1000+ Basics of Economics MCQ for UPSC CSE [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Entry of new firms into a competitive market will shift the supply curve of the:
A. Firm to the left
B. Industry to the right
C. Firm to the right
D. Industry to the left
Answer : B
A. Firm to the left
B. Industry to the right
C. Firm to the right
D. Industry to the left
Answer : B
2. Which one of the following is also known as Plant Curves:
A. Long-run average cost (LAC) curves
B. Short-run average cost (SAC) curves
C. Average variable cost (AVC) curves
D. Average total cost (ATC) curves
Answer : B
A. Long-run average cost (LAC) curves
B. Short-run average cost (SAC) curves
C. Average variable cost (AVC) curves
D. Average total cost (ATC) curves
Answer : B
3. Which of the following is not a feature of isoproduct curves?
A. Are downward sloping to the right
B. Show different input combination producing the same output
C. Intersect each other
D. Are convex to the origin
Answer : C
A. Are downward sloping to the right
B. Show different input combination producing the same output
C. Intersect each other
D. Are convex to the origin
Answer : C
4. The consumer is in equilibrium at the where:
A. Budget line and indifference curve intersect each other
B. Budget line and indifference curve are tangent to each other
C. Budget line and indifference curve are opposite to each other
D. Budget line and indifference curve are parallel to each other
Answer : B
A. Budget line and indifference curve intersect each other
B. Budget line and indifference curve are tangent to each other
C. Budget line and indifference curve are opposite to each other
D. Budget line and indifference curve are parallel to each other
Answer : B
5. Which of the following is assumed to be constant when drawing a demand curve?
A. Consumer tastes
B. Prices of inputs
C. Technology
D. Number of sellers
Answer : A
A. Consumer tastes
B. Prices of inputs
C. Technology
D. Number of sellers
Answer : A
6. Two policy variables, product and selling activities in the theory of firm was introduced by:
A. Chamberline
B. Sraffa
C. Carl marx
D. Robinson
Answer : A
A. Chamberline
B. Sraffa
C. Carl marx
D. Robinson
Answer : A
7. Money spent by a firm on the purchase of capital equipment is:
A. Fixed cost
B. Variable cost
C. Both fixed and variable costs
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Fixed cost
B. Variable cost
C. Both fixed and variable costs
D. None of the above
Answer : A
8. Inputs or Factors of production are defined as:
A. Productive resources such as labor and capital equipment that firms use to manufacture goods and services are called inputs or factors of production
B. Unproductive resources that do not take part in production process are called inputs or factors of production
C. Firms own resources are called inputs or factors of production
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Productive resources such as labor and capital equipment that firms use to manufacture goods and services are called inputs or factors of production
B. Unproductive resources that do not take part in production process are called inputs or factors of production
C. Firms own resources are called inputs or factors of production
D. None of the above
Answer : A
9. If at the unchanged price, the demand for a commodity goes up, or the quantity demanded remains the same when its price goes up, it is called:
