1000+ Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. In the ammonia synthesis reaction, N2 + 3H2 ? 2NH3 + 22.4 kcal, the formation of NH3 will be favoured by
A. High temperature
B. Low pressure
C. Low temperature only
D. Both low temperature and high pressure
Answer : D
A. High temperature
B. Low pressure
C. Low temperature only
D. Both low temperature and high pressure
Answer : D
2. In an ideal gas mixture, fugacity of a species is equal to its
A. Vapor pressure
B. Partial pressure
C. Chemical potential
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Vapor pressure
B. Partial pressure
C. Chemical potential
D. None of these
Answer : B
3. Which is a state function?
A. Specific volume
B. Work
C. Pressure
D. Temperature
Answer : B
A. Specific volume
B. Work
C. Pressure
D. Temperature
Answer : B
4. Internal energy of an element at 1 atm and 25° C is __________ kcal/kg.mole.
A. 0
B. 273
C. 25
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. 0
B. 273
C. 25
D. None of these
Answer : A
5. The quantitative effect of temperature on chemical equilibrium is given by the
A. Vant-Hoff equation
B. Le-Chatelier's principle
C. Arrhenius equation
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Vant-Hoff equation
B. Le-Chatelier's principle
C. Arrhenius equation
D. None of these
Answer : A
6. Which of the following units is not present in both the vapor compression refrigeration system and absorption refrigeration system?
A. Expansion valve
B. Condenser
C. Refrigerator
D. Compressor
Answer : D
A. Expansion valve
B. Condenser
C. Refrigerator
D. Compressor
Answer : D
7. The chemical potential of any constituent of an ideal solution depends on the __________ of the solution.
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Composition
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Composition
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
8. An ideal gas is taken around the cycle ABCA as shown in P-V diagram below: The work done by the gas during the cycle is equal to
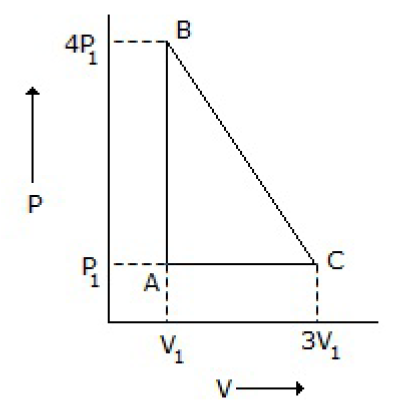
A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C

A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C
9. Which of the following is not an intensive property?
A. Volume
B. Density
C. Temperature
D. Pressure
Answer : A
A. Volume
B. Density
C. Temperature
D. Pressure
Answer : A
10. Pick out the undesirable property for a good refrigerant.
A. High thermal conductivity
B. Low freezing point
C. Large latent heat of vaporisation
D. High viscosity
Answer : D
A. High thermal conductivity
B. Low freezing point
C. Large latent heat of vaporisation
D. High viscosity
Answer : D
11. Clausius-Clapeyron equation is applicable to __________ equilibrium processes.
A. Solid-vapor
B. Solid-liquid
C. Liquid-vapor
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Solid-vapor
B. Solid-liquid
C. Liquid-vapor
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
12. The absolute entropy for all crystalline substances at absolute zero temperature is
A. Zero
B. Negative
C. More than zero
D. Indeterminate
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Negative
C. More than zero
D. Indeterminate
Answer : A
13. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. The net change in entropy in any reversible cycle is always zero
B. The entropy of the system as a whole in an irreversible process increases
C. The entropy of the universe tends to a maximum
D. The entropy of a substance does not remain constant during a reversible adiabatic change
Answer : D
A. The net change in entropy in any reversible cycle is always zero
B. The entropy of the system as a whole in an irreversible process increases
C. The entropy of the universe tends to a maximum
D. The entropy of a substance does not remain constant during a reversible adiabatic change
Answer : D
14. In vapour compression refrigeration system, if the evaporator temperature and the condenser temperatures are -13°C and 37°C respectively, the Carnot COP will be
