Strength of Materials 1000+ MCQ with answer for IIFT
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. Which of the following gas has a minimum molecular mass?
A. Oxygen
B. Nitrogen
C. Hydrogen
D. Methane
Answer : C
A. Oxygen
B. Nitrogen
C. Hydrogen
D. Methane
Answer : C
2. When a system changes its state from one equilibrium state to another equilibrium state, then the path of successive states through which the system has passed, is known as
A. Thermodynamic law
B. Thermodynamic process
C. Thermodynamic cycle
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Thermodynamic law
B. Thermodynamic process
C. Thermodynamic cycle
D. None of these
Answer : B
3. One reversible heat engine operates between 1600 K and T2 K and another reversible heat engine operates between T2 K and 400 K. If both the engines have the same heat input and output, then temperature T2 is equal to
A. 800 K
B. 1000 K
C. 1200 K
D. 1400 K
Answer : A
A. 800 K
B. 1000 K
C. 1200 K
D. 1400 K
Answer : A
4. Formula based on IS codes is based on
A. Straight line formula
B. Eulers formula
C. Rankines formula
D. Secant formula
Answer : D
A. Straight line formula
B. Eulers formula
C. Rankines formula
D. Secant formula
Answer : D
5. For a perfect gas, according to Boyle's law (where p = Absolute pressure, v = Volume, and T = Absolute temperature)
A. p v = constant, if T is kept constant
B. v/T = constant, if p is kept constant
C. p/T = constant, if v is kept constant
D. T/p = constant, if v is kept constant
Answer : A
A. p v = constant, if T is kept constant
B. v/T = constant, if p is kept constant
C. p/T = constant, if v is kept constant
D. T/p = constant, if v is kept constant
Answer : A
6. Otto cycle consists of
A. Two constant volume and two isentropic processes
B. Two constant pressure and two isentropic processes
C. Two constant volume and two isothermal processes
D. One constant pressure, one constant volume and two isentropic processes
Answer : A
A. Two constant volume and two isentropic processes
B. Two constant pressure and two isentropic processes
C. Two constant volume and two isothermal processes
D. One constant pressure, one constant volume and two isentropic processes
Answer : A
7. The hard coke is obtained when carbonisation of coal is carried out at
A. 300° to 500°C
B. 500° to 700°C
C. 700° to 900°C
D. 900° to 1100°C
Answer : D
A. 300° to 500°C
B. 500° to 700°C
C. 700° to 900°C
D. 900° to 1100°C
Answer : D
8. When a gas is heated at constant pressure
A. Its temperature will increase
B. Its volume will increase
C. Both temperature and volume will increase
D. Neither temperature not volume will increase
Answer : C
A. Its temperature will increase
B. Its volume will increase
C. Both temperature and volume will increase
D. Neither temperature not volume will increase
Answer : C
9. When a closely-coiled helical spring of mean diameter (D) is subjected to an axial load (W), the deflection of the spring (?) is given by (where d = Diameter of spring wire, n = No. of turns of the spring, and C = Modulus of rigidity for the spring material)
A. WD3n/Cd?
B. 2WD3n/Cd?
C. 4WD3n/Cd?
D. 8WD3n/Cd?
Answer : D
A. WD3n/Cd?
B. 2WD3n/Cd?
C. 4WD3n/Cd?
D. 8WD3n/Cd?
Answer : D
10. According to Avogadro's law, the density of any two gases is __________ their molecular masses, if the gases are at the same temperature and pressure.
