1000+ Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. With increase in temperature, the internal energy of a substance
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains unchanged
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the substance
Answer : A
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains unchanged
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the substance
Answer : A
2. The value of gas constant 'R' is
A. 1.987 cal/gm mole °K
B. 1.987 BTU/lb. mole °R
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. 1.987 cal/gm mole °K
B. 1.987 BTU/lb. mole °R
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
3. Enthalpy of a gas depends upon its
A. Temperature
B. Mass
C. Volume
D. Pressure
Answer : A
A. Temperature
B. Mass
C. Volume
D. Pressure
Answer : A
4. Compressibility factor for almost all the gases are approximately same at the same
A. Pressure and temperature
B. Reduced pressure and reduced temperature
C. Critical pressure and critical temperature
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Pressure and temperature
B. Reduced pressure and reduced temperature
C. Critical pressure and critical temperature
D. None of these
Answer : B
5. The compressibility factor for an ideal gas is 1. Its value for any other real gas is
A. 1
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. Either (B) or (C), depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : D
A. 1
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. Either (B) or (C), depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : D
6. To obtain integrated form of Clausius-Clapeyron equation, ln (P2/P1) = (?HV/R) (1/T1 - 1/T2) from the exact Clapeyron equation, it is assumed that the
A. Volume of the liquid phase is negligible compared to that of vapour phase
B. Vapour phase behaves as an ideal gas
C. Heat of vaporisation is independent of temperature
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : D
A. Volume of the liquid phase is negligible compared to that of vapour phase
B. Vapour phase behaves as an ideal gas
C. Heat of vaporisation is independent of temperature
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : D
7. If the internal energy of an ideal gas decreases by the same amount as the work done by the system, then the
A. Process must be isobaric
B. Temperature must decrease
C. Process must be adiabatic
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Process must be isobaric
B. Temperature must decrease
C. Process must be adiabatic
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
8. Specific/molar Gibbs free energy for a pure substance does not change during
A. Sublimation
B. Vaporisation
C. Melting
D. Either (A), (B) or (C)
Answer : D
A. Sublimation
B. Vaporisation
C. Melting
D. Either (A), (B) or (C)
Answer : D
9. The free energy change for a chemical reaction is given by (where, K = equilibrium constant)
A. RT ln K
B. -RT ln K
C. -R ln K
D. T ln K
Answer : B
A. RT ln K
B. -RT ln K
C. -R ln K
D. T ln K
Answer : B
10. For a given substance at a specified temperature, activity is __________ to fugacity.
A. Directly proportional
B. Inversely proportional
C. Equal
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Directly proportional
B. Inversely proportional
C. Equal
D. None of these
Answer : A
11. Choose the condition that must be specified in order to liquify CO2 (triple point for CO2 is - 57°C and 5.2 atm).
A. Pressure must be kept below 5.2 atm
B. Temperature must be kept above - 57°C
C. Pressure must be kept below 5.2 atm. and temperature must be kept above 57°C
D. Pressure and temperature must be kept below 5.2 atm. and - 57°C respectively
Answer : D
A. Pressure must be kept below 5.2 atm
B. Temperature must be kept above - 57°C
C. Pressure must be kept below 5.2 atm. and temperature must be kept above 57°C
D. Pressure and temperature must be kept below 5.2 atm. and - 57°C respectively
Answer : D
12. As pressure approaches zero, the ratio of fugacity to pressure (f/P) for a gas approaches
A. Zero
B. Unity
C. Infinity
D. An indeterminate value
Answer : B
A. Zero
B. Unity
C. Infinity
D. An indeterminate value
Answer : B
13. The acentric factor of a materical, '?', is defined as ? = -log10(Prsat)Tr-1 = 0.7, where, Prsat = reduced vapor pressure, Tr = reduced temperature. The value of acentric factor is always
A. > 2
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. < 3
Answer : B
A. > 2
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. < 3
Answer : B
14. One ton of refrigeration capacity is equivalent to the heat removal rate of
