Engineering Mechanics MCQ Solved Paper for SBI Clerk
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The units of moment of inertia of an area are
A. kg-m²
B. m?
C. kg/m²
D. m³
Answer : B
A. kg-m²
B. m?
C. kg/m²
D. m³
Answer : B
2. The resolved part of the resultant of two forces inclined at an angle ? in a given direction is equal to
A. The algebraic sum of the resolved parts of the forces in the given direction
B. The sum of the resolved parts of the forces in the given direction
C. The difference of the forces multiplied by the cosine of ?
D. The sum of the forces multiplied by the sine of ?
Answer : A
A. The algebraic sum of the resolved parts of the forces in the given direction
B. The sum of the resolved parts of the forces in the given direction
C. The difference of the forces multiplied by the cosine of ?
D. The sum of the forces multiplied by the sine of ?
Answer : A
3. The resultant of the following three couples 20 kg force, 0.5 m arm, +ve sense 30 kg force, 1 m arm, -ve sense 40 kg force, 0.25 m arm, +ve sense having arm of 0.5 m will be
A. 20 kg, -ve sense
B. 20 kg, + ve sense
C. 10 kg, + ve sense
D. 10 kg, -ve sense
Answer : A
A. 20 kg, -ve sense
B. 20 kg, + ve sense
C. 10 kg, + ve sense
D. 10 kg, -ve sense
Answer : A
4. When two elastic bodies collide with each other,
A. The two bodies will momentarily come to rest after collision
B. The two bodies tend to compress and deform at the surface of contact
C. The two bodies begin to regain their original shape
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. The two bodies will momentarily come to rest after collision
B. The two bodies tend to compress and deform at the surface of contact
C. The two bodies begin to regain their original shape
D. All of the above
Answer : D
5. Joule is the unit of
A. Force
B. Work
C. Power
D. Velocity
Answer : B
A. Force
B. Work
C. Power
D. Velocity
Answer : B
6. When a person, on a bicycle, drives round a curve, he has to lean __________ to maintain equilibrium.
A. Inward
B. Outward
C. Towards front
D. Towards back
Answer : A
A. Inward
B. Outward
C. Towards front
D. Towards back
Answer : A
7. A couple produces
A. Translatory motion
B. Rotational motion
C. Combined translatory and rotational motion
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Translatory motion
B. Rotational motion
C. Combined translatory and rotational motion
D. None of the above
Answer : B
8. Forces are called concurrent when their lines of action meet in
A. One point
B. Two points
C. Plane
D. Perpendicular planes
Answer : A
A. One point
B. Two points
C. Plane
D. Perpendicular planes
Answer : A
9. In order to completely specify angular displacement by a vector, it must fix
A. Direction of the axis of rotation
B. Magnitude of angular displacement
C. Sense of angular displacement
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. Direction of the axis of rotation
B. Magnitude of angular displacement
C. Sense of angular displacement
D. All of these
Answer : D
10. Two blocks A and B of masses 150 kg and 50 kg respectively are connected by means of a string as shown in the below figure. The tension in all the three strings __________ be same. 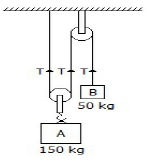
A. Will
B. Will not
C. Either A or B
D. None of these
Answer : A

