NMAT - Basics of Economics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. If the prices of goods rise then:
A. The real income of consumer falls
B. The real income of consumer rises
C. The real income of a consumer remains constant
D. The real income of consumer becomes zero
Answer : A
A. The real income of consumer falls
B. The real income of consumer rises
C. The real income of a consumer remains constant
D. The real income of consumer becomes zero
Answer : A
2. Economics define technology as:
A. Societys knowledge of production
B. Applied science
C. Knowledge of science and mathematics
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Societys knowledge of production
B. Applied science
C. Knowledge of science and mathematics
D. None of the above
Answer : A
3. The Hicksian indirect utility function in the form of equation is:
A. x =f(P)
B. x =a-bp
C.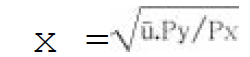
D.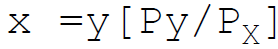
Answer : C
A. x =f(P)
B. x =a-bp
C.
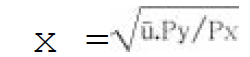
D.
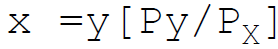
Answer : C
4. Marginal cost curve cuts the average cost curve:
A. At the left of its lowest point
B. At its lowest point
C. At the right of its lowest point
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. At the left of its lowest point
B. At its lowest point
C. At the right of its lowest point
D. None of the above
Answer : B
5. The game theory takes into consideration:
A. Reaction of rival firms
B. Reactions of people
C. No reaction of rival firms
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Reaction of rival firms
B. Reactions of people
C. No reaction of rival firms
D. None of the above
Answer : A
6. A firm is a sum of persons who convert:
A. Goods into services
B. Output into inputs
C. Inputs into outputs
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Goods into services
B. Output into inputs
C. Inputs into outputs
D. None of the above
Answer : C
7. The relationship between price effect, income effect and substitution effect is:
A. P.E = S.E + I.E
B. S.E = P.E +I.E
C. I.E = P.E +S.E
D. S.E = P.E +2I.E
Answer : A
A. P.E = S.E + I.E
B. S.E = P.E +I.E
C. I.E = P.E +S.E
D. S.E = P.E +2I.E
Answer : A
8. Which is not an essential feature of a socialist economy?
A. Social ownership of the means of production
B. Freedom of enterprise
C. Use of centralized planning
D. Government decisions
Answer : B
A. Social ownership of the means of production
B. Freedom of enterprise
C. Use of centralized planning
D. Government decisions
Answer : B
9. If a straight line supply curve makes an intercept on the Y-axis, elasticity of supply is:
A. Equal to unity
B. Less than unity
C. More than unity
D. Zero
Answer : C
A. Equal to unity
B. Less than unity
C. More than unity
D. Zero
Answer : C
10. Demand for a commodity is elastic when it has
A. Only one use
B. Many uses
C. Uses which cannot be postponed
D. Uses very essential for the consumer
Answer : B
A. Only one use
B. Many uses
C. Uses which cannot be postponed
D. Uses very essential for the consumer
Answer : B
11. In the long-run:
A. Fixed cost will be greater than variable cost
B. Variable costs will be greater than fixed costs
C. All costs are variable costs
D. All costs are fixed costs
Answer : C
A. Fixed cost will be greater than variable cost
B. Variable costs will be greater than fixed costs
C. All costs are variable costs
D. All costs are fixed costs
Answer : C
12. One way the government can induce a monopolist to expand his output is by imposing:
A. A specific tax on the monopolists output
B. A price ceiling that make the monopolist lower his price
C. A price floor that make the monopolist raise his price
D. A heavy tax on the monopolists profit
Answer : B
A. A specific tax on the monopolists output
B. A price ceiling that make the monopolist lower his price
C. A price floor that make the monopolist raise his price
D. A heavy tax on the monopolists profit
Answer : B
13. Price discrimination is possible:
A. Only under monopoly situation
B. Under any market form
C. Only under monopolistic competition
D. Only under perfect competition
Answer : A
A. Only under monopoly situation
B. Under any market form
C. Only under monopolistic competition
D. Only under perfect competition
Answer : A
14. If the price of a product falls then quantity demanded tends to increase ceteris paribus because:
A. The MU/P ratio has decreased
B. Of the income and substitution effects
C. Consumers tend to feel poorer when prices fall
D. When price falls the demand curve shifts right
Answer : B
A. The MU/P ratio has decreased
B. Of the income and substitution effects
C. Consumers tend to feel poorer when prices fall
D. When price falls the demand curve shifts right
Answer : B
15. The addition or increment to the total cost involvesd in expanding or contracting output by one unit is called:
A. Fixed cost per unit
B. Variable cost per unit
C. Total cost per unit
D. Marginal cost
Answer : D
A. Fixed cost per unit
B. Variable cost per unit
C. Total cost per unit
D. Marginal cost
Answer : D
16. In short run, a firm can change its:
A. Total production
B. Fixed production
C. Variable production
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Total production
B. Fixed production
C. Variable production
D. None of the above
Answer : C
17. In market sharing cartel model, cartel determines the shares of:
A. the individuals
B. industry
C. firms
D. associations
Answer : C
A. the individuals
B. industry
C. firms
D. associations
Answer : C
18. In the long run average costs curve, a firm can change:
A. Labour
B. Capital
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. Labour
B. Capital
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
19. An increase in the supply of a commodity is caused by:
A. Improvements in its technology
B. Fall in the prices of other commodities
C. Fall in the prices of factors of production
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Improvements in its technology
B. Fall in the prices of other commodities
C. Fall in the prices of factors of production
D. All of the above
Answer : D
20. Monopolistic firm can fix:
A. Both price and output
B. Either price or output
C. Neither price nor output
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Both price and output
B. Either price or output
C. Neither price nor output
D. None of the above
Answer : B
21. The least cost combination of factors x , y and z will generally be the point at which:
A. Price of x = Price of z Price of y Price of x
B. MP of x = MP of y Price of x Price of x
C. MP of x = MP of y = MP of z Price of x Price of y Price of z
D. MP of x = MP of y = MP of z
Answer : C
A. Price of x = Price of z Price of y Price of x
B. MP of x = MP of y Price of x Price of x
C. MP of x = MP of y = MP of z Price of x Price of y Price of z
D. MP of x = MP of y = MP of z
Answer : C
22. Total utility:
A. Diminishes wth increased consumption
B. Reflects the overall level of satisfaction of the consumer
C. Is directly related to the price the consumer is willing to pay for a good or service
D. Is independent of price changes
Answer : B
A. Diminishes wth increased consumption
B. Reflects the overall level of satisfaction of the consumer
C. Is directly related to the price the consumer is willing to pay for a good or service
D. Is independent of price changes
Answer : B
23. If the factors have to be employed in a fixed ratio, then the elasticity of substitution under Leontief technology is:
A. One
B. Zero
C. Two
D. Five
Answer : B
A. One
B. Zero
C. Two
D. Five
Answer : B
24. A profit-maximizing monopolist in two separate markets will:
A. Charge the same price in both markets
B. Always charge a higher price in the market where he sells more
C. Always charge a higher price in the market where he sells less
D. Adjust his sales in the two markets so that his marginal revenue in each market just equals his aggregate marginal cost
Answer : D
A. Charge the same price in both markets
B. Always charge a higher price in the market where he sells more
C. Always charge a higher price in the market where he sells less
D. Adjust his sales in the two markets so that his marginal revenue in each market just equals his aggregate marginal cost
Answer : D
25. In 1932, The nature and significance of economic science was written by:
A. Prof. Adam Smith
B. Prof. Alfred Marshal
C. Prof. Robbins
D. J.S.Mill
Answer : C
A. Prof. Adam Smith
B. Prof. Alfred Marshal
C. Prof. Robbins
D. J.S.Mill
Answer : C
26. The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money is the major work of :
A. N.Kaldor
B. Alfred Marshal
C. J.M.Keynes
D. J.S.Duesenberry
Answer : C
A. N.Kaldor
B. Alfred Marshal
C. J.M.Keynes
