1000+ Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics MCQ for IBPS RRB [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Pick out the extensive property out of the following.
A. Surface tension
B. Free energy
C. Specific heat
D. Refractive index
Answer : B
A. Surface tension
B. Free energy
C. Specific heat
D. Refractive index
Answer : B
2. What is the value of maximum COP in case of absorption refrigeration, if refrigeration provided is at temperature, TR (where, T1 and T2 are source & surrounding temperatures respectively.)?
A. TR/(T2 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
B. TR/(T2 - TR) × T1/(T1 - T2)
C. TR/(T1 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. TR/(T2 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
B. TR/(T2 - TR) × T1/(T1 - T2)
C. TR/(T1 - TR) × (T1 - T2)/T1
D. None of these
Answer : A
3. Which of the following is an undesirable characteristic of a refrigerant?
A. It should be non-explosive
B. It should have a sub-atmospheric vapor pressure at the temperature in refrigerator coils
C. Its vapor pressure at the condenser temperature should be very high
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. It should be non-explosive
B. It should have a sub-atmospheric vapor pressure at the temperature in refrigerator coils
C. Its vapor pressure at the condenser temperature should be very high
D. None of these
Answer : B
4. y = specific heat ratio of an ideal gas is equal to
A. Cp/Cv
B. Cp/(CP-R)
C. 1 + (R/CV)
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Cp/Cv
B. Cp/(CP-R)
C. 1 + (R/CV)
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
5. The fugacity of a gas in a mixture is equal to the product of its mole fraction and its fugacity in the pure state at the total pressure of the mixture. This is
A. The statement as per Gibbs-Helmholtz
B. Called Lewis-Randall rule
C. Henry's law
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. The statement as per Gibbs-Helmholtz
B. Called Lewis-Randall rule
C. Henry's law
D. None of these
Answer : B
6. Fugacity and pressure are numerically equal, when the gas is
A. In standard state
B. At high pressure
C. At low temperature
D. In ideal state
Answer : D
A. In standard state
B. At high pressure
C. At low temperature
D. In ideal state
Answer : D
7. In an isothermal process on an ideal gas, the pressure increases by 0.5 percent. The volume decreases by about __________ percent.
A. 0.25
B. 0.5
C. 0.75
D. 1
Answer : B
A. 0.25
B. 0.5
C. 0.75
D. 1
Answer : B
8. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. The chemical potential of a pure substance depends upon the temperature and pressure
B. The chemical potential of a component in a system is directly proportional to the escaping tendency of that component
C. The chemical potential of ith species (?i) in an ideal gas mixture approaches zero as the pressure or mole fraction (xi) tends to be zero at constant temperature
D. The chemical potential of species 'i' in the mixture (?i) is mathematically represented as,?i = ?(nG)/?ni]T,P,nj where, n, ni and nj respectively denote the total number of moles, moles of ith species and all mole numbers except ith species. 'G' is Gibbs molar free energy
Answer : C
A. The chemical potential of a pure substance depends upon the temperature and pressure
B. The chemical potential of a component in a system is directly proportional to the escaping tendency of that component
C. The chemical potential of ith species (?i) in an ideal gas mixture approaches zero as the pressure or mole fraction (xi) tends to be zero at constant temperature
D. The chemical potential of species 'i' in the mixture (?i) is mathematically represented as,?i = ?(nG)/?ni]T,P,nj where, n, ni and nj respectively denote the total number of moles, moles of ith species and all mole numbers except ith species. 'G' is Gibbs molar free energy
Answer : C
9. Co-efficient of performance for a reversed Carnot cycle working between temperatures T1 and T2 (T1 > T2) is
