Basics of Economics 1000+ MCQ with answer for IIFT
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. In the long-run competitive equilibrium, the theory predicts that:
A. TC = TR and MC = MR
B. Firms operate at a minimum average total cost
C. There is no incentive for entry or exit of firms
D. All these conditions exist
Answer : D
A. TC = TR and MC = MR
B. Firms operate at a minimum average total cost
C. There is no incentive for entry or exit of firms
D. All these conditions exist
Answer : D
2. The cost of firms in cournot model are:
A. identical
B. differential
C. very high
D. very low
Answer : A
A. identical
B. differential
C. very high
D. very low
Answer : A
3. Perfect competition implies:
A. Differentiated goods
B. Homogeneous goods
C. Advertised goods
D. Distress sale of goods
Answer : B
A. Differentiated goods
B. Homogeneous goods
C. Advertised goods
D. Distress sale of goods
Answer : B
4. If the marginal utility is divided by the price of the commodity then it is called:
A. Real Marginal Utility
B. Gross Marginal Utility
C. Weighted Marginal Utility
D. Money Marginal Utility
Answer : C
A. Real Marginal Utility
B. Gross Marginal Utility
C. Weighted Marginal Utility
D. Money Marginal Utility
Answer : C
5. Price discrimination occurs when:
A. Different prices are charged to different consumers for homogenous products
B. Same prices are charged for differentiated products
C. Different prices are charged for homogenous goods for successive units to the same customer
D. Any of the above condition is present
Answer : D
A. Different prices are charged to different consumers for homogenous products
B. Same prices are charged for differentiated products
C. Different prices are charged for homogenous goods for successive units to the same customer
D. Any of the above condition is present
Answer : D
6. When income of the consumer increases then demand curve of an inferior good:
A. Shifts rightward
B. Shifts leftward
C. Does not shift
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Shifts rightward
B. Shifts leftward
C. Does not shift
D. None of the above
Answer : B
7. Rent is a creation of value, not of wealth who made this observation?
A. Adam Smith
B. David Ricardo
C. Alfred Marshal
D. A.C.Pigou
Answer : B
A. Adam Smith
B. David Ricardo
C. Alfred Marshal
D. A.C.Pigou
Answer : B
8. The study of economics just in theoretical way is called:
A. Positive Economics
B. Normative Economics
C. Micro Economics
D. Development Economics
Answer : A
A. Positive Economics
B. Normative Economics
C. Micro Economics
D. Development Economics
Answer : A
9. The competitive equilibrium leads to:
A. The firms producing with excess capacity
B. The firms producing at their minimum costs
C. Firms producing at a cost higher than the minimum
D. Some firms producing under decreasing costs and others under increasing costs
Answer : B
A. The firms producing with excess capacity
B. The firms producing at their minimum costs
C. Firms producing at a cost higher than the minimum
D. Some firms producing under decreasing costs and others under increasing costs
Answer : B
10. Quantity demanded or supplied is measured in:
A. Monetary units
B. Physical units
C. Relative units
D. Constant units
Answer : B
A. Monetary units
B. Physical units
C. Relative units
D. Constant units
Answer : B
11. The monopolist firm is price setter. The price setter firm is one which:
A. Can influence the market price
B. Cannot influence the market price
C. Can sell at zero price
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Can influence the market price
B. Cannot influence the market price
C. Can sell at zero price
D. None of the above
Answer : A
12. The engineering production function and engineering costs curves are concerned with the:
A. Production cost
B. Collection cost
C. Raw material costs
D. Distribution costs
Answer : A
A. Production cost
B. Collection cost
C. Raw material costs
D. Distribution costs
Answer : A
13. Technological efficiency:
A. Is the same as economic efficiency
B. Is achieved when the output produced is maximum for the given level of inputs
C. Means that there is only one way to produce a given quantity of output
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Is the same as economic efficiency
B. Is achieved when the output produced is maximum for the given level of inputs
C. Means that there is only one way to produce a given quantity of output
D. None of the above
Answer : B
14. A monopolist is:
A. Price winner
B. Price searcher
C. Price taker
D. Price leaver
Answer : B
A. Price winner
B. Price searcher
C. Price taker
D. Price leaver
Answer : B
15. An economic model describing the working of an economy consists of:
A. Functional relationships
B. Family relationships
C. Economic position
D. Stagnant relationships
Answer : A
A. Functional relationships
B. Family relationships
C. Economic position
D. Stagnant relationships
Answer : A
16. Total utility:
A. Diminishes with increased consumption
B. Reflects the overall level of satisfaction of the consumer
C. Is directly related to the price the consumer is willing to pay for a good or service
D. Is independent of price changes
Answer : B
A. Diminishes with increased consumption
B. Reflects the overall level of satisfaction of the consumer
C. Is directly related to the price the consumer is willing to pay for a good or service
D. Is independent of price changes
Answer : B
17. The budget constraint equation of the firm is:
A.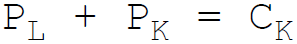
B.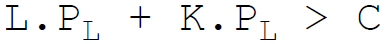
C.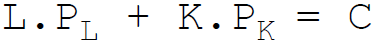
D.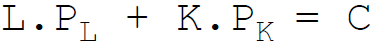
Answer : C
A.