A. 5.2
B. 6.2
C. 0.168
D. Data insufficient, can't be found out
Answer : A
A. 5.2
B. 6.2
C. 0.168
D. Data insufficient, can't be found out
Answer : A
15. A system is said to be isopiestic, if there is no __________ change.
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. None of these
Answer : B
16. For an isothermal reversible compression of an ideal gas
A. Only ?E = 0
B. Only ?H =0
C. ?E = ?H = 0
D. dQ = dE
Answer : C
A. Only ?E = 0
B. Only ?H =0
C. ?E = ?H = 0
D. dQ = dE
Answer : C
17. An isentropic process is carried out at constant
A. Volume
B. Pressure
C. Temperature
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : A
A. Volume
B. Pressure
C. Temperature
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : A
18. Two substances are in equilibrium in a reversible chemical reaction. If the concentration of each substance is doubled, then the value of the equilibrium constant will be
A. Same
B. Doubled
C. Halved
D. One fourth of its original value
Answer : A
A. Same
B. Doubled
C. Halved
D. One fourth of its original value
Answer : A
19. The number of degrees of freedom for a mixture of ice and water (liquid) are
A. 3
B. 2
C. 1
D. 0
Answer : C
A. 3
B. 2
C. 1
D. 0
Answer : C
20. Out of the following refrigeration cycles, which one has maximum COP?
A. Air cycle
B. Carnot cycle
C. Ordinary vapor compression cycle
D. Vapor compression with a reversible expansion engine
Answer : B
A. Air cycle
B. Carnot cycle
C. Ordinary vapor compression cycle
D. Vapor compression with a reversible expansion engine
Answer : B
21. Joule-Thomson co-efficient which is defined as, ? = (?T/?P)H = 1/Cp (?H/?T)P, changes sign at a temperature known as inversion temperature. The value of Joule-Thomson co-efficient at inversion temperature is
A. 0
B. ?
C. +ve
D. -ve
Answer : A
A. 0
B. ?
C. +ve
D. -ve
Answer : A
22. If the molar heat capacities (Cp or Cv) of the reactants and products of a chemical reaction are identical, then, with the increase in temperature, the heat of reaction will
Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain unaltered
D. Increase or decrease; depends on the particular reaction
Answer : C
B. Decrease
C. Remain unaltered
D. Increase or decrease; depends on the particular reaction
Answer : C
23. Domestic refrigerator usually works on the __________ refrigeration cycle.
A. Carnot
B. Air
C. Absorption
D. vapour-ejection
Answer : C
A. Carnot
B. Air
C. Absorption
D. vapour-ejection
Answer : C
24. Heat pump
A. Accomplishes only space heating in winter
B. Accomplishes only space cooling in summer
C. Accomplishes both (A) and (B)
D. Works on Carnot cycle
Answer : C
A. Accomplishes only space heating in winter
B. Accomplishes only space cooling in summer
C. Accomplishes both (A) and (B)
D. Works on Carnot cycle
Answer : C
25. Which of the following is not a unit of the equilibrium constant Kp? (where, ?x = number of moles of products number of moles of reactants)
A. (atm)?x, when ?x is negative
B. (atm)?x, when ?x is positive
C. Dimensionless, when ?x = 0
D. (atm)?x2, when ?x > 0
Answer : D
A. (atm)?x, when ?x is negative
B. (atm)?x, when ?x is positive
C. Dimensionless, when ?x = 0
D. (atm)?x2, when ?x > 0
Answer : D
26. The main feature of Carnot refrigeration cycle is that, it
A. Does not need the addition of external work for its functioning
B. Transfers heat from high temperature to low temperature
C. Accomplishes the reverse effect of the heat engine
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Does not need the addition of external work for its functioning
B. Transfers heat from high temperature to low temperature
C. Accomplishes the reverse effect of the heat engine
D. None of these
Answer : C
27. Which of the following is Clausius-Clapeyron Equation for vaporisation of an ideal gas under the condition that the molar volume of liquid is negligible compared to that of the vapor?
