1000+ Basics of Economics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. If the price of a product falls which of the following would occur?
A. Indifference curves shift down
B. Budget line shifts down
C. Indifference curve shift up
D. Budget line pivots
Answer : D
A. Indifference curves shift down
B. Budget line shifts down
C. Indifference curve shift up
D. Budget line pivots
Answer : D
2. In monopolistic competition, because of difference in choices, the firm charges:
A. Different prices
B. Similar prices
C. High prices
D. Low prices
Answer : A
A. Different prices
B. Similar prices
C. High prices
D. Low prices
Answer : A
3. In the immediate run:
A. Supply curves are inelastic
B. Supply curves are perfectly elastic
C. Demand curves are elastic
D. Supply curves are elastic
Answer : A
A. Supply curves are inelastic
B. Supply curves are perfectly elastic
C. Demand curves are elastic
D. Supply curves are elastic
Answer : A
4. The law of Diminishing Marginal Utility implies that the marginal utility of a good decreases as:
A. It gets more expensive
B. A household consumes more of it
C. Preference changes
D. A households income goes up
Answer : B
A. It gets more expensive
B. A household consumes more of it
C. Preference changes
D. A households income goes up
Answer : B
5. Law of Variable Proportions is regarding in:
A. Short-Run
B. Long-Run
C. Medium-Run
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Short-Run
B. Long-Run
C. Medium-Run
D. None of the above
Answer : A
6. Contraction in demand occurs when:
A. Price increases and demand decreases
B. Price increases but demand also increases
C. Price remains constant but demand falls down
D. Price falls down but demand remains constant
Answer : A
A. Price increases and demand decreases
B. Price increases but demand also increases
C. Price remains constant but demand falls down
D. Price falls down but demand remains constant
Answer : A
7. The Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) Theory is presented by:
A. J.M.Keynes
B. E.D.Domar
C. Adam Smith
D. Gustav Cassel
Answer : D
A. J.M.Keynes
B. E.D.Domar
C. Adam Smith
D. Gustav Cassel
Answer : D
8. Variable cost includes the cost of:
A. Hiring the building for the factory
B. Purchasing heavy machines
C. Paying the manager of the factory
D. Paying the laborers
Answer : D
A. Hiring the building for the factory
B. Purchasing heavy machines
C. Paying the manager of the factory
D. Paying the laborers
Answer : D
9. In monopolistic competition (also in kinked demand curve model), a firm sells the amount where:
A. Individual demand curve (IDC) is equal to proportional demand curve (PDC)
B. Individual demand curve (IDC) is greater than proportional demand curve (PDC)
C. Individual demand curve (IDC) is less than proportional demand curve (PDC)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Individual demand curve (IDC) is equal to proportional demand curve (PDC)
B. Individual demand curve (IDC) is greater than proportional demand curve (PDC)
C. Individual demand curve (IDC) is less than proportional demand curve (PDC)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
10. To calculate the Economic Profit we must deduct which of the following cost from our total revenues?
A. Opportunity cost
B. Direct cost
C. Rent cost
D. Wage cost
Answer : A
A. Opportunity cost
B. Direct cost
C. Rent cost
D. Wage cost
Answer : A
11. Kinked Demand Curve is consistent with which one of the following market situations?
A. Pure competition
B. Pure monopoly
C. Oligopoly
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : C
A. Pure competition
B. Pure monopoly
C. Oligopoly
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : C
12. According to Marshallian approach, utility:
A. Can be added
B. Can be subtracted
C. Can be multiplied
D. Can be divided
Answer : A
A. Can be added
B. Can be subtracted
C. Can be multiplied
D. Can be divided
Answer : A
13. The Hicksian indirect utility function in the form of equation is:
A. x =f(P)
B. x =a-bp
C.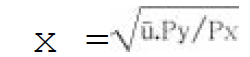
D.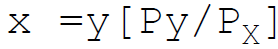
Answer : C
A. x =f(P)
B. x =a-bp
C.
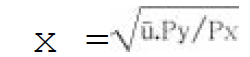
D.