A. T2/(T1 - T2)
B. T1/(T1 - T2)
C. (T1 - T2)/T1
D. (T1 - T2)/T2
Answer : A
A. T2/(T1 - T2)
B. T1/(T1 - T2)
C. (T1 - T2)/T1
D. (T1 - T2)/T2
Answer : A
10. If the internal energy of an ideal gas decreases by the same amount as the work done by the system, then the
A. Process must be isobaric
B. Temperature must decrease
C. Process must be adiabatic
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Process must be isobaric
B. Temperature must decrease
C. Process must be adiabatic
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
11. The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of conservation of
A. Heat
B. Momentum
C. Energy
D. Work
Answer : C
A. Heat
B. Momentum
C. Energy
D. Work
Answer : C
12. The extensive properties are
A. Volume, mass and number of moles
B. Free energy, entropy and enthalpy
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Volume, mass and number of moles
B. Free energy, entropy and enthalpy
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
13. Joule-Thomson co-efficient for a perfect gas is
A. Zero
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : A
14. The value of gas constant 'R' is
A. 1.987 cal/gm mole °K
B. 1.987 BTU/lb. mole °R
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. 1.987 cal/gm mole °K
B. 1.987 BTU/lb. mole °R
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
15. Boiling of liquid is accompanied with increase in the
A. Vapor pressure
B. Specific Gibbs free energy
C. Specific entropy
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : A
A. Vapor pressure
B. Specific Gibbs free energy
C. Specific entropy
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : A
16. Entropy of the system decreases, when
A. Snow melts into water
B. A gas expands spontaneously from high pressure to low pressure
C. Water is converted into ice
D. Both (B) & (C)
Answer : D
A. Snow melts into water
B. A gas expands spontaneously from high pressure to low pressure
C. Water is converted into ice
D. Both (B) & (C)
Answer : D
17. The internal energy of an ideal gas is a function of its __________ only.
A. Molecular size
B. Volume
C. Pressure
D. Temperature
Answer : D
A. Molecular size
B. Volume
C. Pressure
D. Temperature
Answer : D
18. Heat of reaction at constant volume is identified with __________ change.
A. Enthalpy
B. Internal energy
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
A. Enthalpy
B. Internal energy
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
19. Which of the following identities can be most easily used to verify steam table data for superheated steam?
A. (?T/?V)S = (?p/?S)V
B. (?T/?P)S = (?V/?S)P
C. (?P/?T)V = (?S/?V)
D. (?V/?T)P = -(?S/?P)T
Answer : D
A. (?T/?V)S = (?p/?S)V
B. (?T/?P)S = (?V/?S)P
C. (?P/?T)V = (?S/?V)
D. (?V/?T)P = -(?S/?P)T
Answer : D
20. The relation connecting the fugacities of various components in a solution with one another and to composition at constant temperature and pressure is called the __________ equation.
A. Gibbs-Duhem
B. Van Laar
C. Gibbs-Helmholtz
D. Margules
Answer : A
A. Gibbs-Duhem
B. Van Laar
C. Gibbs-Helmholtz
D. Margules
Answer : A
21. On opening the door of an operating refrigerator kept in a closed room, the temperature of the room will
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain same
D. Increase in summer and will decrease in winter
Answer : A
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain same
D. Increase in summer and will decrease in winter
Answer : A
22. The ratio of equilibrium constants (Kp2/Kp1) at two different temperatures is given by
A. (R/?H) (1/T1 - 1/T2)
B. (?H/R) (1/T1 - 1/T2)
C. (?H/R) (1/T2 - 1/T1)
D. (1/R) (1/T1 - 1/T2)
Answer : B
A. (R/?H) (1/T1 - 1/T2)
B. (?H/R) (1/T1 - 1/T2)
C. (?H/R) (1/T2 - 1/T1)
D. (1/R) (1/T1 - 1/T2)
Answer : B
23. Keeping the pressure constant, to double the volume of a given mass of an ideal gas at 27°C, the temperature should be raised to __________ °C.
