1000+ Fluid Mechanics MCQ for SSC CGL [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The bulk modulus of elasticity
A. Has the dimensions of 1/pressure
B. Increases with pressure
C. Is large when fluid is more compressible
D. Is independent of pressure and viscosity
Answer : B
A. Has the dimensions of 1/pressure
B. Increases with pressure
C. Is large when fluid is more compressible
D. Is independent of pressure and viscosity
Answer : B
2. The tendency of a liquid surface to contract is due to the following property
A. Cohesion
B. Adhesion
C. Viscosity
D. Surface tension
Answer : D
A. Cohesion
B. Adhesion
C. Viscosity
D. Surface tension
Answer : D
3. When a body is placed over a liquid, it will float if
A. Gravitational force is equal to the up-thrust of the liquid
B. Gravitational force is less than the up-thrust of the liquid
C. Gravitational force is more than the up-thrust of the liquid
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Gravitational force is equal to the up-thrust of the liquid
B. Gravitational force is less than the up-thrust of the liquid
C. Gravitational force is more than the up-thrust of the liquid
D. None of the above
Answer : B
4. The critical depth meter is used to measure
A. Velocity of flow in an open channel
B. Depth of flow in an open channel
C. Hydraulic jump
D. Depth of channel
Answer : C
A. Velocity of flow in an open channel
B. Depth of flow in an open channel
C. Hydraulic jump
D. Depth of channel
Answer : C
5. A vertical wall is subjected to a pressure due to one kind of liquid, on one of its sides. The total pressure on the wall acts at a distance __________ from the liquid surface.
A. H/3
B. H/2
C. 2H/3
D. 3H/4
Answer : C
A. H/3
B. H/2
C. 2H/3
D. 3H/4
Answer : C
6. Froude's number is the ratio of inertia force to
A. Pressure force
B. Elastic force
C. Gravity force
D. Surface tension force
Answer : C
A. Pressure force
B. Elastic force
C. Gravity force
D. Surface tension force
Answer : C
7. A tank of uniform cross-sectional area (A) containing liquid upto height (H1) has an orifice of cross-sectional area (a) at its bottom. The time required to empty the tank completely will be
A. (2A?H?)/(Cd × a?2g)
B. (2AH?)/(Cd × a?2g)
C. (2AH?3/2)/(Cd × a?2g)
D. (2AH?²)/(Cd × a?2g)
Answer : A
A. (2A?H?)/(Cd × a?2g)
B. (2AH?)/(Cd × a?2g)
C. (2AH?3/2)/(Cd × a?2g)
D. (2AH?²)/(Cd × a?2g)
Answer : A
8. The Metacentric heights of two floating bodies A and B are 1 m and 1.5 m respectively. Select the correct statement.
A. The bodies A and B have equal stability
B. The body A is more stable than body B
C. The body B is more stable than body A
D. The bodies A and B are unstable
Answer : C
A. The bodies A and B have equal stability
B. The body A is more stable than body B
C. The body B is more stable than body A
D. The bodies A and B are unstable
Answer : C
9. A large Reynold number is indication of
A. Smooth and streamline flow
B. Laminar flow
C. Steady flow
D. Highly turbulent flow
Answer : D
A. Smooth and streamline flow
B. Laminar flow
C. Steady flow
D. Highly turbulent flow
Answer : D
10. A nozzle is generally made of
A. Cylindrical shape
B. Convergent shape
C. Divergent shape
D. Convergent-divergent shape
Answer : B
A. Cylindrical shape
B. Convergent shape
C. Divergent shape
D. Convergent-divergent shape
Answer : B
11. Steady flow occurs when
A. The direction and magnitude of the velocity at all points are identical
B. The velocity of successive fluid particles, at any point, is the same at successive periods of time
C. The magnitude and direction of the velocity do not change from point to point in the fluid
D. The fluid particles move in plane or parallel planes and the streamline patterns are identical in each plane
Answer : B
A. The direction and magnitude of the velocity at all points are identical
B. The velocity of successive fluid particles, at any point, is the same at successive periods of time
C. The magnitude and direction of the velocity do not change from point to point in the fluid
D. The fluid particles move in plane or parallel planes and the streamline patterns are identical in each plane
Answer : B
12. The centre of gravity of the volume of the liquid displaced is called
A. Centre of pressure
B. Centre of buoyancy
C. Metacentre
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Centre of pressure
B. Centre of buoyancy
C. Metacentre
D. None of these
Answer : B
