Basics of Economics MCQ Solved Paper for IBPS PO
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Cross-elasticity of demand is measured as:
A. Percentage change in the quantity of a commodity demanded divided by the percentage change in the price of that commodity
B. Percentage change in the quantity of commodity X divided by percentage change in the price of commodity Y
C. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X
D. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X divided by percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity Y
Answer : B
A. Percentage change in the quantity of a commodity demanded divided by the percentage change in the price of that commodity
B. Percentage change in the quantity of commodity X divided by percentage change in the price of commodity Y
C. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X
D. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X divided by percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity Y
Answer : B
2. When at a given price, the quantity demanded of a commodity is more than the quantity supplied, there will be:
A. An upward pressure on price
B. A downward pressure on price
C. Price will remain unaffected
D. All of the above
Answer : A
A. An upward pressure on price
B. A downward pressure on price
C. Price will remain unaffected
D. All of the above
Answer : A
3. Marginal cost curve cuts the average cost curve:
A. At the left of its lowest point
B. At its lowest point
C. At the right of its lowest point
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. At the left of its lowest point
B. At its lowest point
C. At the right of its lowest point
D. None of the above
Answer : B
4. The short run cost curve is U shaped because of:
A. The operation of increasing cost
B. The existence of fixed cost
C. The existence of variable cost
D. All of the above
Answer : C
A. The operation of increasing cost
B. The existence of fixed cost
C. The existence of variable cost
D. All of the above
Answer : C
5. To attain maximum profits during short-run a firm should produce the output that will:
A. Yield maximum total revenue
B. Minimize marginal cost
C. Maximize marginal cost
D. Equate marginal revenue with marginal cost
Answer : D
A. Yield maximum total revenue
B. Minimize marginal cost
C. Maximize marginal cost
D. Equate marginal revenue with marginal cost
Answer : D
6. In monopoly:
A. The producer will often produce a volume that is less than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
B. The producer will often produce a volume that is more than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
C. The consumers will often consume a volume that is more than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. The producer will often produce a volume that is less than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
B. The producer will often produce a volume that is more than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
C. The consumers will often consume a volume that is more than the amount which would maximize the social welfare.
D. None of the above
Answer : A
7. The good will highest income elasticity is:
A. Beef
B. Mutton
C. Bread
D. Motion-picture tickets
Answer : D
A. Beef
B. Mutton
C. Bread
D. Motion-picture tickets
Answer : D
8. If we measure the elasticity of demand with the help of the average and marginal revenue, the formula is:
A. Ed = AR/ (AR- MR)
B. Ed = MR/ (AR-MR)
C. Ed = AR/(MR-AR)
D. Ed = AR/ MR
Answer : A
A. Ed = AR/ (AR- MR)
B. Ed = MR/ (AR-MR)
C. Ed = AR/(MR-AR)
D. Ed = AR/ MR
Answer : A
9. When a consumer reached at the point of saturation then marginal utility (MU) is:
A. Negative
B. One
C. Positive
D. Zero
Answer : D
A. Negative
B. One
C. Positive
D. Zero
Answer : D
10. Each firm in cournot model assumes that its competitor will:
A. change its output
B. not change its output
C. change its price
D. not change its price
Answer : B
A. change its output
B. not change its output
C. change its price
D. not change its price
Answer : B
11. If the price of coffee increases, you would predict that:
A. Demand curve for sugar will shift downward (leftward)
B. Supply curve for sugar will shift leftward (upward)
