1000+ Basics of Economics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The study of economic theory for the sake of certain objective is called:
A. Positive Economics
B. Normative Economics
C. Micro Economics
D. Development Economics
Answer : B
A. Positive Economics
B. Normative Economics
C. Micro Economics
D. Development Economics
Answer : B
2. If the supply and demand increases equally, the price will:
A. Rise
B. Fall
C. Remain unchanged
D. Change depending on respective elasticities
Answer : C
A. Rise
B. Fall
C. Remain unchanged
D. Change depending on respective elasticities
Answer : C
3. Technological Progress (Invention) can be defined as:
A. Technological progress shifts the production function by allowing the firm to achieve more output from a given combination of inputs (or the same output with fewer inputs)
B. Technological progress shifts the production function by allowing the firm to achieve less output from a given combination of inputs (or the same output with more inputs)
C. Technological progress shifts the import function to the right
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Technological progress shifts the production function by allowing the firm to achieve more output from a given combination of inputs (or the same output with fewer inputs)
B. Technological progress shifts the production function by allowing the firm to achieve less output from a given combination of inputs (or the same output with more inputs)
C. Technological progress shifts the import function to the right
D. None of the above
Answer : A
4. Identify the factor, which generally keeps the price elasticity of demand for a commodity low:
A. Variety of uses for that commodity
B. Its low price
C. Close substitutes for that commodity
D. High proportion of the consumers income spent on it
Answer : B
A. Variety of uses for that commodity
B. Its low price
C. Close substitutes for that commodity
D. High proportion of the consumers income spent on it
Answer : B
5. By saying that monopolist create a contrived scarcity, economist mean that monopolist:
A. Restrict output to increase price
B. Produce where MC > P
C. Create a gap b/w quantity demanded and supplied
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Restrict output to increase price