A. Contraction of demand
B. Decrease in demand
C. Increase in demand
D. Extension of demand
Answer : C
A. Contraction of demand
B. Decrease in demand
C. Increase in demand
D. Extension of demand
Answer : C
10. Loanable funds theory of Interest was developed by:
A. Wicksell
B. Robert San
C. Ruskin
D. J.B.Say
Answer : A
A. Wicksell
B. Robert San
C. Ruskin
D. J.B.Say
Answer : A
11. The slope of the iso-cost line (budget line) is determined by:
A. Pricing of two factors
B. Productivity of the two factors
C. Degree of substitutability of two factors
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Pricing of two factors
B. Productivity of the two factors
C. Degree of substitutability of two factors
D. None of the above
Answer : A
12. The supply curve for the short-run competitive firm is the same as:
A. Marginal cost curve
B. Average variable cost curve
C. That part of the marginal cost curve which equals or is greater than AVC
D. Average total cost curve
Answer : C
A. Marginal cost curve
B. Average variable cost curve
C. That part of the marginal cost curve which equals or is greater than AVC
D. Average total cost curve
Answer : C
13. For a commodity giving large consumers surplus, the demand will be:
A. Less elastic
B. More elastic
C. Unit elastic
D. Zero elastic
Answer : B
A. Less elastic
B. More elastic
C. Unit elastic
D. Zero elastic
Answer : B
14. A dominant strategy can best be described as:
A. A strategy taken by a dominant firm
B. A strategy taken by a firm in order to dominate its rivals
C. A strategy that is optimal for a player no matter an opponent does
D. A strategy that leaves every player in a game better off
Answer : C
A. A strategy taken by a dominant firm
B. A strategy taken by a firm in order to dominate its rivals
C. A strategy that is optimal for a player no matter an opponent does
D. A strategy that leaves every player in a game better off
Answer : C
15. If production increases under increasing returns to scale, the cost will:
A. Increase at decreasing rate
B. Increase at constant rate
C. Decrease at increasing rate
D. Increase at increasing rate
Answer : A
A. Increase at decreasing rate
B. Increase at constant rate
C. Decrease at increasing rate
D. Increase at increasing rate
Answer : A
16. In the case where two commodities are good substitutes then cross elasticity will be:
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : A
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : A
17. The Modern and Neo-Keynsian Theory of Interestwas presented by:
A. Gunner Myrdal
B. A.C.Pigou
C. J.M.Keynes
D. J.R.Hicks
Answer : D
A. Gunner Myrdal
B. A.C.Pigou
C. J.M.Keynes
D. J.R.Hicks
Answer : D
18. In cournot model, firms make decisions separately regarding:
A. output
B. input
C. price
D. advertisement
Answer : A
A. output
B. input
C. price
D. advertisement
Answer : A
19. The firms in non-cooperative games:
A. Enforce contracts
B. Make contracts
C. Make negotiations
D. Do not make negotiations
Answer : D
A. Enforce contracts
B. Make contracts
C. Make negotiations
D. Do not make negotiations
Answer : D
20. The sufficient condition of firms equilibrium requires:
A.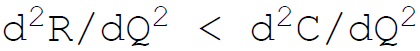
B.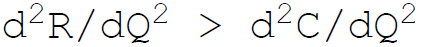
C.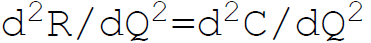
D. none of the above
Answer : A
A.
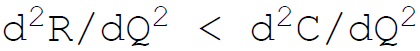
B.
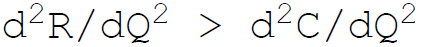
C.
