RBI Grade B officer - Basics of Economics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Which of the following is called Gossens first law?
A. Law of production
B. The Law of Equi-Marginal Utility
C. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
D. Law of Variable Proportions
Answer : C
A. Law of production
B. The Law of Equi-Marginal Utility
C. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
D. Law of Variable Proportions
Answer : C
2. When total product increases at a decreasing rate:
A. MP = AP
B. MP < AP
C. MP > AP =0
D. MP > AP
Answer : D
A. MP = AP
B. MP < AP
C. MP > AP =0
D. MP > AP
Answer : D
3. Duopoly is a market where there are:
A. Two sellers
B. A few sellers
C. Five sellers
D. Many sellers
Answer : A
A. Two sellers
B. A few sellers
C. Five sellers
D. Many sellers
Answer : A
4. Diminishing returns occur when a firm:
A. Starts incurring losses
B. Uses more and more of one input while holding all other inputs constant
C. Does not utilize its inputs efficiently
D. Cuts down on the quantity of all inputs it uses
Answer : B
A. Starts incurring losses
B. Uses more and more of one input while holding all other inputs constant
C. Does not utilize its inputs efficiently
D. Cuts down on the quantity of all inputs it uses
Answer : B
5. If a firm produces zero output in the short period then which statement is true?
A. Its total cost will be zero
B. Its variable cost will be positive
C. Its fixed cost will be positive
D. Its average cost will be zero
Answer : C
A. Its total cost will be zero
B. Its variable cost will be positive
C. Its fixed cost will be positive
D. Its average cost will be zero
Answer : C
6. In economics, Externality means:
A. An externality is a cost or benefit which is not transmitted through prices
B. An externality is a cost or benefit which is transmitted through prices
C. An externality is a production received through external resources
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. An externality is a cost or benefit which is not transmitted through prices
B. An externality is a cost or benefit which is transmitted through prices
C. An externality is a production received through external resources
D. None of the above
Answer : A
7. If production increases under increasing returns to scale, the cost will:
A. Increase at decreasing rate
B. Increase at constant rate
C. Decrease at increasing rate
D. Increase at increasing rate
Answer : A
A. Increase at decreasing rate
B. Increase at constant rate
C. Decrease at increasing rate
D. Increase at increasing rate
Answer : A
8. In cournot model, firms face:
A. Negatively sloped demand curve
B. Positively sloped demand curve
C. Horizontal demand curve
D. Vertical demand curve
Answer : A
A. Negatively sloped demand curve
B. Positively sloped demand curve
C. Horizontal demand curve
D. Vertical demand curve
Answer : A
9. The demand curve in monopolistic competition (also in kinked demand curve model), which shows the share of a firm in market is called:
