Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 1000+ MCQ with answer for RBI Grade B officer
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. In the ammonia synthesis reaction, N2 + 3H2 ? 2NH3 + 22.4 kcal, the formation of NH3 will be favoured by
A. High temperature
B. Low pressure
C. Low temperature only
D. Both low temperature and high pressure
Answer : D
A. High temperature
B. Low pressure
C. Low temperature only
D. Both low temperature and high pressure
Answer : D
2. Any substance above its critical temperature exists as
A. Saturated vapour
B. Solid
C. Gas
D. Liquid
Answer : C
A. Saturated vapour
B. Solid
C. Gas
D. Liquid
Answer : C
3. In a P-V diagram (for an ideal gas), an isothermal curve will coincide within adiabatic curve (through a point), when
A. Cp < Cv
B. Cp = Cv
C. Cp > Cv
D. C ? Cv
Answer : B
A. Cp < Cv
B. Cp = Cv
C. Cp > Cv
D. C ? Cv
Answer : B
4. __________ functions are exemplified by heat and work.
A. Path
B. Point
C. State
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Path
B. Point
C. State
D. None of these
Answer : A
5. Which of the following processes cannot be made reversible even under ideal condition of operation?
A. Free expansion of a gas
B. Compression of air in a compressor
C. Expansion of steam in a turbine
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : A
A. Free expansion of a gas
B. Compression of air in a compressor
C. Expansion of steam in a turbine
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : A
6. In case of a close thermodynamic system, there is __________ across the boundaries.
A. No heat and mass transfer
B. No mass transfer but heat transfer
C. Mass and energy transfer
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. No heat and mass transfer
B. No mass transfer but heat transfer
C. Mass and energy transfer
D. None of these
Answer : B
7. The difference between isothermal compressibility and adiabatic compressibility for an ideal gas is
A. 0
B. +ve
C. -ve
D. ?
Answer : B
A. 0
B. +ve
C. -ve
D. ?
Answer : B
8. If the vapour pressure at two temperatures of a solid phase in equilibrium with its liquid phase are known, then the latent heat of fusion can be calculated by the
A. Maxwell's equation
B. Clausius-Clapeyron Equation
C. Van Laar equation
D. Nernst Heat Theorem
Answer : B
A. Maxwell's equation
B. Clausius-Clapeyron Equation
C. Van Laar equation
D. Nernst Heat Theorem
Answer : B
9. What is the value of Joule-Thomson co-efficient for an ideal gas?
A. +ve
B. -ve
C. 0
D. ?
Answer : C
A. +ve
B. -ve
C. 0
D. ?
Answer : C
10. When a gas is expanded from high pressure region to low pressure region; temperature change occurs. This phenomenon is related to the
A. Gibbs-Duhem equation
B. Gibbs-Helmholtz equation
C. Third law of thermodynamics
D. Joule-Thomson effect
Answer : D
A. Gibbs-Duhem equation
B. Gibbs-Helmholtz equation
C. Third law of thermodynamics
D. Joule-Thomson effect
Answer : D
11. The value of gas constant 'R' is
A. 1.987 cal/gm mole °K
B. 1.987 BTU/lb. mole °R
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. 1.987 cal/gm mole °K
B. 1.987 BTU/lb. mole °R
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
12. Entropy of a substance remains constant during a/an __________ change.
A. Reversible isothermal
B. Irreversible isothermal
C. Reversible adiabatic
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Reversible isothermal
B. Irreversible isothermal
C. Reversible adiabatic
D. None of these
Answer : C
13. The third law of thermodynamics states that the
A. Heat capacity of a crystalline solid is zero at absolute zero temperature
B. Heat transfer from low temperature to high temperature source is not possible without external work
C. Gases having same reduced properties behaves similarly
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Heat capacity of a crystalline solid is zero at absolute zero temperature