A. 270
B. 327
C. 300
D. 540
Answer : B
A. 270
B. 327
C. 300
D. 540
Answer : B
24. The compressibility factor for an ideal gas is 1. Its value for any other real gas is
A. 1
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. Either (B) or (C), depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : D
A. 1
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. Either (B) or (C), depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : D
25. Tea kept in a thermos flask is vigorously shaken. If the tea is considered as a system, then its temperature will
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain unchanged
D. First fall and then rise
Answer : A
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain unchanged
D. First fall and then rise
Answer : A
26. An ideal gas is taken around the cycle ABCA as shown in P-V diagram below: The work done by the gas during the cycle is equal to
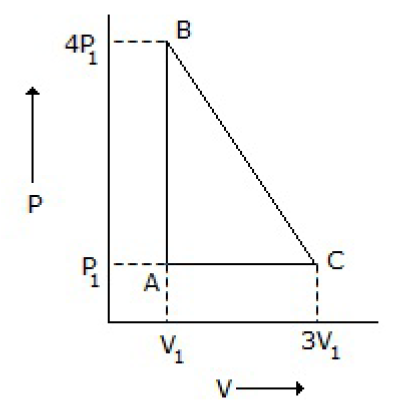
A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C

A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C
27. For a reversible process involving only pressure-volume work
A. (dF)T, p < 0
B. (dF)T, p > 0
C. (dF)T, p = 0
D. (dA)T, v < 0
Answer : C
A. (dF)T, p < 0
B. (dF)T, p > 0
C. (dF)T, p = 0
D. (dA)T, v < 0
Answer : C
28. An irreversible process
A. Is the analog of linear frictionless motion in machines
B. Is an idealised visualisation of behaviour of a system
C. Yields the maximum amount of work
D. Yields an amount of work less than that of a reversible process
Answer : D
A. Is the analog of linear frictionless motion in machines
B. Is an idealised visualisation of behaviour of a system
C. Yields the maximum amount of work
D. Yields an amount of work less than that of a reversible process
Answer : D
29. For an exothermic reaction
A. Only enthalpy change (?H) is negative
B. Only internal energy change (?E) is negative
C. Both ?H and ?E are negative
D. Enthalpy change is zero
Answer : C
A. Only enthalpy change (?H) is negative
B. Only internal energy change (?E) is negative
C. Both ?H and ?E are negative
D. Enthalpy change is zero
Answer : C
30. Trouton's ratio of __________ liquids is calculated using Kistyakowsky equation.
A. Polar
B. Non-polar
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
A. Polar
B. Non-polar
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
31. With increase in temperature, the internal energy of a substance
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains unchanged
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the substance
Answer : A
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains unchanged
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the substance
Answer : A
32. Which of the following is an extensive property of a system?
A. Heat capacity
B. Molal heat capacity
C. Pressure
D. Concentration
Answer : A
A. Heat capacity
B. Molal heat capacity
C. Pressure
D. Concentration
Answer : A
33. In case of an __________ process, the temperature of the system increases.
A. Isothermal compression
B. Isothermal expansion
C. Adiabatic expansion
D. Adiabatic compression
Answer : D
A. Isothermal compression
B. Isothermal expansion
C. Adiabatic expansion
D. Adiabatic compression
Answer : D
34. The four properties of a system viz. P, V, T, S are related by __________ equation.
A. Gibbs-Duhem
B. Gibbs-Helmholtz
C. Maxwell's
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Gibbs-Duhem
B. Gibbs-Helmholtz
C. Maxwell's
D. None of these
Answer : C
35. Refrigerants commonly used for domestic refrigerators are
A. Ethyl chloride or methyl chloride
B. Freon-12
C. Propane
D. NH3 or CO2
Answer : A
A. Ethyl chloride or methyl chloride
B. Freon-12
C. Propane
D. NH3 or CO2
Answer : A
36. For the reversible exothermic reaction, N2 + 3H2 ? 2NH3, increase of pressure would
A. Shift the equilibrium towards right
B. Give higher yield of NH3
C. Both (B) and (C)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Shift the equilibrium towards right
B. Give higher yield of NH3
C. Both (B) and (C)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
37. Partial molar free energy of an element A in solution is same as its
A. Chemical potential
B. Activity
C. Fugacity
D. Activity co-efficient
Answer : A
A. Chemical potential
B. Activity
C. Fugacity
D. Activity co-efficient
Answer : A
38. Cv is given by
A. (?E/?T)V
B. (?E/?V)T
C. (?E/?P)V
D. (?V/?T)P
Answer : A
A. (?E/?T)V
