Basics of Economics 1000+ MCQ with answer for SBI PO
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. We can measure consumers surplus with the help of
A. TU curve
B. MU curve
C. Supply curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. TU curve
B. MU curve
C. Supply curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
2. Nash equilibrium is applicable in case of:
A. Cournot model
B. Edgeworth model
C. Chamberline model
D. Sweezy model
Answer : A
A. Cournot model
B. Edgeworth model
C. Chamberline model
D. Sweezy model
Answer : A
3. In monopolistic competition, the real differentiation in products is due to difference in:
A. Style
B. Consumer
C. Cost
D. Material
Answer : D
A. Style
B. Consumer
C. Cost
D. Material
Answer : D
4. The difference between average cost and average revenue is:
A. Total profit
B. Average profit
C. Net profit
D. Marginal profit
Answer : B
A. Total profit
B. Average profit
C. Net profit
D. Marginal profit
Answer : B
5. When SAC curve rises, SMC curve lies its:
A. Below
B. Above
C. Equal level
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Below
B. Above
C. Equal level
D. None of the above
Answer : B
6. Microeconomics deals with the:
A. Allocation of resources of the economy as between production of different goods and services
B. Determination of prices of goods and services
C. Behavior of industrial decision makers
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Allocation of resources of the economy as between production of different goods and services
B. Determination of prices of goods and services
C. Behavior of industrial decision makers
D. All of the above
Answer : D
7. A monopolist:
A. Can not influence the market
B. Can influence the market
C. Is a price taker
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Can not influence the market
B. Can influence the market
C. Is a price taker
D. None of the above
Answer : B
8. The relationship between AC and MC curves depend upon the behavior of:
A. AP curves
B. MP curves
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. AP curves
B. MP curves
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
9. Total profits are maximized at the point where:
A. TR equals TC
B. The TR curve and the TC curve intersect such that TR and TC lie at the same point
C. The TR curve and the TC curve are parallel and TC exceeds TR
D. The TR curve and the TC curve are parallel and TR exceeds TC
Answer : D
A. TR equals TC
B. The TR curve and the TC curve intersect such that TR and TC lie at the same point
C. The TR curve and the TC curve are parallel and TC exceeds TR
D. The TR curve and the TC curve are parallel and TR exceeds TC
Answer : D
10. The situation of single buyer and single seller is called:
A. Monopoly
B. Multi-plant monopolist
C. Bilateral monopoly
D. Price discrimination
Answer : C
A. Monopoly
B. Multi-plant monopolist
C. Bilateral monopoly
D. Price discrimination
Answer : C
11. The number of firms in monopolistic competition normally range between:
A. 14 to 28
B. 14 to 80
C. 14 to 38
D. 14 to 60
Answer : B
A. 14 to 28
B. 14 to 80
C. 14 to 38
D. 14 to 60
Answer : B
12. In a socialist (communist) economy the invisible hand:
A. Guides most resource allocation decisions
B. Operates effectively only in the labor market
C. Operates effectively only in the market for capital
D. Is prevented from operating effectively
Answer : D
A. Guides most resource allocation decisions
B. Operates effectively only in the labor market
C. Operates effectively only in the market for capital
D. Is prevented from operating effectively
Answer : D
13. If as a result of a decrease in price, total outlay (expenditures) on a commodity increases, its price-elasticity of demand is:
A. Perfectly elastic (infinitely elastic)
B. Relatively elastic (greater than one elasticity)
C. Unit elastic
D. Relatively inelastic (less than one elasticity)
Answer : B
A. Perfectly elastic (infinitely elastic)
B. Relatively elastic (greater than one elasticity)
C. Unit elastic
D. Relatively inelastic (less than one elasticity)
Answer : B
14. In monopoly, new firms:
A. Can enter and exit
B. Partially can enter and exit
C. Cannot enter
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Can enter and exit
B. Partially can enter and exit
C. Cannot enter
D. None of the above
Answer : C
15. As the price of diamond is higher, so it has:
A. Higher marginal valuation for consumer
B. Lower marginal cost for producer
C. Higher marginal cost for producer
D. Both (a) and (c)
Answer : D
A. Higher marginal valuation for consumer
B. Lower marginal cost for producer
C. Higher marginal cost for producer
D. Both (a) and (c)
Answer : D
16. A market-clearing price:
A. Is a disequilibrium price
B. Is an equilibrium price
C. Means a shortage exists as a market is cleared
D. Must be set by the government
Answer : B
A. Is a disequilibrium price
B. Is an equilibrium price
C. Means a shortage exists as a market is cleared
D. Must be set by the government
Answer : B
17. If the increase in demand is more than the increase in supply, the price will:
A. Rise
B. Fall
C. Remain the same
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Rise
B. Fall
C. Remain the same
D. None of the above
Answer : A
18. The demand curve in monopolistic competition (also in kinked demand curve model), which shows the share of a firm in market is called:
A. Relative demand curve
B. Proportional demand curve
C. Productive demand curve
D. Differential demand curve
Answer : B
A. Relative demand curve
B. Proportional demand curve
C. Productive demand curve
D. Differential demand curve
Answer : B
19. MRSxy measures:
A. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and still remain on the same indifference curve
B. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and still remain on the same indifference curve
C. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and move to a higher indifference curve
D. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and move to a higher indifference curve
Answer : B
A. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and still remain on the same indifference curve
B. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and still remain on the same indifference curve
C. The amount of Y a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of X and move to a higher indifference curve
D. The amount of X a consumer is willing to give up to obtain one additional unit of Y and move to a higher indifference curve
