Basics of Economics MCQ Solved Paper for XAT
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. In modern theory of costs, a firm normally utilizes:
A. 2/3 of capacity of its plants
B. 3/4 of capacity of its plants
C. 1/3 of capacity of its plants
D. 1/2 of capacity of its plants
Answer : A
A. 2/3 of capacity of its plants
B. 3/4 of capacity of its plants
C. 1/3 of capacity of its plants
D. 1/2 of capacity of its plants
Answer : A
2. When the slope of a demand curve is infinite (also known as horizontal demand curve) then elasticity will be:
A. Zero (perfectly inelastic)
B. Equal to one (unitary elastic)
C. Infinite (perfectly elastic)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Zero (perfectly inelastic)
B. Equal to one (unitary elastic)
C. Infinite (perfectly elastic)
D. None of the above
Answer : A
3. Utility is a function of:
A. Price
B. Quantity
C. Supply
D. Demand
Answer : B
A. Price
B. Quantity
C. Supply
D. Demand
Answer : B
4. When total product (TP) is maximum:
A. MP is negative
B. MP is infinite
C. MP is zero
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. MP is negative
B. MP is infinite
C. MP is zero
D. None of the above
Answer : C
5. The slope of indifference curve shows:
A. Income level
B. Satisfaction level
C. Marginal rate of substitution
D. Demand level
Answer : C
A. Income level
B. Satisfaction level
C. Marginal rate of substitution
D. Demand level
Answer : C
6. If two goods are complements then indifference curve (IC) will be:
A. Straight line
B. Convex to origin
C. Concave to origin
D. Lshaped
Answer : D
A. Straight line
B. Convex to origin
C. Concave to origin
D. Lshaped
Answer : D
7. Which of the following statement is wrong?
A. A utility function refers to a particular individual and reflects the tastes of that individual
B. When the tastes of an individual changes, his utility function changes(shifts)
C. Different individuals usually have different tastes and thus have different utility functions
D. Different individuals have same tastes and thus have the same utility function
Answer : D
A. A utility function refers to a particular individual and reflects the tastes of that individual
B. When the tastes of an individual changes, his utility function changes(shifts)
C. Different individuals usually have different tastes and thus have different utility functions
D. Different individuals have same tastes and thus have the same utility function
Answer : D
8. An optimum level of a firms output is:
A. Where marginal cost is minimum
B. Where average cost is minimum
C. Where both the marginal and the average cost curves are at their respective minimum
D. Where the firm earns the maximum profits
Answer : B
A. Where marginal cost is minimum
B. Where average cost is minimum
C. Where both the marginal and the average cost curves are at their respective minimum
D. Where the firm earns the maximum profits
Answer : B
9. According to Cobb-Douglas, in production function the marginal product of labor is:
A.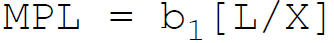
B.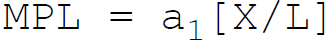
C.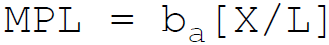
D.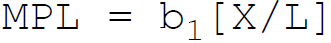
Answer : D
A.
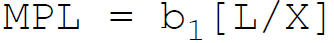
B.
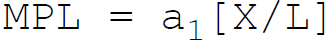
C.
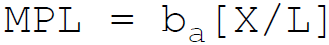
D.