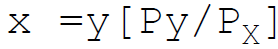
Answer : C
14. If a firm is producing output at a point where diminishing returns have set in, this means that:
A. Each additional unit of output will be more expensive to produce
B. Each additional unit of output will require increasing amount of inputs
C. Marginal product of the variable factor of production decreases as the quantity increases
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Each additional unit of output will be more expensive to produce
B. Each additional unit of output will require increasing amount of inputs
C. Marginal product of the variable factor of production decreases as the quantity increases
D. All of the above
Answer : D
15. The right of individuals to control productive resources is known as:
A. Monopoly
B. Private property
C. Workable competition
D. Oligopoly
Answer : B
A. Monopoly
B. Private property
C. Workable competition
D. Oligopoly
Answer : B
16. If a commodity sold under monopoly is got free of cost, then MC will be:
A. Zero
B. Identical with the MR
C. A horizontal straight line
D. Infinite
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Identical with the MR
C. A horizontal straight line
D. Infinite
Answer : A
17. Engel curves shows that:
A. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of price
B. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of satisfaction
C. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of income
D. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of taxes
Answer : C
A. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of price
B. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of satisfaction
C. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of income
D. How commoditys consumption rate differs at various levels of taxes
Answer : C
18. Iso-product curve (isoquant) shows:
A. A given quantity of output that can be produced by various combinations of two inputs
B. Varying quantities of output that can be produced by the same combination of two factors
C. Combination of two factors that can give the least cost of production
D. Combination of two goods that cost the same amount to the producer
Answer : A
A. A given quantity of output that can be produced by various combinations of two inputs
B. Varying quantities of output that can be produced by the same combination of two factors
C. Combination of two factors that can give the least cost of production
D. Combination of two goods that cost the same amount to the producer
Answer : A
19. In non-collusive oligopoly firms enter into:
A. Secret agreements
B. No secret agreements
C. Bad habits
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Secret agreements
B. No secret agreements
C. Bad habits
D. None of the above
Answer : B
20. If the commodity is normal then price effect is:
A. Negative
B. Inverse
C. Positive
D. Both (a) and(b)
Answer : D
A. Negative
B. Inverse
C. Positive
D. Both (a) and(b)
Answer : D
21. In perfectly competitive markets, the profit maximization rule can be represented by:
A. MR=ATC
B. P=ATC
C. P=MC
D. P=AC
Answer : C
B. P=ATC
C. P=MC
D. P=AC
Answer : C
22. Marginal cost is always:
A. Less than the average cost
B. More than the average cost
C. Equal to the average cost at minimum point
D. Never equal to the average cost
Answer : C
A. Less than the average cost
B. More than the average cost
C. Equal to the average cost at minimum point
D. Never equal to the average cost
Answer : C
23. An indifference curve slopes down towards right since more of one commodity and less of another result in:
A. Same satisfaction
B. Greater satisfaction
C. Maximum satisfaction
D. Decreasing expenditure
Answer : A
A. Same satisfaction
B. Greater satisfaction
C. Maximum satisfaction
D. Decreasing expenditure
Answer : A
24. If a new production technology for producing compact discs is developed and new firms are attracted to this field:
A. The supply curve will shift down or right
B. The supply curve will shift up or left
C. Both demand and supply curve shifts would occur
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. The supply curve will shift down or right
B. The supply curve will shift up or left
C. Both demand and supply curve shifts would occur
D. None of the above
Answer : A
25. In respect of which of the following category of goods is consumers surplus highest?
A. Giffen goods
B. Necessities
C. Luxuries
D. Prestige goods
Answer : B
A. Giffen goods
B. Necessities
C. Luxuries
D. Prestige goods
Answer : B
26. Any straight line supply which cuts the x-axis will have:
A. Zero elasticity
B. An elasticity greater than one
C. Unitary elasticity of supply
D. An elasticity less than one
Answer : B
A. Zero elasticity
B. An elasticity greater than one
C. Unitary elasticity of supply
D. An elasticity less than one
Answer : B
27. Airlines that try to lower fares in order to increase revenues believe that demand for airline services is:
A. Price elastic
B. Price inelastic
C. Income elastic
D. Income inelastic
Answer : A
A. Price elastic
B. Price inelastic
C. Income elastic
D. Income inelastic
Answer : A
28. The main contribution of Prof. R.G.D.Allen is in the field of:
A. fixation of price
B. Arc elasticity of demand
C. Cross elasticity of demand
D. Wage theory
Answer : B
A. fixation of price
B. Arc elasticity of demand
C. Cross elasticity of demand
D. Wage theory
Answer : B
29. A monopolist is:
A. Price winner
B. Price searcher
C. Price taker
D. Price leaver
Answer : B
A. Price winner
B. Price searcher
C. Price taker
D. Price leaver
Answer : B
30. The firms in non-cooperative games:
A. Enforce contracts
B. Make contracts
C. Make negotiations
D. Do not make negotiations
Answer : D
A. Enforce contracts
B. Make contracts
C. Make negotiations
D. Do not make negotiations
Answer : D
31. In case the two commodities are complements, cross elasticity will be:
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : C
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : C
32. The production techniques are technically efficient:
A. Bellow the lower ridge line
B. Above the upper ridge line
C. Between the two ridge lines
D. On the upper ridge line
Answer : C
A. Bellow the lower ridge line
B. Above the upper ridge line
C. Between the two ridge lines
D. On the upper ridge line
Answer : C
33. Indifference curve represents:
A. Only two commodities
B. Only three commodities
C. More than three commodities
D. Any number of commodities
Answer : A
A. Only two commodities
B. Only three commodities
C. More than three commodities
D. Any number of commodities
Answer : A
34. In the case of complements, the cross demand curve slopes:
A. Downwards to the right
B. Upwards to the right
C. Backwards to the top
D. Inwards at the bottom
Answer : A
A. Downwards to the right
B. Upwards to the right
C. Backwards to the top
D. Inwards at the bottom
Answer : A
35. The point where the supply and demand curves intersect on a graph determines:
A. Market price
B. Equilibrium price
C. Long-term price
D. Short-term price
Answer : B
A. Market price
B. Equilibrium price
C. Long-term price
D. Short-term price
Answer : B
36. Now-a-days in real life, we are unable to fined:
A. Monopoly
B. Perfect competition
C. Imperfect competition
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : B
A. Monopoly
B. Perfect competition
C. Imperfect competition
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : B
37. The vertical demand curve for a commodity shows that its demand is:
A. Highly elastic
B. Perfectly inelastic
C. Fairly elastic
D. Moderately elastic
Answer : B
A. Highly elastic
B. Perfectly inelastic
C. Fairly elastic
D. Moderately elastic
Answer : B
38. Necessary condition for consumer equilibrium is:
A.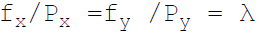
B.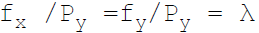
C.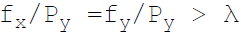
D.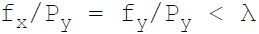
Answer : A
A.