A. d ln p/dt = Hvap/RT2
B. d ln p/dt = RT2/Hvap
C. dp/dt = RT2/Hvap
D. dp/dt = Hvap/RT2
Answer : A
A. d ln p/dt = Hvap/RT2
B. d ln p/dt = RT2/Hvap
C. dp/dt = RT2/Hvap
D. dp/dt = Hvap/RT2
Answer : A
28. A thermodynamic system is taken from state A to B along ACB and is brought back to A along BDA as shown below in the P-V diagram. The net work done during the complete cycle is given by the area covered by
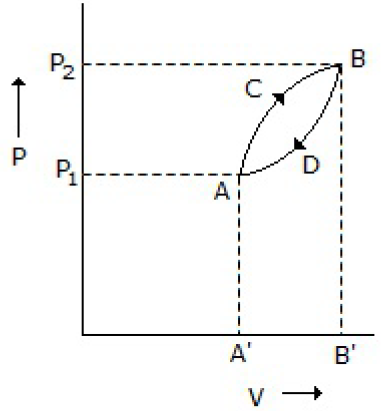
A. P1ACBP2P1
B. ACBB1A1A
C. ACBDA
D. ADBB1A1A
Answer : C

A. P1ACBP2P1
B. ACBB1A1A
C. ACBDA
D. ADBB1A1A
Answer : C
29. 1m3 of an ideal gas at 500 K and 1000 kPa expands reversibly to 5 times its initial volume in an insulated container. If the specific heat capacity (at constant pressure) of the gas is 21 J/mole . K, the final temperature will be
A. 35 K
B. 174 K
C. 274 K
D. 154 K
Answer : C
A. 35 K
B. 174 K
C. 274 K
D. 154 K
Answer : C
30. Heat of formation of an element in its standard state is
A. 0
B. < 0
C. > 0
D. A function of pressure
Answer : A
A. 0
B. < 0
C. > 0
D. A function of pressure
Answer : A
31. When a gas is subjected to adiabatic expansion, it gets cooled due to
A. Decrease in velocity
B. Decrease in temperature
C. Decrease in kinetic energy
D. Energy spent in doing work
Answer : D
A. Decrease in velocity
B. Decrease in temperature
C. Decrease in kinetic energy
D. Energy spent in doing work
Answer : D
32. Pick out the wrong statement
A. Phase rule variables are intensive properties
B. Heat and work are both state function
C. The work done by expansion of a gas in vacuum is zero
D. CP and CV are state function
Answer : B
A. Phase rule variables are intensive properties
B. Heat and work are both state function
C. The work done by expansion of a gas in vacuum is zero
D. CP and CV are state function
Answer : B
33. The value of gas constant 'R' is
A. 1.987 cal/gm mole °K
B. 1.987 BTU/lb. mole °R
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. 1.987 cal/gm mole °K
B. 1.987 BTU/lb. mole °R
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
34. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. At constant pressure, solubility of a gas in a liquid diminishes with rise in temperature
