Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC CGL
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. One ton of refrigeration capacity is equivalent to the heat removal rate of
A. 50 kcal/hr
B. 200 BTU/hr
C. 200 BTU/minute
D. 200 BTU/day
Answer : C
A. 50 kcal/hr
B. 200 BTU/hr
C. 200 BTU/minute
D. 200 BTU/day
Answer : C
2. Melting of ice is an example of an __________ process.
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : B
3. The equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction at two different temperatures is given by
A. Kp2/Kp1 = - (?H/R) (1/T2 - 1/T1)
B. Kp2/Kp1 = (?H/R) (1/T2 - 1/T1)
C. Kp2/Kp1 = ?H (1/T2 - 1/T1)
D. Kp2/Kp1 = - (1/R) (1/T2 - 1/T1)
Answer : A
A. Kp2/Kp1 = - (?H/R) (1/T2 - 1/T1)
B. Kp2/Kp1 = (?H/R) (1/T2 - 1/T1)
C. Kp2/Kp1 = ?H (1/T2 - 1/T1)
D. Kp2/Kp1 = - (1/R) (1/T2 - 1/T1)
Answer : A
4. Joule-Thomson co-efficient for a perfect gas is
A. Zero
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. None of these
Answer : A
5. __________ calorimeter is normally used for measuring the dryness fraction of steam, when it is very low.
A. Bucket
B. Throttling
C. Separating
D. A combination of separating & throttling
Answer : D
A. Bucket
B. Throttling
C. Separating
D. A combination of separating & throttling
Answer : D
6. During adiabatic expansion of gas
A. Pressure remains constant
B. Pressure is increased
C. Temperature remains constant
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Pressure remains constant
B. Pressure is increased
C. Temperature remains constant
D. None of these
Answer : D
7. A system is said to be isopiestic, if there is no __________ change.
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Volume
D. None of these
Answer : B
8. Clapeyron Equation deals with the
A. Rate of change of vapour pressure with temperature
B. Effect of an inert gas on vapour pressure
C. Calculation of ?F for spontaneous phase change
D. Temperature dependence of heat of phase transition
Answer : A
A. Rate of change of vapour pressure with temperature
B. Effect of an inert gas on vapour pressure
C. Calculation of ?F for spontaneous phase change
D. Temperature dependence of heat of phase transition
Answer : A
9. The temperature at which a real gas obeys the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is called __________ temperature.
A. Boyle
B. Inversion
C. Critical
D. Reduced
Answer : A
A. Boyle
B. Inversion
C. Critical
D. Reduced
Answer : A
10. Adiabatic compression of a saturated water vapour makes it
A. Supersaturated
B. Superheated
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
A. Supersaturated
B. Superheated
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
11. The variation of heat of reaction with temperature at constant pressure is given by the __________ law.
A. Kelvin's
B. Antoines
C. Kirchoffs
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Kelvin's
B. Antoines
C. Kirchoffs
D. None of these
Answer : C
12. Which of the following behaves most closely like an ideal gas?
A. He
B. N2
C. O2
D. H2
Answer : A
A. He
B. N2
C. O2
D. H2
Answer : A
13. PVy = constant, holds good for an isentropic process, which is
A. Reversible and isothermal
B. Isothermal and irreversible
C. Reversible and adiabatic
D. Adiabatic and irreversible
Answer : C
A. Reversible and isothermal
B. Isothermal and irreversible
C. Reversible and adiabatic
D. Adiabatic and irreversible
Answer : C
14. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. A refrigeration cycle violates the second law of thermodynamics
B. Refrigeration cycle is normally represented by a temperature vs. entropy plot
C. In a refrigerator, work required decreases as the temperature of the refrigerator and the temperature at which heat is rejected increases
D. One ton of refrigeration is equivalent to the rate of heat absorption equal to 3.53 kW
Answer : A
A. A refrigeration cycle violates the second law of thermodynamics
B. Refrigeration cycle is normally represented by a temperature vs. entropy plot
C. In a refrigerator, work required decreases as the temperature of the refrigerator and the temperature at which heat is rejected increases
D. One ton of refrigeration is equivalent to the rate of heat absorption equal to 3.53 kW
Answer : A
15. The standard state of a gas (at a given temperature) is the state in which fugacity is equal to
A. Unity
B. Activity
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Unity
B. Activity
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
16. To obtain integrated form of Clausius-Clapeyron equation, ln (P2/P1) = (?HV/R) (1/T1 - 1/T2) from the exact Clapeyron equation, it is assumed that the
A. Volume of the liquid phase is negligible compared to that of vapour phase
B. Vapour phase behaves as an ideal gas
C. Heat of vaporisation is independent of temperature
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : D
A. Volume of the liquid phase is negligible compared to that of vapour phase
B. Vapour phase behaves as an ideal gas
C. Heat of vaporisation is independent of temperature
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : D
17. The temperature at which a real gas obeys the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is called the __________ temperature.
