Strength of Materials MCQ Solved Paper for SBI PO
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. According to First law of thermodynamics,
A. Total internal energy of a system during a process remains constant
B. Total energy of a system remains constant
C. Workdone by a system is equal to the heat transferred by the system
D. Internal energy, enthalpy and entropy during a process remain constant
Answer : B
A. Total internal energy of a system during a process remains constant
B. Total energy of a system remains constant
C. Workdone by a system is equal to the heat transferred by the system
D. Internal energy, enthalpy and entropy during a process remain constant
Answer : B
2. Strain is equal to (where l = Original length, and ?l = Change in length)
A. l/?l
B. ?l/l
C. l.?l
D. l + ?l
Answer : B
A. l/?l
B. ?l/l
C. l.?l
D. l + ?l
Answer : B
3. The maximum bending moment for the beam shown in the below figure, is
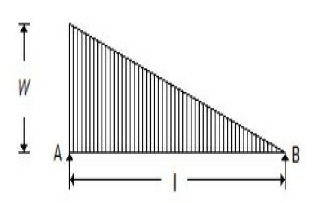
A. wl²/3?3
B. wl²/6?3
C. wl²/9?3
D. wl²/12?3
Answer : C

A. wl²/3?3
B. wl²/6?3
C. wl²/9?3
D. wl²/12?3
Answer : C
4. Diesel cycle consists of following four processes
A. Two isothermal and two isentropic
B. Two isentropic and two constant volumes
C. Two isentropic, one constant volume and one constant pressure
D. Two isentropic and two constant pressures
Answer : C
A. Two isothermal and two isentropic
B. Two isentropic and two constant volumes
C. Two isentropic, one constant volume and one constant pressure
D. Two isentropic and two constant pressures
Answer : C
5. A composite bar made up of steel and copper bars of equal lengths are heated through 100°C. The stresses developed shall be
A. Tensile in both the material
B. Tensile in steel and compressive in copper
C. Compressive in steel and tensile in copper
D. Compressive in both the materials
Answer : D
A. Tensile in both the material
B. Tensile in steel and compressive in copper
C. Compressive in steel and tensile in copper
D. Compressive in both the materials
Answer : D
6. A masonry dam may fail due to
A. Tension in the masonry of the dam and its base
B. Overturning of the dam
C. Crushing of masonry at the base of the dam
D. Any one of the above
Answer : D
A. Tension in the masonry of the dam and its base
B. Overturning of the dam
C. Crushing of masonry at the base of the dam
D. Any one of the above
Answer : D
7. When a gas is heated at constant volume
A. Its temperature will increase
B. Its pressure will increase
C. Both temperature and pressure will increase
D. Neither temperature nor pressure will increase
Answer : C
A. Its temperature will increase
B. Its pressure will increase
C. Both temperature and pressure will increase
D. Neither temperature nor pressure will increase
Answer : C
8. When coal is first dried and then crushed to a fine powder by pulverising machine, the resulting fuel is called
A. Wood charcoal
B. Bituminous coal
C. Briquetted coal
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Wood charcoal
B. Bituminous coal
C. Briquetted coal
D. None of these
Answer : D
9. Carbonisation of coal consists of
A. Drying and crushing the coal to a fine powder
B. Moulding the finely ground coal under pressure with or without a binding material
C. Heating the wood with a limited supply of air to temperature not less than 280°C
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. Drying and crushing the coal to a fine powder
B. Moulding the finely ground coal under pressure with or without a binding material
C. Heating the wood with a limited supply of air to temperature not less than 280°C
D. None of the above
Answer : D
10. The ratio of root mean square velocity to average velocity of gas molecules at a particular temperature is
A. 0.086
B. 1.086
C. 1.086
D. 4.086
Answer : B
A. 0.086
B. 1.086
C. 1.086
D. 4.086
Answer : B
11. When a bar is subjected to a change of temperature and its deformation is prevented, the stress induced in the bar is
A. Tensile stress
B. Compressive stress
C. Shear stress
D. Thermal stress
Answer : D
A. Tensile stress
B. Compressive stress
C. Shear stress
D. Thermal stress
Answer : D
12. A thin mild steel wire is loaded by adding loads in equal increments till it breaks. The extensions noted with increasing loads will behave as under
A. Uniform throughout
B. Increase uniformly
C. First increase and then decrease
D. Increase uniformly first and then increase rapidly
Answer : D
A. Uniform throughout
B. Increase uniformly
C. First increase and then decrease
D. Increase uniformly first and then increase rapidly
Answer : D
13. Steam coal is a
A. Pulverised coal
B. Brown coal
C. Coking bituminous coal
D. Non-coking bituminous coal
Answer : D
A. Pulverised coal
B. Brown coal
C. Coking bituminous coal
D. Non-coking bituminous coal
Answer : D
14. The behaviour of a perfect gas, undergoing any change in the variables which control physical properties, is governed by
