1000+ Basics of Economics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. A monopolist has control over the price he charges for his product. He will be able to maximize his profit by:
A. Lowering the price, if the demand curve is elastic
B. Lowering the price, if the demand curve is inelastic
C. Rising the price, if the demand curve is elastic
D. None of the above is applicable
Answer : A
A. Lowering the price, if the demand curve is elastic
B. Lowering the price, if the demand curve is inelastic
C. Rising the price, if the demand curve is elastic
D. None of the above is applicable
Answer : A
2. Which form of market structure is characterized by interdependence in decision-making as between the different competing firms?
A. Oligopoly
B. Perfect competition
C. Imperfect competition
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Oligopoly
B. Perfect competition
C. Imperfect competition
D. None of the above
Answer : A
3. The slope of the iso-cost line (budget line) is determined by:
A. Pricing of two factors
B. Productivity of the two factors
C. Degree of substitutability of two factors
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Pricing of two factors
B. Productivity of the two factors
C. Degree of substitutability of two factors
D. None of the above
Answer : A
4. Which cost increases continuously with the increase in production?
A. Average cost
B. Marginal cost
C. Fixed cost
D. Variable cost
Answer : D
A. Average cost
B. Marginal cost
C. Fixed cost
D. Variable cost
Answer : D
5. Total variable cost curve:
A. Steps downwards at first and then upwards
B. Steps upwards, then remains constant and then falls
C. Steps downwards
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Steps downwards at first and then upwards
B. Steps upwards, then remains constant and then falls
C. Steps downwards
D. None of the above
Answer : A
6. The situation of single buyer and single seller is called:
A. Monopoly
B. Multi-plant monopolist
C. Bilateral monopoly
D. Price discrimination
Answer : C
A. Monopoly
B. Multi-plant monopolist
C. Bilateral monopoly
D. Price discrimination
Answer : C
7. In case of monopoly, TR curve rises at a:
A. Constant rate
B. Decreasing rate
C. Increasing rate
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Constant rate
B. Decreasing rate
C. Increasing rate
D. None of the above
Answer : B
8. In Revealed Preference Theory, a consumer reveals preference for bundle of:
A. Two goods
B. A few goods
C. One good
D. Many goods
Answer : A
A. Two goods
B. A few goods
C. One good
D. Many goods
Answer : A
9. Pure monopoly exists:
A. When there is a single producer
B. When there is a single producer without any close substitute
C. When there is a single producer with close substitutes
D. When a few producers control the industry
Answer : B
A. When there is a single producer
B. When there is a single producer without any close substitute
C. When there is a single producer with close substitutes
D. When a few producers control the industry
Answer : B
10. Labor theory was firstly rejected by:
A. Adam Smith
B. Karl Marx
C. Ricardo
D. Pigou
Answer : B
A. Adam Smith
B. Karl Marx
C. Ricardo
D. Pigou
Answer : B
11. In case of monopoly, when total revenue is maximum:
A. MR is positive
B. MR falls
C. MR rises
D. MR is zero
Answer : D
A. MR is positive
B. MR falls
C. MR rises
D. MR is zero
Answer : D
12. Marginal revenue from a given output:
A. The price at which the marginal unit sells
B. Total revenue sale of all units divided by volume of sales
C. Average revenue of total output average revenue of last unit
D. The change in total revenue resulting from the sale of one unit more of output
Answer : D
A. The price at which the marginal unit sells
B. Total revenue sale of all units divided by volume of sales
C. Average revenue of total output average revenue of last unit
D. The change in total revenue resulting from the sale of one unit more of output
Answer : D
13. Engel curves shows that:
A. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of price
B. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of satisfaction
C. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of income
D. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of taxes
Answer : C
A. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of price
B. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of satisfaction
C. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of income
D. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of taxes
