CLAT PG - Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Which of the following is not an intensive property?
A. Molar heat capacity
B. Internal energy
C. Viscosity
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Molar heat capacity
B. Internal energy
C. Viscosity
D. None of these
Answer : B
2. Melting of ice is an example of an __________ process.
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : B
3. Compound having large heat of formation is
A. More stable
B. Less stable
C. Not at all stable (like nascent O2)
D. Either more or less stable; depends on the compound
Answer : A
A. More stable
B. Less stable
C. Not at all stable (like nascent O2)
D. Either more or less stable; depends on the compound
Answer : A
4. A large iceberg melts at the base, but not at the top, because of the reason that
A. Ice at the base contains impurities which lowers its melting point
B. Due to the high pressure at the base, its melting point reduces
C. The iceberg remains in a warmer condition at the base
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : B
A. Ice at the base contains impurities which lowers its melting point
B. Due to the high pressure at the base, its melting point reduces
C. The iceberg remains in a warmer condition at the base
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : B
5. An ideal gas is taken around the cycle ABCA as shown in P-V diagram below: The work done by the gas during the cycle is equal to
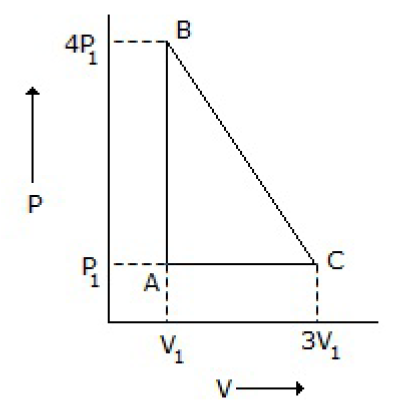
A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C

A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C
6. Internal energy is equal to the heat absorbed in case of a/an __________ process.
A. Constant volume
B. Polytropic
C. Adiabatic
D. Constant pressure
Answer : A
A. Constant volume
B. Polytropic
C. Adiabatic
D. Constant pressure
Answer : A
7. A gas performs the maximum work, when it expands
A. Non-uniformly
B. Adiabatically
C. Isobarically
D. Isothermally
Answer : C
A. Non-uniformly
B. Adiabatically
C. Isobarically
D. Isothermally
Answer : C
8. __________ law of thermodynamics ascertains the direction of a particular spontaneous process.
A. Zeroth
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
Answer : C
A. Zeroth
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
Answer : C
9. Ideal refrigeration cycle is
A. Same as Carnot cycle
B. Same as reverse Carnot cycle
C. Dependent on the refrigerant's properties
D. The least efficient of all refrigeration processes
Answer : B
A. Same as Carnot cycle
B. Same as reverse Carnot cycle
C. Dependent on the refrigerant's properties
D. The least efficient of all refrigeration processes
Answer : B
10. Change of state namely evaporation condensation, freezing and melting is an __________ process.
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isobaric
D. Isochoric
Answer : A
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Isobaric
D. Isochoric
Answer : A
11. Equation which relates pressure, volume and temperature of a gas is called the
A. Equation of state
B. Gibbs Duhem equation
C. Ideal gas equation
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Equation of state
B. Gibbs Duhem equation
C. Ideal gas equation
D. None of these
Answer : A
12. Pick out the correct statement.
A. The available energy in an isolated system for all irreversible (real) processes decreases
B. The efficiency of a Carnot engine increases, if the sink temperature is decreased
C. The reversible work for compression in non-flow process under isothermal condition is the change in Helmholtz free energy
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. The available energy in an isolated system for all irreversible (real) processes decreases
B. The efficiency of a Carnot engine increases, if the sink temperature is decreased
C. The reversible work for compression in non-flow process under isothermal condition is the change in Helmholtz free energy
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
13. The molar excess Gibbs free energy, gE, for a binary liquid mixture at T and P is given by, (gE/RT) = A . x1. x2, where A is a constant. The corresponding equation for ln y1, where y1 is the activity co-efficient of component 1, is