B. (?E/?V)T
C. (?E/?P)V
D. (?V/?T)P
Answer : A
39. The efficiency of an Otto engine compared to that of a diesel engine, for the same compression ratio will be
A. More
B. Less
C. Same
D. Data insufficient to predict
Answer : A
A. More
B. Less
C. Same
D. Data insufficient to predict
Answer : A
40. What is the value of Joule-Thomson co-efficient for an ideal gas?
A. +ve
B. -ve
C. 0
D. ?
Answer : C
A. +ve
B. -ve
C. 0
D. ?
Answer : C
41. Degree of freedom of the system ice-watervapour will be
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
42. Boyle's law for gases states that
A. P ? 1/V, when temperature is constant
B. P ? 1/V, when temperature & mass of the gas remain constant
C. P ? V, at constant temperature & mass of the gas
D. P/V = constant, for any gas
Answer : B
A. P ? 1/V, when temperature is constant
B. P ? 1/V, when temperature & mass of the gas remain constant
C. P ? V, at constant temperature & mass of the gas
D. P/V = constant, for any gas
Answer : B
43. Chemical potential (an intensive property) of a substance is a force that drives the chemical system to equilibrium and is equal to its partial molar properties. The ratio of chemical potential to free energy of a pure substance at constant temperature and pressure is
A. 0
B. 1
C. ?
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. 0
B. 1
C. ?
D. None of these
Answer : B
44. Critical compressibility factor for all substances
A. Are more or less constant (vary from 0.2 to 0.3)
B. Vary as square of the absolute temperature
C. Vary as square of the absolute pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Are more or less constant (vary from 0.2 to 0.3)
B. Vary as square of the absolute temperature
C. Vary as square of the absolute pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
45. Measurement of thermodynamic property of temperature is facilitated by __________ law of thermodynamics.
A. 1st
B. Zeroth
C. 3rd
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. 1st
B. Zeroth
C. 3rd
D. None of these
Answer : B
46. Solid and liquid phases of a substance are in equilibrium at the
A. Critical temperature
B. Melting point
C. Freezing point
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Critical temperature
B. Melting point
C. Freezing point
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
47. When dilute aqueous solutions of two salts are mixed, the process is associated with
A. Decrease in temperature
B. Increase in temperature
C. No change in temperature
D. Change in temperature which is a function of composition
Answer : B
A. Decrease in temperature
B. Increase in temperature
C. No change in temperature
D. Change in temperature which is a function of composition
Answer : B
48. Out of the following refrigeration cycles, which one has maximum COP?
A. Air cycle
B. Carnot cycle
C. Ordinary vapor compression cycle
D. Vapor compression with a reversible expansion engine
Answer : B
A. Air cycle
B. Carnot cycle
C. Ordinary vapor compression cycle
D. Vapor compression with a reversible expansion engine
Answer : B
49. A refrigeration cycle is a reversed heat engine. Which of the following has the maximum value of the co-efficient of performance (COP) for a given refrigeration effect?
A. Vapor compression cycle using expansion valve
B. Air refrigeration cycle
C. Vapor compression cycle using expansion engine
D. Carnot refrigeration cycle
Answer : D
A. Vapor compression cycle using expansion valve
B. Air refrigeration cycle
C. Vapor compression cycle using expansion engine
D. Carnot refrigeration cycle
Answer : D
50. The following heat engine produces power of 100,000 kW. The heat engine operates between 800 K and 300 K. It has a thermal efficiency equal to 50% of that of the Carnot engine for the same temperature. The rate at which heat is absorbed from the hot reservoir is
A. 100,000 kW
B. 160,000 kW
C. 200,000 kW
D. 320,000 kW
Answer : D
A. 100,000 kW
B. 160,000 kW
C. 200,000 kW
D. 320,000 kW
Answer : D
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Current Affairs October 2022 MCQ for SSC CGL [Solved]
SSC JHT - Construction Planning and Management 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Networking 1000+ MCQ with answer for GRE
DRDO - Fluid Mechanics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
LIC AAO - Microsoft Excel 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Manufacturing & Production Engineering MCQ for LSAT [Solved]