A. Equal to
B. Directly proportional to
C. Inversely proportional to
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Equal to
B. Directly proportional to
C. Inversely proportional to
D. None of these
Answer : B
11. Proof resilience per material is known as
A. Resilience
B. Proof resilience
C. Modulus of resilience
D. Toughness
Answer : C
A. Resilience
B. Proof resilience
C. Modulus of resilience
D. Toughness
Answer : C
12. In a reversible adiabatic process, the ratio of T1/T2 is equal to
A. (p2/p1)? - 1/ ?
B. (p1/p2)? - 1/ ?
C. (v2/v1)? - 1/ ?
D. (v1/v2)? - 1/ ?
Answer : B
A. (p2/p1)? - 1/ ?
B. (p1/p2)? - 1/ ?
C. (v2/v1)? - 1/ ?
D. (v1/v2)? - 1/ ?
Answer : B
13. In the tensile test, the phenomenon of slow extension of the material, i. e. stress increasing with the time at a constant load is called
A. Creeping
B. Yielding
C. Breaking
D. Plasticity
Answer : A
A. Creeping
B. Yielding
C. Breaking
D. Plasticity
Answer : A
14. The bending moment at a point on a beam is the algebraic ________ of all the moments on either side of the point.
A. Sum
B. Difference
C. Multiplication
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Sum
B. Difference
C. Multiplication
D. None of the above
Answer : A
15. The materials having same elastic properties in all directions are called
A. Ideal materials
B. Uniform materials
C. Isotropic materials
D. Piratical materials
Answer : C
A. Ideal materials
B. Uniform materials
C. Isotropic materials
D. Piratical materials
Answer : C
16. When a body is subjected to biaxial stress i.e. direct stresses (?x) and (?y) in two mutually perpendicular planes accompanied by a simple shear stress (?xy), then minimum normal stress is
A. (?x + ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
B. (?x + ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
C. (?x - ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
D. (?x - ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
Answer : B
A. (?x + ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
B. (?x + ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
C. (?x - ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
D. (?x - ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
Answer : B
17. Modular ratio of two materials is the ratio of
A. Strains
B. Stress and strain
C. Shear stress and shear strain
D. Moduli and elasticity
Answer : D
A. Strains
B. Stress and strain
C. Shear stress and shear strain
D. Moduli and elasticity
Answer : D
18. A closely-coiled helical spring is cut into two halves. The stiffness of the resulting spring will be
A. Same
B. Double
C. Half
D. One-fourth
Answer : B
A. Same
B. Double
C. Half
D. One-fourth
Answer : B
19. The ratio of the largest load in a test to the original cross-sectional area of the test piece is called
A. Elastic limit
B. Yield stress
C. Ultimate stress
D. Breaking stress
Answer : C
A. Elastic limit
B. Yield stress
C. Ultimate stress
D. Breaking stress
Answer : C
20. Percentage reduction in area erforming tensile test on cast iron may be of the order of
A. 50 %
B. 25 %
C. 20 %
D. 30 %
Answer : C
A. 50 %
B. 25 %
C. 20 %
D. 30 %
Answer : C
21. In an extensive property of a thermodynamic system
A. Extensive heat is transferred
B. Extensive work is done
C. Extensive energy is utilised
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Extensive heat is transferred
B. Extensive work is done
C. Extensive energy is utilised
D. None of these
Answer : D
22. A shaft revolving at ? rad/s transmits torque (T) in Nm. The power developed is
A. T.? watts
B. 2?. T.? watts
C. 2?. T.?/75 watts
D. 2?. T.?/4500 watts
Answer : A
A. T.? watts
B. 2?. T.? watts
C. 2?. T.?/75 watts
D. 2?. T.?/4500 watts
Answer : A
23. Within elastic limit, stress is
A. Inversely proportional to strain
B. Directly proportional to strain
C. Square root of strain
D. Equal to strain
Answer : B
A. Inversely proportional to strain
B. Directly proportional to strain
C. Square root of strain
D. Equal to strain
Answer : B
24. The heat energy stored in the gas and used for raising the temperature of the gas is known as
A. External energy
B. Internal energy
C. Kinetic energy
D. Molecular energy
Answer : B
A. External energy
B. Internal energy
C. Kinetic energy
D. Molecular energy
Answer : B
25. The unit of energy is S. I. units is
A. Joule (J)
B. Joule metre (Jm)
C. Watt (W)
D. Joule/metre (J/m)
Answer : A
A. Joule (J)
B. Joule metre (Jm)
C. Watt (W)
D. Joule/metre (J/m)
Answer : A
26. The ratio of elongation in a prismatic bar due to its own weight (W) as compared to another similar bar carrying an additional weight (W) will be
A. 1 : 2
B. 1 : 3
C. 1 : 4
D. 1 : 2.5
Answer : B
A. 1 : 2
B. 1 : 3
C. 1 : 4
D. 1 : 2.5
Answer : B
27. The atomic mass of sulphur is
A. 12
B. 14
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : D
A. 12
B. 14
C. 16
D. 32
Answer : D
28. The state of stress at a point in a loaded member is shown in the below figure. The magnitude of maximum shear stress is
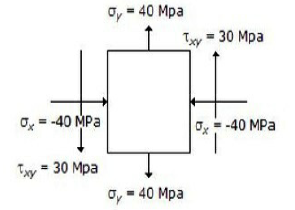
A. 10 MPa
B. 30 MPa
C. 50 MPa
D. 100 MPa
Answer : C

