cantilever beam of length l and carrying a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length will be
A. A right angled triangle
B. An isosceles triangle
C. An equilateral triangle
D. A rectangle
Answer : A
A. A right angled triangle
B. An isosceles triangle
C. An equilateral triangle
D. A rectangle
Answer : A
18. One kg of ethylene (C2H4) requires 2 kg of oxygen and produces 22/7 kg of carbon dioxide and __________ kg of water or steam.
A. 9/7
B. 11/7
C. 7/4
D. 1/4
Answer : A
A. 9/7
B. 11/7
C. 7/4
D. 1/4
Answer : A
19. The torsional rigidity of a shaft is expressed by the
A. Maximum torque it can transmit
B. Number of cycles it undergoes before failure
C. Elastic limit up to which it resists torsion, shear and bending stresses
D. Torque required to produce a twist of one radian per unit length of shaft
Answer : D
A. Maximum torque it can transmit
B. Number of cycles it undergoes before failure
C. Elastic limit up to which it resists torsion, shear and bending stresses
D. Torque required to produce a twist of one radian per unit length of shaft
Answer : D
20. Within elastic limit, stress is
A. Inversely proportional to strain
B. Directly proportional to strain
C. Square root of strain
D. Equal to strain
Answer : B
A. Inversely proportional to strain
B. Directly proportional to strain
C. Square root of strain
D. Equal to strain
Answer : B
21. The efficiency of the dual combustion cycle for the same compression ratio is __________ Diesel cycle.
A. Greater than
B. Less than
C./strong> Equal to
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Greater than
B. Less than
C./strong> Equal to
D. None of these
Answer : A
22. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of the unit mass of gas through one degree at constant volume, is called
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. Kilo Joule
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. Kilo Joule
D. None of these
Answer : A
23. The property of a material by virtue of which a body returns to its original, shape after removal of the load is called
A. Plasticity
B. Elasticity
C. Ductility
D. Malleability
Answer : B
A. Plasticity
B. Elasticity
C. Ductility
D. Malleability
Answer : B
24. If percentage reduction in area of a certain specimen made of material 'A' under tensile test is 60% and the percentage reduction in area of a specimen with same dimensions made of material 'B' is 40%, then
A. The material A is more ductile than material B
B. The material B is more ductile than material A
C. The ductility of material A and B is equal
D. The material A is brittle and material B is ductile
Answer : A
A. The material A is more ductile than material B
B. The material B is more ductile than material A
C. The ductility of material A and B is equal
D. The material A is brittle and material B is ductile
Answer : A
25. The mass of excess air supplied is equal to
A. (23/100) × Mass of excess carbon
B. (23/100) × Mass of excess oxygen
C. (100/23) × Mass of excess carbon
D. (100/23) × Mass of excess oxygen
Answer : D
A. (23/100) × Mass of excess carbon
B. (23/100) × Mass of excess oxygen
C. (100/23) × Mass of excess carbon
D. (100/23) × Mass of excess oxygen
Answer : D
26. The gas in cooling chamber of a closed cycle gas turbine is cooled at
A. Constant volume
B. Constant temperature
C. Constant pressure
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Constant volume
B. Constant temperature
C. Constant pressure
D. None of these
Answer : C