B. Heat transfer from low temperature to high temperature source is not possible without external work
C. Gases having same reduced properties behaves similarly
D. None of these
Answer : A
14. Free energy change at equilibrium is
A. Zero
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. Indeterminate
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. Indeterminate
Answer : A
15. Adiabatic compression of a saturated water vapour makes it
A. Supersaturated
B. Superheated
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
A. Supersaturated
B. Superheated
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
16. Which of the following identities can be most easily used to verify steam table data for superheated steam?
A. (?T/?V)S = (?p/?S)V
B. (?T/?P)S = (?V/?S)P
C. (?P/?T)V = (?S/?V)T
D. (?V/?T)P = -(?S/?P)T
Answer : D
A. (?T/?V)S = (?p/?S)V
B. (?T/?P)S = (?V/?S)P
C. (?P/?T)V = (?S/?V)T
D. (?V/?T)P = -(?S/?P)T
Answer : D
17. The extensive properties are
A. Volume, mass and number of moles
B. Free energy, entropy and enthalpy
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Volume, mass and number of moles
B. Free energy, entropy and enthalpy
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
18. To obtain integrated form of Clausius-Clapeyron equation, ln (P2/P1) = (?HV/R) (1/T1 - 1/T2) from the exact Clapeyron equation, it is assumed that the
A. Volume of the liquid phase is negligible compared to that of vapour phase
B. Vapour phase behaves as an ideal gas
C. Heat of vaporisation is independent of temperature
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : D
A. Volume of the liquid phase is negligible compared to that of vapour phase
B. Vapour phase behaves as an ideal gas
C. Heat of vaporisation is independent of temperature
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : D
19. The necessary condition for phase equilibrium in a multiphase system of N components is that the
A. Chemical potentials of a given component should be equal in all phases
B. Chemical potentials of all components should be same in a particular phase
C. Sum of the chemical potentials of any given component in all the phases should be the same
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Chemical potentials of a given component should be equal in all phases
B. Chemical potentials of all components should be same in a particular phase
C. Sum of the chemical potentials of any given component in all the phases should be the same
D. None of these
Answer : A
20. Heat evolved/absorbed during conversion of a substance from one allotropic form to another is termed as the heat of
A. Fusion
B. Vaporisation
C. Transition
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Fusion
B. Vaporisation
C. Transition
D. None of these
Answer : C
21. A refrigeration cycle is the same as a __________ cycle,
A. Turbine
B. Heat engine
C. Reversed heat engine
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Turbine
B. Heat engine
C. Reversed heat engine
D. None of these
Answer : C
22. The work done in isothermal compression compared to that in adiabatic compression will be
A. Less
B. More
C. Same
D. More or less depending upon the extent of work done
Answer : B
A. Less
B. More
C. Same
D. More or less depending upon the extent of work done
Answer : B
23. Melting of ice exemplifies a/an
A. Adiabatic process
B. Endothermic reaction
C. Exothermic reaction
D. Process involving a chemical reaction
Answer : B
A. Adiabatic process
B. Endothermic reaction
C. Exothermic reaction
D. Process involving a chemical reaction
Answer : B
24. The compressibility factor of a gas is given by (where, V1 = actual volume of the gas V2 = gas volume predicted by ideal gas law)