A. Will
B. Will not
C. Either A or B
D. None of these
Answer : A
11. The forces, which meet at one point and their lines of action also lie on the same plane, are known as
A. Coplanar concurrent forces
B. Coplanar non-concurrent forces
C. Non-coplanar concurrent forces
D. Non-coplanar non-concurrent forces
Answer : A
A. Coplanar concurrent forces
B. Coplanar non-concurrent forces
C. Non-coplanar concurrent forces
D. Non-coplanar non-concurrent forces
Answer : A
12. The process of finding out the resultant force is called __________ of forces.
A. Composition
B. Resolution
C. Decomposition
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Composition
B. Resolution
C. Decomposition
D. None of these
Answer : A
13. The range of projectile will be maximum for a given velocity of projectile, when the angle of projection (?) is
A. ?/2
B. 30° + ?/2
C. 45° + ?/2
D. 60° + ?/2
Answer : C
A. ?/2
B. 30° + ?/2
C. 45° + ?/2
D. 60° + ?/2
Answer : C
14. The algebraic sum of moments of the forces forming couple about any point in their plane is
A. Equal to the moment of the couple
B. Constant
C. Both of above are correct
D. Both of above are wrong
Answer : A
A. Equal to the moment of the couple
B. Constant
C. Both of above are correct
D. Both of above are wrong
Answer : A
15. If three forces acting in different planes can be represented by a triangle, these will be in
A. Non-equilibrium
B. Partial equilibrium
C. Full equilibrium
D. Unpredictable
Answer : A
A. Non-equilibrium
B. Partial equilibrium
C. Full equilibrium
D. Unpredictable
Answer : A
16. Limiting force of friction is the
A. Tangent of angle between normal reaction and the resultant of normal reaction and limiting friction
B. Ratio of limiting friction and normal reaction
C. The friction force acting when the body is just about to move
D. The friction force acting when the body is in motion
Answer : C
A. Tangent of angle between normal reaction and the resultant of normal reaction and limiting friction
B. Ratio of limiting friction and normal reaction
C. The friction force acting when the body is just about to move
D. The friction force acting when the body is in motion
Answer : C
17. The horizontal range of a projectile (R) is given by
A. R = u² cos2?/g
B. R = u² sin2?/g
C. R = u² cos?/g
D. R = u² sin?/g
Answer : B
A. R = u² cos2?/g
B. R = u² sin2?/g
C. R = u² cos?/g
D. R = u² sin?/g
Answer : B
18. The maximum velocity of a particle moving with simple harmonic motion is
A. ?
B. ?r
C. ?2r
D. ?/r
Answer : B
A. ?
B. ?r
C. ?2r
D. ?/r
Answer : B
19. The unit of force in S.I. system of units is
A. Dyne
B. Kilogram
C. Newton
D. Watt
Answer : C
A. Dyne
B. Kilogram
C. Newton
D. Watt
Answer : C
20. Which of the following do not have identical dimensions?
A. Momentum and impulse
B. Torque and energy
C. Torque and work
D. Moment of a force and angular momentum.
Answer : D
A. Momentum and impulse
B. Torque and energy
C. Torque and work
D. Moment of a force and angular momentum.
Answer : D
21. When the lift is moving upwards with some acceleration, the pressure exerted by a man is __________ to its acceleration.
A. Directly proportional
B. Inversely proportional
C. Cube root
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Directly proportional
B. Inversely proportional
C. Cube root
D. None of these
Answer : A
22. The moment of inertia of a square of side (a) about an axis through its centre of gravity is
A. a4/4
B. a4/8
C. a4/12
D. a4/36
Answer : C
A. a4/4
B. a4/8
C. a4/12
D. a4/36
Answer : C
23. In ideal machines
A. Mechanical advantage is greater than velocity ratio
B. Mechanical advantage is equal to velocity ratio
C. Mechanical advantage is less than velocity ratio
D. Mechanical advantage is unity
Answer : B
A. Mechanical advantage is greater than velocity ratio
B. Mechanical advantage is equal to velocity ratio
C. Mechanical advantage is less than velocity ratio
D. Mechanical advantage is unity
Answer : B
24. The loss of kinetic energy during inelastic impact, is given by (where m1 = Mass of the first body, m2 = Mass of the second body, and u1 and u2 = Velocities of the first and second bodies respectively.)
A. [m? m?/2(m? + m?)] (u? - u?)²
B. [2(m? + m?)/m? m?] (u? - u?)²
C. [m? m?/2(m? + m?)] (u?² - u?²)
D. [2(m? + m?)/m? m?] (u?² - u?²)
Answer : A
A. [m? m?/2(m? + m?)] (u? - u?)²
B. [2(m? + m?)/m? m?] (u? - u?)²
C. [m? m?/2(m? + m?)] (u?² - u?²)
D. [2(m? + m?)/m? m?] (u?² - u?²)
Answer : A
25. The moment of a force
A. Is the turning effect produced by a force, on the body, on which it acts
B. Is equal to the product of force acting on the body and the perpendicular distance of a point and the line of action of the force
C. Is equal to twice the area of the triangle, whose base is the line representing the force and whose vertex is the point, about which the moment is taken
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Is the turning effect produced by a force, on the body, on which it acts
B. Is equal to the product of force acting on the body and the perpendicular distance of a point and the line of action of the force
C. Is equal to twice the area of the triangle, whose base is the line representing the force and whose vertex is the point, about which the moment is taken