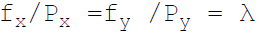
B.
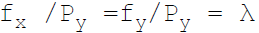
C.
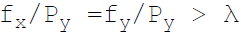
D.
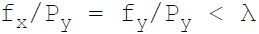
Answer : A
39. Which of the following is assumed to be constant when drawing a demand curve?
A. Consumer tastes
B. Prices of inputs
C. Technology
D. Number of sellers
Answer : A
A. Consumer tastes
B. Prices of inputs
C. Technology
D. Number of sellers
Answer : A
40. The production process is:
A. Consuming goods and services
B. Transforming inputs into outputs
C. Wasting goods and services
D. Buying goods and services
Answer : B
A. Consuming goods and services
B. Transforming inputs into outputs
C. Wasting goods and services
D. Buying goods and services
Answer : B
41. If production increases under increasing returns to scale, the cost will:
A. Increase at decreasing rate
B. Increase at constant rate
C. Decrease at increasing rate
D. Increase at increasing rate
Answer : A
A. Increase at decreasing rate
B. Increase at constant rate
C. Decrease at increasing rate
D. Increase at increasing rate
Answer : A
42. If a straight line supply curve makes an intercept on the Y-axis, elasticity of supply is:
A. Equal to unity
B. Less than unity
C. More than unity
D. Zero
Answer : C
A. Equal to unity
B. Less than unity
C. More than unity
D. Zero
Answer : C
43. The long run total cost is attained by:
A. LMC.Q
B. AC.Q
C. LC.Q
D. LAC.Q
Answer : D
A. LMC.Q
B. AC.Q
C. LC.Q
D. LAC.Q
Answer : D
44. A loss bearing firm will continue to produce in the short run so long as the price at least covers:
A. Average variable cost
B. Average fixed cost
C. Average variable cost + average fixed cost
D. Marginal costs
Answer : A
A. Average variable cost
B. Average fixed cost
C. Average variable cost + average fixed cost
D. Marginal costs
Answer : A
45. The indirect utility function is a homogeneous function of:
A. degree one
B. degree zero
C. degree less than one
D. degree greater than one
Answer : B
A. degree one
B. degree zero
C. degree less than one
D. degree greater than one
Answer : B
46. We can measure consumers surplus with the help of
A. TU curve
B. MU curve
C. Supply curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. TU curve
B. MU curve
C. Supply curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
47. Income effect operates through an increase
A. In nominal income
B. In money income
C. In wages
D. In real income because of the fall of price of a commodity
Answer : D
A. In nominal income
B. In money income
C. In wages
D. In real income because of the fall of price of a commodity
Answer : D
48. When at a given price, the quantity supplied of a commodity is more than the quantity demanded, there will be:
A. An upward pressure on price
B. A downward pressure on price
C. Price will remain unaffected
D. All of the above
Answer : B
A. An upward pressure on price
B. A downward pressure on price
C. Price will remain unaffected
D. All of the above
Answer : B
49. Price discrimination is possible:
A. When elasticities of demand in different markets are the same at the ruling price
B. When elasticities of demand are different in different markets at the ruling price
C. When elasticities cannot be known
D. When elasticities of demands are zero in different markets at the rulling price
Answer : B
A. When elasticities of demand in different markets are the same at the ruling price
B. When elasticities of demand are different in different markets at the ruling price
C. When elasticities cannot be known
D. When elasticities of demands are zero in different markets at the rulling price
Answer : B
50. At low prices, demand is likely to be:
A. More elastic
B. Less elastic
C. Unit elastic
D. Perfectly inelastic
Answer : B
A. More elastic
B. Less elastic
C. Unit elastic
D. Perfectly inelastic
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Transformation of Sentences 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC MTS
1000+ Hydraulics & Fluid Machineries MCQ for NDA [Solved]
Selenium automation 1000+ MCQ with answer for IBPS SO
1000+ IBPS Common Written Exam (PO/MT) Main 2016 Solved Paper Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Problems on Trains Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Concrete Technology and Design MCQ for ESIC [Solved]