NMAT - Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The change in Gibbs free energy for vaporisation of a pure substance is
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. May be positive or negative
Answer : C
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. May be positive or negative
Answer : C
2. When dilute aqueous solutions of two salts are mixed, the process is associated with
A. Decrease in temperature
B. Increase in temperature
C. No change in temperature
D. Change in temperature which is a function of composition
Answer : B
A. Decrease in temperature
B. Increase in temperature
C. No change in temperature
D. Change in temperature which is a function of composition
Answer : B
3. For an ideal gas, the enthalpy
A. Increases with rise in pressure
B. Decreases with rise in pressure
C. Is independent of pressure
D. Is a path function
Answer : C
A. Increases with rise in pressure
B. Decreases with rise in pressure
C. Is independent of pressure
D. Is a path function
Answer : C
4. When liquid and vapour phases of one component system are in equilibrium (at a given temperature and pressure), the molar free energy is
A. More in vapour phase
B. More in liquid phase
C. Same in both the phases
D. Replaced by chemical potential which is more in vapour phase
Answer : C
A. More in vapour phase
B. More in liquid phase
C. Same in both the phases
D. Replaced by chemical potential which is more in vapour phase
Answer : C
5. Sound waves propagation in air exemplifies an __________ process.
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Adiabatic
B. Isothermal
C. Isometric
D. None of these
Answer : A
6. Equation which relates pressure, volume and temperature of a gas is called the
A. Equation of state
B. Gibbs Duhem equation
C. Ideal gas equation
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Equation of state
B. Gibbs Duhem equation
C. Ideal gas equation
D. None of these
Answer : A
7. In an irreversible process
A. Tds = dE - dW = 0
B. dE - dW - Tds = 0
C. Tds - dE + dW < 0
D. Tds - dT + dW < 0
Answer : C
A. Tds = dE - dW = 0
B. dE - dW - Tds = 0
C. Tds - dE + dW < 0
D. Tds - dT + dW < 0
Answer : C
8. Lowering of condenser temperature (keeping the evaporator temperature constant) in case of vapour compression refrigeration system results in
A. Increased COP
B. Same COP
C. Decreased COP
D. Increased or decreased COP; depending upon the type of refrigerant
Answer : A
A. Increased COP
B. Same COP
C. Decreased COP
D. Increased or decreased COP; depending upon the type of refrigerant
Answer : A
9. The temperature at which a real gas obeys the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is called the __________ temperature.
A. Critical
B. Boyle
C. Inversion
D. Reduced
Answer : B
A. Critical
B. Boyle
C. Inversion
D. Reduced
Answer : B
10. The number of degrees of freedom for an azeotropic mixture in a two component vapour-liquid equilibria is/are
A. Zero
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
Answer : B
A. Zero
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
Answer : B
11. A gas shows deviation from ideal behaviour at
A. Low pressure and high temperature
B. Low pressure and low temperature
C. Low temperature and high pressure
D. High temperature and high pressure
Answer : C
A. Low pressure and high temperature
B. Low pressure and low temperature
C. Low temperature and high pressure
D. High temperature and high pressure
Answer : C
12. Pick out the correct statement.
A. Entropy and enthalpy are path functions
B. In a closed system, the energy can be exchanged with the surrounding, while matter cannot be exchanged
C. All the natural processes are reversible in nature
D. Work is a state function
Answer : C
A. Entropy and enthalpy are path functions
B. In a closed system, the energy can be exchanged with the surrounding, while matter cannot be exchanged
C. All the natural processes are reversible in nature
D. Work is a state function
Answer : C
13. A cylinder contains 640 gm of liquid oxygen. The volume occupied (in litres) by the oxygen, when it is released and brought to standard conditions (0°C, 760 mm Hg) will be __________ litres.