A. Relative demand curve
B. Proportional demand curve
C. Productive demand curve
D. Differential demand curve
Answer : B
A. Relative demand curve
B. Proportional demand curve
C. Productive demand curve
D. Differential demand curve
Answer : B
10. Which of the following is not a feature of isoproduct curves?
A. Are downward sloping to the right
B. Show different input combination producing the same output
C. Intersect each other
D. Are convex to the origin
Answer : C
A. Are downward sloping to the right
B. Show different input combination producing the same output
C. Intersect each other
D. Are convex to the origin
Answer : C
11. In dominant price leadership model, the small firms are like:
A. monopolistic firms
B. monopoly
C. competitive firms
D. none of the above
Answer : C
A. monopolistic firms
B. monopoly
C. competitive firms
D. none of the above
Answer : C
12. The engineering production function and engineering costs curves are concerned with the:
A. Production cost
B. Collection cost
C. Raw material costs
D. Distribution costs
Answer : A
A. Production cost
B. Collection cost
C. Raw material costs
D. Distribution costs
Answer : A
13. Selling costs are incurred under monopolistic competition to:
A. Attract more customers
B. Prevent its customers from going to others
C. Establish superiority of its product on the others
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Attract more customers
B. Prevent its customers from going to others
C. Establish superiority of its product on the others
D. All of the above
Answer : D
14. The MRTS along an iso-quant goes on to:
A. Appear
B. Diminish
C. Prominent
D. Increase
Answer : B
A. Appear
B. Diminish
C. Prominent
D. Increase
Answer : B
15. For the given production function, technical inefficiency is defined as:
A. Sets of points relating production function that maximizes output given input (labor) i.e. Q = f(L, K)
B. Sets of points relating production function that produces less output than possible for a given set of input (labor) i.e. Q < f(L, K)
C. Use of imported technology
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Sets of points relating production function that maximizes output given input (labor) i.e. Q = f(L, K)
B. Sets of points relating production function that produces less output than possible for a given set of input (labor) i.e. Q < f(L, K)
C. Use of imported technology
D. None of the above
Answer : B
16. The firms in non-cooperative games:
A. Enforce contracts
B. Make contracts
C. Make negotiations
D. Do not make negotiations
Answer : D
A. Enforce contracts
B. Make contracts
C. Make negotiations
D. Do not make negotiations
Answer : D
17. If money income is given then consumer is in equilibrium when:
A. MU < P
B. MU >P
C. MU = P
D. MU = 0
Answer : C
A. MU < P
B. MU >P
C. MU = P
D. MU = 0
Answer : C
18. The study of economics just in theoretical way is called:
A. Positive Economics
B. Normative Economics
C. Micro Economics
D. Development Economics
Answer : A
A. Positive Economics
B. Normative Economics
C. Micro Economics
D. Development Economics
Answer : A
19. Substitution effect means a consumer
A. Shifts away from the commodity the price of which has fallen
B. Shifts in favour of a commodity the price of which has risen
C. Shifts away from a commodity the price of which has risen, in favour of a commodity the price of which has fallen
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Shifts away from the commodity the price of which has fallen
B. Shifts in favour of a commodity the price of which has risen
C. Shifts away from a commodity the price of which has risen, in favour of a commodity the price of which has fallen
D. None of the above
Answer : C
20. Marginal Productivity Theory deals with the theory of:
A. Distribution
B. Exchange
C. Market structure
D. Consumer behaviour
Answer : A
A. Distribution
B. Exchange
C. Market structure
D. Consumer behaviour
Answer : A
21. In which case the elasticity shown by the different points of a curve is the same?
A. A straight line curve
B. A downward sloping demand curve
C. A rectangular hyperbola demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. A straight line curve
B. A downward sloping demand curve
C. A rectangular hyperbola demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : C
22. Abstinence or Waiting theory of Interest was presented by:
A. Lord Keynes
B. J.S.Mill
C. Alfred Marshal
D. Prof.Senior
Answer : D
A. Lord Keynes
B. J.S.Mill
C. Alfred Marshal
D. Prof.Senior
Answer : D
23. The firm producing at the minimum point of the AC curve is said to be:
A. Operating under diminishing cost
B. Making optimum use of plant capacity
C. Operating at excess capacity
D. Operating under increasing costs
Answer : B
A. Operating under diminishing cost
B. Making optimum use of plant capacity
C. Operating at excess capacity
D. Operating under increasing costs
Answer : B
24. In the range of excess capacity, the average costs are:
A. Maximum
B. Minimum
C. Equal to one
D. Equal to zero
Answer : B
A. Maximum
B. Minimum
C. Equal to one
D. Equal to zero
Answer : B
25. The cobweb model will divergent when the slope of:
A. Demand curve is more than supply curve
B. Supply curve is more than demand curve
C. Supply curve is equal to demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Demand curve is more than supply curve
B. Supply curve is more than demand curve
C. Supply curve is equal to demand curve
D. None of the above
Answer : B
26. Ceteris paribus clause in the law of demand means:
A. The price of substitute does not change
B. The taste of the consumer does not change
C. The income of the consumer does not change
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. The price of substitute does not change
B. The taste of the consumer does not change
C. The income of the consumer does not change
D. All of the above
Answer : D
27. Supply curves are most elastic:
A. In the long-run
B. In the short-run
C. For luxuries
D. In the immediate-run
Answer : A
A. In the long-run
B. In the short-run
C. For luxuries
D. In the immediate-run
Answer : A
28. In monopoly, when average revenue curve falls:
A. MR constant
B. MR rises
C. MR falls
D. MR is zero
Answer : C
A. MR constant
B. MR rises
C. MR falls
D. MR is zero
Answer : C
29. According to Cobb-Douglas, in production function the marginal product of labor is:
A.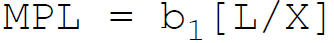
B.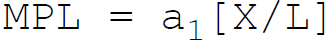
C.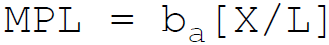
D.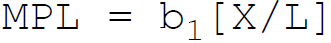
Answer : D
A.