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. All of these
Answer : D
15. Which of the following is an intensive property of a thermodynamic system?
A. Volume
B. Temperature
C. Mass
D. Energy
Answer : B
A. Volume
B. Temperature
C. Mass
D. Energy
Answer : B
16. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of __________ water through one degree is called kilojoules.
A. 1 g
B. 10 g
C. 100 g
D. 1000 g
Answer : D
A. 1 g
B. 10 g
C. 100 g
D. 1000 g
Answer : D
17. The tensile strength of the welded joint for double fillet is (where s = Leg or size of the weld, l = Length of weld, and ?t = Allowable tensile stress for weld metal)
A. 0.5 s.l.?t
B. s.l.?t
C. ?2 s.l.?t
D. 2.s.l.?t
Answer : C
A. 0.5 s.l.?t
B. s.l.?t
C. ?2 s.l.?t
D. 2.s.l.?t
Answer : C
18. According to Avogadro's law, the density of any two gases is __________ their molecular masses, if the gases are at the same temperature and pressure.
A. Equal to
B. Directly proportional to
C. Inversely proportional to
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Equal to
B. Directly proportional to
C. Inversely proportional to
D. None of these
Answer : B
19. The deformation per unit length is called
A. Tensile stress
B. Compressive stress
C. Shear stress
D. Strain
Answer : D
A. Tensile stress
B. Compressive stress
C. Shear stress
D. Strain
Answer : D
20. Which of the following is a reversible non-flow process?
A. Isochoric process
B. Isobaric process
C. Hyperbolic process
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. Isochoric process
B. Isobaric process
C. Hyperbolic process
D. All of these
Answer : D
21. The maximum shear stress, in the given figure, is equal to __________ of the Mohr's circle.
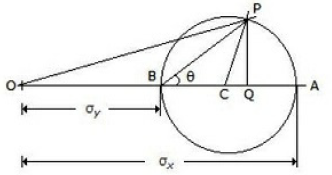
A. Radius
B. Diameter
C. Circumference
D. Area
Answer : A

A. Radius
B. Diameter
C. Circumference
D. Area
Answer : A
22. When a body is subjected to two equal and opposite pushes, as a result of which the body tends to reduce its length, then
A. The stress and strain induced is compressive
B. The stress and strain induced is tensile
C. Both A and B is correct
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. The stress and strain induced is compressive
B. The stress and strain induced is tensile
C. Both A and B is correct
D. None of these
Answer : A
23. The root mean square velocity of the gas molecules is given by (where k = Boltzmann's constant, T = Absolute temperature, and m = Mass of one molecule of a gas)