A. V1/V2
B. V2/V1
C. V1 - V2
D. V1.V2
Answer : A
A. V1/V2
B. V2/V1
C. V1 - V2
D. V1.V2
Answer : A
25. Forward reaction will be favoured for the exothermic reaction, represented by CO + H2O ? CO2 + H2, by
A. Low temperature and high pressure
B. Low temperature and low pressure
C. High temperature and high pressure
D. High temperature and low pressure
Answer : A
A. Low temperature and high pressure
B. Low temperature and low pressure
C. High temperature and high pressure
D. High temperature and low pressure
Answer : A
26. Mollier diagram is a plot of
A. Temperature vs. enthalpy
B. Temperature vs. enthalpy
C. Entropy vs. enthalpy
D. Temperature vs. internal energy
Answer : C
A. Temperature vs. enthalpy
B. Temperature vs. enthalpy
C. Entropy vs. enthalpy
D. Temperature vs. internal energy
Answer : C
27. Pick out the extensive property out of the following.
A. Surface tension
B. Free energy
C. Specific heat
D. Refractive index
Answer : B
A. Surface tension
B. Free energy
C. Specific heat
D. Refractive index
Answer : B
28. Free energy
A. Decreases in all spontaneous (or irreversible) processes
B. Change during a spontaneous process has a negative value
C. Remains unchanged in reversible processes carried at constant temperature and pressure
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Decreases in all spontaneous (or irreversible) processes
B. Change during a spontaneous process has a negative value
C. Remains unchanged in reversible processes carried at constant temperature and pressure
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
29. In an isothermal process on an ideal gas, the pressure increases by 0.5 percent. The volume decreases by about __________ percent.
A. 0.25
B. 0.5
C. 0.75
D. 1
Answer : B
A. 0.25
B. 0.5
C. 0.75
D. 1
Answer : B
30. For an irreversible process involving only pressure-volume work
A. (dF)T, p <0
B. (dF)T, p = 0
C. (dF)T, p > 0
D. (dA)T, v >0
Answer : A
A. (dF)T, p <0
B. (dF)T, p = 0
C. (dF)T, p > 0
D. (dA)T, v >0
Answer : A
31. Chemical potential is a/an
A. Extensive property
B. Intensive property
C. Force which drives the chemical system to equilibrium
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Extensive property
B. Intensive property
C. Force which drives the chemical system to equilibrium
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
32. In an irreversible process
A. Tds = dE - dW = 0
B. dE - dW - Tds = 0
C. Tds - dE + dW < 0
D. Tds - dT + dW < 0
Answer : C
A. Tds = dE - dW = 0
B. dE - dW - Tds = 0
C. Tds - dE + dW < 0
D. Tds - dT + dW < 0
Answer : C
33. The equation Tds = dE - PdV applies to
A. Single phase fluid of varying composition
B. Single phase fluid of constant composition
C. Open as well as closed systems
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Single phase fluid of varying composition
B. Single phase fluid of constant composition
C. Open as well as closed systems
D. Both (B) and (C)
Answer : D
34. As the entropy of the universe is increasing, day by day, the work producing capacity of a heat engine is
A. Not changed
B. Decreasing
C. Increasing
D. Data sufficient, can't be predicted
Answer : B
A. Not changed
B. Decreasing
C. Increasing
D. Data sufficient, can't be predicted
Answer : B
35. The compressibility factor for an ideal gas is 1. Its value for any other real gas is
A. 1
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. Either (B) or (C), depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : D
A. 1
B. < 1
C. > 1
D. Either (B) or (C), depends on the nature of the gas
Answer : D
36. The unity of Planck's constant 'h' in the equation, E = hv is
A. J/s
B. J.S
C. J/kmol
D. kmol/J
Answer : B
A. J/s
B. J.S
C. J/kmol
D. kmol/J
Answer : B
37. Which of the following units is not present in both the vapor compression refrigeration system and absorption refrigeration system?