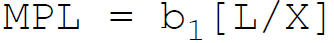
B.
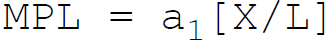
C.
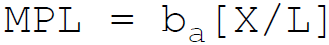
D.
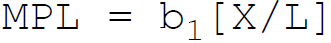
Answer : D
30. Who wrote Mathematical Analysis for Economists?
A. J.P.Lewis
B. R.G.D.Allen
C. Paul A.Samuelson
D. E.D.Domar
Answer : B
A. J.P.Lewis
B. R.G.D.Allen
C. Paul A.Samuelson
D. E.D.Domar
Answer : B
31. Demand of a commodity is elastic when:
A. Change in its price causes a proportionately greater change in its quantity demanded
B. Change in its price does not change its quantity demanded
C. Change in consumers income causes change in demand
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Change in its price causes a proportionately greater change in its quantity demanded
B. Change in its price does not change its quantity demanded
C. Change in consumers income causes change in demand
D. None of the above
Answer : A
32. Equilibrium of a discriminating monopolist requires the fulfillment of which one of the following conditions?
A. It must be profitable to him to sell output in more than one market
B. Marginal revenue in both markets must be the same
C. Marginal revenue in both markets must also be equal to the marginal cost of producing the monopolists aggregate output
D. All the above
Answer : D
A. It must be profitable to him to sell output in more than one market
B. Marginal revenue in both markets must be the same
C. Marginal revenue in both markets must also be equal to the marginal cost of producing the monopolists aggregate output
D. All the above
Answer : D
33. The main contribution of Prof. R.G.D.Allen is in the field of:
A. fixation of price
B. Arc elasticity of demand
C. Cross elasticity of demand
D. Wage theory
Answer : B
A. fixation of price
B. Arc elasticity of demand
C. Cross elasticity of demand
D. Wage theory
Answer : B
34. The cost of firms in cournot model are:
A. identical
B. differential
C. very high
D. very low
Answer : A
A. identical
B. differential
C. very high
D. very low
Answer : A
35. If the commodity is normal then fall in price will result in:
A. Increase the quantity demanded
B. Fixed the quantity demanded
C. Decrease the quantity demanded
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Increase the quantity demanded