13. Stoke is the unit of
A. Kinematic viscosity in C. G. S. units
B. Kinematic viscosity in M. K. S. units
C. Dynamic viscosity in M. K. S. units
D. Dynamic viscosity in S. I. units
Answer : A
A. Kinematic viscosity in C. G. S. units
B. Kinematic viscosity in M. K. S. units
C. Dynamic viscosity in M. K. S. units
D. Dynamic viscosity in S. I. units
Answer : A
14. Free surface of a liquid tends to contract to the smallest possible area due to force of
A. Surface tension
B. Viscosity
C. Friction
D. Cohesion
Answer : A
A. Surface tension
B. Viscosity
C. Friction
D. Cohesion
Answer : A
15. Two dimensional flows occurs when
A. The direction and magnitude of the velocity at all points are identical
B. The velocity of successive fluid particles, at any point, is the same at successive periods of time
C. The magnitude and direction of the velocity do not change from point to point in the fluid
D. The fluid particles move in plane or parallel planes and the streamline patterns are identical in each plane
Answer : D
A. The direction and magnitude of the velocity at all points are identical
B. The velocity of successive fluid particles, at any point, is the same at successive periods of time
C. The magnitude and direction of the velocity do not change from point to point in the fluid
D. The fluid particles move in plane or parallel planes and the streamline patterns are identical in each plane
Answer : D
16. A water tank contains 1.3 m deep water. The pressure exerted by the water per metre length of the tank is
A. 2.89 kN
B. 8.29 kN
C. 9.28 kN
D. 28.9 kN
Answer : B
A. 2.89 kN
B. 8.29 kN
C. 9.28 kN
D. 28.9 kN
Answer : B
17. The dynamic viscosity of gases __________ with rise in temperature.
A. Remain unaffected
B. Increases
C. Decreases
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Remain unaffected
B. Increases
C. Decreases
D. None of these
Answer : B
18. In the case of steady flow of a fluid, the acceleration of any fluid particle is
A. Constant
B. Variable
C. Zero
D. Zero under limiting conditions
Answer : C
A. Constant
B. Variable
C. Zero
D. Zero under limiting conditions
Answer : C
19. A liquid compressed in cylinder has a volume of 0.04 m3 at 50 kg/cm² and a volume of 0.039 m3 at 150 kg/cm². The bulk modulus of elasticity of liquid is
A. 400 kg/cm²
B. 4000 kg/cm²
C. 40 × 10? kg/cm²
D. 40 × 10? kg/cm²
Answer : B
A. 400 kg/cm²
B. 4000 kg/cm²
C. 40 × 10? kg/cm²
D. 40 × 10? kg/cm²
Answer : B
20. Hydrometer is used to determine
A. Specific gravity of liquids
B. Specific gravity of solids
C. Specific gravity of gases
D. Relative humidity
Answer : A
A. Specific gravity of liquids
B. Specific gravity of solids
C. Specific gravity of gases
D. Relative humidity
Answer : A
21. A perfect gas
A. Has constant viscosity
B. Has zero viscosity
C. Is in compressible
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. Has constant viscosity
B. Has zero viscosity
C. Is in compressible
D. None of the above
Answer : D
22. The velocity corresponding to Reynold number of 2800, is called
A. Sub-sonic velocity
B. Super-sonic velocity
C. Lower critical velocity
D. Higher critical velocity
Answer : D
A. Sub-sonic velocity
B. Super-sonic velocity
C. Lower critical velocity
D. Higher critical velocity
Answer : D
23. The discharge through a channel of trapezoidal section is maximum when
A. Width of channel at the top is equal to twice the width at the bottom
B. Depth of channel is equal to the width at the bottom
C. The sloping side is equal to half the width at the top
D. The sloping side is equal to the width at the bottom
Answer : C
A. Width of channel at the top is equal to twice the width at the bottom
B. Depth of channel is equal to the width at the bottom
C. The sloping side is equal to half the width at the top
D. The sloping side is equal to the width at the bottom
Answer : C
24. Principle of similitude forms the basis of
A. Comparing two identical equipments
B. Designing models so that the result can be converted to prototypes
C. Comparing similarity between design and actual equipment
D. Hydraulic designs
Answer : B
A. Comparing two identical equipments
B. Designing models so that the result can be converted to prototypes
C. Comparing similarity between design and actual equipment
D. Hydraulic designs
Answer : B
25. A compound pipe is required to be replaced by a new pipe. The two pipes are said to be equivalent, if
