Which of the following is responsible for the formation of an embryonic shoot called axillary bud?
Lateral meristem
Apical meristem
Intercalary meristem
Both
Correct Answer :
C. Intercalary meristem
Apical meristem is a completely undifferentiated meristematic tissue found in the buds and growing tips of roots in plants. Its main function is to begin growth of new cells in young seedlings at the tips of roots and shoots (forming buds, among other things). The axillary bud is an embryonic shoot which lies at the junction of the stem and petiole of a plant. As the apical meristem grows and forms leaves, it leaves behind a region of meristematic cells at the node between the stem and the leaf.
Related Questions
Match column-I with column-II and choose the correct option.
| Column -I | Column -II |
|---|---|
| A. Bulliform cells | I. Initiation of lateral roots |
| B. Pericycle | II. Root |
| C. Endarch xylem | III. Grasses |
| D. Exarch xylem | IV. Dicot leaf |
| E. Bundle sheath cells | V. Stem |
A III, B V, C IV, D I, E II
A II, B V, C I, D III, E IV
A II, B IV, C I, D III, E V
A III, B I, C V, D II, E IV
Why grafting is successful in dicots ?
In dicots vascular bundles are arranged in a ring.
Dicots have cambium for secondary growth.
In dicots vessels with elements are arranged end to end.
Cork cambium is present in dicots
During the formation of leaves and elongation of stem, some cells left behind from the shoot apical meristem, constitute the
lateral meristem
axillary bud
cork cambium
fascicular cambium
Match the elements of xylem given in column I with their character given in the column II and choose the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| A. Xylem vessels | I. Store food materials |
| B. Xylem tracheids | II. Obliterated lumen |
| C. Xylem fibres | III. Perforated plates |
| D. Xylem parenchyma | IV. Chisel-like ends |
A IV; B III; C II; D I
A III; B II; C I; D IV
A II; B I; C IV; D III
A III; B IV; C II; D I
Match column-I with column-II and choose the correct option.
| A. Spring wood or | I. Lighter in colour early wood |
|---|---|
| B. Autumn wood or | II. High density late wood |
| .. | III. Low density |
| .. | IV. Darker in colour |
| .. | V. Larger number of xylem elements |
| .. | VI. Vessels with wider cavity |
| .. | VII. Lesser number of xylem elements |
| .. | VIII. Vessels with small cavity |
Which of the following combination is correct ?
A II, IV, VII, VIII; B I, III, V, VI
A I, II, VII, VIII; B III, IV, V, VI
A I, III, V, VI; B II, IV, VII, VIII
A I, III, VII, VIII; B II, IV, V, VI
Which of the following statement(s) is/are not correct?
- Cork cambium is also called phellogen.
- Cork is also called phellem.
- Secondary cortex is also called periderm.
- Cork cambium, cork and secondary cortex are collectively called phelloderm.
(iii) and (iv)
(i) and (ii)
(ii) and (iii)
(ii) and (iv)
Which of the following statements are correct ?
- Xylem transports water and minerals.
- Gymnosperms lack sieve tubes and companion cells in phloem.
- The first formed primary xylem is called metaxylem.
- Phloem fibres (bast fibres) are made up of collenchymatous cells.
(i) and (iii)
(i) and (ii)
(iii) and (iv)
(i) and (iv)
Apical, intercalary and lateral meristems are differentiated on the basis of
origin
function
position
development
Lignin is the important constituent in the cell wall of
phloem
parenchyma
xylem
cambium
Match the names of the structures given in column-I with the functions given in column-II, choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the two columns :
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| (Structure) | (Function) |
| A. Stomata | I. Protection of stem |
| B. Bark | II. Plant movement |
| C. Cambium | III. Secondary growth |
| D. Cuticle | IV. Transpiration |
| V. Prevent the loss of water | ... |
A V, B III, C I, D IV
A I, B IV, C V, D III
A II, B IV, C I, D III
A IV, B I, C III, D V
The __________ occurs in layers below the epidermis in dicotyledonous plants.
parenchyma
sclerenchyma
collenchyma
aerenchyma
Which of the following process helps the trichomes in preventing water loss?
Where companion cells helps in maintaining the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.
Where plants absorb water through the roots and then give off water vapor through pores in their leaves.
Where activity of cork cambium builds pressure on the remaining layers peripheral to phellogen and ultimately these layers dies and slough off.
None of the above
The apical meristem of the root is present
in all the roots.
only in radicals.
only in tap roots.
only in adventitious roots.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct ?
- Uneven thickening of cell wall is characteristic of sclerenchyma.
- Periblem forms cortex of the stem and the root.
- Tracheids are the chief water transporting elements in gymnosperms.
- Companion cell is devoid of nucleus at maturity.
- The commercial cork is obtained from Quercus suber.
(i) and (iv) only
(ii) and (v) only
(iii) and (iv) only
(ii), (iii) and (v) only
Cork is formed from
phellogen
vascular cambium
phloem
xylem
A narrow layer of thin walled cells found between phloem/ bark and wood of a dicot is
cork cambium
vascular cambium
endodermis
both (a) & (c)
In stems, the protoxylem lies towards the _____________ and the metaxylem lies towards the ____________ of the organ.
centre; periphery
periphery; centre
periphery; periphery
centre; centre
T.S. of dicot leaf passing through the midrib is given below. Certain parts have been marked by alphabets (A to H). Choose the option showing their correct labelling.