B. Normally, the gases which are easily liquefied are more soluble in common solvents
C. The gases which are capable of forming ions in aqueous solution are much more soluble in water than in other solvents
D. At constant pressure, solubility of a gas in a liquid increases with rise in temperature
Answer : A
A. At constant pressure, solubility of a gas in a liquid diminishes with rise in temperature
B. Normally, the gases which are easily liquefied are more soluble in common solvents
C. The gases which are capable of forming ions in aqueous solution are much more soluble in water than in other solvents
D. At constant pressure, solubility of a gas in a liquid increases with rise in temperature
Answer : A
35. Internal energy is equal to the heat absorbed in case of a/an __________ process.
A. Constant volume
B. Polytropic
C. Adiabatic
D. Constant pressure
Answer : A
A. Constant volume
B. Polytropic
C. Adiabatic
D. Constant pressure
Answer : A
36. Gibbs free energy at constant pressure and temperature under equilibrium conditions is
A. ?
B. 0
C. Maximum
D. Minimum
Answer : D
A. ?
B. 0
C. Maximum
D. Minimum
Answer : D
37. For the reversible exothermic reaction, N2 + 3H2 ? 2NH3, increase of pressure would
A. Shift the equilibrium towards right
B. Give higher yield of NH3
C. Both (B) and (C)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Shift the equilibrium towards right
B. Give higher yield of NH3
C. Both (B) and (C)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
38. The free energy change for a chemical reaction is given by (where, K = equilibrium constant)
A. RT ln K
B. -RT ln K
C. -R ln K
D. T ln K
Answer : B
A. RT ln K
B. -RT ln K
C. -R ln K
D. T ln K
Answer : B
39. The co-efficient of performance (COP) of a refrigerating system, which is its index of performance, is defined as the ratio of useful refrigeration to the net work. The units of __________ and COP are the same.
A. Kinematic viscosity
B. Work
C. Temperature
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Kinematic viscosity
B. Work
C. Temperature
D. None of these
Answer : D
40. Which of the following is not an intensive property?
A. Molar heat capacity
B. Internal energy
C. Viscosity
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Molar heat capacity
B. Internal energy
C. Viscosity
D. None of these
Answer : B
41. For equilibrium process (i.e. reversible) in an isolated system
A. ds = 0
B. ds < 0
C. ds > 0
D. ds = Constant
Answer : A
A. ds = 0
B. ds < 0
C. ds > 0
D. ds = Constant
Answer : A
42. The freezing point of a liquid decreases when the pressure is increased, if the liquid __________ while freezing.
A. Contracts
B. Expands
C. Does not change in volume
D. Either (A), (B) or (C)
Answer : A
A. Contracts
B. Expands
C. Does not change in volume
D. Either (A), (B) or (C)
Answer : A
43. The molar excess Gibbs free energy, gE, for a binary liquid mixture at T and P is given by, (gE/RT) = A . x1. x2, where A is a constant. The corresponding equation for ln y1, where y1 is the activity co-efficient of component 1, is
A. A . x22
B. Ax1
C. Ax2
D. Ax12
Answer : A
A. A . x22
B. Ax1
C. Ax2
D. Ax12
Answer : A
44. After throttling, gas temperature
A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. Remain same
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : A
A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. Remain same
D. May increase or decrease; depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : A
45. Fugacity and pressure are numerically equal, when the gas is
A. In standard state
B. At high pressure
C. At low temperature
D. In ideal state
Answer : D
A. In standard state
B. At high pressure
C. At low temperature
D. In ideal state
Answer : D
46. The enthalpy change when ammonia gas is dissolved in water is called the heat of
A. Solution
B. Formation
C. Dilution
D. Combustion
Answer : A
A. Solution
B. Formation
C. Dilution
D. Combustion
Answer : A
47. In the equation, PVn = constant, if the value of n = 1, then it represents a reversible __________ process.
A. Isothermal
B. Isobaric
C. Polytropic
D. Adiabatic
Answer : A
A. Isothermal
B. Isobaric
C. Polytropic
D. Adiabatic
Answer : A
48. __________ explains the equilibrium constant for any chemical reaction.
A. Henry's law
B. Law of mass action
C. Hess's law
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Henry's law
B. Law of mass action
C. Hess's law
D. None of these
Answer : B
49. When a gas in a vessel expands, its internal energy decreases. The process involved is
A. Reversible
B. Irreversible
C. Isothermal
D. Adiabatic
Answer : A
A. Reversible
B. Irreversible
C. Isothermal
D. Adiabatic
Answer : A
50. What happens in a reversible adiabatic expansion process?
A. Heating takes place
B. Cooling takes place
C. Pressure is constant
D. Temperature is constant
Answer : B
A. Heating takes place
B. Cooling takes place
C. Pressure is constant
D. Temperature is constant
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Visual Basic MCQ for IBPS RRB [Solved]
ISRO Recruitment - General knowledge 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Airport Engineering Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
SSC GD - The Living World 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
CTET - Chemical Process 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Puzzle MCQ Solved Paper for UPSC CSE