A. A . x22
B. Ax1
C. Ax2
D. Ax12
Answer : A
A. A . x22
B. Ax1
C. Ax2
D. Ax12
Answer : A
14. Which of the following is not a reversible process?
A. Expansion of an ideal gas against constant pressure
B. Atmospheric pressure vaporisation of water at 100°C
C. Solution of NaCl in water at 50°C
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Expansion of an ideal gas against constant pressure
B. Atmospheric pressure vaporisation of water at 100°C
C. Solution of NaCl in water at 50°C
D. None of these
Answer : C
15. All gases above its inversion temperature, in a throttling process will show
A. A heating effect
B. No change in temperature
C. A cooling effect
D. Either (A) or (C)
Answer : A
A. A heating effect
B. No change in temperature
C. A cooling effect
D. Either (A) or (C)
Answer : A
16. In any spontaneous process,
A. Only F decreases
B. Only A decreases
C. Both F and A decreases
D. Both F and A increase
Answer : C
A. Only F decreases
B. Only A decreases
C. Both F and A decreases
D. Both F and A increase
Answer : C
17. What happens in a reversible adiabatic compression?
A. Heating occurs
B. Cooling occurs
C. Pressure is constant
D. Temperature is constant
Answer : A
A. Heating occurs
B. Cooling occurs
C. Pressure is constant
D. Temperature is constant
Answer : A
18. Isobaric process means a constant process.
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. Entropy
Answer : B
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. Entropy
Answer : B
19. Lowering of condenser temperature (keeping the evaporator temperature constant) in case of vapour compression refrigeration system results in
A. Increased COP
B. Same COP
C. Decreased COP
D. Increased or decreased COP; depending upon the type of refrigerant
Answer : A
A. Increased COP
B. Same COP
C. Decreased COP
D. Increased or decreased COP; depending upon the type of refrigerant
Answer : A
20. Which of the following is not a unit of the equilibrium constant Kp? (where, ?x = number of moles of products number of moles of reactants)
A. (atm)?x, when ?x is negative
B. (atm)?x, when ?x is positive
C. Dimensionless, when ?x = 0
D. (atm)?x2, when ?x > 0
Answer : D
A. (atm)?x, when ?x is negative
B. (atm)?x, when ?x is positive
C. Dimensionless, when ?x = 0
D. (atm)?x2, when ?x > 0
Answer : D
21. For an ideal gas, the activity co-efficient is
A. Directly proportional to pressure
B. Inversely proportional to pressure
C. Unity at all pressures
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Directly proportional to pressure