A. 448
B. 224
C. 22.4
D. Data insufficient; can't be computed
Answer : A
A. 448
B. 224
C. 22.4
D. Data insufficient; can't be computed
Answer : A
14. For an ideal gas, the chemical potential is given by
A. RT d ln P
B. R d ln P
C. R d ln f
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. RT d ln P
B. R d ln P
C. R d ln f
D. None of these
Answer : A
15. Van Laar equation deals with the activity coefficients in
A. Binary solutions
B. Ternary solutions
C. Azeotropic mixture only
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Binary solutions
B. Ternary solutions
C. Azeotropic mixture only
D. None of these
Answer : A
16. Which of the following is not an intensive property?
A. Volume
B. Density
C. Temperature
D. Pressure
Answer : A
A. Volume
B. Density
C. Temperature
D. Pressure
Answer : A
17. Which of the following is not an intensive property?
A. Molar heat capacity
B. Internal energy
C. Viscosity
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Molar heat capacity
B. Internal energy
C. Viscosity
D. None of these
Answer : B
18. Which of the following is not a common refrigerant?
A. Freon-12
B. Ethylene
C. Ammonia
D. Carbon dioxide
Answer : B
A. Freon-12
B. Ethylene
C. Ammonia
D. Carbon dioxide
Answer : B
19. For a real gas, the chemical potential is given by
A. RT d ln P
B. RT d ln f
C. R d ln f
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. RT d ln P
B. RT d ln f
C. R d ln f
D. None of these
Answer : B
20. Minimum number of phases that exists in a system is 1. Number of chemical species in a colloidal system is
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer : B
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer : B
21. Ideal refrigeration cycle is
A. Same as Carnot cycle
B. Same as reverse Carnot cycle
C. Dependent on the refrigerant's properties
D. The least efficient of all refrigeration processes
Answer : B
A. Same as Carnot cycle
B. Same as reverse Carnot cycle
C. Dependent on the refrigerant's properties
D. The least efficient of all refrigeration processes
Answer : B
22. The enthalpy change when ammonia gas is dissolved in water is called the heat of
A. Solution
B. Formation
C. Dilution
D. Combustion
Answer : A
A. Solution
B. Formation
C. Dilution
D. Combustion
Answer : A
23. The main feature of Carnot refrigeration cycle is that, it
A. Does not need the addition of external work for its functioning
B. Transfers heat from high temperature to low temperature
C. Accomplishes the reverse effect of the heat engine
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Does not need the addition of external work for its functioning
B. Transfers heat from high temperature to low temperature
C. Accomplishes the reverse effect of the heat engine
D. None of these
Answer : C
24. When liquid and vapour phase of multi-component system are in equilibrium (at a given temperature and pressure), then chemical potential of each component is
A. Same in both the phases
B. Zero in both the phases
C. More in vapour phase
D. More in liquid phase
Answer : A
A. Same in both the phases
B. Zero in both the phases
C. More in vapour phase
D. More in liquid phase
Answer : A
25. Which is not a refrigerant?
A. SO2
B. NH3
C. CCl2F2
D. C2H4Cl2
Answer : D
A. SO2
B. NH3
C. CCl2F2
D. C2H4Cl2
Answer : D
26. High __________ is an undesirable property for a good refrigerant.
A. Specific heat
B. Latent heat of vaporisation
C. Viscosity
D. Specific vapor volume
Answer : C
A. Specific heat
B. Latent heat of vaporisation
C. Viscosity
D. Specific vapor volume
Answer : C
27. Enthalpy changes over a constant pressure path are always zero for __________ gas.
A. Any
B. A perfect
C. An easily liquefiable
D. A real
Answer : B
A. Any
B. A perfect
C. An easily liquefiable
D. A real
Answer : B
28. For a reversible process involving only pressure-volume work
A. (dF)T, p < 0
B. (dF)T, p > 0
C. (dF)T, p = 0
D. (dA)T, v < 0
Answer : C
A. (dF)T, p < 0
B. (dF)T, p > 0
C. (dF)T, p = 0
D. (dA)T, v < 0
Answer : C
29. Gibbs free energy of mixing at constant pressure and temperature is always
A. 0
B. ?
C. + ve
D. - ve
Answer : D
A. 0
B. ?
C. + ve
D. - ve
Answer : D
30. Clapeyron Equation deals with the
A. Rate of change of vapour pressure with temperature
B. Effect of an inert gas on vapour pressure
C. Calculation of ?F for spontaneous phase change
D. Temperature dependence of heat of phase transition
Answer : A
A. Rate of change of vapour pressure with temperature
B. Effect of an inert gas on vapour pressure
C. Calculation of ?F for spontaneous phase change
D. Temperature dependence of heat of phase transition
Answer : A
31. Boyle's law for gases states that
A. P ? 1/V, when temperature is constant
B. P ? 1/V, when temperature & mass of the gas remain constant
C. P ? V, at constant temperature & mass of the gas
D. P/V = constant, for any gas
Answer : B
A. P ? 1/V, when temperature is constant
B. P ? 1/V, when temperature & mass of the gas remain constant
C. P ? V, at constant temperature & mass of the gas
D. P/V = constant, for any gas
Answer : B
32. Those solutions in which there is no volume change upon mixing the components in the liquid state and which, when diluted do not undergo any heat change (i.e. heat of dilution is zero), are called __________ solutions.