B. Produce where MC > P
C. Create a gap b/w quantity demanded and supplied
D. None of the above
Answer : A
6. Total utility and price are:
A. Directly related
B. Unrelated
C. Closely related
D. Negatively related
Answer : B
A. Directly related
B. Unrelated
C. Closely related
D. Negatively related
Answer : B
7. At the point where a straight line demand curve meets the quantity axis (x-axis), elasticity of demand is:
A. Equal to zero
B. Equal to one
C. Equal to infinite
D. More than one
Answer : A
A. Equal to zero
B. Equal to one
C. Equal to infinite
D. More than one
Answer : A
8. Consumers Surplus can also be defined as:
A. Extra price benefits
B. Shortage of quantity
C. Surplus of quantity
D. Difference between actual price and potential price
Answer : D
A. Extra price benefits
B. Shortage of quantity
C. Surplus of quantity
D. Difference between actual price and potential price
Answer : D
9. Selling costs are incurred under monopolistic competition to:
A. Attract more customers
B. Prevent its customers from going to others
C. Establish superiority of its product on the others
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Attract more customers
B. Prevent its customers from going to others
C. Establish superiority of its product on the others
D. All of the above
Answer : D
10. The maximization of output subject to cost requires equilibrium at the:
A. Lowest isoquant
B. Lowest isocost line
C. Highest isoquant
D. Highest isocost line
Answer : C
A. Lowest isoquant
B. Lowest isocost line
C. Highest isoquant
D. Highest isocost line
Answer : C
11. Supply and demand changes have their most rapid impact in:
A. Auction market
B. Contract markets
C. Market for commercial office space
D. Natural gas market
Answer : A
A. Auction market
B. Contract markets
C. Market for commercial office space
D. Natural gas market
Answer : A
12. Who formulated the Post-Keynsian Theory of Distribution and Growth?
A. J.M.Keynes
B. N.Kaldor
C. C.P.Kindleberger
D. Irving Fisher
Answer : B
A. J.M.Keynes
B. N.Kaldor
C. C.P.Kindleberger
D. Irving Fisher
Answer : B
13. Identify the author of The Affluent Society?
A. Gunnar Myrdal
B. N.Kaldor
C. A.C.Pigou
D. J.K.Galbraith
Answer : D
A. Gunnar Myrdal
B. N.Kaldor
C. A.C.Pigou
D. J.K.Galbraith
Answer : D
14. Robbins definition of economics was criticised by:
A. Alfred Marshal
B. Adam Smith
C. J.B.Clark
D. Hicks, Longe and Durbin
Answer : D
A. Alfred Marshal
B. Adam Smith
C. J.B.Clark
D. Hicks, Longe and Durbin
Answer : D
15. In dominant price leadership model, the small firms are like:
A. monopolistic firms
B. monopoly
C. competitive firms
D. none of the above
Answer : C
A. monopolistic firms
B. monopoly
C. competitive firms
D. none of the above
Answer : C
16. According to Chamberlin, the activity of a monopolistic competitive firm:
A. Get noticed by the rival firms
B. Get unnoticed by the rival firms
C. Get noticed by the employees of the rival firms
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Get noticed by the rival firms
B. Get unnoticed by the rival firms
C. Get noticed by the employees of the rival firms
D. None of the above
Answer : B
17. An inferior good/ commodity is inferior for:
A. Every consumer
B. Most consumers
C. All consumers
D. Some consumers and not for others
Answer : D
A. Every consumer
B. Most consumers
C. All consumers
D. Some consumers and not for others
Answer : D
18. Profits of a firm will be calculated taking into account the units produced and the difference between:
A. Real cost and money cost
B. Variable cost and fixed cost
C. Average cost and average revenue
D. Marginal cost and average cost
Answer : C
A. Real cost and money cost
B. Variable cost and fixed cost
C. Average cost and average revenue
D. Marginal cost and average cost
Answer : C
19. The budget line is described by each of the following except:
A. Prices of products are assumed to be fixed
B. The consumer need not to spend all his income
C. Consumer income is assumed to be fixed
D. The slope represents relative prices
Answer : B
A. Prices of products are assumed to be fixed
B. The consumer need not to spend all his income
C. Consumer income is assumed to be fixed
D. The slope represents relative prices
Answer : B
20. The falling part of total Utility (TU) curve shows:
A. Increasing marginal utility
B. Decreasing marginal utility
C. Zero marginal utility
D. Negative marginal utility
Answer : D
A. Increasing marginal utility
B. Decreasing marginal utility
C. Zero marginal utility
D. Negative marginal utility
Answer : D
21. The Law of Equi-Marginal Utility refers to:
A. Marginal utility of commodity X
B. Marginal utility of commodity Y
C. Marginal utility per rupee spent on X and Y commodities
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Marginal utility of commodity X
B. Marginal utility of commodity Y
C. Marginal utility per rupee spent on X and Y commodities
D. None of the above
Answer : C
22. In substitution effect, we:
A. Move to another indifference curve
B. Move along given indifference curve
C. Move to a higher indifference curve
D. Move to a lower indifference curve
Answer : B
A. Move to another indifference curve
B. Move along given indifference curve