A. Critical
B. Boyle
C. Inversion
D. Reduced
Answer : B
A. Critical
B. Boyle
C. Inversion
D. Reduced
Answer : B
18. Which of the following is a thermodynamic property of a system?
A. Concentration
B. Mass
C. Temperature
D. Entropy
Answer : D
A. Concentration
B. Mass
C. Temperature
D. Entropy
Answer : D
19. For a constant volume process __________ by the system is used only to increase the internal energy.
A. Heat absorbed
B. Work done
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : A
A. Heat absorbed
B. Work done
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : A
20. For a spontaneous process, free energy
A. Is zero
B. Increases
C. Decreases whereas the entropy increases
D. And entropy both decrease
Answer : C
A. Is zero
B. Increases
C. Decreases whereas the entropy increases
D. And entropy both decrease
Answer : C
21. For an ideal gas, the enthalpy
A. Increases with rise in pressure
B. Decreases with rise in pressure
C. Is independent of pressure
D. Is a path functio
Answer : C
A. Increases with rise in pressure
B. Decreases with rise in pressure
C. Is independent of pressure
D. Is a path functio
Answer : C
22. Cv for an ideal gas
A. Does not depend upon temperature
B. Is independent of pressure only
C. Is independent of volume only
D. Is independent of both pressure and volume
Answer : D
A. Does not depend upon temperature
B. Is independent of pressure only
C. Is independent of volume only
D. Is independent of both pressure and volume
Answer : D
23. For an ideal gas, the activity co-efficient is
A. Directly proportional to pressure
B. Inversely proportional to pressure
C. Unity at all pressures
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Directly proportional to pressure
B. Inversely proportional to pressure
C. Unity at all pressures
D. None of these
Answer : C
24. A cylinder contains 640 gm of liquid oxygen. The volume occupied (in litres) by the oxygen, when it is released and brought to standard conditions (0°C, 760 mm Hg) will be __________ litres.
A. 448
B. 224
C. 22.4
D. Data insufficient; can't be computed
Answer : A
A. 448
B. 224
C. 22.4
D. Data insufficient; can't be computed
Answer : A
25. When pressure is applied on the system, ice ? water, then
A. Equilibrium cannot be established
B. More ice will be formed
C. More water will be formed
D. Evaporation of water will take place
Answer : C
A. Equilibrium cannot be established
B. More ice will be formed
C. More water will be formed
D. Evaporation of water will take place
Answer : C
26. Requisites of a reversible process is that the
A. System and surroundings pressure be equal
B. Friction in the system should be absent
C. System and surroundings temperature be equal
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. System and surroundings pressure be equal
B. Friction in the system should be absent
C. System and surroundings temperature be equal
D. None of these
Answer : B
27. Keeping the pressure constant, to double the volume of a given mass of an ideal gas at 27°C, the temperature should be raised to __________ °C.