A. Length of both the pipes is same
B. Diameter of both the pipes is same
C. Loss of head and discharge of both the pipes is same
D. Loss of head and velocity of flow in both the pipes is same
Answer : C
A. Length of both the pipes is same
B. Diameter of both the pipes is same
C. Loss of head and discharge of both the pipes is same
D. Loss of head and velocity of flow in both the pipes is same
Answer : C
26. The velocity of the liquid flowing through the divergent portion of a Venturimeter
A. Remains constant
B. Increases
C. Decreases
D. Depends upon mass of liquid
Answer : C
A. Remains constant
B. Increases
C. Decreases
D. Depends upon mass of liquid
Answer : C
27. The purpose of a surge tank is
A. To control the pressure variations due to rapid changes in the pipe line flow
B. To eliminate water hammer possibilities
C. To regulate flow of water to turbines by providing necessary retarding head of water
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. To control the pressure variations due to rapid changes in the pipe line flow
B. To eliminate water hammer possibilities
C. To regulate flow of water to turbines by providing necessary retarding head of water
D. All of the above
Answer : D
28. A balloon lifting in air follows the following principle
A. Law of gravitation
B. Archimedes principle
C. Principle of buoyancy
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Law of gravitation
B. Archimedes principle
C. Principle of buoyancy
D. All of the above
Answer : D
29. The flow of water through the hole in the bottom of a wash basin is an example of
A. Steady flow
B. Uniform flow
C. Free vortex
D. Forced vortex
Answer : C
A. Steady flow
B. Uniform flow
C. Free vortex
D. Forced vortex
Answer : C
30. The units of dynamic or absolute viscosity are
A. Metres² per sec
B. kg sec/meter
C. Newton-sec per meter
D. Newton-sec² per meter
Answer : C
A. Metres² per sec
B. kg sec/meter
C. Newton-sec per meter
D. Newton-sec² per meter
Answer : C
31. According to the principle of buoyancy a body totally or partially immersed in a fluid will be lifted up by a force equal to
A. The weight of the body
B. More than the weight of the body
C. Less than the weight of the body
D. Weight of the fluid displaced by the body
Answer : D
A. The weight of the body
B. More than the weight of the body
C. Less than the weight of the body
D. Weight of the fluid displaced by the body
Answer : D
32. The divergent portion of a Venturimeter is made longer than convergent portion in order to
A. Avoid the tendency of breaking away the stream of liquid
B. To minimise frictional losses
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Avoid the tendency of breaking away the stream of liquid
B. To minimise frictional losses
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
33. The two important forces for a floating body are
A. Buoyancy, gravity
B. Buoyancy, pressure
C. Buoyancy, inertial
D. Inertial, gravity
Answer : A
A. Buoyancy, gravity
B. Buoyancy, pressure
C. Buoyancy, inertial
D. Inertial, gravity
Answer : A
34. The hydraulic gradient line lies over the centre line of the pipe by an amount equal to the
A. Pressure head
B. Velocity head
C. Pressure head + velocity head
D. Pressure head - velocity head
Answer : A
A. Pressure head
B. Velocity head
C. Pressure head + velocity head
D. Pressure head - velocity head
Answer : A
35. Non uniform flow occurs when
A. The direction and magnitude of the velocity at all points are identical
B. The velocity of successive fluid particles, at any point, is the same at successive periods of time
C. Velocity, depth, pressure, etc. change from point to point in the fluid flow.
D. The fluid particles move in plane or parallel planes and the streamline patterns are identical in each plane
Answer : C
A. The direction and magnitude of the velocity at all points are identical
B. The velocity of successive fluid particles, at any point, is the same at successive periods of time
C. Velocity, depth, pressure, etc. change from point to point in the fluid flow.
D. The fluid particles move in plane or parallel planes and the streamline patterns are identical in each plane
Answer : C
36. A vertically immersed surface is shown in the below figure. The distance of its centre of pressure from the water surface is 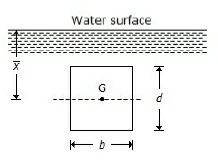
A. (bd²/12) + x?
B. (d²/12 x?) + x?
C. b²/12 + x?
D. d²/12 + x?
Answer : B