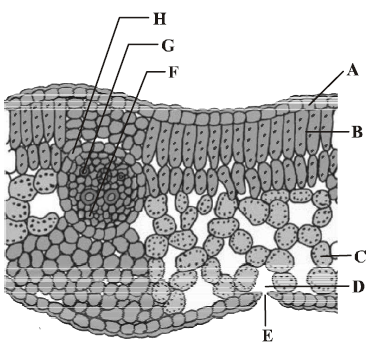
A Epidermis, B Spongy mesophyll, C Palisade mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Stoma, F Phloem, G Xylem, H Bundle sheath
A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Epidermis, G Xylem, H Phloem
A Epidermis, C Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
Xylem functions as a conducting tissue for water and minerals from _________to the ______and__________.
roots, stems, leaves
stems, roots, leaves
leaves, stems, roots
leaves, stems, leaves
Bast fibres are made up of _____________cells.
sclerenchymatous
chlorenchymatous
parenchymatous
aerenchymatous
Which of the following statements is correct?
Lenticels occur in most woody trees.
Sclerenchymatous cells are usually present in cortex.
The vascular tissue system is divided into three main zones- cortex, pericycle and pith.
The conjoint vascular bundles usually have the xylem located only on the outer side of the phloem.
Choose the correct labelling of (A J) in the given figure of T.S. of monocot root.

A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pericycle, G Pith, H Phloem, I Metaxylem.
A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pith, G Pericycle, H Metaxylem, I Phloem.
A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Pericycle, F Phloem, G Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
A Root hair, B Cortex, C Epiblema, D Pericycle, E Endodermis, F Pith, G Phloem, H Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
Which of following helps bamboo and grasses to elongate ?
Apical meristems
Lateral meristems
Secondary meristems
Intercalary meristems
In the given columns, column I contain structures of female reproductive system and column II contain its feature. Select the correct match.
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| A. Lateral meristem | (i) Fascicular vascular cambium, interfascicular cambium and cork cambium. |
| B. Apical meristem | (ii) Produces dermal tissue, ground tissues and vascular tissue. |
| C. Bast fibres | (iii) Generally absent in primary phloem but found in secondary phloem. |
| D. Sap wood | (iv) Involved in the conduction of water and minerals from the root to leaf. |
A - (i), B - (ii), C - (iii), D - (iv)
A - (iii), B - (i), C - (ii), D - (iv)
A - (i), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (ii)
A - (ii), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (i)
Which meristem helps in increasing girth?
Lateral meristem
Intercalary meristem
Primary meristem
Apical meristem
Which of the following pair of match is not correct?
Pith - Large and well developed in monocotyledonous root.
Root hairs - Helps in preventing water loss due to transpiration
Sieve tube elements - Its functions are controlled by the nucleus of companion cells.
Stomatal apparatus - Consists of stomatal aperture, guard cells and surrounding subsidiary cells
Sclerenchyma usually___________and_____________ protoplasts.
live, without
dead, with
live, with
dead, without
Match the terms given in column I with their features given in column II and choose the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| (Terms) | (Features) |
| A. Fibres | (i) Cells are living and thin walled with cellulosic cell wall, store food materials in the form of starch or fat |
| B. Sclereids | (ii) Main water conductive cells of the pteridophytes and the gymnosperms |
| C. Tracheids | (iii) Thick walled, elongated and pointed cells, generally occurring in groups |
| D. Vessels | (iv) Long cylindrical tube like structure and cells are devoid of protoplasm. Characteristic feature of angiosperms |
| E. Xylem parenchyma | (v) Reduced form of sclerenchyma cells with highly thickened lignified cellular walls that form small bundles of durable layers of tissue in most plants. |
A - (i), B - (ii), C - (iii), D - (iv), E - (v)
A - (iii), B - (v), C - (ii), D - (iv), E - (i)
A - (iii), B - (i), C - (v), D - (ii), E - (iv)
A - (v), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (i), E - (ii)
The given figure shows the secondary growth in a dicot stem. Their parts are marked as A, B, C, D, E & F. Choose the correct labelling of the parts marked as A to F.
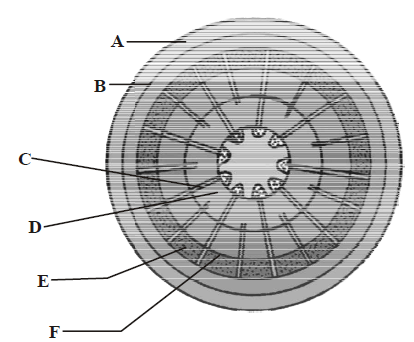
A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Medullary rays, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Cambium ring
A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Medullary rays, D Secondary phloem, E Secondary xylem, F Cambium ring
A Phellogen, B Phellem, C Medullary rays, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Cambium ring
A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Cambium ring, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Medullary rays
A vascular bundle in which the protoxylem is pointing to the periphery is called __________.
endarch
exarch
radial
closed