D. J.S.Duesenberry
Answer : C
27. In case of monopoly, TR curve rises at a:
A. Constant rate
B. Decreasing rate
C. Increasing rate
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Constant rate
B. Decreasing rate
C. Increasing rate
D. None of the above
Answer : B
28. If the supply curve is not a straight line but curvilinear, the elasticity on all points of the supply curve is:
A. Equal
B. Different
C. Zero
D. Infinity
Answer : B
A. Equal
B. Different
C. Zero
D. Infinity
Answer : B
29. The market demand for any commodity is the:
A. Average requirement for it in any given place
B. Amount of it wanted at any given price
C. Amount that people would like to buy during a period at different prices
D. Quantity needed to maintain a given standard of living
Answer : C
A. Average requirement for it in any given place
B. Amount of it wanted at any given price
C. Amount that people would like to buy during a period at different prices
D. Quantity needed to maintain a given standard of living
Answer : C
30. Selling costs are incurred under monopolistic competition to:
A. Attract more customers
B. Prevent its customers from going to others
C. Establish superiority of its product on the others
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Attract more customers
B. Prevent its customers from going to others
C. Establish superiority of its product on the others
D. All of the above
Answer : D
31. Each firm in cournot model assumes that its competitor will:
A. change its output
B. not change its output
C. change its price
D. not change its price
Answer : B
A. change its output
B. not change its output
C. change its price
D. not change its price
Answer : B
32. If a person behaves against the laws of economics then:
A. He should be condemned
B. He may lose his respect from society
C. He should be punished
D. He should not be punished or even criticised
Answer : D
A. He should be condemned
B. He may lose his respect from society
C. He should be punished
D. He should not be punished or even criticised
Answer : D
33. Ordinal approach includes arranging:
A. The different combinations of X and Y in any way the consumer wants
B. The different combinations of X and Y higher and lower and measuring the difference of utility between them
C. The different combinations of X and Y higher and lower and not measuring the difference of utility between them
D. None of above
Answer : C
A. The different combinations of X and Y in any way the consumer wants
B. The different combinations of X and Y higher and lower and measuring the difference of utility between them
C. The different combinations of X and Y higher and lower and not measuring the difference of utility between them
D. None of above
Answer : C
34. The marshallian indirect utility function in the form of equation is:
A. x =a-bp
B. x =b-ap
C.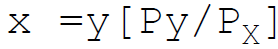
D. x = f(P)
Answer : C
A. x =a-bp
B. x =b-ap
C.
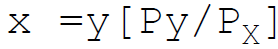
D. x = f(P)
Answer : C
35. LMC represents change in LTC (long-run total cost) due to producing an additional unit of a good while the fixed and variable factors:
A. Cannot be changed
B. Can be changed
C. Can partially be changed
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Cannot be changed
B. Can be changed
C. Can partially be changed
D. None of the above
Answer : B
36. Contraction of demand means:
A. Less quantity demanded at the same price
B. Less quantity demanded at a higher price
C. Less quantity demanded at a lower price
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Less quantity demanded at the same price
B. Less quantity demanded at a higher price
C. Less quantity demanded at a lower price
D. None of the above
Answer : B
37. In the modern theory of costs, the level of production which the firm considers feasible is known as:
A. Input factor
B. Heavy factor
C. Output factor
D. Load factor
Answer : D
A. Input factor
B. Heavy factor
C. Output factor
D. Load factor
Answer : D
38. In perfect cartel, the:
A. Perfect competition price is charged
B. Monopoly price is charged
C. Monopoly price is not charged
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Perfect competition price is charged
B. Monopoly price is charged
C. Monopoly price is not charged
D. None of the above
Answer : B
39. In case of straight-line isoquant, the factors are not substituted because they are each others:
A. Imperfect substitutes
B. Perfect substitutes
C. Complements
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Imperfect substitutes
B. Perfect substitutes
C. Complements
D. None of the above
Answer : B
40. Consumer surplus is the difference between
A. Price demanded and price paid
B. Price quoted and price actually paid
C. Price that a consumer is willing to pay and the price actually paid
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Price demanded and price paid
B. Price quoted and price actually paid
C. Price that a consumer is willing to pay and the price actually paid
D. None of the above
Answer : C
41. The consumer is in equilibrium at the where:
A. Budget line and indifference curve intersect each other
B. Budget line and indifference curve are tangent to each other
C. Budget line and indifference curve are opposite to each other
D. Budget line and indifference curve are parallel to each other
Answer : B
A. Budget line and indifference curve intersect each other
B. Budget line and indifference curve are tangent to each other
C. Budget line and indifference curve are opposite to each other
D. Budget line and indifference curve are parallel to each other
Answer : B
42. When there is decrease in demand the demand curve:
A. Moves (shifts) towards the axis
B. Moves (shifts) away from the axis
C. Remains unchanged
D. All of the above
Answer : A
A. Moves (shifts) towards the axis
B. Moves (shifts) away from the axis
C. Remains unchanged
D. All of the above
Answer : A
43. If demand increased and supply decreased then:
A. Quantity exchanged might rise or fall and price would rise
B. Quantity exchanged would rise and price would fall
C. Quantity exchanged would rise and price might rise or fall
D. Both quantities exchanged and price would rise
Answer : A
A. Quantity exchanged might rise or fall and price would rise
B. Quantity exchanged would rise and price would fall
C. Quantity exchanged would rise and price might rise or fall
D. Both quantities exchanged and price would rise
Answer : A
44. In case of short-run, the supply curve of an industry is the horizontal summation of:
A. Marginal cost curves
B. Average cost curves
C. Total cost curves
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Marginal cost curves
B. Average cost curves
C. Total cost curves
D. None of the above
Answer : A
45. A firm can never produce in the middle area of input space, in case of:
A. Concave isoquant
B. Convex isoquant
C. Constant isoquant
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Concave isoquant
B. Convex isoquant
C. Constant isoquant
D. None of the above
Answer : A
46. According to Saint Thomas Aquinas value is determined by God, but prices by:
A. Consumers
B. Employees
C. People
D. Labor
Answer : C
A. Consumers
B. Employees
C. People
D. Labor
Answer : C
47. The costs faced by the firm against variable factors are:
A. Variable costs
B. Fixed costs
C. Average costs
D. Marginal costs
Answer : A
A. Variable costs
B. Fixed costs
C. Average costs
D. Marginal costs
Answer : A
48. Elasticity (E) expressed by the term, 1>E>0, is:
A. Perfectly elastic
B. Relatively elastic
C. Unitary elastic
D. Relatively inelastic
Answer : D
A. Perfectly elastic
B. Relatively elastic
C. Unitary elastic
D. Relatively inelastic
Answer : D
49. Which of the following pairs of commodities is an example of substitutes?
A. Tea and sugar
B. Tea and coffee
C. Pen and ink
D. Shirt and trousers
Answer : B
A. Tea and sugar
B. Tea and coffee
C. Pen and ink
D. Shirt and trousers
Answer : B
50. Production function shows:
A. Technical relationship between inputs and output
B. Profitability production
C. Relation between MR and MC
D. Relation between AR and AC
Answer : A
A. Technical relationship between inputs and output
B. Profitability production
C. Relation between MR and MC
D. Relation between AR and AC
Answer : A
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Cell - the unit of life Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ IBPS Common Written Exam (PO/MT) Main 2016 Solved Paper Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ General Science Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 1000+ MCQ with answer for SBI Clerk
Engineering Mechanics 1000+ MCQ with answer for XAT
1000+ Fill in the blanks Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]