A. 270
B. 327
C. 300
D. 540
Answer : B
A. 270
B. 327
C. 300
D. 540
Answer : B
28. A change in state involving a decrease in entropy can be spontaneous, only if
A. It is exothermic
B. It is isenthalpic
C. It takes place isothermally
D. It takes place at constant volume
Answer : A
A. It is exothermic
B. It is isenthalpic
C. It takes place isothermally
D. It takes place at constant volume
Answer : A
29. Domestic refrigerator usually works on the __________ refrigeration cycle.
A. Carnot
B. Air
C. Absorption
D. vapour-ejection
Answer : C
A. Carnot
B. Air
C. Absorption
D. vapour-ejection
Answer : C
30. No work is done by the system, when a reaction occurs at constant
A. Volume
B. Temperature
C. Pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Volume
B. Temperature
C. Pressure
D. None of these
Answer : A
31. The root mean square speed of molecules of a gas is equal to (where, m = mass of the molecule K = Boltzmanns constant, T = absolute temperature)
A. ?(2KT/m)
B. ?(3KT/m)
C. ?(6KT/m)
D. 3KT/m
Answer : B
A. ?(2KT/m)
B. ?(3KT/m)
C. ?(6KT/m)
D. 3KT/m
Answer : B
32. Solubility of a substance which dissolves with an increase in volume and liberation of heat will be favoured by the
A. Low pressure and high temperature
B. Low pressure and low temperature
C. High pressure and low temperature
D. High pressure and high temperature
Answer : B
A. Low pressure and high temperature
B. Low pressure and low temperature
C. High pressure and low temperature
D. High pressure and high temperature
Answer : B
33. First law of thermodynamics deals with the
A. Direction of energy transfer
B. Reversible processes only
C. Irreversible processes only
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Direction of energy transfer
B. Reversible processes only
C. Irreversible processes only
D. None of these
Answer : A
34. Fugacity is a measure of the
A. Escaping tendencies of the same substance in different phases of a system
B. Relative volatility of a mixture of two miscible liquids
C. Behaviour of ideal gases
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Escaping tendencies of the same substance in different phases of a system
B. Relative volatility of a mixture of two miscible liquids
C. Behaviour of ideal gases
D. None of these
Answer : A
35. The compressibility factor of a gas is given by (where, V1 = actual volume of the gas V2 = gas volume predicted by ideal gas law)
A. V1/V2
B. V2/V1
C. V1 - V2
D. V1.V2
Answer : A
A. V1/V2
B. V2/V1
C. V1 - V2
D. V1.V2
Answer : A
36. The expression, ?G = nRT. ln(P2/P1), gives the free energy change
A. With pressure changes at constant temperature
B. Under reversible isothermal volume change
C. During heating of an ideal gas
D. During cooling of an ideal gas
Answer : A
A. With pressure changes at constant temperature
B. Under reversible isothermal volume change
C. During heating of an ideal gas
D. During cooling of an ideal gas
Answer : A
37. Which of the following diagrams does not represent an Otto cycle?
A.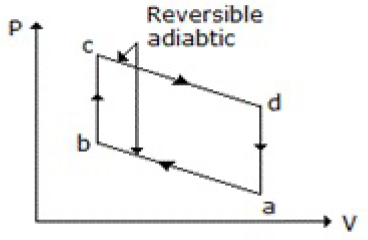
B.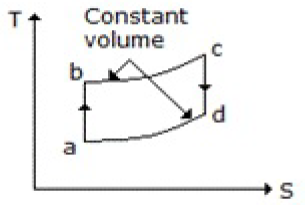
C.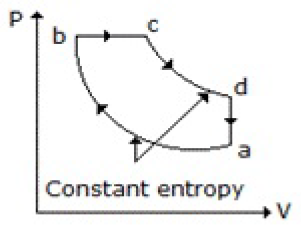
D. None of these
Answer : C
A.

B.

C.

D. None of these
Answer : C
38. The freezing point of a liquid decreases when the pressure is increased, if the liquid __________ while freezing.
A. Contracts
B. Expands
C. Does not change in volume
D. Either (A), (B) or (C)
Answer : A
A. Contracts
B. Expands
C. Does not change in volume
D. Either (A), (B) or (C)
Answer : A
39. Isotherm on an enthalpy-concentration diagram, for an ideal solution will be a
A. Straight line
B. Sine curve
C. Parabola
D. Hyperbola
Answer : A
A. Straight line
B. Sine curve
C. Parabola
D. Hyperbola
Answer : A
40. __________ does not change during phase transformation processes like sublimation, melting & vaporisation.