A. Ideal
B. Real
C. Isotonic
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Ideal
B. Real
C. Isotonic
D. None of these
Answer : A
33. The chemical potential of any constituent of an ideal solution depends on the __________ of the solution.
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Composition
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
A. Temperature
B. Pressure
C. Composition
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : D
34. There is a change in __________ during the phase transition.
A. Volume
B. Pressure
C. Temperature
D. All a, b & c
Answer : A
A. Volume
B. Pressure
C. Temperature
D. All a, b & c
Answer : A
35. Fugacity is a measure of the
A. Escaping tendencies of the same substance in different phases of a system
B. Relative volatility of a mixture of two miscible liquids
C. Behaviour of ideal gases
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Escaping tendencies of the same substance in different phases of a system
B. Relative volatility of a mixture of two miscible liquids
C. Behaviour of ideal gases
D. None of these
Answer : A
36. Which of the following is a widely used refrigerant in vapour compression refrigeration system (using large centrifugal compressor)?
A. Freon
B. Liquid sulphur dioxide
C. Methyl chloride
D. Ammonia
Answer : A
A. Freon
B. Liquid sulphur dioxide
C. Methyl chloride
D. Ammonia
Answer : A
37. All gases above its inversion temperature, in a throttling process will show
A. A heating effect
B. No change in temperature
C. A cooling effect
D. Either (A) or (C)
Answer : A
A. A heating effect
B. No change in temperature
C. A cooling effect
D. Either (A) or (C)
Answer : A
38. An ideal gas is taken around the cycle ABCA as shown in P-V diagram below: The work done by the gas during the cycle is equal to
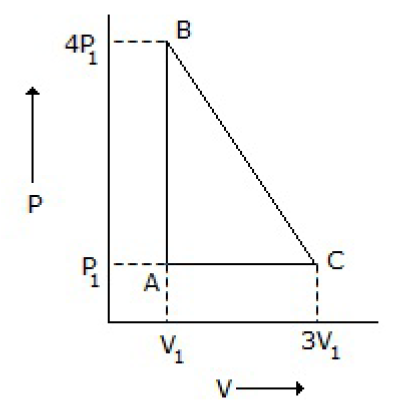
A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C

A. 12 P1V1
B. 6 P1 V1
C. 3 P1V1
D. P1 V1
Answer : C
39. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. The chemical potential of a pure substance depends upon the temperature and pressure
B. The chemical potential of a component in a system is directly proportional to the escaping tendency of that component
C. The chemical potential of ith species (?i) in an ideal gas mixture approaches zero as the pressure or mole fraction (xi) tends to be zero at constant temperature
D. The chemical potential of species 'i' in the mixture (?i) is mathematically represented as,?i = ?(nG)/?ni]T,P,nj where, n, ni and nj respectively denote the total number of moles, moles of ith species and all mole numbers except ith species. 'G' is Gibbs molar free energy
Answer : C
A. The chemical potential of a pure substance depends upon the temperature and pressure
B. The chemical potential of a component in a system is directly proportional to the escaping tendency of that component
C. The chemical potential of ith species (?i) in an ideal gas mixture approaches zero as the pressure or mole fraction (xi) tends to be zero at constant temperature
D. The chemical potential of species 'i' in the mixture (?i) is mathematically represented as,?i = ?(nG)/?ni]T,P,nj where, n, ni and nj respectively denote the total number of moles, moles of ith species and all mole numbers except ith species. 'G' is Gibbs molar free energy