Answer : B
20. In short run, a firm would remain in business as long as which one of the following of cost is covered?
A. Total costs
B. Fixed costs
C. Variable costs
D. Constant costs
Answer : C
A. Total costs
B. Fixed costs
C. Variable costs
D. Constant costs
Answer : C
21. Using total revenue and total cost, a profit maximizing firm will be equilibrium at a point:
A. Where the gap between the two is the smallest
B. Where the gap between the two is the greatest
C. Where the two become equal
D. None of the above
Answer : /strong> B
A. Where the gap between the two is the smallest
B. Where the gap between the two is the greatest
C. Where the two become equal
D. None of the above
Answer : /strong> B
22. If the demand curve is horizontal then its slope is:
A. Infinite
B. Zero
C. Equal to one
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Infinite
B. Zero
C. Equal to one
D. None of the above
Answer : A
23. Which of the following curves is a rectangular hyperbola?
A. ATC
B. AVC
C. AFC
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. ATC
B. AVC
C. AFC
D. None of the above
Answer : C
24. Identify the coefficient of price-elasticity of demand when the percentage increase in the quantity of a commodity demanded is smaller than the percentage fall in its price:
A. Equal to one
B. Greater than one
C. Smaller than one
D. Zero
Answer : C
A. Equal to one
B. Greater than one
C. Smaller than one
D. Zero
Answer : C
25. The isoquant approach is based upon:
A. One output
B. One input
C. Two outputs
D. Two inputs
Answer : D
A. One output
B. One input
C. Two outputs
D. Two inputs
Answer : D
26. Income-elasticity of demand is expressed as:
A. % change in quantity demanded % change in income
B. % change in income % change in quantity demanded
C. Change in income Change in quantity demanded
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. % change in quantity demanded % change in income
B. % change in income % change in quantity demanded
C. Change in income Change in quantity demanded
D. None of the above
Answer : A
27. Normal profits are considered as:
A. Explicit costs
B. Implicit costs
C. Social costs
D. Private cost
Answer : B
A. Explicit costs
B. Implicit costs
C. Social costs
D. Private cost
Answer : B
28. The products, under monopolistic competition are differentiated, yet they are:
A. Complements
B. Close substitutes
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Complements
B. Close substitutes
C. Both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer : B
29. In short run, a firm can change its:
A. Total production
B. Fixed production
C. Variable production
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Total production
B. Fixed production
C. Variable production
D. None of the above
Answer : C
30. In which case the elasticity shown by the different points of a curve is the same?
A. A straight line curve
B. A downward sloping demand curve
C. A rectangular hyperbola demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. A straight line curve
B. A downward sloping demand curve
C. A rectangular hyperbola demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : C
31. The central problem of economics is:
A. Declining productivity
B. Increasing consumption
C. Limited material wants
D. Limited resources and unlimited wants
Answer : D
A. Declining productivity
B. Increasing consumption
C. Limited material wants
D. Limited resources and unlimited wants
Answer : D
32. In the case of superior (normal) commodity, the income elasticity of demand is:
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : A
A. Positive
B. Unitary
C. Negative
D. Infinite
Answer : A
33. Theory of revealed preference is based on:
A. Weak orderings
B. Neutral orderings
C. Partial orderings
D. Strong orderings
Answer : D
A. Weak orderings
B. Neutral orderings
C. Partial orderings
D. Strong orderings
Answer : D
34. When elasticity of demand is one (e=1), then following the formula MR=P[1-1/e], the MR will:
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. None of the above
Answer : C
35. An optimum level of a firms output is:
A. Where marginal cost is minimum
B. Where average cost is minimum
C. Where both the marginal and the average cost curves are at their respective minimum
D. Where the firm earns the maximum profits
Answer : B
A. Where marginal cost is minimum
B. Where average cost is minimum
C. Where both the marginal and the average cost curves are at their respective minimum
D. Where the firm earns the maximum profits
Answer : B
36. The income effect means that consumer purchase more when:
A. Price falls
B. Price increases
C. Price is unchanged
D. Taste changed
Answer : A
A. Price falls
B. Price increases
C. Price is unchanged
D. Taste changed
Answer : A
37. In 1932, The nature and significance of economic science was written by:
A. Prof. Adam Smith
B. Prof. Alfred Marshal
C. Prof. Robbins
D. J.S.Mill
Answer : C
A. Prof. Adam Smith
B. Prof. Alfred Marshal
C. Prof. Robbins
D. J.S.Mill
Answer : C
38. The long run average cost curve is the envelope of:
A. SACs
B. LACs
C. SMCs
D. LMCs
Answer : A
A. SACs
B. LACs
C. SMCs
D. LMCs
Answer : A
39. If the consumers expect that the price of computers will decrease in next year then:
A. Current demand for computers will fall
B. Current demand for computers will rise
C. Current demand will change unpredictably
D. Current supply of computers will rise
Answer : A
A. Current demand for computers will fall
B. Current demand for computers will rise
C. Current demand will change unpredictably
D. Current supply of computers will rise
Answer : A
40. In market sharing cartel model, cartel determines the shares of:
A. the individuals
B. industry
C. firms
D. associations
Answer : C
A. the individuals
B. industry
C. firms
D. associations
Answer : C
41. A producer attains the least cost combination when the relation between Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution (MRTS) and price (P) of the factors x and y is:
A.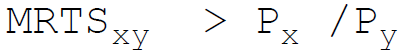
B.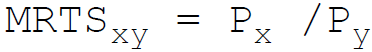
C.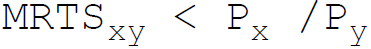
D.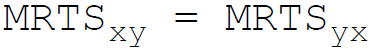
Answer : B
A.