B. Fixed the quantity demanded
C. Decrease the quantity demanded
D. None of the above
Answer : A
36. If the price of a product falls which of the following would occur?
A. Indifference curves shift down
B. Budget line shifts down
C. Indifference curve shift up
D. Budget line pivots
Answer : D
A. Indifference curves shift down
B. Budget line shifts down
C. Indifference curve shift up
D. Budget line pivots
Answer : D
37. In substitution effect and income effect:
A. The substitution effect is more certain
B. The income effect is more certain
C. The substitution effect is uncertain
D. The income effect is always positive
Answer : A
A. The substitution effect is more certain
B. The income effect is more certain
C. The substitution effect is uncertain
D. The income effect is always positive
Answer : A
38. Isocost line shows the combinations of labor and capital where a firms budget is:
A. Fully spent
B. Half spent
C. Partially spent
D. Nearly spent
Answer : A
A. Fully spent
B. Half spent
C. Partially spent
D. Nearly spent
Answer : A
39. An inferior good/ commodity is inferior for:
A. Every consumer
B. Most consumers
C. All consumers
D. Some consumers and not for others
Answer : D
A. Every consumer
B. Most consumers
C. All consumers
D. Some consumers and not for others
Answer : D
40. The number of sellers in oligopoly are:
A. Two
B. Many
C. Four
D. Very few
Answer : D
A. Two
B. Many
C. Four
D. Very few
Answer : D
41. A monopolist is:
A. Price winner
B. Price searcher
C. Price taker
D. Price leaver
Answer : B
A. Price winner
B. Price searcher
C. Price taker
D. Price leaver
Answer : B
42. The total utility (TU) curve is:
A. Concave to X-axis
B. Convex to X-axis
C. Concave to Y-axis
D. Convex to Y-axis
Answer : A
A. Concave to X-axis
B. Convex to X-axis
C. Concave to Y-axis
D. Convex to Y-axis
Answer : A
43. The short-run periods in monopolistic competition are:
A. Parallel to each other
B. Dependent upon each other
C. Independent of each other
D. Zero
Answer : C
A. Parallel to each other
B. Dependent upon each other
C. Independent of each other
D. Zero
Answer : C
44. When SAC curve rises, SM curve lies its:
A. Below
B. Above
C. Equal level
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. Below
B. Above
C. Equal level
D. None of the above
Answer : B
45. A market demand schedule is obtained by adding individual demand schedules:
A. Horizontally
B. Vertically
C. Permanently
D. Perpetually
Answer : A
A. Horizontally
B. Vertically
C. Permanently
D. Perpetually
Answer : A
46. Ordinal approach includes arranging:
A. The different combinations of X and Y in any way the consumer wants
B. The different combinations of X and Y higher and lower and measuring the difference of utility between them
C. The different combinations of X and Y higher and lower and not measuring the difference of utility between them
D. None of above
Answer : C
A. The different combinations of X and Y in any way the consumer wants
B. The different combinations of X and Y higher and lower and measuring the difference of utility between them
C. The different combinations of X and Y higher and lower and not measuring the difference of utility between them
D. None of above
Answer : C
47. The imaginary differentiation is attributed to difference in:
A. Style
B. Salesmanship
C. Locality
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. Style
B. Salesmanship
C. Locality
D. All of these
Answer : D
48. In monopolistic competition, the firms have to face:
A. Same cost conditions
B. Different cost conditions
C. Same price conditions
D. Same products conditions
Answer : B
A. Same cost conditions
B. Different cost conditions
C. Same price conditions
D. Same products conditions
Answer : B
49. Elasticity of supply means change in supply due to change in:
A. Price of the commodity
B. Conditions of supply
C. Taste of the consumer
D. Demand for the commodity
Answer : A
A. Price of the commodity
B. Conditions of supply
C. Taste of the consumer
D. Demand for the commodity
Answer : A
50. The Tit for Tat strategy means cooperation by the 2nd firm if:
A. 1st firm does not cooperate
B. 1st firm cooperates
C. 1st firm collapses
D. None of the above
Answer : B
A. 1st firm does not cooperate
B. 1st firm cooperates
C. 1st firm collapses
D. None of the above
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
IBPS SO - Senile enlargement of the prostate 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Airport Engineering MCQ Solved Paper for CAT
RBI Grade B officer - Current Affairs November 2022 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Microsoft PowerPoint 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC JE
1000+ Tumors of the prostate Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
RRB NTPC - Engineering Materials 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download