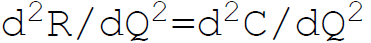
D. none of the above
Answer : A
21. The Lambda or Langrange Multiplier is a:
A. Analyst
B. Catalyst
C. Pessimist
D. Optimist
Answer : B
B. Catalyst
C. Pessimist
D. Optimist
Answer : B
22. In cournot model, firms face:
A. Negatively sloped demand curve
B. Positively sloped demand curve
C. Horizontal demand curve
D. Vertical demand curve
Answer : A
A. Negatively sloped demand curve
B. Positively sloped demand curve
C. Horizontal demand curve
D. Vertical demand curve
Answer : A
23. The goods sold by firms under monopolistic competition are technological as well as:
A. Economic complements
B. Economic substitutes
C. Economic inferiors
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Economic complements
B. Economic substitutes
C. Economic inferiors
D. None of the above
Answer : B
24. Cross-elasticity of demand or cross-price elasticity between two independent goods will be:
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Infinite
D. Zero
Answer : D
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Infinite
D. Zero
Answer : D
25. Which is not a central problem of an economy?
A. What to produce
B. How to produce
C. How to maximize private profit
D. For whom to produce
Answer : C
A. What to produce
B. How to produce
C. How to maximize private profit
D. For whom to produce
Answer : C
26. Under perfect competition, a firm will be in equilibrium if:
A. MC = MR
B. MC cuts the MR from below
C. MC rises when it cuts the MR
D. All the above three conditions are fulfilled
Answer : D
A. MC = MR
B. MC cuts the MR from below
C. MC rises when it cuts the MR
D. All the above three conditions are fulfilled
Answer : D
27. Change in demand (rise and fall of demand) is:
A. Due to change in price while other factors remain constant
B. Due to change in factors other than price
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Due to change in price while other factors remain constant
B. Due to change in factors other than price
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : B
28. Law of variable proportions is based on the assumption of:
A. Short period of time
B. Long period of time
C. Timeless production relationship
D. All of the above
Answer : A
A. Short period of time
B. Long period of time
C. Timeless production relationship
D. All of the above
Answer : A
29. Price mechanism has also given the name:
A. Labor theory
B. Production theory
C. Laisseze-faire
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Labor theory
B. Production theory
C. Laisseze-faire
D. None of the above
Answer : C
30. Average Revenue means:
A. Per unit revenue received from all the units sold by the producer
B. Revenue of the units having average size
C. Total number of units× Revenue per unit
D. Total revenue × Number of units sold
Answer : A
A. Per unit revenue received from all the units sold by the producer
B. Revenue of the units having average size
C. Total number of units× Revenue per unit
D. Total revenue × Number of units sold
Answer : A
31. The Hicksian indirect utility function in the form of equation is:
A. x =f(P)
B. x =a-bp
C.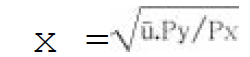
D.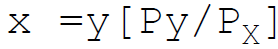
Answer : C
A. x =f(P)
B. x =a-bp
C.
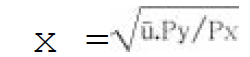
D.
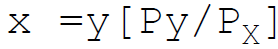
Answer : C
32. With which of the following concepts is the name of J.M.Keynes particularly associated?
A. Marginal propensity to consume
B. Marginal propensity to save
C. Liquidity preference
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Marginal propensity to consume
B. Marginal propensity to save
C. Liquidity preference
D. All of the above
Answer : D
33. In monopoly:
A. The producer will often produce a volume that is less than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
B. The producer will often produce a volume that is more than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
C. The consumers will often consume a volume that is more than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. The producer will often produce a volume that is less than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
B. The producer will often produce a volume that is more than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
C. The consumers will often consume a volume that is more than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
D. None of the above
Answer : A
34. A country is advised to devalue (reduce external value of) its currency only when its exports face:
A. Inelastic demand in foreign markets
B. Elastic demand in foreign markets
C. Unit elastic demand in foreign markets
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Inelastic demand in foreign markets