A. (bd²/12) + x?
B. (d²/12 x?) + x?
C. b²/12 + x?
D. d²/12 + x?
Answer : B
37. The normal stress is same in all directions at a point in a fluid
A. Only when the fluid is frictionless
B. Only when the fluid is incompressible and has zero viscosity
C. When there is no motion of one fluid layer relative to an adjacent layer
D. Irrespective of the motion of one fluid layer relative to an adjacent layer
Answer : C
A. Only when the fluid is frictionless
B. Only when the fluid is incompressible and has zero viscosity
C. When there is no motion of one fluid layer relative to an adjacent layer
D. Irrespective of the motion of one fluid layer relative to an adjacent layer
Answer : C
38. The atmospheric pressure at sea level is
A. 103 kN/m2
B. 10.3 m of water
C. 760 mm of mercury
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. 103 kN/m2
B. 10.3 m of water
C. 760 mm of mercury
D. All of these
Answer : D
39. The value of the coefficient of compressibility for water at ordinary pressure and temperature in kg/cm is equal to
A. 2100
B. 2700
C. 10,000
D. 21,000
Answer : D
A. 2100
B. 2700
C. 10,000
D. 21,000
Answer : D
40. For similarity, in addition to models being geometrically similar to prototype, the following in both cases should also be equal
A. Ratio of inertial force to force due to viscosity
B. Ratio of inertial force to force due to gravitation
C. Ratio of inertial force to force due to surface tension
D. All the four ratios of inertial force to force due to viscosity, gravitation, surface tension, and elasticity
Answer : D
A. Ratio of inertial force to force due to viscosity
B. Ratio of inertial force to force due to gravitation
C. Ratio of inertial force to force due to surface tension
D. All the four ratios of inertial force to force due to viscosity, gravitation, surface tension, and elasticity
Answer : D
41. Coefficient of resistance is the ratio of
A. Actual velocity of jet at vena-contracta to the theoretical velocity
B. Area of jet at vena-contracta to the area of orifice
C. Loss of head in the orifice to the head of water available at the exit of the orifice
D. Actual discharge through an orifice to the theoretical discharge
Answer : C
A. Actual velocity of jet at vena-contracta to the theoretical velocity
B. Area of jet at vena-contracta to the area of orifice
C. Loss of head in the orifice to the head of water available at the exit of the orifice
D. Actual discharge through an orifice to the theoretical discharge
Answer : C
42. A manometer is used to measure
A. Low pressure
B. Moderate pressure
C. High pressure
D. Atmospheric pressure
Answer : C
A. Low pressure
B. Moderate pressure
C. High pressure
D. Atmospheric pressure
Answer : C
43. A structure used to dam up a stream or river over which the water flows is called
A. Orifice
B. Notch
C. Weir
D. Dam
Answer : C
A. Orifice
B. Notch
C. Weir
D. Dam
Answer : C
44. Capillary action is due to the
A. Surface tension
B. Cohesion of the liquid
C. Adhesion of the liquid molecules and the molecules on the surface of a solid
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Surface tension
B. Cohesion of the liquid
C. Adhesion of the liquid molecules and the molecules on the surface of a solid
D. All of the above
Answer : D
45. The total pressure on a horizontally immersed surface is (where w = Specific weight of the liquid, A = Area of the immersed surface, and x = Depth of the centre of gravity of the immersed surface from the liquid surface)
A. wA
B. wx
C. wAx
D. wA/x
Answer : C
A. wA
B. wx
C. wAx
D. wA/x
Answer : C
46. Bulk modulus of a fluid is the ratio of
A. Shear stress to shear strain
B. Increase in volume to the viscosity of fluid
C. Increase in pressure to the volumetric strain
D. Critical velocity to the viscosity of fluid
Answer : C
A. Shear stress to shear strain
B. Increase in volume to the viscosity of fluid
C. Increase in pressure to the volumetric strain
D. Critical velocity to the viscosity of fluid
Answer : C
47. A flow in which the viscosity of fluid is dominating over the inertia force is called
A. Steady flow
B. Unsteady flow
C. Laminar flow
D. Turbulent flow
Answer : C
A. Steady flow
B. Unsteady flow
C. Laminar flow
D. Turbulent flow
Answer : C
48. The equation of continuity holds good when the flow
A. Is steady
B. Is one dimensional
C. Velocity is uniform at all the cross sections
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Is steady
B. Is one dimensional
C. Velocity is uniform at all the cross sections
D. All of the above
Answer : D
49. Unit of surface tension is
A. Energy/unit area
B. Velocity/unit area
C. Both of the above
D. It has no units
Answer : A
A. Energy/unit area
B. Velocity/unit area
C. Both of the above
D. It has no units
Answer : A
50. The stability of a dam is checked for
A. Tension at the base
B. Overturning of the wall or dam
C. Sliding of the wall or dam
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. Tension at the base
B. Overturning of the wall or dam
C. Sliding of the wall or dam
D. All of these
Answer : D
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Current Affairs June 2017 MCQ Solved Paper for SSC CPO
1000+ General Science Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Current Affairs May 2017 MCQ for SSC MTS [Solved]
Cell - the unit of life MCQ Solved Paper for IIFT
Tumors of the prostate MCQ Solved Paper for RRB Group D
1000+ Sentence Correction Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]