A. Expansion valve
B. Condenser
C. Refrigerator
D. Compressor
Answer : D
A. Expansion valve
B. Condenser
C. Refrigerator
D. Compressor
Answer : D
38. The gas law (PV = RT) is true for an __________ change.
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Isothermal
B. Adiabatic
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
39. At normal boiling point, molar entropy of vaporisation is __________ Joule/K°.mole.
A. 72
B. 92
C. 142
D. 192
Answer : B
A. 72
B. 92
C. 142
D. 192
Answer : B
40. The fugacity of a gas in a mixture is equal to the product of its mole fraction and its fugacity in the pure state at the total pressure of the mixture. This is
A. The statement as per Gibbs-Helmholtz
B. Called Lewis-Randall rule
C. Henry's law
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. The statement as per Gibbs-Helmholtz
B. Called Lewis-Randall rule
C. Henry's law
D. None of these
Answer : B
41. In an ideal gas mixture, fugacity of a species is equal to its
A. Vapor pressure
B. Partial pressure
C. Chemical potential
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Vapor pressure
B. Partial pressure
C. Chemical potential
D. None of these
Answer : B
42. COP of a refrigerator drawing 1 kW of power per ton of refrigeration is about
A. 0.5
B. 3.5
C. 4.5
D. 8.5
Answer : B
A. 0.5
B. 3.5
C. 4.5
D. 8.5
Answer : B
43. Gibbs free energy of mixing at constant pressure and temperature is always
A. 0
B. ?
C. + ve
D. - ve
Answer : D
A. 0
B. ?
C. + ve
D. - ve
Answer : D
A. 448
B. 224
C. 22.4
D. Data insufficient; can't be computed
Answer : A
45. Sublimation temperature of dry ice (solid CO2) is __________ °C.
A. -273
B. 0
C. -78
D. 5
Answer : C
A. -273
B. 0
C. -78
D. 5
Answer : C
46. The most important application of distribution law is in
A. Evaporation
B. Liquid extraction
C. Drying
D. Distillation
Answer : B
A. Evaporation
B. Liquid extraction
C. Drying
D. Distillation
Answer : B
47. Critical compressibility factor for all substances
A. Are more or less constant (vary from 0.2 to 0.3)
B. Vary as square of the absolute temperature
C. Vary as square of the absolute pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Are more or less constant (vary from 0.2 to 0.3)
B. Vary as square of the absolute temperature
C. Vary as square of the absolute pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
48. For an isothermal reversible compression of an ideal gas
A. Only ?E = 0
B. Only ?H =0
C. ?E = ?H = 0
D. dQ = dE
Answer : C
A. Only ?E = 0
B. Only ?H =0
C. ?E = ?H = 0
D. dQ = dE
Answer : C
49. Gibbs-Duhem equation
A. States that n1d?1 + n2d?2 + ....njd?j = 0, for a system of definite composition at constant temperature and pressure
B. Applies only to binary systems
C. Finds no application in gas-liquid equilibria involved in distillation
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. States that n1d?1 + n2d?2 + ....njd?j = 0, for a system of definite composition at constant temperature and pressure
B. Applies only to binary systems
C. Finds no application in gas-liquid equilibria involved in distillation
D. None of these
Answer : A
50. An ideal monatomic gas is taken round the cycle ABCDA as shown below in the P-V diagram. The work done during the cycle is
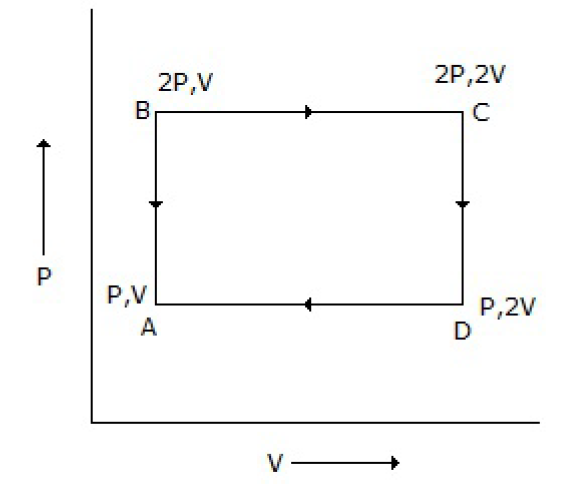
A. PV
B. 2PV
C. PV/2
D. 0
Answer : A

A. PV
B. 2PV
C. PV/2
D. 0
Answer : A
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Operating System 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC CPO
1000+ Error Detection Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Electrical Circuits Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
DRDO - Power Plant Engineering 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Power Plant Engineering MCQ Solved Paper for SSC Scientific Assistant
1000+ Asp Programming MCQ for SSC Scientific Assistant [Solved]