B. Elastic demand in foreign markets
C. Unit elastic demand in foreign markets
D. None of the above
Answer : B
35. Which of the following is not characteristic of perfect competition?
A. Freedom of entry and exit
B. Each seller is a price taker
C. Perfect information about prices
D. Heterogeneous products
Answer : D
A. Freedom of entry and exit
B. Each seller is a price taker
C. Perfect information about prices
D. Heterogeneous products
Answer : D
36. When there is decrease in demand the demand curve:
A. Moves (shifts) towards the axis
B. Moves (shifts) away from the axis
C. Remains unchanged
D. All of the above
Answer : A
A. Moves (shifts) towards the axis
B. Moves (shifts) away from the axis
C. Remains unchanged
D. All of the above
Answer : A
37. Consumer surplus is the difference between
A. Price demanded and price paid
B. Price quoted and price actually paid
C. Price that a consumer is willing to pay and the price actually paid
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Price demanded and price paid
B. Price quoted and price actually paid
C. Price that a consumer is willing to pay and the price actually paid
D. None of the above
Answer : C
38. If a monopolist is producing under decreasing cost conditions, increase in demand is beneficial to the society because:
A. Consumers get better quality goods
B. Cost of production falls and hence price will follow
C. Goods will be sold in many markets
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Consumers get better quality goods
B. Cost of production falls and hence price will follow
C. Goods will be sold in many markets
D. None of the above
Answer : B
39. In the short-run, the competitive firm can maximize its profits (or minimize its losses) by:
A. Equating price and marginal revenue
B. Equating price and average total cost
C. Increasing marginal cost and lowering fixed costs
D. Equating marginal cost and marginal revenue
Answer : D
A. Equating price and marginal revenue
B. Equating price and average total cost
C. Increasing marginal cost and lowering fixed costs
D. Equating marginal cost and marginal revenue
Answer : D
40. If there are many firms producing similar but differentiated products, the competition is generally said to be:
A. Oligopoly
B. Pure competition
C. Perfect competition
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : D
A. Oligopoly
B. Pure competition
C. Perfect competition
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : D
41. The good will highest income elasticity is:
A. Beef
B. Mutton
C. Bread
D. Motion-picture tickets
Answer : D
A. Beef
B. Mutton
C. Bread
D. Motion-picture tickets
Answer : D
42. Under perfect competition, the average revenue, marginal revenue and price are shown:
A. By a same single curve
B. By three different curves
C. By downward sloping curve
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. By a same single curve
B. By three different curves
C. By downward sloping curve
D. None of the above
Answer : A
43. Airlines that try to lower fares in order to increase revenues believe that demand for airline services is:
A. Price elastic
B. Price inelastic
C. Income elastic
D. Income inelastic
Answer : A
A. Price elastic
B. Price inelastic
C. Income elastic
D. Income inelastic
Answer : A
44. The long run average cost curve is the envelope of:
A. SACs
B. LACs
C. SMCs
D. LMCs
Answer : A
A. SACs
B. LACs
C. SMCs
D. LMCs
Answer : A
45. The demand curve of a firm in monopolistic competition is:
A. Negatively sloped
B. Vertical
C. Horizontal
D. Positively sloped
Answer : A
A. Negatively sloped
B. Vertical
C. Horizontal
D. Positively sloped
Answer : A
46. Micro economics is concerned with:
A. Product markets
B. Factor markets
C. Supply and demand
D. a, b and c
Answer : D
A. Product markets
B. Factor markets
C. Supply and demand
D. a, b and c
Answer : D
47. The factors of production in perfect competition are:
A. Stagnant
B. Mobile
C. Immobile
D. Rare
Answer : B
A. Stagnant
B. Mobile
C. Immobile
D. Rare
Answer : B
48. The budget constraint can be written as:
A. X.PX + Y.PY = 1
B. X.PX + Y.PY < 1
C. X.PX + Y.PY > 1
D. X.PX + Y.PY = 0
Answer : A
A. X.PX + Y.PY = 1
B. X.PX + Y.PY < 1
C. X.PX + Y.PY > 1
D. X.PX + Y.PY = 0
Answer : A
49. Utility means:
A. The want- satisfying power of a commodity
B. Usefulness of commodity
C. Eating of commodity
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. The want- satisfying power of a commodity
B. Usefulness of commodity
C. Eating of commodity
D. None of these
Answer : A
50. A maximin strategy:
A. Maximizes the minimum gain that can be earned
B. Maximizes the gain of one player, but minimizes the gain of the opponent
C. Minimizes the maximum gain that can be earned
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Maximizes the minimum gain that can be earned
B. Maximizes the gain of one player, but minimizes the gain of the opponent
C. Minimizes the maximum gain that can be earned
D. None of the above
Answer : A
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Senile enlargement of the prostate 1000+ MCQ with answer for NDA
Linux OS 1000+ MCQ with answer for IBPS RRB
Classifications of Animal Kindom MCQ Solved Paper for SSC GD
1000+ Building Materials MCQ for SSC CHSL [Solved]
Chemical Engineering Basics MCQ Solved Paper for SSC CGL
1000+ Java Programming MCQ for XAT [Solved]