B. Inversely proportional to pressure
C. Unity at all pressures
D. None of these
Answer : C
22. Solid and liquid phases of a substance are in equilibrium at the
A. Critical temperature
B. Melting point
C. Freezing point
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Critical temperature
B. Melting point
C. Freezing point
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
23. Second law of thermodynamics is concerned with the
A. Amount of energy transferred
B. Direction of energy transfer
C. Irreversible processes only
D. Non-cyclic processes only
Answer : B
A. Amount of energy transferred
B. Direction of energy transfer
C. Irreversible processes only
D. Non-cyclic processes only
Answer : B
24. A Carnot cycle consists of the following steps:
A. Two isothermal and two isentropic
B. Two isobaric and two isothermal
C. Two isochoric and two isobaric
D. Two isothermals and two isochoric
Answer : A
A. Two isothermal and two isentropic
B. Two isobaric and two isothermal
C. Two isochoric and two isobaric
D. Two isothermals and two isochoric
Answer : A
25. When pressure is applied on the system, ice ? water, then
A. Equilibrium cannot be established
B. More ice will be formed
C. More water will be formed
D. Evaporation of water will take place
Answer : C
A. Equilibrium cannot be established
B. More ice will be formed
C. More water will be formed
D. Evaporation of water will take place
Answer : C
26. Joule-Thomson effect i.e., a throttling process is a constant __________ process.
A. Entropy
B. Temperature
C. Internal energy
D. Enthalpy
Answer : D
A. Entropy
B. Temperature
C. Internal energy
D. Enthalpy
Answer : D
27. The equation DU = Tds - PdV is applicable to infinitesimal changes occuring in
A. An open system of constant composition
B. A closed system of constant composition
C. An open system with changes in composition
D. A closed system with changes in composition
Answer : D
A. An open system of constant composition
B. A closed system of constant composition
C. An open system with changes in composition
D. A closed system with changes in composition
Answer : D
28. Claude's liquefaction process employs the cooling of gases by
A. Expansion in an engine
B. Following a constant pressure cycle
C. Throttling
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Expansion in an engine
B. Following a constant pressure cycle
C. Throttling
D. None of these
Answer : A
29. The number of degrees of freedom for a mixture of ice and water (liquid) are
A. 3
B. 2
C. 1
D. 0
Answer : C
A. 3
B. 2
C. 1
D. 0
Answer : C
30. Claude gas liquefaction process employs cooling
A. At constant pressure
B. By throttling
C. By expansion in an engine
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. At constant pressure
B. By throttling
C. By expansion in an engine
D. None of these
Answer : C
31. Grams of butane (C4H10) formed by the liquefaction of 448 litres of the gas (measured at (STP) would be
A. 580
B. 640
C. 1160
D. Data insufficient; can't be computed
Answer : C
A. 580
B. 640
C. 1160
D. Data insufficient; can't be computed
Answer : C
32. No work is done by the system, when a reaction occurs at constant
A. Volume
B. Temperature
C. Pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Volume
B. Temperature
C. Pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
33. What happens in a reversible adiabatic expansion process?
A. Heating takes place
B. Cooling takes place
C. Pressure is constant
D. Temperature is constant
Answer : B
A. Heating takes place
B. Cooling takes place
C. Pressure is constant
D. Temperature is constant
Answer : B
34. Dryness fraction of wet steam is defined as the ratio of mass of vapour in the mixture to the mass of mixture __________ calorimeter is not used for measuring the dryness fraction of steam.
A. Bomb
B. Separating
C. Bucket
D. Throttling
Answer : A
A. Bomb
B. Separating
C. Bucket
D. Throttling
Answer : A
35. Gibbs free energy of mixing at constant pressure and temperature is always
A. 0
B. ?
C. + ve
D. - ve
Answer : D
A. 0
B. ?
C. + ve
D. - ve
Answer : D
36. Which of the following is Clausius-Clapeyron Equation for vaporisation of an ideal gas under the condition that the molar volume of liquid is negligible compared to that of the vapor?
A. d ln p/dt = Hvap/RT2
B. d ln p/dt = RT2/Hvap
C. dp/dt = RT2/Hvap
D. dp/dt = Hvap/RT2
Answer : A
A. d ln p/dt = Hvap/RT2
B. d ln p/dt = RT2/Hvap
C. dp/dt = RT2/Hvap
D. dp/dt = Hvap/RT2
Answer : A
37. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. Trouton's ratio of non-polar liquids is calculated using Kistyakowsky equation
B. Thermal efficiency of a Carnot engine is always less than 1
C. An equation relating pressure, volume and temperature of a gas is called ideal gas equation
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Trouton's ratio of non-polar liquids is calculated using Kistyakowsky equation