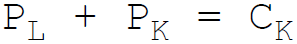
B.
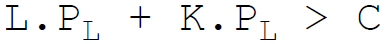
C.
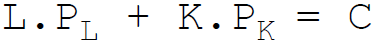
D.
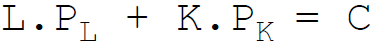
Answer : C
18. According to law of Equi-Marginal Utility when price of commodity falls then we bought:
A. More units
B. Less units
C. Same units
D. Zero units
Answer : A
A. More units
B. Less units
C. Same units
D. Zero units
Answer : A
19. The demand of the necessities is:
A. More elastic
B. Less elastic
C. Unit elastic
D. Zero elastic
Answer : B
A. More elastic
B. Less elastic
C. Unit elastic
D. Zero elastic
Answer : B
20. An iso-product (an isoquant) curve slopes:
A. Downward to the left
B. Downward to the right
C. Upward to the right
D. Upward to the left
Answer : B
A. Downward to the left
B. Downward to the right
C. Upward to the right
D. Upward to the left
Answer : B
21. If there are many producers, each of whom has an individual production possibility curve, then the lowest marginal cost producer of good X is the producer:
A. Who must sacrifice fewer units of every other goods than any other producer
B. Who can produce more X per hour than any other producerC. Who must sacrifice more units of every other goods than any other producer
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Who must sacrifice fewer units of every other goods than any other producer
B. Who can produce more X per hour than any other producer
D. None of the above
Answer : A
22. Economics define technology as:
A. Societys knowledge of production
B. Applied science
C. Knowledge of science and mathematics
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Societys knowledge of production
B. Applied science
C. Knowledge of science and mathematics
D. None of the above
Answer : A
23. Equilibrium of a firm represents maximization of profits as well as:
A. Maximization of losses
B. Minimization of losses
C. Minimization of profits
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Maximization of losses
B. Minimization of losses
C. Minimization of profits
D. None of the above
Answer : B
24. The fixed cost of a firm:
A. Are fixed even in the long period
B. When expressed as an average, show a continuous decline with increase of output
C. Do not reflect diminishing marginal returns
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Are fixed even in the long period
B. When expressed as an average, show a continuous decline with increase of output
C. Do not reflect diminishing marginal returns
D. None of the above
Answer : A
25. The slope of an iso-quant represents:
A. MRS
B. MRT
C. MRTS
D. MRPS
Answer : C
A. MRS
B. MRT
C. MRTS
D. MRPS
Answer : C
26. If the price of Pepsi Cola goes down, you would predict:
A. An increase in supply of coca cola
B. A decrease in supply of coca cola
C. An increase in demand for coca cola
D. A decrease in demand for coca cola
Answer : D
A. An increase in supply of coca cola
B. A decrease in supply of coca cola
C. An increase in demand for coca cola
D. A decrease in demand for coca cola
Answer : D
27. Demand of a commodity is elastic when:
A. Change in its price causes a proportionately greater change in its quantity demanded
B. Change in its price does not change its quantity demanded
C. Change in consumers income causes change in demand
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Change in its price causes a proportionately greater change in its quantity demanded
B. Change in its price does not change its quantity demanded
C. Change in consumers income causes change in demand
D. None of the above
Answer : A
28. When total product (TP) is maximum:
A. MP is negative
B. MP is infinite
C. MP is zero
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. MP is negative
B. MP is infinite
C. MP is zero
D. None of the above
Answer : C
29. The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money is the major work of :
A. N.Kaldor
B. Alfred Marshal
C. J.M.Keynes
D. J.S.Duesenberry
Answer : C
A. N.Kaldor
B. Alfred Marshal
C. J.M.Keynes
D. J.S.Duesenberry
Answer : C
30. The slope of the iso-cost line (budget line) is determined by:
A. Pricing of two factors
B. Productivity of the two factors
C. Degree of substitutability of two factors
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Pricing of two factors
B. Productivity of the two factors
C. Degree of substitutability of two factors
D. None of the above
Answer : A
31. If two goods have same marginal utility for a consumer then:
A. He will consume only one of them
B. He will consume equal quantities of them
C. He will be willing to pay the same price for each of them
D. The total utility gained from each of them is equal
Answer : C
A. He will consume only one of them
B. He will consume equal quantities of them
C. He will be willing to pay the same price for each of them
D. The total utility gained from each of them is equal
Answer : C
32. On a straight line demand curve, elasticity of demand at the midpoint is:
A. Equal to zero
B. Equal to one
C. Equal to infinity
D. More than one
Answer : B
A. Equal to zero
B. Equal to one
C. Equal to infinity
D. More than one
Answer : B
33. The good will highest income elasticity is:
A. Beef
B. Mutton
C. Bread
D. Motion-picture tickets
Answer : D
A. Beef
B. Mutton
C. Bread
D. Motion-picture tickets
Answer : D
34. Excess capacity is not found under:
A. Monopoly
B. Monopolistic competition
C. Perfect competition
D. Oligopoly
Answer : C
A. Monopoly
B. Monopolistic competition
C. Perfect competition
D. Oligopoly
Answer : C
35. In case of monopoly, TR curve rises at a:
A. Constant rate
B. Decreasing rate
C. Increasing rate
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Constant rate
B. Decreasing rate
C. Increasing rate