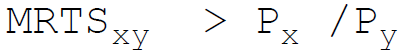
B.
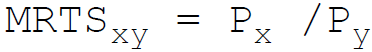
C.
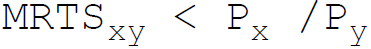
D.
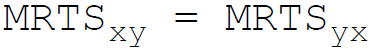
Answer : B
42. The act of producing the output from more than one plant is concerned with:
A. Monopoly
B. Multi-plant monopoly
C. Bilateral monopoly
D. Price discrimination
Answer : B
A. Monopoly
B. Multi-plant monopoly
C. Bilateral monopoly
D. Price discrimination
Answer : B
43. The demand curve of ostentation goods (Veblen goods) will be:
A. Negatively sloped
B. Positively sloped
C. Parallel to X-axis
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Negatively sloped
B. Positively sloped
C. Parallel to X-axis
D. None of the above
Answer : B
44. In sweezy model (kinked demand curve model), the role of MC curve:
A. Can be ignored
B. Cannot be ignored
C. Partially be ignored
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Can be ignored
B. Cannot be ignored
C. Partially be ignored
D. None of the above
Answer : A
45. Market demand curve is:
A. Vertical summation of individual demand curves
B. Upward summation of individual demand curves
C. Downward summation of individual demand curves
D. Horizontal summation of individual demand curves
Answer : D
A. Vertical summation of individual demand curves
B. Upward summation of individual demand curves
C. Downward summation of individual demand curves
D. Horizontal summation of individual demand curves
Answer : D
46. Marginal cost curve cuts the average cost curve:
A. At the left of its lowest point
B. At its lowest point
C. At the right of its lowest point
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. At the left of its lowest point
B. At its lowest point
C. At the right of its lowest point
D. None of the above
Answer : B
47. The necessary condition of firms equilibrium requires:
A. dR/dQ + dC/dQ = 0
B. dR/dQ - dC/dQ = 0
C. dC/dQ - dR/dQ = 0
D. dR/dQ > dC/dQ > 0
Answer : B
A. dR/dQ + dC/dQ = 0
B. dR/dQ - dC/dQ = 0
C. dC/dQ - dR/dQ = 0
D. dR/dQ > dC/dQ > 0
Answer : B
48. A loss bearing firm will continue to produce in the short run so long as the price at least covers:
A. Average variable cost
B. Average fixed cost
C. Average variable cost + average fixed cost
D. Marginal costs
Answer : A
A. Average variable cost
B. Average fixed cost
C. Average variable cost + average fixed cost
D. Marginal costs
Answer : A
49. The Law of Proportionality is another name of:
A. The law of diminishing marginal utility
B. The law of demand
C. The Law of Diminishing Returns
D. The law of supply
Answer : C
A. The law of diminishing marginal utility
B. The law of demand
C. The Law of Diminishing Returns
D. The law of supply
Answer : C
50. In the short-run, in which one of the following situations would a competitive seller close down (shut-down)?
A. When he cannot produce at an economic profit
B. When price falls short of average variable cost at every level of output
C. When price falls short of average fixed cost at every level of output
D. When price falls short of average total cost at every level of output
Answer : B
A. When he cannot produce at an economic profit
B. When price falls short of average variable cost at every level of output
C. When price falls short of average fixed cost at every level of output
D. When price falls short of average total cost at every level of output
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Microsoft Access Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ PhotoShop MCQ for CTET [Solved]
CAT - Puzzle 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Urology Basic Science MCQ Solved Paper for IBPS SO
1000+ Chemical Engineering Basics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Kidney cysts and tumors Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]