27. The stress at which extension of the material takes place more quickly as compared to the increase in load is called
A. Elastic point of the material
B. Plastic point of the material
C. Breaking point of the material
D. Yielding point of the material
Answer : D
A. Elastic point of the material
B. Plastic point of the material
C. Breaking point of the material
D. Yielding point of the material
Answer : D
28. The efficiency of the Carnot cycle is (where T1 and T2 = Highest and lowest temperature during the cycle)
A. (T1/T2) - 1
B. 1 - (T1/T2)
C. 1 - (T2/T1)
D. 1 + (T2/T1)
Answer : C
A. (T1/T2) - 1
B. 1 - (T1/T2)
C. 1 - (T2/T1)
D. 1 + (T2/T1)
Answer : C
29. The efficiency of Joule cycle is
A. Greater than Carnot cycle
B. Less than Carnot cycle
C. Equal to Carnot cycle
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Greater than Carnot cycle
B. Less than Carnot cycle
C. Equal to Carnot cycle
D. None of these
Answer : B
30. The tensile strength of the welded joint for double fillet is (where s = Leg or size of the weld, l = Length of weld, and ?t = Allowable tensile stress for weld metal)
A. 0.5 s.l.?t
B. s.l.?t
C. ?2 s.l.?t
D. 2.s.l.?t
Answer : C
A. 0.5 s.l.?t
B. s.l.?t
C. ?2 s.l.?t
D. 2.s.l.?t
Answer : C
31. During a tensile test on a specimen of 1 cm cross-section, maximum load observed was 8 tonnes and area of cross-section at neck was 0.5 cm². Ultimate tensile strength of specimen is
A. 4 tonnes/ cm²
B. 8 tonnes/ cm²
C. 16 tonnes/ cm²
D. 22 tonnes/ cm²
Answer : B
A. 4 tonnes/ cm²
B. 8 tonnes/ cm²
C. 16 tonnes/ cm²
D. 22 tonnes/ cm²
Answer : B
32. Carnot cycle has maximum efficiency for
A. Petrol engine
B. Diesel engine
C. Reversible engine
D. Irreversible engine
Answer : C
A. Petrol engine
B. Diesel engine
C. Reversible engine
D. Irreversible engine
Answer : C
33. The efficiency and work ratio of a simple gas turbine cycle are
A. Very low
B. Low
C. High
D. Very high
Answer : A
A. Very low
B. Low
C. High
D. Very high
Answer : A
34. The efficiency of Diesel cycle approaches to Otto cycle efficiency when
A. Cut-off is increased
B. Cut-off is decreased
C. Cut-off is zero
D. Cut-off is constant
Answer : C
A. Cut-off is increased
B. Cut-off is decreased
C. Cut-off is zero
D. Cut-off is constant
Answer : C
35. Producer gas is obtained by
A. Partial combustion of coal, coke, anthracite coal or charcoal in a mixed air steam blast
B. Carbonisation of bituminous coal
C. Passing steam over incandescent coke
D. Passing air and a large amount of steam over waste coal at about 650°C
Answer : A
A. Partial combustion of coal, coke, anthracite coal or charcoal in a mixed air steam blast
B. Carbonisation of bituminous coal
C. Passing steam over incandescent coke
D. Passing air and a large amount of steam over waste coal at about 650°C
Answer : A
36. When a body is subjected to three mutually perpendicular stresses, of equal intensity, the ratio of direct stress to the corresponding volumetric strain is known as
A. Young's modulus
B. Modulus of rigidity
C. Bulk modulus
D. Poisson's ratio
Answer : C
A. Young's modulus
B. Modulus of rigidity
C. Bulk modulus
D. Poisson's ratio
Answer : C
37. The volumetric or molar specific heat at constant pressure is the product of
A. Molecular mass of the gas and the specific heat at constant volume
B. Atomic mass of the gas and the gas constant
C. Molecular mass of the gas and the gas constant
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. Molecular mass of the gas and the specific heat at constant volume