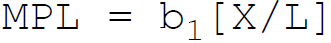
Answer : D
10. Which of the following is not characteristic of perfect competition?
A. Freedom of entry and exit
B. Each seller is a price taker
C. Perfect information about prices
D. Heterogeneous products
Answer : D
A. Freedom of entry and exit
B. Each seller is a price taker
C. Perfect information about prices
D. Heterogeneous products
Answer : D
11. The Modern and Neo-Keynsian Theory of Interestwas presented by:
A. Gunner Myrdal
B. A.C.Pigou
C. J.M.Keynes
D. J.R.Hicks
Answer : D
A. Gunner Myrdal
B. A.C.Pigou
C. J.M.Keynes
D. J.R.Hicks
Answer : D
12. Competitors in monopolistic competition have full control over:
A. The price of their product
B. Product quality
C. The shape of the market demand curve
D. The elasticity of product substitution
Answer : B
A. The price of their product
B. Product quality
C. The shape of the market demand curve
D. The elasticity of product substitution
Answer : B
13. Which of the following theories of trade cycle was presented by William Jevons?
A. Sunspot Theory
B. Monetary Theory
C. Saving-Investment Theory
D. Innovation Theory
Answer : A
A. Sunspot Theory
B. Monetary Theory
C. Saving-Investment Theory
D. Innovation Theory
Answer : A
14. If the demand for good is less elastic and government levied a tax per unit of output, the price per unit for the firm would:
A. Rise by the amount of the tax
B. Rise by more than the amount of the tax
C. Rise by less than the amount of the tax
D. Remain the same
Answer : B
A. Rise by the amount of the tax
B. Rise by more than the amount of the tax
C. Rise by less than the amount of the tax
D. Remain the same
Answer : B
15. If the commodity is inferior then the increase in income of the consumer results in:
A. More purchase
B. Less purchase
C. Same purchase
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. More purchase
B. Less purchase
C. Same purchase
D. None of the above
Answer : B
16. A budget line shows:
A. Quantities of commodity X which a consumer could buy with no amount of Y
B. Quantities of commodity Y which a consumer could buy with no amount of X
C. The different combinations of X and Y that the consumer could buy
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Quantities of commodity X which a consumer could buy with no amount of Y
B. Quantities of commodity Y which a consumer could buy with no amount of X
C. The different combinations of X and Y that the consumer could buy
D. All of the above
Answer : D
17. The right of individuals to control productive resources is known as:
A. Monopoly
B. Private property
C. Workable competition
D. Oligopoly
Answer : B
A. Monopoly
B. Private property
C. Workable competition
D. Oligopoly
Answer : B
18. Cross-elasticity of demand is measured as:
A. Percentage change in the quantity of a commodity demanded divided by the percentage change in the price of that commodity
B. Percentage change in the quantity of commodity X divided by percentage change in the price of commodity Y
C. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X
D. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X divided by percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity Y
Answer : B
A. Percentage change in the quantity of a commodity demanded divided by the percentage change in the price of that commodity
B. Percentage change in the quantity of commodity X divided by percentage change in the price of commodity Y
C. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X
D. Percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity X divided by percentage change in the quantity demanded of commodity Y