A. 50 kcal/hr
B. 200 BTU/hr
C. 200 BTU/minute
D. 200 BTU/day
Answer : C
A. 50 kcal/hr
B. 200 BTU/hr
C. 200 BTU/minute
D. 200 BTU/day
Answer : C
15. (1/V) (?V/?T)P is the mathematical expression
A. Joule-Thomson co-efficient
B. Specific heat at constant pressure (Cp)
C. co-efficient of thermal expansion
D. Specific heat at constant volume (CV)
Answer : C
A. Joule-Thomson co-efficient
B. Specific heat at constant pressure (Cp)
C. co-efficient of thermal expansion
D. Specific heat at constant volume (CV)
Answer : C
16. Fugacity is a measure of the
A. Escaping tendencies of the same substance in different phases of a system
B. Relative volatility of a mixture of two miscible liquids
C. Behaviour of ideal gases
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Escaping tendencies of the same substance in different phases of a system
B. Relative volatility of a mixture of two miscible liquids
C. Behaviour of ideal gases
D. None of these
Answer : A
17. A gas shows deviation from ideal behaviour at
A. Low pressure and high temperature
B. Low pressure and low temperature
C. Low temperature and high pressure
D. High temperature and high pressure
Answer : C
A. Low pressure and high temperature
B. Low pressure and low temperature
C. Low temperature and high pressure
D. High temperature and high pressure
Answer : C
18. In case of steady flow compression polytropic process (PVn = constant), the work done on air is the lowest, when
A. n = y = 1.4
B. n = 0
C. n = 1
D. n = 1.66
Answer : C
A. n = y = 1.4
B. n = 0
C. n = 1
D. n = 1.66
Answer : C
19. Number of degrees of freedom for a three phase system in equilibrium comprising of three nonreacting chemical species is
A. 2
B. 0
C. 1
D. 3
Answer : A
A. 2
B. 0
C. 1
D. 3
Answer : A
20. __________ explains the equilibrium constant for any chemical reaction.
A. Henry's law
B. Law of mass action
C. Hess's law
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Henry's law
B. Law of mass action
C. Hess's law
D. None of these
Answer : B
21. Boyle's law for gases states that
A. P ? 1/V, when temperature is constant
B. P ? 1/V, when temperature & mass of the gas remain constant
C. P ? V, at constant temperature & mass of the gas
D. P/V = constant, for any gas
Answer : B
A. P ? 1/V, when temperature is constant
B. P ? 1/V, when temperature & mass of the gas remain constant
C. P ? V, at constant temperature & mass of the gas
D. P/V = constant, for any gas
Answer : B
22. Law of corresponding states says that
A. Two different gases behave similarly, if their reduced properties (i.e. P, V and T) are same
B. The surface of separation (i. e. the meniscus) between liquid and vapour phase disappears at the critical temperature
C. No gas can be liquefied above the critical temperature, howsoever high the pressure may be.
D. The molar heat of energy of gas at constant volume should be nearly constant (about 3 calories)
Answer : A
A. Two different gases behave similarly, if their reduced properties (i.e. P, V and T) are same
B. The surface of separation (i. e. the meniscus) between liquid and vapour phase disappears at the critical temperature
C. No gas can be liquefied above the critical temperature, howsoever high the pressure may be.
D. The molar heat of energy of gas at constant volume should be nearly constant (about 3 calories)
Answer : A
23. Free energy changes for two reaction mechanism 'X' and 'Y are respectively - 15 and - 5 units. It implies that X is
A. Slower than Y
B. Faster than Y
C. Three times slower than Y
D. Three times faster than Y
Answer : B
A. Slower than Y
B. Faster than Y
C. Three times slower than Y
D. Three times faster than Y
Answer : B
24. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. The values of (?P/?V)T and (?2P/?V2)T are zero for a real gas at its critical point
B. Heat transferred is equal to the change in the enthalpy of the system, for a constant pressure, non-flow, mechanically reversible process
C. Thermal efficiency of a Carnot engine depends upon the properties of the working fluid besides the source & sink temperatures
D. During a reversible adiabatic process, the entropy of a substance remains constant
Answer : C
A. The values of (?P/?V)T and (?2P/?V2)T are zero for a real gas at its critical point
B. Heat transferred is equal to the change in the enthalpy of the system, for a constant pressure, non-flow, mechanically reversible process
C. Thermal efficiency of a Carnot engine depends upon the properties of the working fluid besides the source & sink temperatures
