In second degree price discrimination, monopolist takes away :
All of the consumer surplus
All of the producer surplus
Some part of the consumer surplus
None of them
Correct Answer :
C. Some part of the consumer surplus
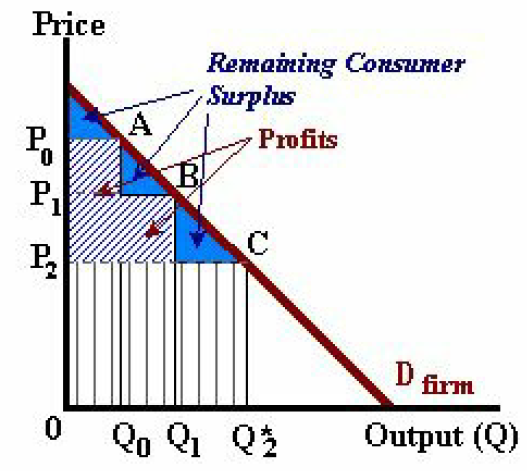
Second Degree Price Discrimination The second type of price discrimination involves the establishment of a pricing structure for a particular good based on the number of units sold. Quantity discounts are a common example. In this case the seller charges a higher per-unit price for fewer units sold and a lower per-unit price for larger quantities purchased. In this case the seller is attempting to extract some of the consumer's surplus value as profits with residual surplus remaining with the consumer over and above the actual price paid. Like the case of first degree price discrimination, the firm will produce a level of output where the price charged just covers the marginal costs of production. In the diagram below, we find an example of a firm charging three different prices for the same product. The price P0 is charged per unit if the buyer chooses to buy Q0 units of the good. A lower price P1 is charged for a greater quantity Q1 and the price P2 is charged for the quantity Q*2 (the level of output such that P2 = MC -- the marginal costs of production):
Figure 3, Second Degree Price Discrimination
Common examples of first degree price discrimination include car sales at most dealerships where the customer rarely expects to pay full sticker price, scalpers of concert and sporting-event tickets, and road-side sellers of fruit and produce.
Related Questions
In 1890, Principles of Economics was written by:
Prof. Robbins
Alfred Marshal
Prof. Senior
Adam Smith
The kinked demand curve comes into being where:
Proportional demand curve (PDC) and individual demand curve (IDC) intersect each other
Proportional demand curve (PDC) and individual demand curve (IDC) are parallel to each other
Proportional demand curve (PDC) and individual demand curve (IDC) repel each other
None of the above
Given a U shaped average cost curve, the relationship between average cost and marginal cost is such that marginal cost must always be:
Falling when average cost is falling
Rising when average cost is falling
Falling when average cost is rising
Rising when average cost is rising
In perfect competition, the slope of the total revenue curve of a firm is equal to the:
Market price
AVC
TFC
AFC
One common definition of a luxury good is a good with income elasticity:
Greater than one
Equal to one
Less than one but more than zero
None of the above
In income effect, we:
Move to another indifference curve
Move along given indifference curve
Move to lower indifference curve
Move to upper indifference curve
Total costs in the short-term (short-run) are classified into fixed costs and variable costs. Which one of the following is a variable cost?
Cost of raw materials
Cost of equipment
Interest payment on past borrowing
Payment of rent on buildings
Money spent by a firm on the purchase of capital equipment is:
Fixed cost
Variable cost
Both fixed and variable costs
None of the above
Neutral Technological Progress can be defined as:
Technological progress that causes to raise the marginal product of capital and labor in the same proportion
Technological progress that causes the marginal product of capital to increase relative to the marginal product of labor
Technological progress that causes the marginal product of labor to increase relative to the marginal product of capital
None of the above
If demand is elastic and supply is inelastic then the burden of a tax on the good will be:
Borne mostly by producers
Borne mostly by consumers
Borne mostly by government
Shared equally by producers and consumers
In the case of a giffen good, the income effect:
Is equal to the substitution effect
More than offsets the substitution effect
Reinforces the substitution effect
Only partially offsets the substitution effect
If by doubling all inputs in the long run output is less than double, it is a case of:
Increasing returns to scale
Decreasing returns to scale
Constant returns to scale
Variable returns to scale
The main contribution of Prof.Robbins is in the field of:
human welfare
national income
multiplicity of wants and scarcity of resources
theory of production
Change in quantity demanded (expansion and contraction of demand) is:
Due to change in price while other factors remain constant
Due to change in factors other than price
Both a and b
None of the above
Production indifference curve (isoquant) is a curve which shows:
Equal level of output
Unequal level of outputs
Equal level of inputs
Unequal level of inputs
The MC curve cuts the AVC and ATC curves:
At different points
At the falling parts of each
At their respective minimums
At the rising parts of each
Cross-elasticity of demand or cross-price elasticity between two substitutes will be:
Negative
Positive
Infinite
Zero
At the point where a straight line demand curve meets the quantity axis (x-axis), elasticity of demand is:
Equal to zero
Equal to one
Equal to infinite
More than one
The good will highest income elasticity is:
Beef
Mutton
Bread
Motion-picture tickets
Which is not an essential feature of a socialist economy?
Social ownership of the means of production
Freedom of enterprise
Use of centralized planning
Government decisions
The cost curves of the firm shift due to changes in:
Input prices
Technological innovations
Both of them
None of them
A firm considering what type of new plant to build is involved in a:
Immediate-run decision
Market period decision
Short-run decision
Long-run decision
The horizontal demand curve for a commodity shows that its demand is:
Highly elastic
Perfectly inelastic
Perfectly elastic
Zero elastic
If X and Y are close substitutes, a fall in price of X will lead to:
Increase in demand for Y
Decrease in demand for Y
Increase in demand for both X and Y
Increase in demand for Y
Perfect competition implies:
Differentiated goods
Homogeneous goods
Advertised goods
Distress sale of goods
When income of the consumer increases then demand curve of an inferior good:
Shifts rightward
Shifts leftward
Does not shift
None of the above
At a point below the middle of a straight line demand curve, elasticity of demand is:
Less than one
Equal to one
More than one
Equal to infinity
In long run, a firm can change:
Fixed factors
Variable factors
Both of them
None of them
When the income of consumer increases then budget line will:
Get steeper
Shift parallel to right
To get flatter
To shift upward
Which describes a competitive market?
Many buyers and many sellers
One seller, many buyers
One buyer, many sellers
Few sellers, many buyers