D. None of the above
Answer : B
36. When price increases and with it the total outlay on a commodity also increases, it is a case of:
A. Perfect elasticity (infinitely elastic)
B. Relative elasticity (greater than one elasticity)
C. Perfect inelasticity (zero elasticity)
D. Relative inelasticity (less than one elasticity)
Answer : D
A. Perfect elasticity (infinitely elastic)
B. Relative elasticity (greater than one elasticity)
C. Perfect inelasticity (zero elasticity)
D. Relative inelasticity (less than one elasticity)
Answer : D
37. Now-a-days in real life, we are unable to fined:
A. Monopoly
B. Perfect competition
C. Imperfect competition
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : B
A. Monopoly
B. Perfect competition
C. Imperfect competition
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : B
38. Price effect occurs on the higher IC in case of:
A. Slutsky approach
B. Hicksian approach
C. Marshallian approach
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Slutsky approach
B. Hicksian approach
C. Marshallian approach
D. None of the above
Answer : A
39. Theory of revealed preference is based on:
A. Weak orderings
B. Neutral orderings
C. Partial orderings
D. Strong orderings
Answer : D
A. Weak orderings
B. Neutral orderings
C. Partial orderings
D. Strong orderings
Answer : D
40. Cross-elasticity of demand or cross-price elasticity between two complements will be:
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Infinite
D. Zero
Answer : A
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Infinite
D. Zero
Answer : A
41. When the output of a firm is increasing, its average fixed cost:
A. Declines continuously
B. Remains constant
C. Rises continuously
D. Declines and then rises
Answer : A
A. Declines continuously
B. Remains constant
C. Rises continuously
D. Declines and then rises
Answer : A
42. Ceteris paribus clause in the law of demand means:
A. The price of substitute does not change
B. The taste of the consumer does not change
C. The income of the consumer does not change
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. The price of substitute does not change
B. The taste of the consumer does not change
C. The income of the consumer does not change
D. All of the above
Answer : D
43. If the slope of the isoquant is equal to the slope of isocost, then isoquant is:
A. Concave to the origin
B. Convex to the origin
C. Tangent to the origin
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Concave to the origin
B. Convex to the origin
C. Tangent to the origin
D. None of the above
Answer : B
44. A price is a ratio of exchange between:
A. Money nd exchange
B. Quantity and production
C. Production and consumption
D. Money and quantity
Answer : D
A. Money nd exchange
B. Quantity and production
C. Production and consumption
D. Money and quantity
Answer : D
45. A profit-maximizing monopolist in two separate markets will:
A. Charge the same price in both markets
B. Always charge a higher price in the market where he sells more
C. Always charge a higher price in the market where he sells less
D. Adjust his sales in the two markets so that his marginal revenue in each market just equals his aggregate marginal cost
Answer : D
A. Charge the same price in both markets
B. Always charge a higher price in the market where he sells more
C. Always charge a higher price in the market where he sells less
D. Adjust his sales in the two markets so that his marginal revenue in each market just equals his aggregate marginal cost
Answer : D
46. If there are many firms producing similar but differentiated products, the competition is generally said to be:
A. Oligopoly
B. Pure competition
C. Perfect competition
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : D
A. Oligopoly
B. Pure competition
C. Perfect competition
D. Monopolistic competition
Answer : D
47. When at a given price, the quantity demanded of a commodity is more than the quantity supplied, there will be:
A. An upward pressure on price
B. A downward pressure on price
C. Price will remain unaffected
D. All of the above
Answer : A
A. An upward pressure on price
B. A downward pressure on price
C. Price will remain unaffected
D. All of the above
Answer : A
48. Rational economic behavior on the part of the consumer means that he will:
A. Save as much of his income as possible
B. Spend as much of his income as possible
C. Buy everything at the lowest possible price
D. Make wise choices among available economic goods
Answer : D
A. Save as much of his income as possible
B. Spend as much of his income as possible
C. Buy everything at the lowest possible price
D. Make wise choices among available economic goods
Answer : D
49. Which of the following is called Gossens first law?
A. Law of production
B. The Law of Equi-Marginal Utility
C. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
D. Law of Variable Proportions
Answer : C
A. Law of production
B. The Law of Equi-Marginal Utility
C. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
D. Law of Variable Proportions
Answer : C
50. When marginal costs curve cuts average costs curve, average costs are:
A. Maximum
B. Zero
C. Minimum
D. Equal to one
Answer : C
A. Maximum
B. Zero
C. Minimum
D. Equal to one
Answer : C
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Industrial Engineering & Production Management Test MCQ Solved Paper for GRE
1000+ C Programming Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Phylum - Coelentrata MCQ Solved Paper for SSC JE
Urothelial tumors of the upper & lower urinary tracts MCQ Solved Paper for NMAT
CLAT PG - JavaScript 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Tumors of the prostate 1000+ MCQ with answer for RBI Grade B officer