A. ?(KT/m)
B. ?(2KT/m)
C. ?(3KT/m)
D. ?(5KT/m)
Answer : C
A. ?(KT/m)
B. ?(2KT/m)
C. ?(3KT/m)
D. ?(5KT/m)
Answer : C
24. Which of the following gas is mostly used in town for street and domestic lighting and heating?
A. Producer gas
B. Coal gas
C. Mond gas
D. Coke oven gas
Answer : B
A. Producer gas
B. Coal gas
C. Mond gas
D. Coke oven gas
Answer : B
25. An isothermal process is governed by
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. Avogadro's law
Answer : A
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. Avogadro's law
Answer : A
26. The cycle in which heat is supplied at constant volume and rejected at constant pressure is known as
A. Dual combustion cycle
B. Diesel cycle
C. Atkinson cycle
D. Rankine cycle
Answer : C
A. Dual combustion cycle
B. Diesel cycle
C. Atkinson cycle
D. Rankine cycle
Answer : C
27. Which of the following is the correct statement?
A. For a given compression ratio, both Otto and Diesel cycles have the same efficiency.
B. For a given compression ratio, Otto cycle is more efficient than Diesel cycle.
C. For a given compression ratio, Diesel cycle is more efficient than Otto cycle.
D. The efficiency of Otto or Diesel cycle has nothing to do with compression ratio.
Answer : B
A. For a given compression ratio, both Otto and Diesel cycles have the same efficiency.
B. For a given compression ratio, Otto cycle is more efficient than Diesel cycle.
C. For a given compression ratio, Diesel cycle is more efficient than Otto cycle.
D. The efficiency of Otto or Diesel cycle has nothing to do with compression ratio.
Answer : B
28. Which of the following is the extensive property of a thermodynamic system?
A. Pressure
B. Volume
C. Temperature
D. Density
Answer : B
A. Pressure
B. Volume
C. Temperature
D. Density
Answer : B
29. The property of a material which allows it to be drawn into a smaller section is called
A. Plasticity
B. Ductility
C. Elasticity
D. Malleability
Answer : B
A. Plasticity
B. Ductility
C. Elasticity
D. Malleability
Answer : B
30. The gas constant (R) is equal to the __________ of two specific heats.
A. Sum
B. Difference
C. Product
D. Ratio
Answer : B
A. Sum
B. Difference
C. Product
D. Ratio
Answer : B
31. One kilowatt is equal to
A. 1 N-m/s
B. 100 N-m
C. 1000 N-m/s
D. 1 × 106 N-m/s
Answer : C
A. 1 N-m/s
B. 100 N-m
C. 1000 N-m/s
D. 1 × 106 N-m/s
Answer : C
32. A process, in which the working substance neither receives nor gives out heat to its surroundings during its expansion or compression, is called
A. Isothermal process
B. Hyperbolic process
C. Adiabatic process
D. Polytropic process
Answer : C
A. Isothermal process
B. Hyperbolic process
C. Adiabatic process
D. Polytropic process
Answer : C
33. Which of the following statement is correct?
A. The heat and work are boundary phenomena
B. The heat and work represent the energy crossing the boundary of the system
C. The heat and work are path functions
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. The heat and work are boundary phenomena