B. Thermal efficiency of a Carnot engine is always less than 1
C. An equation relating pressure, volume and temperature of a gas is called ideal gas equation
D. None of these
Answer : C
38. In the reaction, C + O2 ? CO2; ?H = - 94 kcal. What is the heat content (enthalpy) of O2?
A. -94 kcal
B. > -94 kcal
C. < - 94 kcal
D. Zero
Answer : D
A. -94 kcal
B. > -94 kcal
C. < - 94 kcal
D. Zero
Answer : D
39. (?H/?T)P is the mathematical expression for
A. CV
B. Entropy change
C. Gibbs free energy
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. CV
B. Entropy change
C. Gibbs free energy
D. None of these
Answer : D
40. When a gas is expanded from high pressure region to low pressure region; temperature change occurs. This phenomenon is related to the
A. Gibbs-Duhem equation
B. Gibbs-Helmholtz equation
C. Third law of thermodynamics
D. Joule-Thomson effect
Answer : D
A. Gibbs-Duhem equation
B. Gibbs-Helmholtz equation
C. Third law of thermodynamics
D. Joule-Thomson effect
Answer : D
41. A gas shows deviation from ideal behaviour at
A. Low pressure and high temperature
B. Low pressure and low temperature
C. Low temperature and high pressure
D. High temperature and high pressure
Answer : C
A. Low pressure and high temperature
B. Low pressure and low temperature
C. Low temperature and high pressure
D. High temperature and high pressure
Answer : C
42. The expression for entropy change given by, ?S = - nR ln (P2/P1), holds good for
A. Expansion of a real gas
B. Reversible isothermal volume change
C. Heating of an ideal gas
D. Cooling of a real gas
Answer : B
A. Expansion of a real gas
B. Reversible isothermal volume change
C. Heating of an ideal gas
D. Cooling of a real gas
Answer : B
43. As the entropy of the universe is increasing, day by day, the work producing capacity of a heat engine is
A. Not changed
B. Decreasing
C. Increasing
D. Data sufficient, can't be predicted
Answer : B
A. Not changed
B. Decreasing
C. Increasing
D. Data sufficient, can't be predicted
Answer : B
44. Which of the following processes cannot be made reversible even under ideal condition of operation?
A. Free expansion of a gas
B. Compression of air in a compressor
C. Expansion of steam in a turbine
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : A
A. Free expansion of a gas
B. Compression of air in a compressor
C. Expansion of steam in a turbine
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : A
45. Pick out the correct statement.
A. Like internal energy and enthalpy, the absolute value of standard entropy for elementary substances is zero
B. Melting of ice involves increase in enthalpy and a decrease in randomness
C. The internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on its pressure
D. Maximum work is done under reversible conditions
Answer : D
A. Like internal energy and enthalpy, the absolute value of standard entropy for elementary substances is zero
B. Melting of ice involves increase in enthalpy and a decrease in randomness
C. The internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on its pressure
D. Maximum work is done under reversible conditions
Answer : D
46. In a turbine, the fluid expands almost
A. Isothermally
B. Isobarically
C. Adiabatically
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Isothermally
B. Isobarically
C. Adiabatically
D. None of these
Answer : C
47. In the ammonia synthesis reaction, N2 + 3H2 ? 2NH3 + 22.4 kcal, the formation of NH3 will be favoured by
A. High temperature
B. Low pressure
C. Low temperature only
D. Both low temperature and high pressure
Answer : D
A. High temperature
B. Low pressure
C. Low temperature only
D. Both low temperature and high pressure
Answer : D
48. In case of a close thermodynamic system, there is __________ across the boundaries.
A. No heat and mass transfer
B. No mass transfer but heat transfer
C. Mass and energy transfer
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. No heat and mass transfer
B. No mass transfer but heat transfer
C. Mass and energy transfer
D. None of these
Answer : B
49. Pick out the undesirable property for a good refrigerant.
A. High thermal conductivity
B. Low freezing point
C. Large latent heat of vaporisation
D. High viscosity
Answer : D
A. High thermal conductivity
B. Low freezing point
C. Large latent heat of vaporisation
D. High viscosity
Answer : D
50. In case of the decomposition of hydroiodic acid (2HI ? H2 + I2), addition of H2 (at equilibrium condition) will
A. Increase the partial pressure of I2
B. Decrease the partial pressure of HI
C. Diminish the degree of dissociation of HI
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Increase the partial pressure of I2
B. Decrease the partial pressure of HI
C. Diminish the degree of dissociation of HI
D. None of these
Answer : C
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Current Affairs June 2017 MCQ Solved Paper for SSC Stenographer
NMAT - Compressors, Gas Turbines & Jet Engines 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
SSC MTS - Windows 2000 Server 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Biological Classification 1000+ MCQ with answer for UPSC CDS
Phylum - Protozoa MCQ Solved Paper for ISRO Recruitment
JEE Main - IBPS Common Written Exam (PO/MT) Main 2016 Solved Paper 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download