D. During a reversible adiabatic process, the entropy of a substance remains constant
Answer : C
25. Maximum work that could be secured by expanding the gas over a given pressure range is the __________ work.
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isentropic
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isentropic
D. None of these
Answer : A
26. Molar heat capacity of water in equilibrium with ice at constant pressure is __________ Kcal/kg mole. °K
A. 0
B. ?
C. 50
D. 100
Answer : B
A. 0
B. ?
C. 50
D. 100
Answer : B
27. Consider the process A & B shown in the figure given below: In this case, it is possible that
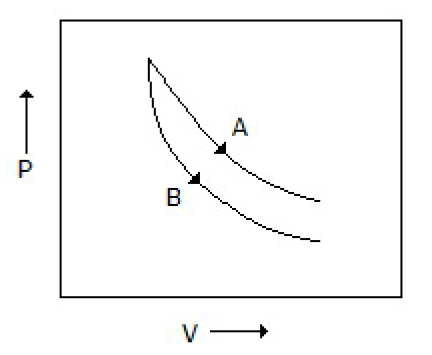
A. Both the processes are adiabatic
B. Both the processes are isothermal
C. Process A is isothermal while B is adiabatic
D. Process A is adiabatic while B is isothermal
Answer : C

A. Both the processes are adiabatic
B. Both the processes are isothermal
C. Process A is isothermal while B is adiabatic
D. Process A is adiabatic while B is isothermal
Answer : C
28. Trouton's ratio is given by (where ?b, = molal heat of vaporisation of a substance at its normal boiling point, kcal/kmol Tb = normal boiling point, °K)
A. ?b/Tb
B. Tb/?b
C. ?(?b/Tb)
D. ?(Tb/?b)
Answer : A
A. ?b/Tb
B. Tb/?b
C. ?(?b/Tb)
D. ?(Tb/?b)
Answer : A
29. The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of conservation of
A. Heat
B. Momentum
C. Energy
D. Work
Answer : C
A. Heat
B. Momentum
C. Energy
D. Work
Answer : C
30. For an irreversible process involving only pressure-volume work
A. (dF)T, p <0
B. (dF)T, p = 0
C. (dF)T, p > 0
D. (dA)T, v >0
Answer : A
A. (dF)T, p <0
B. (dF)T, p = 0
C. (dF)T, p > 0
D. (dA)T, v >0
Answer : A
31. The main feature of Carnot refrigeration cycle is that, it
A. Does not need the addition of external work for its functioning
B. Transfers heat from high temperature to low temperature
C. Accomplishes the reverse effect of the heat engine
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Does not need the addition of external work for its functioning
B. Transfers heat from high temperature to low temperature
C. Accomplishes the reverse effect of the heat engine
D. None of these
Answer : C
32. The absolute entropy for all crystalline substances at absolute zero temperature is
A. Zero
B. Negative
C. More than zero
D. Indeterminate
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Negative
C. More than zero
D. Indeterminate
Answer : A
33. Gibbs-Duhem equation
A. States that n1d?1 + n2d?2 + ....njd?j = 0, for a system of definite composition at constant temperature and pressure
B. Applies only to binary systems
C. Finds no application in gas-liquid equilibria involved in distillation
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. States that n1d?1 + n2d?2 + ....njd?j = 0, for a system of definite composition at constant temperature and pressure
B. Applies only to binary systems
C. Finds no application in gas-liquid equilibria involved in distillation
D. None of these
Answer : A
34. In an irreversible process
A. Tds = dE - dW = 0
B. dE - dW - Tds = 0
C. Tds - dE + dW < 0
D. Tds - dT + dW < 0
Answer : C
A. Tds = dE - dW = 0
B. dE - dW - Tds = 0
C. Tds - dE + dW < 0
D. Tds - dT + dW < 0
Answer : C
35. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. A closed system does not permit exchange of mass with its surroundings but may permit exchange of energy.
B. An open system permits exchange of both mass and energy with its surroundings
C. The term microstate is used to characterise an individual, whereas macro-state is used to designate a group of micro-states with common characteristics
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. A closed system does not permit exchange of mass with its surroundings but may permit exchange of energy.