B. The heat and work represent the energy crossing the boundary of the system
C. The heat and work are path functions
D. All of the above
Answer : D
34. The most probable velocity of the gas molecules is given by
A. ?(KT/m)
B. ?(2KT/m)
C. ?(3KT/m)
D. ?(5KT/m)
Answer : B
A. ?(KT/m)
B. ?(2KT/m)
C. ?(3KT/m)
D. ?(5KT/m)
Answer : B
35. The compression ratio for petrol engines is
A. 3 to 6
B. 5 to 8
C. 10 to 20
D. 15 to 30
Answer : B
A. 3 to 6
B. 5 to 8
C. 10 to 20
D. 15 to 30
Answer : B
36. The mass of carbon per kg of flue gas is given by
A. (11/3) CO2 + (3/7) CO
B. (3/7) CO2 + (11/3) CO
C. (7/3) CO2 + (3/11) CO
D. (3/11) CO2 + (7/3) CO
Answer : A
A. (11/3) CO2 + (3/7) CO
B. (3/7) CO2 + (11/3) CO
C. (7/3) CO2 + (3/11) CO
D. (3/11) CO2 + (7/3) CO
Answer : A
37. Diesel cycle consists of __________ processes.
A. Two constant volume and two isentropic
B. Two constant pressure and two isentropic
C. Two constant volume and two isothermal
D. One constant pressure, one constant volume and two isentropic
Answer : D
A. Two constant volume and two isentropic
B. Two constant pressure and two isentropic
C. Two constant volume and two isothermal
D. One constant pressure, one constant volume and two isentropic
Answer : D
38. The stress at which extension of the material takes place more quickly as compared to the increase in load is called
A. Elastic point of the material
B. Plastic point of the material
C. Breaking point of the material
D. Yielding point of the material
Answer : D
A. Elastic point of the material
B. Plastic point of the material
C. Breaking point of the material
D. Yielding point of the material
Answer : D
39. Producer gas is obtained by
A. Partial combustion of coal, coke, anthracite coal or charcoal in a mixed air steam blast
B. Carbonisation of bituminous coal
C. Passing steam over incandescent coke
D. Passing air and a large amount of steam over waste coal at about 650°C
Answer : A
A. Partial combustion of coal, coke, anthracite coal or charcoal in a mixed air steam blast
B. Carbonisation of bituminous coal
C. Passing steam over incandescent coke
D. Passing air and a large amount of steam over waste coal at about 650°C
Answer : A
40. In a uniform bar, supported at one end in position, the maximum stress under self weight of bar shall occur at the
A. Middle of bar
B. Supported end
C. Bottom end
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Middle of bar
B. Supported end
C. Bottom end
D. None of these
Answer : B
41. The amount of heat generated per kg of fuel is known as
A. Calorific value
B. Heat energy
C. Lower calorific value
D. Higher calorific value
Answer : A
A. Calorific value
B. Heat energy
C. Lower calorific value
D. Higher calorific value
Answer : A
42. When a closely-coiled helical spring of mean diameter (D) is subjected to an axial load (W), the deflection of the spring (?) is given by (where d = Diameter of spring wire, n = No. of turns of the spring, and C = Modulus of rigidity for the spring material)
A. WD3n/Cd?
B. 2WD3n/Cd?
C. 4WD3n/Cd?
D. 8WD3n/Cd?
Answer : D
A. WD3n/Cd?
B. 2WD3n/Cd?
C. 4WD3n/Cd?
D. 8WD3n/Cd?
Answer : D
43. For same compression ratio and for same heat added
A. Otto cycle is more efficient than Diesel cycle
B. Diesel cycle is more efficient than Otto cycle
C. Efficiency depends on other factors
D. Both Otto and Diesel cycles are equally efficient
Answer : A
A. Otto cycle is more efficient than Diesel cycle
B. Diesel cycle is more efficient than Otto cycle
C. Efficiency depends on other factors
D. Both Otto and Diesel cycles are equally efficient
Answer : A
44. A cycle consisting of two adiabatic and two constant pressure processes is known as
A. Otto cycle
B. Ericsson cycle
C. Joule cycle
D. Stirling cycle
Answer : C
A. Otto cycle
B. Ericsson cycle
C. Joule cycle
D. Stirling cycle
Answer : C
45. A cycle consisting of one constant pressure, one constant volume and two isentropic processes is known as
A. Carnot cycle
B. Stirling cycle
C. Otto cycle
D. Diesel cycle
Answer : D
A. Carnot cycle
B. Stirling cycle
C. Otto cycle
D. Diesel cycle
Answer : D
46. The extremeties of any diameter on Mohr's circle represent
A. Principal stresses
B. Normal stresses on planes at 45°
C. Shear stresses on planes at 45°
D. Normal and shear stresses on a plane
Answer : B
A. Principal stresses
B. Normal stresses on planes at 45°
C. Shear stresses on planes at 45°
D. Normal and shear stresses on a plane
Answer : B
47. The shear force at the centre of a simply supported beam with a gradually varying load from zero at both ends to w per metre at the centre, is
A. Zero
B. wl/4
C. wl/2
D. wl²/2
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. wl/4
C. wl/2
D. wl²/2
Answer : A
48. The property of a material by virtue of which it can be beaten or rolled into plates is called
A. Malleability
B. Ductility
C. Plasticity
D. Elasticity
Answer : A
A. Malleability
B. Ductility
C. Plasticity
D. Elasticity
Answer : A
49. If the rivets in adjacent rows are staggered and the outermost row has only one rivets, the arrangement of the rivets is called
A. Chain riveting
B. Zigzag riveting
C. Diamond riveting
D. Crisscross riveting
Answer : C
A. Chain riveting
B. Zigzag riveting
C. Diamond riveting
D. Crisscross riveting
Answer : C
50. A riveted joint in which the number otrivets decrease from innermost to outer most rows is called
A. Chain riveted joint
B. Diamond riveted joint
C. Crisscross riveted joint
D. Zigzag riveted joint
Answer : B
A. Chain riveted joint
B. Diamond riveted joint
C. Crisscross riveted joint
D. Zigzag riveted joint
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Current Affairs February 2023 MCQ for SSC Stenographer [Solved]
1000+ Engineering Mechanics MCQ for RRB JE [Solved]
Refrigeration & Air-Conditioning 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC Stenographer
Transformation of Sentences MCQ Solved Paper for RRB NTPC
1000+ Chemical Engineering Plant Economics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Fill in the blanks Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]