B. Atomic mass of the gas and the gas constant
C. Molecular mass of the gas and the gas constant
D. None of the above
Answer : D
38. One molecule of oxygen is __________ times heavier than the hydrogen atom.
A. 12
B. 14
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : D
A. 12
B. 14
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : D
39. The value of specific heat at constant pressure (cp) is __________ that of at constant volume (cv).
A. Less than
B. Equal to
C. More than
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Less than
B. Equal to
C. More than
D. None of these
Answer : C
40. The efficiency of Diesel cycle depends upon
A. Temperature limits
B. Pressure ratio
C. Compression ratio
D. Cut-off ratio and compression ratio
Answer : D
A. Temperature limits
B. Pressure ratio
C. Compression ratio
D. Cut-off ratio and compression ratio
Answer : D
41. The percentage reduction in area of a cast iron specimen during tensile test would be of the order of
A. More than 50 %
B. 25-50 %
C. 10-25 %
D. Negligible
Answer : D
A. More than 50 %
B. 25-50 %
C. 10-25 %
D. Negligible
Answer : D
42. The mass of flue gas per kg of fuel is the ratio of the
A. Mass of oxygen in 1 kg of flue gas to the mass of oxygen in 1 kg of fuel
B. Mass of oxygen in 1 kg of fuel to the mass of oxygen in 1 kg of flue gas
C. Mass of carbon in 1 kg of flue gas to the mass of carbon in 1 kg of fuel
D. Mass of carbon in 1 kg of fuel to the mass of carbon in 1 kg of flue gas
Answer : C
A. Mass of oxygen in 1 kg of flue gas to the mass of oxygen in 1 kg of fuel
B. Mass of oxygen in 1 kg of fuel to the mass of oxygen in 1 kg of flue gas
C. Mass of carbon in 1 kg of flue gas to the mass of carbon in 1 kg of fuel
D. Mass of carbon in 1 kg of fuel to the mass of carbon in 1 kg of flue gas
Answer : C
43. Which of the following gas has the highest calorific value?
A. Coal gas
B. Producer gas
C. Mond gas
D. Blast furnace gas
Answer : A
A. Coal gas
B. Producer gas
C. Mond gas
D. Blast furnace gas
Answer : A
44. For the beam shown in the below figure, the shear force diagram between A and B is
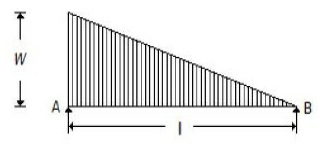
A. A horizontal line
B. A vertical line
C. An inclined line
D. A parabolic curve
Answer : D

A. A horizontal line
B. A vertical line
C. An inclined line
D. A parabolic curve
Answer : D
45. The absolute zero pressure can be attained at a temperature of
A. 0°C
B. 273°C
C. 273 K
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. 0°C
B. 273°C
C. 273 K
D. None of these
Answer : D
46. The general gas energy equation is (where Q1 - 2 = Heat supplied, dU = Change in internal energy, and W1 - 2 = Work done in heat units)
A. Q1 - 2 = dU + W1 - 2
B. Q1 - 2 = dU - W1 - 2
C. Q1 - 2 = dU/W1 - 2
D. Q1 - 2 = dU × W1 - 2
Answer : A
A. Q1 - 2 = dU + W1 - 2
B. Q1 - 2 = dU - W1 - 2
C. Q1 - 2 = dU/W1 - 2
D. Q1 - 2 = dU × W1 - 2
Answer : A
47. Coke is produced
A. When coal is first dried and then crushed to a fine powder by pulverising machine
B. From the finely ground coal by moulding under pressure with or without a binding material
C. When coal is strongly heated continuously for 42 to 48 hours in the absence of air in a closed vessel
D. By heating wood with a limited supply of air to a temperature not less than 280°C
Answer : C
A. When coal is first dried and then crushed to a fine powder by pulverising machine
B. From the finely ground coal by moulding under pressure with or without a binding material
C. When coal is strongly heated continuously for 42 to 48 hours in the absence of air in a closed vessel
D. By heating wood with a limited supply of air to a temperature not less than 280°C
Answer : C
48. When gas is heated at constant pressure, the heat supplied is utilised in
A. Increasing the internal energy of gas
B. Doing some external work
C. Increasing the internal energy of gas and also for doing some external work
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Increasing the internal energy of gas
B. Doing some external work
C. Increasing the internal energy of gas and also for doing some external work
D. None of the above
Answer : C
49. If Th is the torque resisting capacity of a hollow shaft and Ts is that of a solid shaft, of the same material, length and weight. Then,
A. Th > Ts
B. Th < Ts
C. Th = Ts
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Th > Ts
B. Th < Ts
C. Th = Ts
D. None of these
Answer : A
50. Which of the following has the minimum atomic mass?
A. Oxygen
B. Sulphur
C. Nitrogen
D. Carbon
Answer : D
A. Oxygen
B. Sulphur
C. Nitrogen
D. Carbon
Answer : D
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Human reproductive system Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Networking 1000+ MCQ with answer for UPSC CSE
1000+ Computer Fundamental MCQ for UPSC CSE [Solved]
IBPS PO - Atomic Structure 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
GMAT - Current Affairs June 2017 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Microsoft Excel 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC CGL