Answer : C
40. Pick out the wrong statement.
A. System (of partially miscible liquid pairs), in which the mutual solubility increases with rise in temperature, are said to possess an upper consolute temperature
B. Systems, in which the mutual solubility increases with decrease in temperature, are said to possess lower consolute temperature
C. Nicotine-water system shows both an upper as well as a lower consolute temperature, implying that they are partially miscible between these two limiting temperatures
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. System (of partially miscible liquid pairs), in which the mutual solubility increases with rise in temperature, are said to possess an upper consolute temperature
B. Systems, in which the mutual solubility increases with decrease in temperature, are said to possess lower consolute temperature
C. Nicotine-water system shows both an upper as well as a lower consolute temperature, implying that they are partially miscible between these two limiting temperatures
D. None of these
Answer : D
41. Rotary lime kiln is an example of a/an __________ system.
A. Closed
B. Open
C. Isolated
D. Non-thermodynamic
Answer : B
A. Closed
B. Open
C. Isolated
D. Non-thermodynamic
Answer : B
42. Out of the following refrigeration cycles, which one has the minimum COP (Co-efficient of performance)?
A. Air cycle
B. Carnot cycle
C. Ordinary vapour compression cycle
D. Vapour compression with a reversible expansion engine
Answer : A
A. Air cycle
B. Carnot cycle
C. Ordinary vapour compression cycle
D. Vapour compression with a reversible expansion engine
Answer : A
43. A large iceberg melts at the base, but not at the top, because of the reason that
A. Ice at the base contains impurities which lowers its melting point
B. Due to the high pressure at the base, its melting point reduces
C. The iceberg remains in a warmer condition at the base
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : B
A. Ice at the base contains impurities which lowers its melting point
B. Due to the high pressure at the base, its melting point reduces
C. The iceberg remains in a warmer condition at the base
D. All (A), (B) and (C)
Answer : B
44. What is the number of degrees of freedom for liquid water in equilibrium with a mixture of nitrogen and water vapor?
A. 2
B. 0
C. 3
D. 1
Answer : A
A. 2
B. 0
C. 3
D. 1
Answer : A
45. To obtain integrated form of Clausius-Clapeyron equation, ln (P2/P1) = (?HV/R) (1/T1 - 1/T2) from the exact Clapeyron equation, it is assumed that the
A. Volume of the liquid phase is negligible compared to that of vapour phase
B. Vapour phase behaves as an ideal gas
C. Heat of vaporisation is independent of temperature
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : D
A. Volume of the liquid phase is negligible compared to that of vapour phase
B. Vapour phase behaves as an ideal gas
C. Heat of vaporisation is independent of temperature
D. All (A), (B) & (C)
Answer : D
46. Entropy is a/an
A. State function
B. Macroscopic property
C. Extensive property
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. State function
B. Macroscopic property
C. Extensive property
D. None of these
Answer : D
47. A system undergoes a change from a given initial state to a given final state either by an irreversible process or by a reversible process, then (where, ? S1 and ? SR are the entropy changes of the system for the irreversible and reversible processes respectively)
A. ? S1 is always < ? SR
B. ? S1 is sometimes > ? SR
C. ? S1 is always > ? SR
D. ? S1 is always = ? SR
Answer : C
A. ? S1 is always < ? SR
B. ? S1 is sometimes > ? SR
C. ? S1 is always > ? SR
D. ? S1 is always = ? SR
Answer : C
48. The adiabatic throttling process of a perfect gas is one of constant enthalpy
A. In which there is a temperature drop
B. Which is exemplified by a non-steady flow expansion
C. Which can be performed in a pipe with a constriction
D. In which there is an increase in temperature
Answer : C
A. In which there is a temperature drop
B. Which is exemplified by a non-steady flow expansion
C. Which can be performed in a pipe with a constriction
D. In which there is an increase in temperature
Answer : C
49. Pick out the undesirable property for a good refrigerant.
A. High thermal conductivity
B. Low freezing point
C. Large latent heat of vaporisation
D. High viscosity
Answer : D
A. High thermal conductivity
B. Low freezing point
C. Large latent heat of vaporisation
D. High viscosity
Answer : D
50. A solid is transformed into vapour without going to the liquid phase at
A. Triple point
B. Boiling point
C. Below triple point
D. Always
Answer : A
A. Triple point
B. Boiling point
C. Below triple point
D. Always
Answer : A
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Multimedia and Graphics MCQ Solved Paper for RBI Assistant
Atomic Structure 1000+ MCQ with answer for RRB JE
1000+ Sentence Correction MCQ for CTET [Solved]
Periodic Classification of Elements MCQ Solved Paper for LSAT
Active and Passive Voice 1000+ MCQ with answer for RRB Group D
XAT - Multimedia and Graphics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download