Answer : C
14. Law of Returns to Scale shows:
A. Technical relationship between input of a variable factor and the resulting output
B. Any economic relationship between input and output
C. An output maximizing relationship
D. A relationship with input changing and corresponding changes in output
Answer : A
A. Technical relationship between input of a variable factor and the resulting output
B. Any economic relationship between input and output
C. An output maximizing relationship
D. A relationship with input changing and corresponding changes in output
Answer : A
15. A price is a ratio of exchange between:
A. Money and exchange
B. Quantity and production
C. Production and consumption
D. Money and quantity
Answer : D
A. Money and exchange
B. Quantity and production
C. Production and consumption
D. Money and quantity
Answer : D
16. The Strategy of Economic Development is the work of:
A. S.Kuznets
B. H.Liebenstein
C. A.O.Hirshman
D. Alfred Marshal
Answer : C
A. S.Kuznets
B. H.Liebenstein
C. A.O.Hirshman
D. Alfred Marshal
Answer : C
17. In the case of superior (normal) commodity, the income elasticity of demand is:
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : A
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : A
18. If the marginal utility is divided by the price of the commodity then it is called:
A. Real Marginal Utility
B. Gross Marginal Utility
C. Weighted Marginal Utility
D. Money Marginal Utility
Answer : C
A. Real Marginal Utility
B. Gross Marginal Utility
C. Weighted Marginal Utility
D. Money Marginal Utility
Answer : C
19. Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility is practically untrue because:
A. It is given to a lot of criticism
B. It is too difficult to be explained
C. It is based on assumptions which are unreal
D. Economists do not agree on this
Answer : C
A. It is given to a lot of criticism
B. It is too difficult to be explained
C. It is based on assumptions which are unreal
D. Economists do not agree on this
Answer : C
20. If a consumer buys a product that costs Rs.3 and provides an additional 18 units of satisfaction, then for this purchase:
A. Total utility will increase by 6 units
B. The marginal utility per rupee is 6
C. The consumer will buy more because marginal utility is positive
D. The consumer obtained an extra54 units
Answer : B
A. Total utility will increase by 6 units
B. The marginal utility per rupee is 6
C. The consumer will buy more because marginal utility is positive
D. The consumer obtained an extra54 units
Answer : B
21. The feasible part of the demand curve for the monopolist who is charging high price will be:
A. The elastic part of a demand curve
B. The inelastic part of a demand curveC. The constant elastic part of the demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. The elastic part of a demand curve
B. The inelastic part of a demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
22. The firms in non-cooperative games:
A. Enforce contracts
B. Make contracts
C. Make negotiations
D. Do not make negotiations
Answer : D
A. Enforce contracts
B. Make contracts
C. Make negotiations
D. Do not make negotiations
Answer : D
23. In Revealed Preference Theory, Samuelson proves P.E = S.E + I.E :
A. With using indifference curves
B. With using MRS
C. Without using indifference curve
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. With using indifference curves
B. With using MRS
C. Without using indifference curve
D. None of the above
Answer : C
24. The supply curve would probably shift to the right if:
A. Resource( factors of production) used in production became more costly
B. The technology of production improves
C. Consumers income increased
D. Some sellers left the market
Answer : B
A. Resource( factors of production) used in production became more costly
B. The technology of production improves
C. Consumers income increased
D. Some sellers left the market
Answer : B
25. Market demand curve is:
A. Vertical summation of individual demand curves
B. Upward summation of individual demand curves
C. Downward summation of individual demand curves
D. Horizontal summation of individual demand curves
Answer : D
A. Vertical summation of individual demand curves
B. Upward summation of individual demand curves
C. Downward summation of individual demand curves
D. Horizontal summation of individual demand curves
Answer : D
26. If as a result of an increase in prices, total outlay (expenditures) on a commodity decreases, its price-elasticity of demand is:
A. Perfect elastic (infinitely elastic)
B. Relatively elastic (greater than one elasticity)
C. Unit elastic
D. Relatively inelastic (less than one elasticity)
Answer : B
A. Perfect elastic (infinitely elastic)
B. Relatively elastic (greater than one elasticity)
C. Unit elastic
D. Relatively inelastic (less than one elasticity)
Answer : B
27. If a straight line supply curve passes through the point of origin O, the elasticity of supply is:
A. Zero
B. Infinity
C. Unity
D. More than unity
Answer : C
A. Zero
B. Infinity
C. Unity
D. More than unity
Answer : C
28. The giffen paradox is an exception to law of:
A. Supply
B. Demand
C. Production
D. Consumption
Answer : B
A. Supply
B. Demand
C. Production
D. Consumption
Answer : B
29. When the slope of a demand curve is infinite (also known as horizontal demand curve) then elasticity will be:
A. Zero (perfectly inelastic)
B. Equal to one (unitary elastic)
C. Infinite (perfectly elastic)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Zero (perfectly inelastic)
B. Equal to one (unitary elastic)
C. Infinite (perfectly elastic)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
30. Identify the author of The Affluent Society?
A. Gunnar Myrdal
B. N.Kaldor
C. A.C.Pigou
D. J.K.Galbraith
Answer : D
A. Gunnar Myrdal
B. N.Kaldor
C. A.C.Pigou
D. J.K.Galbraith
Answer : D
31. If Marginal Utility (MU) is zero, then total utility is:
A. Maximum
B. Minimum
C. Infinite
D. Not measureable
Answer : A
A. Maximum
B. Minimum
C. Infinite
D. Not measureable
Answer : A
32. In the long-run:
A. Fixed cost will be greater than variable cost
B. Variable costs will be greater than fixed costs
C. All costs are variable costs
D. All costs are fixed costs
Answer : C
A. Fixed cost will be greater than variable cost
B. Variable costs will be greater than fixed costs
C. All costs are variable costs
D. All costs are fixed costs
Answer : C
33. MRSxy measures:
A. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and still remain on the same indifference curve
B. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and still remain on the same indifference curve
C. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and move to a higher indifference curve
D. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and move to a higher indifference curve
Answer : B
A. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and still remain on the same indifference curve
B. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and still remain on the same indifference curve
C. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and move to a higher indifference curve
D. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and move to a higher indifference curve
Answer : B
34. Government planners play a central role in allocating resources:
A. Only under socialism(communism)
B. Only under capitalism
C. Under both (a) and (b)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Only under socialism(communism)
B. Only under capitalism
C. Under both (a) and (b)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
35. In case of giffin good, price effect is:
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Neutral
D. Infinite
Answer : A
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Neutral
D. Infinite
Answer : A
36. Marginal utility equals:
A. Slope of total utility curve
B. Slope of average utility curve
C. Slope of marginal utility curve
D. Slope of total revenue curve
Answer : A
A. Slope of total utility curve
B. Slope of average utility curve
C. Slope of marginal utility curve
D. Slope of total revenue curve
Answer : A
37. According to Cobb-Douglas, in production function the marginal product of labor is:
A.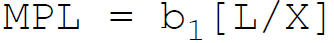
B.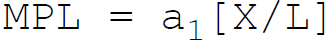
C.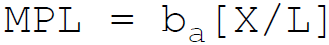
D.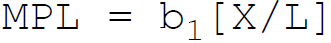
Answer : D
A.
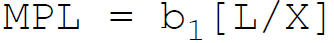
B.
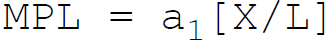
C.
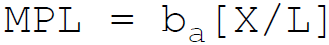
D.