C. Move to a higher indifference curve
D. Move to a lower indifference curve
Answer : B
23. In long run, a firm can change:
A. Fixed factors
B. Variable factors
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. Fixed factors
B. Variable factors
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
24. If a firm is producing output at a point where diminishing returns have set in, this means that:
A. Each additional unit of output will be more expensive to produce
B. Each additional unit of output will require increasing amount of inputs
C. Marginal product of the variable factor of production decreases as the quantity increases
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Each additional unit of output will be more expensive to produce
B. Each additional unit of output will require increasing amount of inputs
C. Marginal product of the variable factor of production decreases as the quantity increases
D. All of the above
Answer : D
25. The cross-price elasticity of the demand for orange juice with respect to the price of apple juice is probably:
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Near infinite
D. Zero
Answer : B
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Near infinite
D. Zero
Answer : B
26. According to Marginalists, the price of any commodity is determined by:
A. Marginal usefulness
B. Marginal cost
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. Marginal usefulness
B. Marginal cost
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
27. Under the perfect competition, the transportation cost:
A. Is considered to be negligible and thus ignored
B. Is considered to be vital for the calculation of total cost
C. Is charged along with the price of the commodity
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Is considered to be negligible and thus ignored
B. Is considered to be vital for the calculation of total cost
C. Is charged along with the price of the commodity
D. None of the above
Answer : A
28. Under pure monopoly, there will be:
A. No distinction between firm and industry
B. One firm and no industry
C. No firm and no industry
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. No distinction between firm and industry
B. One firm and no industry
C. No firm and no industry
D. None of the above
Answer : A
29. If a commodity sold under monopoly is got free of cost, then MC will be:
A. Zero
B. Identical with the MR
C. A horizontal straight line
D. Infinite
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Identical with the MR
C. A horizontal straight line
D. Infinite
Answer : A
30. Identify the work of T.W.Schultz:
A. Transforming Traditional Agriculture
B. Productivity and Technical Change
C. Jobs, Poverty and the Green Revolution
D. Causes of Poverty
Answer : A
A. Transforming Traditional Agriculture
B. Productivity and Technical Change
C. Jobs, Poverty and the Green Revolution
D. Causes of Poverty
Answer : A
31. Variable cost includes the cost of:
A. Hiring the building for the factory
B. Purchasing heavy machines
C. Paying the manager of the factory
D. Paying the laborers
Answer : D
A. Hiring the building for the factory
B. Purchasing heavy machines
C. Paying the manager of the factory
D. Paying the laborers
Answer : D
32. If the price of a product falls then quantity demanded tends to increase ceteris paribus because:
A. The MU/P ratio has decreased
B. Of the income and substitution effects
C. Consumers tend to feel poorer when prices fall
D. When price falls the demand curve shifts right
Answer : B
A. The MU/P ratio has decreased
B. Of the income and substitution effects
C. Consumers tend to feel poorer when prices fall
D. When price falls the demand curve shifts right
Answer : B
33. In Edgeworth model, prices oscillate between:
A. Firms and industry price
B. Monopoly and duopoly price
C. Competitive and monopoly price
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Firms and industry price
B. Monopoly and duopoly price
C. Competitive and monopoly price
D. None of the above
Answer : C
34. If Cobb-Douglas production function is homogeneous of degree less than one (n<1), then it shows:
A. Constant returns to scale
B. Increasing returns to scale
C. Decreasing returns to scale
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Constant returns to scale
B. Increasing returns to scale
C. Decreasing returns to scale
D. None of the above
Answer : C
35. A country is advised to devalue (reduce external value of) its currency only when its exports face:
A. Inelastic demand in foreign markets
B. Elastic demand in foreign markets
C. Unit elastic demand in foreign markets
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Inelastic demand in foreign markets
B. Elastic demand in foreign markets
C. Unit elastic demand in foreign markets
D. None of the above
Answer : B
36. The pay-off matrix shows:
A. Possible outcomes
B. Possible benefits
C. Possible losses
D. None of them
Answer : A
A. Possible outcomes
B. Possible benefits
C. Possible losses
D. None of them
Answer : A
37. Under which of the following forms of the market structure does a firm have no control over the price of its product?