A. Entropy
B. Gibbs free energy
C. Internal energy
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : B
A. Entropy
B. Gibbs free energy
C. Internal energy
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : B
41. Critical temperature is defined as the temperature above which a gas will
A. Not liquify (barring exceptions)
B. Immediately liquify
C. Never liquify however high the pressure may be
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Not liquify (barring exceptions)
B. Immediately liquify
C. Never liquify however high the pressure may be
D. None of these
Answer : C
42. In any spontaneous process,
A. Only F decreases
B. Only A decreases
C. Both F and A decreases
D. Both F and A increase
Answer : C
A. Only F decreases
B. Only A decreases
D. Both F and A increase
Answer : C
43. Joule-Thomson co-efficient depends on the
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Both (A) & (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : C
44. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. The values of (?P/?V)T and (?2P/?V2)T are zero for a real gas at its critical point
B. Heat transferred is equal to the change in the enthalpy of the system, for a constant pressure, non-flow, mechanically reversible process
C. Thermal efficiency of a Carnot engine depends upon the properties of the working fluid besides the source & sink temperatures
D. During a reversible adiabatic process, the entropy of a substance remains constant
Answer : C
A. The values of (?P/?V)T and (?2P/?V2)T are zero for a real gas at its critical point
B. Heat transferred is equal to the change in the enthalpy of the system, for a constant pressure, non-flow, mechanically reversible process
C. Thermal efficiency of a Carnot engine depends upon the properties of the working fluid besides the source & sink temperatures
D. During a reversible adiabatic process, the entropy of a substance remains constant
Answer : C
45. Entropy of the system decreases, when
A. Snow melts into water
B. A gas expands spontaneously from high pressure to low pressure
C. Water is converted into ice
D. Both (B) & (C)
Answer : D
A. Snow melts into water
B. A gas expands spontaneously from high pressure to low pressure
C. Water is converted into ice
D. Both (B) & (C)
Answer : D
46. Fugacity co-efficient of a substance is the ratio of its fugacity to
A. Mole fraction
B. Activity
C. Pressure
D. Activity co-efficient
Answer : C
A. Mole fraction
B. Activity
C. Pressure
D. Activity co-efficient
Answer : C
47. Heat of reaction at constant volume is identified with __________ change.
A. Enthalpy
B. Internal energy
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
A. Enthalpy
B. Internal energy
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. Neither (A) nor (B)
Answer : B
48. Heat evolved/absorbed during conversion of a substance from one allotropic form to another is termed as the heat of
A. Fusion
B. Vaporisation
C. Transition
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Fusion
B. Vaporisation
C. Transition
D. None of these
Answer : C
49. Pick out the correct statement.
A. A real gas on expansion in vacuum gets heated up
B. An ideal gas on expansion in vacuum gets cooled
C. An ideal gas on expansion in vacuum gets heated up
D. A real gas on expansion in vacuum cools down whereas ideal gas remains unaffected
Answer : D
A. A real gas on expansion in vacuum gets heated up
B. An ideal gas on expansion in vacuum gets cooled
C. An ideal gas on expansion in vacuum gets heated up
D. A real gas on expansion in vacuum cools down whereas ideal gas remains unaffected
Answer : D
50. Compressibility factor for almost all the gases are approximately same at the same
A. Pressure and temperature
B. Reduced pressure and reduced temperature
C. Critical pressure and critical temperature
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Pressure and temperature
B. Reduced pressure and reduced temperature
C. Critical pressure and critical temperature
D. None of these
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Current Affairs November 2022 Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Current Affairs August 2017 Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Clause Analysis MCQ Solved Paper for RRB JE
LIC AAO - Visual Basic .NET 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Fluid Mechanics MCQ for CTET [Solved]
Construction Planning and Management MCQ Solved Paper for SSC GD