A. 10 MPa
B. 30 MPa
C. 50 MPa
D. 100 MPa
Answer : C
29. Which of the following is an irreversible cycle?
A. Carnot
B. Stirling
C. Ericsson
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. Carnot
B. Stirling
C. Ericsson
D. None of the above
Answer : D
30. The fuel mostly used in blast furnace for extracting pig iron from iron ores is
A. Hard coke
B. Soft coke
C. Pulverised coal
D. Bituminous coal
Answer : A
A. Hard coke
B. Soft coke
C. Pulverised coal
D. Bituminous coal
Answer : A
31. The area under the temperature-entropy curve (T - s curve) of any thermodynamic process represents
A. Heat absorbed
B. Heat rejected
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Heat absorbed
B. Heat rejected
C. Either (A) or (B)
D. None of these
Answer : C
32. The distillation carried out in such a way that the liquid with the lowest boiling point is first evaporated and recondensed, then the liquid with the next higher boiling point is then evaporated and recondensed, and so on until all the available liquid fuels are separately recovered in the sequence of their boiling points. Such a process is called
A. Cracking
B. Carbonisation
C. Fractional distillation
D. Full distillation
Answer : C
A. Cracking
B. Carbonisation
C. Fractional distillation
D. Full distillation
Answer : C
33. The kinetic energy per kg molecule of any gas at absolute temperature T is equal to (where Ru = Universal gas constant)
A. Ru × T
B. 1.5 Ru × T
C. 2 Ru × T
D. 3 Ru × T
Answer : B
A. Ru × T
B. 1.5 Ru × T
C. 2 Ru × T
D. 3 Ru × T
Answer : B
34. The entropy of water at 0°C is assumed to be
A. 1
B. 0
C. -1
D. 10
Answer : B
A. 1
B. 0
C. -1
D. 10
Answer : B
35. The stress induced in a body, when suddenly loaded, is ________ the stress induced when the same load is applied gradually.
A. Equal to
B. One-half
C. Twice
D. Four times
Answer : C
A. Equal to
B. One-half
C. Twice
D. Four times
Answer : C
36. One kilowatt is equal to
A. 1 N-m/s
B. 100 N-m
C. 1000 N-m/s
D. 1 × 106 N-m/s
Answer : C
A. 1 N-m/s
B. 100 N-m
C. 1000 N-m/s
D. 1 × 106 N-m/s
Answer : C
37. The efficiency and work ratio of a simple gas turbine cycle are
A. Low
B. Very low
C. High
D. Very high
Answer : B
A. Low
B. Very low
C. High
D. Very high
Answer : B
38. Strain is equal to (where l = Original length, and ?l = Change in length)
A. l/?l
B. ?l/l
C. l.?l
D. l + ?l
Answer : B
A. l/?l
B. ?l/l
C. l.?l
D. l + ?l
Answer : B
39. If Kh is the torque resisting capacity of a hollow shaft and Ks is that of a solid shaft, of the same material, length and weight. Then,
A. Kh > Ks
B. Kh < Ks
C. Kh = Ks
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Kh > Ks
B. Kh < Ks
C. Kh = Ks
D. None of these
Answer : A
40. The shear force at the centre of a simply supported beam with a gradually varying load from zero at both ends to w per metre at the centre, is
A. Zero
B. wl/4
C. wl/2
D. wl²/2
Answer : A
A. Zero
B. wl/4
C. wl/2
D. wl²/2
Answer : A
41. A series of operations, which takes place in a certain order and restore the initial conditions at the end, is known as
A. Reversible cycle
B. Irreversible cycle
C. Thermodynamic cycle
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Reversible cycle
B. Irreversible cycle
C. Thermodynamic cycle
D. None of these
Answer : C
42. When a bar is subjected to a change of temperature and its deformation is prevented, the stress induced in the bar is
A. Tensile stress
B. Compressive stress
C. Shear stress
D. Thermal stress
Answer : D