A. Monopoly
B. Monopolistic competition
C. Oligopoly
D. Perfect competition
Answer : D
A. Monopoly
B. Monopolistic competition
C. Oligopoly
D. Perfect competition
Answer : D
38. In 1776, a famous book An enquiry into the nature and causes of the wealth of nation was written by:
A. J.S.Mill
B. Adam Smith
C. Robert Malthus
D. David Ricardo
Answer : B
A. J.S.Mill
B. Adam Smith
C. Robert Malthus
D. David Ricardo
Answer : B
39. The cost of one thing in terms of the alternative given up is known as:
A. Production cost
B. Physical cost
C. Real cost
D. Opportunity cost
Answer : D
A. Production cost
B. Physical cost
C. Real cost
D. Opportunity cost
Answer : D
40. The isoquant which are generated by CES (constant elasticity of substitution) production function are always:
A. Positively sloped
B. Negatively sloped
C. Concave to the origin
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Positively sloped
B. Negatively sloped
C. Concave to the origin
D. None of the above
Answer : B
41. The minimization of costs subject to output requires equilibrium at the lowest:
A. Isoquant line
B. Isocost line
C. Indifference curve
D. Price line
Answer : B
A. Isoquant line
B. Isocost line
C. Indifference curve
D. Price line
Answer : B
42. The indifference curve technique:
A. Helps in separating the income effect and the substitution effect
B. Does not help in separating the two effects
C. Mixed up the two effects
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Helps in separating the income effect and the substitution effect
B. Does not help in separating the two effects
C. Mixed up the two effects
D. None of the above
Answer : A
43. Whish of the following represents the average revenue curve of a firm?
A. The curve representing the cost per unit of output
B. The demad curve of consumers for the firms product
C. Total receipts realized by the firm
D. All of the above
Answer : B
A. The curve representing the cost per unit of output
B. The demad curve of consumers for the firms product
C. Total receipts realized by the firm
D. All of the above
Answer : B
44. Each short run average cost curve:
A. Has to touch the long run cost curve
B. Has to cross the long run cost curve
C. Has to lie above all points on the long run cost curve
D. Coincides with the long run cost curve at some point
Answer : D
A. Has to touch the long run cost curve
B. Has to cross the long run cost curve
C. Has to lie above all points on the long run cost curve
D. Coincides with the long run cost curve at some point
Answer : D
45. Who is the author of Choice of Technique?
A. K.N.Raj
B. Amartiya Sen
C. A.C.Pigou
D. Alfred Marshal
Answer : B
A. K.N.Raj
B. Amartiya Sen
C. A.C.Pigou
D. Alfred Marshal
Answer : B
46. Total variable costs in equation form are:
A.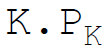
B.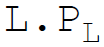
C.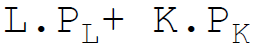
D.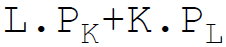
Answer : B
A.
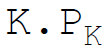
B.
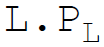
C.
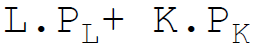
D.
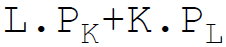
Answer : B
47. The advertisement and other selling activities:
A. Lessen the differentiation
B. Widen the differentiation
C. Does not effect the differentiation
D. All of the above
Answer : B
A. Lessen the differentiation
B. Widen the differentiation
C. Does not effect the differentiation
D. All of the above
Answer : B
48. We can find total utility by:
A. Multiplying the number of unit by its marginal utility
B. Adding up the marginal utility of all units
C. Multiplying price by number of units
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Multiplying the number of unit by its marginal utility
B. Adding up the marginal utility of all units
C. Multiplying price by number of units
D. None of the above
Answer : B
49. Which is the other name that is given to the average revenue curve?
A. Profit curve
B. Demand curve
C. Average cost curve
D. Indifference curve
Answer : B
A. Profit curve
B. Demand curve
C. Average cost curve
D. Indifference curve
Answer : B
50. In real life, brand loyalty is a barrier to:
A. Enter the new firms
B. Exit the new firms
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Enter the new firms
B. Exit the new firms
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : A
Sharing is caring
Related Post
IBPS RRB - Applied Mechanics and Graphic Statics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Error Detection MCQ for SSC JHT [Solved]
1000+ Word Power Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
DRDO - Adobe Flash 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
RRB Group D - Engineering Mechanics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Visual Basic .NET 1000+ MCQ with answer for CLAT PG