C. Demand curve for bread will shift downward (leftward)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Demand curve for sugar will shift downward (leftward)
B. Supply curve for sugar will shift leftward (upward)
C. Demand curve for bread will shift downward (leftward)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
12. As the price of diamond is higher, so it has:
A. Higher marginal valuation for consumer
B. Lower marginal cost for producer
C. Higher marginal cost for producer
D. Both (a) and (c)
Answer : D
A. Higher marginal valuation for consumer
B. Lower marginal cost for producer
C. Higher marginal cost for producer
D. Both (a) and (c)
Answer : D
13. In Recardian theory of value, the stress has been made on:
A. Marginal cost
B. Production cost
C. Labor cost
D. Supply cost
Answer : A
A. Marginal cost
B. Production cost
C. Labor cost
D. Supply cost
Answer : A
14. In case of monopoly:
A. MR
C. MR=AR
D. AR=0
Answer : A
A. MR
C. MR=AR
D. AR=0
Answer : A
15. The main contribution of Alfred Marshal is in the field of:
A. Research in mathematical economics
B. Economics of labor
C. Theory of production
D. Theory of demand
Answer : D
A. Research in mathematical economics
B. Economics of labor
C. Theory of production
D. Theory of demand
Answer : D
16. The feasible part of the demand curve for the monopolist who is charging high price will be:
A. The elastic part of a demand curve
B. The inelastic part of a demand curve
C. The constant elastic part of the demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. The elastic part of a demand curve
B. The inelastic part of a demand curve
C. The constant elastic part of the demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
17. If the commodity is normal then fall in price will result in:
A. Increase the quantity demanded
B. Fixed the quantity demanded
C. Decrease the quantity demanded
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Increase the quantity demanded
B. Fixed the quantity demanded
C. Decrease the quantity demanded
D. None of the above
Answer : A
18. Nash equilibrium is applicable in case of:
A. Cournot model
B. Edgeworth model
C. Chamberline model
D. Sweezy model
Answer : A
A. Cournot model
B. Edgeworth model
C. Chamberline model
D. Sweezy model
Answer : A
19. The output where TC = TR & AC = AR:
A. Break-even point
B. Load point
C. Shut-down point
D. Revenue cost point
Answer : A
A. Break-even point
B. Load point
C. Shut-down point
D. Revenue cost point
Answer : A
20. In the case of substitutes, the cross demand curve slopes
A. Downwards to the right
B. Upwards to the right
C. Backwards to the right
D. Inwards at the bottom
Answer : B
A. Downwards to the right
B. Upwards to the right
C. Backwards to the right
D. Inwards at the bottom
Answer : B
21. The income consumption curve (ICC) is the locus of points of consumer equilibrium resulting:
A. Only when the price of commodity X changes
B. Only when the price of commodity Y changes
C. Only when the consumers income i varied
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Only when the price of commodity X changes
B. Only when the price of commodity Y changes
C. Only when the consumers income i varied
D. None of the above
Answer : C
22. In long run, a firm can change:
A. Fixed factors
B. Variable factors
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. Fixed factors
B. Variable factors
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
23. The law of variable proportions comes into being when:
A. All factors are variable
B. There is a fixed factor and variable factor
C. All factors are non-variable
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. All factors are variable
B. There is a fixed factor and variable factor
C. All factors are non-variable
D. None of the above
Answer : B
24. A producer attains the least cost combination when the relation between Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution (MRTS) and price (P) of the factors x and y is:
A.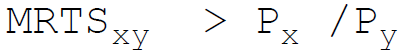
B.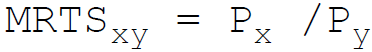
C.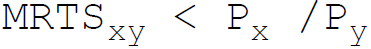
D.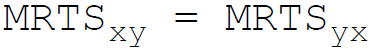
Answer : B
A.
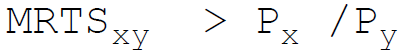
B.
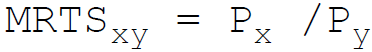
C.
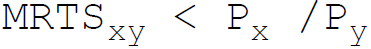
D.