A. Tensile stress
B. Compressive stress
C. Shear stress
D. Thermal stress
Answer : D
43. Otto cycle efficiency is higher than Diesel cycle efficiency for the same compression ratio and heat input because in Otto cycle
A. Combustion is at constant volume
B. Expansion and compression are isentropic
C. Maximum temperature is higher
D. Heat rejection is lower
Answer : D
A. Combustion is at constant volume
B. Expansion and compression are isentropic
C. Maximum temperature is higher
D. Heat rejection is lower
Answer : D
44. A molecule consisting of one atom is known as
A. Mono-atomic
B. Di-atomic
C. Tri-atomic
D. Poly-atomic
Answer : A
A. Mono-atomic
B. Di-atomic
C. Tri-atomic
D. Poly-atomic
Answer : A
45. Which is the incorrect statement about Carnot cycle?
A. It is used as the alternate standard of comparison of all heat engines.
B. All the heat engines are based on Carnot cycle.
C. It provides concept of maximising work output between the two temperature limits.
D. All of the above
Answer : B
A. It is used as the alternate standard of comparison of all heat engines.
B. All the heat engines are based on Carnot cycle.
C. It provides concept of maximising work output between the two temperature limits.
D. All of the above
Answer : B
46. For the same maximum pressure and temperature,
A. Otto cycle is more efficient than Diesel cycle
B. Diesel cycle is more efficient than Otto cycle
C. Dual cycle is more efficient than Otto and Diesel cycles
D. Dual cycle is less efficient than Otto and Diesel cycles
Answer : B
A. Otto cycle is more efficient than Diesel cycle
B. Diesel cycle is more efficient than Otto cycle
C. Dual cycle is more efficient than Otto and Diesel cycles
D. Dual cycle is less efficient than Otto and Diesel cycles
Answer : B
47. The stress necessary to initiate yielding is
A. Considerably greater than that necessary to continue it
B. Considerably lesser than that necessary to continue it
C. Greater than that necessary to stop it
D. Lesser than that necessary to stop it
Answer : A
A. Considerably greater than that necessary to continue it
B. Considerably lesser than that necessary to continue it
C. Greater than that necessary to stop it
D. Lesser than that necessary to stop it
Answer : A
48. When wood is heated with a limited supply of air to a temperature not less than 280°C, the resulting fuel is
A. Coke
B. Wood charcoal
C. Bituminous coal
D. Briquetted coal
Answer : B
A. Coke
B. Wood charcoal
C. Bituminous coal
D. Briquetted coal
Answer : B
49. The root mean square velocity of the gas molecules is given by (where k = Boltzmann's constant, T = Absolute temperature, and m = Mass of one molecule of a gas)
A. ?(KT/m)
B. ?(2KT/m)
C. ?(3KT/m)
D. ?(5KT/m)
Answer : C
A. ?(KT/m)
B. ?(2KT/m)
C. ?(3KT/m)
D. ?(5KT/m)
Answer : C
50. The stress induced in a body due to suddenly applied load compared to when it is applied gradually is
A. Same
B. Half
C. Two times
D. Four times
Answer : C
A. Same
B. Half
C. Two times
D. Four times
Answer : C
Sharing is caring
Related Post
CAT - Current Affairs February 2023 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
RRB ALP - Biological Classification 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Chemical Engineering Basics MCQ for LIC AAO [Solved]
IBPS RRB - General Physics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
NMAT - Asp Programming 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Current Affairs January 2023 MCQ for GATE [Solved]