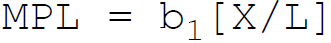
Answer : D
38. 4.The Law of Diminishing Returns according to the modern view, applies to:
A. Agriculture
B. All fields of production
C. Industry
D. Services
Answer : B
A. Agriculture
B. All fields of production
C. Industry
D. Services
Answer : B
39. Supply and demand changes have their most rapid impact in:
A. Auction market
B. Contract markets
C. Market for commercial office space
D. Natural gas market
Answer : A
A. Auction market
B. Contract markets
C. Market for commercial office space
D. Natural gas market
Answer : A
40. The ordinary demand curve is also called:
A. Marshallian demand curve
B. Hicksian demand curve
C. Slutsky demand curve
D. All the above
Answer : A
A. Marshallian demand curve
B. Hicksian demand curve
C. Slutsky demand curve
D. All the above
Answer : A
41. In centralized cartel, the firms are like:
A. Price takers
B. Price setters
C. Price discriminators
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Price takers
B. Price setters
C. Price discriminators
D. None of the above
Answer : A
42. When total revenue is maximum in monopoly, elasticity of demand is:
A. E =1
B. E >1
C. E <1
D. E =0
Answer : A
A. E =1
B. E >1
C. E <1
D. E =0
Answer : A
43. When the consumer is in equilibrium not only his income is fully spent, but the ratio of marginal utility and price is:
A. Increased
B. Equalized
C. Prominent
D. Zero
Answer : B
A. Increased
B. Equalized
C. Prominent
D. Zero
Answer : B
44. In monopoly, when average revenue curve falls:
A. MR constant
B. MR rises
C. MR falls
D. MR is zero
Answer : C
A. MR constant
B. MR rises
C. MR falls
D. MR is zero
Answer : C
45. If at the unchanged price, the demand for a commodity goes up, or the quantity demanded remains the same when its price goes up, it is called:
A. Contraction of demand
B. Decrease in demand
C. Increase in demand
D. Extension of demand
Answer : C
A. Contraction of demand
B. Decrease in demand
C. Increase in demand
D. Extension of demand
Answer : C
46. Under the perfect competition, the transportation cost:
A. Is considered to be negligible and thus ignored
B. Is considered to be vital for the calculation of total cost
C. Is charged along with the price of the commodity
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Is considered to be negligible and thus ignored
B. Is considered to be vital for the calculation of total cost
C. Is charged along with the price of the commodity
D. None of the above
Answer : A
47. In monopolistic competition (also in kinked demand curve model), a firm sells the amount where:
A. Individual demand curve (IDC) is equal to proportional demand curve (PDC)
B. Individual demand curve (IDC) is greater than proportional demand curve (PDC)
C. Individual demand curve (IDC) is less than proportional demand curve (PDC)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Individual demand curve (IDC) is equal to proportional demand curve (PDC)
B. Individual demand curve (IDC) is greater than proportional demand curve (PDC)
C. Individual demand curve (IDC) is less than proportional demand curve (PDC)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
48. While buying two goods X and Y with unequal prices, to maximize total utility from his income, a consumer should get:
A. Equal MU from both commodities X and Y
B. More MU from commodity X than from commodity Y
C. More MU from commodity Y than from commodity X
D. Equal marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity X and commodity Y
Answer : D
A. Equal MU from both commodities X and Y
B. More MU from commodity X than from commodity Y
C. More MU from commodity Y than from commodity X
D. Equal marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity X and commodity Y
Answer : D
49. By reducing the prices of its products below those of its competitors, a perfectly competitive seller:
A. Reduces its revenues
B. Increases its revenues
C. Can sell nothing
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Reduces its revenues
B. Increases its revenues
C. Can sell nothing
D. None of the above
Answer : A
50. The elasticity of demand is equal to slope of demand function divided by:
A. Average demand function
B. Qualified demand function
C. Constructive demand function
D. Relative demand function
Answer : A
A. Average demand function
B. Qualified demand function
C. Constructive demand function
D. Relative demand function
Answer : A
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Current Affairs August 2017 1000+ MCQ with answer for SBI PO
SSC CGL - Airport Engineering 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Php Programming MCQ for UPSC CSE [Solved]
Power Plant Engineering MCQ Solved Paper for RRB ALP
SSC Scientific Assistant - Automobile Engineering 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Transformation of Sentences Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]