B. An open system permits exchange of both mass and energy with its surroundings
C. The term microstate is used to characterise an individual, whereas macro-state is used to designate a group of micro-states with common characteristics
D. None of the above
Answer : D
36. If two gases have same reduced temperature and reduced pressure, then they will have the same
A. Volume
B. Mass
C. Critical temperature
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Volume
B. Mass
C. Critical temperature
D. None of these
Answer : D
37. Co-efficient of performance for a reversed Carnot cycle working between temperatures T1 and T2 (T1 > T2) is
A. T2/(T1 - T2)
B. T1/(T1 - T2)
C. (T1 - T2)/T1
D. (T1 - T2)/T2
Answer : A
A. T2/(T1 - T2)
B. T1/(T1 - T2)
C. (T1 - T2)/T1
D. (T1 - T2)/T2
Answer : A
38. In Joule-Thomson porous plug experiment, the
A. Enthalpy does not remain constant
B. Entire apparatus is exposed to surroundings
C. Temperature remains constant
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Enthalpy does not remain constant
B. Entire apparatus is exposed to surroundings
C. Temperature remains constant
D. None of these
Answer : D
39. The heat capacities for the ideal gas state depend upon the
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
40. Thermal efficiency of a Carnot engine can approac 100%, only when the temperature of the
A. Cold reservoir approaches zero
B. Hot reservoir approaches infinity
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Cold reservoir approaches zero
B. Hot reservoir approaches infinity
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
41. Work done in case of free expansion is
A. Indeterminate
B. Zero
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Indeterminate
B. Zero
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : B
42. Compressibility factor-reduced pressure plot on reduced co-ordinates facilitates
A. Use of only one graph for all gases
B. Covering of wide range
C. Easier plotting
D. More accurate plotting
Answer : A
A. Use of only one graph for all gases
B. Covering of wide range
C. Easier plotting
D. More accurate plotting
Answer : A
43. Which of the following is not an intensive property?
A. Chemical potential
B. Surface tension
C. Heat capacity
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Chemical potential
B. Surface tension
C. Heat capacity
D. None of these
Answer : C
44. The enthalpy change when ammonia gas is dissolved in water is called the heat of
A. Solution
B. Formation
C. Dilution
D. Combustion
Answer : A
A. Solution
B. Formation
C. Dilution
D. Combustion
Answer : A
45. For an ideal gas, the internal energy depends upon its __________ only.
A. Molecular size
B. Temperature
C. Volume
D. Pressure
Answer : B
A. Molecular size
B. Temperature
C. Volume
D. Pressure
Answer : B
46. The unit of equilibrium constant of a chemical reaction is the same as that of
A. Molar concentration
B. Temperature
C. Internal energy
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Molar concentration
B. Temperature
C. Internal energy
D. None of these
Answer : D
47. The co-efficient of performance (COP) of a refrigerating system, which is its index of performance, is defined as the ratio of useful refrigeration to the net work. The units of __________ and COP are the same.
A. Kinematic viscosity
B. Work
C. Temperature
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Kinematic viscosity
B. Work
C. Temperature
D. None of these
Answer : D
48. Degree of freedom of the system ice-watervapour will be
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
Answer : A
49. The internal energy of an ideal gas does not change in a reversible __________ process.
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isobaric
D. Isometric
Answer : A
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isobaric
D. Isometric
Answer : A
50. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. The net change in entropy in any reversible cycle is always zero
B. The entropy of the system as a whole in an irreversible process increases
C. The entropy of the universe tends to a maximum
D. The entropy of a substance does not remain constant during a reversible adiabatic change
Answer : D
A. The net change in entropy in any reversible cycle is always zero
B. The entropy of the system as a whole in an irreversible process increases
C. The entropy of the universe tends to a maximum
D. The entropy of a substance does not remain constant during a reversible adiabatic change
Answer : D
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Building Materials 1000+ MCQ with answer for FCI Recruitment
Current Affairs June 2017 1000+ MCQ with answer for UPSC CSE
Linux OS 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC GD
NDA - Machine Design 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Machine Design MCQ for LIC ADO [Solved]
Idioms & Phrases 1000+ MCQ with answer for NDA