D. All of the above
Answer : D
26. The potential energy of a vertically raised body is __________ the kinetic energy of a vertically falling body.
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : A
27. According to Newton's first law of motion,
A. Everybody continues in its state of rest or of uniform motion, in a straight line, unless it is acted upon by some external force
B. The rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the impressed force, and takes place in the same direction, in which the force acts
C. To every action, there is always an equal and opposite reaction
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Everybody continues in its state of rest or of uniform motion, in a straight line, unless it is acted upon by some external force
B. The rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the impressed force, and takes place in the same direction, in which the force acts
C. To every action, there is always an equal and opposite reaction
D. None of the above
Answer : A
28. The rate of doing work is known as
A. Potential energy
B. Kinetic energy
C. Power
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Potential energy
B. Kinetic energy
C. Power
D. None of these
Answer : C
29. The periodic time of one oscillation for a simple pendulum is (where l = Length of the pendulum.)
A. (1/2?). ?(l/g)
B. (1/2?). ?(g/l)
C. 2?. ?(l/g)
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. (1/2?). ?(l/g)
B. (1/2?). ?(g/l)
C. 2?. ?(l/g)
D. None of these
Answer : C
30. The range of projectile (R) on an upward inclined plane is
A. g. cos² ?/2u². sin (? + ?). cos ?
B. 2u². sin (? + ?). cos ?/g. cos² ?
C. g. cos² ?/2u². sin (? - ?). cos ?
D. 2u². sin (? - ?). cos ?/g. cos² ?
Answer : D
A. g. cos² ?/2u². sin (? + ?). cos ?
B. 2u². sin (? + ?). cos ?/g. cos² ?
C. g. cos² ?/2u². sin (? - ?). cos ?
D. 2u². sin (? - ?). cos ?/g. cos² ?
Answer : D
31. The force required to move the body up the plane will be minimum if it makes an angle with the inclined plane __________ the angle of friction.
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : A
32. The length of a second's pendulum is
A. 94.9 cm
B. 99.4 cm
C. 100 cm
D. 101 cm
Answer : B
A. 94.9 cm
B. 99.4 cm
C. 100 cm
D. 101 cm
Answer : B
33. A force acting on a body may
A. Change its motion
B. Balance the other forces acting on it
C. Retard its motion
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Change its motion
B. Balance the other forces acting on it
C. Retard its motion
D. All of the above
Answer : D
34. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
A. The tangent of the angle of friction is equal to coefficient of friction
B. The angle of repose is equal to angle of friction
C. The tangent of the angle of repose is equal to coefficient of friction
D. The sine of the angle of repose is equal to coefficient to friction
Answer : D
A. The tangent of the angle of friction is equal to coefficient of friction
B. The angle of repose is equal to angle of friction
C. The tangent of the angle of repose is equal to coefficient of friction
D. The sine of the angle of repose is equal to coefficient to friction
Answer : D
35. The centre of gravity of a quadrant of a circle lies along its central radius (r) at a distance of
A. 0.5r
B. 0.6 r
C. 0.7 r
D. 0.8 r
Answer : B
A. 0.5r
B. 0.6 r
C. 0.7 r
D. 0.8 r
Answer : B
36. Effect of a force on a body depends upon
A. Magnitude
B. Direction
C. Position or line of action
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Magnitude
B. Direction
C. Position or line of action
D. All of the above
Answer : D
37. A framed structure, as shown in the below figure, is a 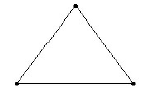
A. Perfect frame
B. Deficient frame
C. Redundant frame
D. None of the above
Answer : A