Answer : B
19. Indifference curve approach (ordinal approach) is superior to utility approach (cardinal approach) because:
A. In ordinal approach we can separate the income effect from the substitution effect of a price change
B. In ordinal approach we can study the consumer behavior more closely
C. In ordinal approach the consumer is assumed more rational
D. In ordinal approac the consumer has more income
Answer : A
A. In ordinal approach we can separate the income effect from the substitution effect of a price change
B. In ordinal approach we can study the consumer behavior more closely
C. In ordinal approach the consumer is assumed more rational
D. In ordinal approac the consumer has more income
Answer : A
20. The slutsky demand curve includes:
A. Income effect
B. Price effect
C. Substitution effect
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Income effect
B. Price effect
C. Substitution effect
D. None of the above
Answer : B
21. The cost that a firm incurs in purchasing or hiring any factor of production is referred to as:
A. Explicit cost
B. Implicit cost
C. Variable cost
D. Fixed cost
Answer : A
A. Explicit cost
B. Implicit cost
C. Variable cost
D. Fixed cost
Answer : A
22. Who finalized the model of monopolistic competition?
A. Ricardo
B. Marshal
C. Chamberlin
D. Mrs. Robinson
Answer : C
A. Ricardo
B. Marshal
C. Chamberlin
D. Mrs. Robinson
Answer : C
23. Stable cobweb model is a:
A. Simple model
B. Dynamic model
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
A. Simple model
B. Dynamic model
C. Both of them
D. None of them
Answer : C
24. When a consumer reached at the point of saturation then marginal utility (MU) is:
A. Negative
B. One
C. Positive
D. Zero
Answer : D
A. Negative
B. One
C. Positive
D. Zero
Answer : D
25. Marshallian demand function is also known as:
A. Utility demand function
B. Compensated demand function
C. Collective demand function
D. Relative demand function
Answer : B
A. Utility demand function
B. Compensated demand function
C. Collective demand function
D. Relative demand function
Answer : B
26. The long run average cost curve is:
A. Cup-shaped
B. Oval-shaped
C. Saucer-shaped
D. Glass-shaped
Answer : C
A. Cup-shaped
B. Oval-shaped
C. Saucer-shaped
D. Glass-shaped
Answer : C
27. Regarding economic decisions, economics of uncertainty identifies:
A. No risks
B. Risks
C. Safety
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. No risks
B. Risks
C. Safety
D. None of the above
Answer : B
28. Classical production function is:
A. Q = f(L)
B. U =f(X)
C. Q =f(K)
D. Q =f(L,K)
Answer : D
A. Q = f(L)
B. U =f(X)
C. Q =f(K)
D. Q =f(L,K)
Answer : D
29. If at the unchanged price, the demand for a commodity goes up, or the quantity demanded remains the same when its price goes up, it is called:
A. Contraction of demand
B. Decrease in demand
C. Increase in demand
D. Extension of demand
Answer : C
A. Contraction of demand
B. Decrease in demand
C. Increase in demand
D. Extension of demand
Answer : C
30. In the long-run competitive equilibrium:
A. There is tendency for firms to enter but not leave the industry
B. Firms have no tendency either to enter or to leave the industry
C. Some firms may enter while the others may leave the market even after the equilibrium of the industry
D. Entry or exit of the firms cannot be predicted
Answer : C
A. There is tendency for firms to enter but not leave the industry
B. Firms have no tendency either to enter or to leave the industry
C. Some firms may enter while the others may leave the market even after the equilibrium of the industry
D. Entry or exit of the firms cannot be predicted
Answer : C
31. One common definition of a luxury good is a good with income elasticity:
A. Greater than one
B. Equal to one
C. Less than one but more than zero
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Greater than one
B. Equal to one
C. Less than one but more than zero
D. None of the above
Answer : A
32. A firms profit is equal to:
A. R-C
B. R>C
C. R
Answer : A
A. R-C
B. R>C
C. R
Answer : A
33. In an indifference curve diagram, when the price of a product increases, the decline in quantity demanded that results if consumers utility or welfare is kept constant is referred to as the:
A. Utility effect
B. Budget line effect
C. Substitution effect
D. Income effect
Answer : C
A. Utility effect
B. Budget line effect
C. Substitution effect
D. Income effect
Answer : C
34. For monopolistic competitive firm:
A. P=AR and P>MR
B. P
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. P=AR and P>MR
B. P
D. None of the above
Answer : A
35. Who wrote Economics of Imperfect Competition?
A. E.H.Chamberlin
B. Joan Robinson
C. E.A.G.Robinson
D. J.M.Keynes
Answer : B
A. E.H.Chamberlin
B. Joan Robinson
C. E.A.G.Robinson
D. J.M.Keynes
Answer : B
36. While buying two goods X and Y with unequal prices, to maximize total utility from his income, a consumer should get:
A. Equal MU from both commodities X and Y
B. More MU from commodity X than from commodity Y
C. More MU from commodity Y than from commodity X
D. Equal marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity X and commodity Y
Answer : D
A. Equal MU from both commodities X and Y
B. More MU from commodity X than from commodity Y
C. More MU from commodity Y than from commodity X
D. Equal marginal utility from the last rupee spent on commodity X and commodity Y
Answer : D
37. Which of the following is the work of A.C.Pigou?
A. Economics of Welfare
B. Commerce and Trade
C. Industrial Economics
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Economics of Welfare
B. Commerce and Trade
C. Industrial Economics
D. None of the above
Answer : A
38. Isocost line shows the combinations of labor and capital where a firms budget is:
A. Fully spent
B. Half spent
C. Partially spent
D. Nearly spent
Answer : A
A. Fully spent
B. Half spent
C. Partially spent
D. Nearly spent
Answer : A
39. Slope of a demand curve is:
A. Not relevant to elasticity
B. The only factor determining elasticity
C. Only one of the factors influencing elasticity
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Not relevant to elasticity
B. The only factor determining elasticity
C. Only one of the factors influencing elasticity
D. None of the above
Answer : B
40. When the law of demand operates the demand curve:
A. Slopes downward
B. Slopes upward
C. Becomes horizontal
D. Becomes vertical
Answer : A
A. Slopes downward
B. Slopes upward
C. Becomes horizontal
D. Becomes vertical
Answer : A
41. The main contribution of Prof. Lord Keynes is in the field of:
A. Determination of the rate of interest
B. Determination of the market price
C. Determination of the wage rate
D. Determination of production of firm
Answer : A
A. Determination of the rate of interest
B. Determination of the market price
C. Determination of the wage rate
D. Determination of production of firm
Answer : A
42. Marginal Productivity Theory deals with the theory of:
A. Distribution
B. Exchange
C. Market structure
D. Consumer behaviour
Answer : A
A. Distribution
B. Exchange
C. Market structure
D. Consumer behaviour
Answer : A
strong>43. At final equilibrium in cournot model, each firm sells:
A. 1/2 of the total market demand
B. 1/4 of the total market demand
C. 1/3 of the total market demand
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. 1/2 of the total market demand
B. 1/4 of the total market demand
C. 1/3 of the total market demand
D. None of the above
Answer : C
44. The output where TC = TR & AC = AR:
A. Break-even point
B. Load point
C. Shut-down point
D. Revenue cost point
Answer : A
A. Break-even point
B. Load point
C. Shut-down point
D. Revenue cost point
Answer : A
45. In modern cost theory, AVC= b1 and MC= b1 in the range of:
A. Excess capacity
B. Reserve capacity
C. Limited capacity
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Excess capacity
B. Reserve capacity
C. Limited capacity
D. None of the above
Answer : B
46. Cross-elasticity of demand or cross-price elasticity between two complements will be:
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Infinite
D. Zero
Answer : A
A. Negative
B. Positive
C. Infinite
D. Zero
Answer : A
47. If production increases under increasing returns to scale, the cost will:
A. Increase at decreasing rate
B. Increase at constant rate
C. Decrease at increasing rate
D. Increase at increasing rate
Answer : A
A. Increase at decreasing rate
B. Increase at constant rate
C. Decrease at increasing rate
D. Increase at increasing rate
Answer : A
48. A market demand schedule is obtained by adding individual demand schedules:
A. Horizontally
B. Vertically
C. Permanently
D. Perpetually
Answer : A
A. Horizontally
B. Vertically
C. Permanently
D. Perpetually
Answer : A
49. In monopolistic competition, the real differentiation in products is due to difference in:
A. Style
B. Consumer
C. Cost
D. Material
Answer : D
A. Style
B. Consumer
C. Cost
D. Material
Answer : D
50. The effect of consumer boycotts usually is:
A. A rise in the price of the product
B. A decrease in the demand for the product
C. A decrease in the supply of the product
D. An increase in the quantity supplied of the product
Answer : B
A. A rise in the price of the product
B. A decrease in the demand for the product
C. A decrease in the supply of the product
D. An increase in the quantity supplied of the product
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Human reproductive system MCQ for SBI PO [Solved]
CTET - Urologic infections and inflammations 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Error Detection Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
General Biology Set 2 1000+ MCQ with answer for RBI Grade B officer
1000+ Idioms & Phrases Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Planet Kingdom 1000+ MCQ with answer for XAT