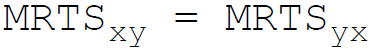
Answer : B
25. In Bertrand model, the entry of new firms is:
A. banned
B. allowed
C. partially allowed
D. none of the above
Answer : A
A. banned
B. allowed
C. partially allowed
D. none of the above
Answer : A
26. Increasing returns imply:
A. Constant average cost
B. Diminishing cost per unit of output
C. Optimum use of capital and factor
D. External economies
Answer : B
A. Constant average cost
B. Diminishing cost per unit of output
C. Optimum use of capital and factor
D. External economies
Answer : B
27. Loanable funds theory of Interest was developed by:
A. Wicksell
B. Robert San
C. Ruskin
D. J.B.Say
Answer : A
A. Wicksell
B. Robert San
C. Ruskin
D. J.B.Say
Answer : A
28. In dominant strategies I am doing the best, I can no matter:
A. What you do
B. What you are doing
C. What you not do
D. None of them
Answer : A
A. What you do
B. What you are doing
C. What you not do
D. None of them
Answer : A
29. In which case the elasticity shown by the different points of a curve is the same?
A. A straight line curve
B. A downward sloping demand curve
C. A rectangular hyperbola demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. A straight line curve
B. A downward sloping demand curve
C. A rectangular hyperbola demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : C
30. If the commodity is normal then the Income Effect (I.E) and the Substitution Effect (S.E):
A. Both move together and reinforce each other
B. One moves and the other remains constant
C. Move in the opposite direction and neutralize each other
D. Both remain constant
Answer : A
A. Both move together and reinforce each other
B. One moves and the other remains constant
C. Move in the opposite direction and neutralize each other
D. Both remain constant
Answer : A
31. Microeconomics is also known as:
A. Price theory
B. Demand theory
C. Supply theory
D. Income theory
Answer : A
A. Price theory
B. Demand theory
C. Supply theory
D. Income theory
Answer : A
32. Supply of a commodity refers to:
A. Total stock of a commodity in the market
B. Total production of a commodity during the year
C. Total production plus total stock of a commodity
D. Amount of commodity offered for sale at some price at a particular place and time
Answer : D
A. Total stock of a commodity in the market
B. Total production of a commodity during the year
C. Total production plus total stock of a commodity
D. Amount of commodity offered for sale at some price at a particular place and time
Answer : D
33. There is no difference between fixed and variable factors in the:
A. Long run
B. Short run
C. Average run
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Long run
B. Short run
C. Average run
D. None of the above
Answer : A
34. In joint-profit maximization cartel, central agency sets the:
A. Output
B. Input
C. Demand
D. Price
Answer : D
A. Output
B. Input
C. Demand
D. Price
Answer : D
35. Which is the other name that is given to the average revenue curve?
A. Profit curve
B. Demand curve
C. Average cost curve
D. Indifference curve
Answer : B
A. Profit curve
B. Demand curve
C. Average cost curve
D. Indifference curve
Answer : B
36. Along an isoquant, output remains same, and capital labor ratio:
A. Is also same
B. Is different
C. Is constant
D. Is zero
Answer : B
A. Is also same
B. Is different
C. Is constant
D. Is zero
Answer : B
37. The non-price competition cartel is a:
A. stable cartel
B. unstable cartel
C. prominent cartel
D. special cartel
Answer : B
A. stable cartel
B. unstable cartel
C. prominent cartel
D. special cartel
Answer : B
38. Which of the following is the work of A.C.Pigou?
A. Economics of Welfare
B. Commerce and Trade
C. Industrial Economics
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Economics of Welfare
B. Commerce and Trade
C. Industrial Economics
D. None of the above
Answer : A
39. Nash Equilibrium is stable:
A. They involve dominant strategies
B. They involves constant-sum games
C. Once the strategies are chosen, no player has an incentive to deviate unilaterally from them
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. They involve dominant strategies
B. They involves constant-sum games
C. Once the strategies are chosen, no player has an incentive to deviate unilaterally from them
D. None of the above
Answer : C
40. The falling part of total Utility (TU) curve shows:
A. Increasing marginal utility
B. Decreasing marginal utility
C. Zero marginal utility
D. Negative marginal utility
Answer : D
A. Increasing marginal utility
B. Decreasing marginal utility
C. Zero marginal utility
D. Negative marginal utility
Answer : D
41. Of the following, which one corresponds to fixed cost?
A. Payments for raw materials
B. Labor cost
C. Transportation charges
D. Insurance premium on property
Answer : D
A. Payments for raw materials
B. Labor cost
C. Transportation charges
D. Insurance premium on property
Answer : D
42. Which of the following is not characteristic of perfect competition?
A. Freedom of entry and exit
B. Each seller is a price taker
C. Perfect information about prices
D. Heterogeneous products
Answer : D
A. Freedom of entry and exit
B. Each seller is a price taker
C. Perfect information about prices
D. Heterogeneous products
Answer : D
43. The total utility is gained by consuming:
A. The last unit of a good
B. All the units of a good
C. The first unit of a good
D. The average unit of a good
Answer B
A. The last unit of a good
B. All the units of a good
C. The first unit of a good
D. The average unit of a good
Answer B
44. A demand curve is not related to:
A. The price of the commodity
B. The time period
C. The price of substitutes
D. Any of the above
Answer : C
A. The price of the commodity
B. The time period
C. The price of substitutes
D. Any of the above
Answer : C
45. The cost of production is faced by a:
A. Producer
B. Consumer
C. Seller
D. Firm
Answer : D
A. Producer
B. Consumer
C. Seller
D. Firm
Answer : D
46. Discriminating monopoly implies that the monopolist charges different prices for his commodity:
A. From different groups of consumers
B. For different uses
C. At different places
D. Any of the above
Answer : D
A. From different groups of consumers
B. For different uses
C. At different places
D. Any of the above
Answer : D
47. If less is demanded at the same price or same quantity demanded at a lower price, it is a case of:
A. Contraction of demand
B. Decrease in demand
C. Increase in demand
D. Extension of demand
Answer : B
A. Contraction of demand
B. Decrease in demand
C. Increase in demand
D. Extension of demand
Answer : B
48. The Strategy of Economic Development is the work of:
A. S.Kuznets
B. H.Liebenstein
C. A.O.Hirshman
D. Alfred Marshal
Answer : C
A. S.Kuznets
B. H.Liebenstein
C. A.O.Hirshman
D. Alfred Marshal
Answer : C
49. If demand is elastic and supply is inelastic then the burden of a tax on the good will be:
A. Borne mostly by producers
B. Borne mostly by consumers
C. Borne mostly by government
D. Shared equally by producers and consumers
Answer : A
A. Borne mostly by producers
B. Borne mostly by consumers
C. Borne mostly by government
D. Shared equally by producers and consumers
Answer : A
50. The number of sellers in oligopoly are:
A. Two
B. Many
C. Four
D. Very few
Answer : D
A. Two
B. Many
C. Four
D. Very few
Answer : D
Sharing is caring
Related Post
IBPS PO - Power Plant Engineering 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Hydraulics & Fluid Machineries MCQ for NDA [Solved]
RRB NTPC - Chemical Process 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Steam Boilers, Engines, Nozzles & Turbines Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
SSC GD - CorelDraw 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Periodic Classification of Elements MCQ for XAT [Solved]