A. Perfect frame
B. Deficient frame
C. Redundant frame
D. None of the above
Answer : A
38. Which is the correct statement about law of polygon of forces?
A. If any number of forces acting at a point can be represented by the sides of a polygon taken in order, then the forces are in equilibrium
B. If any number of forces acting at a point can be represented in direction and magnitude by the sides of a polygon, then the forces are in equilibrium
C. If a polygon representing forces acting at a point is closed then forces are in equilibrium
D. If any number of forces acting at a point can be represented in direction and magnitude by the sides of a polygon taken in order, then the forces are in equilibrium
Answer : D
A. If any number of forces acting at a point can be represented by the sides of a polygon taken in order, then the forces are in equilibrium
B. If any number of forces acting at a point can be represented in direction and magnitude by the sides of a polygon, then the forces are in equilibrium
C. If a polygon representing forces acting at a point is closed then forces are in equilibrium
D. If any number of forces acting at a point can be represented in direction and magnitude by the sides of a polygon taken in order, then the forces are in equilibrium
Answer : D
39. The bellow figure shows the two equal forces at right angles acting at a point. The value of force R acting along their bisector and in opposite direction is 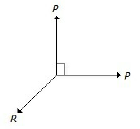
A. P/2
B. 2P
C. ?2 × P
D. P/?2
Answer : C

A. P/2
B. 2P
C. ?2 × P
D. P/?2
Answer : C
40. The static friction
A. Bears a constant ratio to the normal reaction between the two surfaces
B. Is independent of the area of ontact, between the two surfaces
C. Always acts in a direction, opposite to that in which the body tends to move
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Bears a constant ratio to the normal reaction between the two surfaces
B. Is independent of the area of ontact, between the two surfaces
C. Always acts in a direction, opposite to that in which the body tends to move
D. All of the above
Answer : D
41. A body will begin to move down an inclined plane if the angle of inclination of the plane is _________ the angle of friction.
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : C
42. The forces, which meet at one point, but their lines of action do not lie in a plane, are called
A. Coplanar non-concurrent forces
B. Non-coplanar concurrent forces
C. Non-coplanar non-concurrent forces
D. Intersecting forces
Answer : B
A. Coplanar non-concurrent forces
B. Non-coplanar concurrent forces
C. Non-coplanar non-concurrent forces
D. Intersecting forces
Answer : B
43. A smooth cylinder lying on its convex surface remains in __________ equilibrium.
A. Stable
B. Unstable
C. Neutral
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Stable
B. Unstable
C. Neutral
D. None of these
Answer : B
44. If the number of pulleys in a system is equal to its velocity ratio, then it is a __________ system of pulleys
A. First
B. Second
C. Third
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. First
B. Second
C. Third
D. None of these
Answer : B
45. For a self locking machine, the efficiency must be
A. Equal to 50 %
B. Less than 50 %
C. Greater than 50 %
D. 100 %
Answer : B
A. Equal to 50 %
B. Less than 50 %
C. Greater than 50 %
D. 100 %
Answer : B
46. The C.G. of a plane lamina will not be at its geometrical centre in the case of a
A. Right angled triangle
B. Equilateral triangle
C. Square
D. Circle
Answer : A
A. Right angled triangle
B. Equilateral triangle
C. Square
D. Circle
Answer : A
47. Which of the following is the example of lever of first order?
A. Arm of man
B. Pair of scissors
C. Pair of clinical tongs
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Arm of man
B. Pair of scissors
C. Pair of clinical tongs
D. All of the above
Answer : D
48. The energy possessed by a body, for doing work by virtue of its position, is called
A. Potential energy
B. Kinetic energy
C. Electrical energy
D. Chemical energy
Answer : A
A. Potential energy
B. Kinetic energy
C. Electrical energy
D. Chemical energy
Answer : A
49. The centre of gravity of a uniform lamina lies at
A. The centre of heavy portion
B. The bottom surface
C. The midpoint of its axis
D. All of the above
Answer : C
A. The centre of heavy portion
B. The bottom surface
C. The midpoint of its axis
D. All of the above
Answer : C
50. The centre of percussion of a solid cylinder of radius r resting on a horizontal plane will be
A. r/2
B. 2r/3
C. r/A
D. 3r/2
Answer : D
A. r/2
B. 2r/3
C. r/A
D. 3r/2
Answer : D
Sharing is caring
Related Post
State of Matter MCQ Solved Paper for RBI Grade B officer
1000+ Engineering Materials Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Engineering Drawing MCQ Solved Paper for DRDO
1000+ English Grammer MCQ for GMAT [Solved]
Building Materials MCQ Solved Paper for CAT
1000+ General Science MCQ for SSC Scientific Assistant [Solved]