1000+ Strength of Materials Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The energy absorbed in a body, when it is strained within the elastic limits, is known as
A. Strain energy
B. Resilience
C. Proof resilience
D. Modulus of resilience
Answer : A
A. Strain energy
B. Resilience
C. Proof resilience
D. Modulus of resilience
Answer : A
2. When a body is subjected to a direct tensile stress (?x) in one plane accompanied by a simple shear stress (?xy), the minimum normal stress is
A. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
B. (?x/2) - (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
C. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² - 4 ?²xy)
D. (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
Answer : B
A. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
B. (?x/2) - (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
C. (?x/2) + (1/2) × ?(?x² - 4 ?²xy)
D. (1/2) × ?(?x² + 4 ?²xy)
Answer : B
3. The stress at which extension of the material takes place more quickly as compared to the increase in load is called
A. Elastic point of the material
B. Plastic point of the material
C. Breaking point of the material
D. Yielding point of the material
Answer : D
A. Elastic point of the material
B. Plastic point of the material
C. Breaking point of the material
D. Yielding point of the material
Answer : D
4. The process is adiabatic, if the value of n in the equation pvn = C, is
A. 0
B. 1
C. ?
D. ?
Answer : C
A. 0
B. 1
C. ?
D. ?
Answer : C
5. In S. I. units, the value of the universal gas constant is
A. 8.314 J/kg mole-K
B. 83.14 J/kgmole-K
C. 831.4 J/kgmole-K
D. 8314 J/kgmole-K
Answer : D
A. 8.314 J/kg mole-K
B. 83.14 J/kgmole-K
C. 831.4 J/kgmole-K
D. 8314 J/kgmole-K
Answer : D
6. In an isothermal process,
A. There is no change in temperature
B. There is no change in enthalpy
C. There is no change in internal energy
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. There is no change in temperature
B. There is no change in enthalpy
C. There is no change in internal energy
D. All of these
Answer : D
7. A fletched beam is used to
A. Change the shape of the beam
B. Effect the saving in material
C. Equalise the strength in tension and compression
D. Increase the cross-section of the beam
Answer : C
A. Change the shape of the beam
B. Effect the saving in material
C. Equalise the strength in tension and compression
D. Increase the cross-section of the beam
Answer : C
8. The ultimate tensile stress of mild steel compared to ultimate compressive stress is
A. Same
B. More
C. Less
D. Unpredictable
Answer : B
A. Same
B. More
C. Less
D. Unpredictable
Answer : B
9. The lower layer of the beam as shown in the below figure, will be
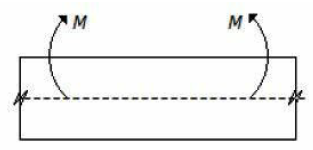
A. In tension
B. In compression
C. Neither in tension nor in compression
D. None of these
Answer : A

A. In tension
B. In compression
C. Neither in tension nor in compression
D. None of these
Answer : A
10. Strain is defined as the ratio of
A. Change in volume to original volume
B. Change in length to original length
C. Change in cross-sectional area to original cross-sectional area
D. Any one of the above
Answer : D
A. Change in volume to original volume
B. Change in length to original length
C. Change in cross-sectional area to original cross-sectional area
D. Any one of the above
Answer : D
11. The heat and mechanical energies are mutually convertible. This statement was established by
A. Boyle
B. Charles
C. Joule
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Boyle
B. Charles
C. Joule
D. None of these
Answer : C
12. During which of the following process does heat rejection takes place in Carnot cycle?
A. Isothermal expansion
B. Isentropic expansion
C. Isothermal compression
D. Isentropic compression
Answer : C
A. Isothermal expansion
B. Isentropic expansion
C. Isothermal compression
D. Isentropic compression
Answer : C
13. A beam is loaded as cantilever. If the load at the end is increased, the failure will occur
A. In the middle
B. At the tip below the load
C. At the support
D. Anywhere
Answer : D
A. In the middle
B. At the tip below the load
C. At the support
D. Anywhere
Answer : D
14. The fuel mostly used in steam boilers is
A. Brown coal
B. Peat
C. Coking bituminous coal
D. Non-coking bituminous coal
Answer : D
A. Brown coal
B. Peat
C. Coking bituminous coal
D. Non-coking bituminous coal
Answer : D
15. Which of the following statement is correct?
A. The increase in entropy is obtained from a given quantity of heat at a low temperature.
B. The change in entropy may be regarded as a measure of the rate of the availability or unavailability of heat for transformation into work.
C. The entropy represents the maximum amount of work obtainable per degree drop in temperature.
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. The increase in entropy is obtained from a given quantity of heat at a low temperature.
B. The change in entropy may be regarded as a measure of the rate of the availability or unavailability of heat for transformation into work.
C. The entropy represents the maximum amount of work obtainable per degree drop in temperature.
D. All of the above
Answer : D
16. A cube subjected to three mutually perpendicular stress of equal intensity p expenses a volumetric strain
A. 3p/E × (2/m - 1)
B. 3p/E × (2 - m)
C. 3p/E × (1 - 2/m)
D. E/3p × (2/m - 1)
Answer : C
A. 3p/E × (2/m - 1)
B. 3p/E × (2 - m)
C. 3p/E × (1 - 2/m)
D. E/3p × (2/m - 1)
Answer : C
17. Those substances which have so far not been resolved by any means into other substances of simpler form are called
A. Elements
B. Compounds
C. Atoms
D. Molecules
Answer : A
A. Elements
B. Compounds
C. Atoms
D. Molecules
Answer : A
18. The efficiency of the Carnot cycle may be increased by
A. Increasing the highest temperature
B. Decreasing the highest temperature
C. Increasing the lowest temperature
D. Keeping the lowest temperature constant
Answer : A
A. Increasing the highest temperature
B. Decreasing the highest temperature
C. Increasing the lowest temperature
D. Keeping the lowest temperature constant
Answer : A
19. The deformation per unit length is called
A. Tensile stress
B. Compressive stress
C. Shear stress
D. Strain
Answer : D
A. Tensile stress
B. Compressive stress
C. Shear stress
D. Strain
Answer : D
20. The temperature at which the volume of a gas becomes zero is called
A. Absolute scale of temperature
B. Absolute zero temperature
C. Absolute temperature
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Absolute scale of temperature
B. Absolute zero temperature
C. Absolute temperature
D. None of these
Answer : B
21. When a perfect gas is expanded through an aperture of minute dimensions, the process is known as
A. Isothermal process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Free expansion process
D. Throttling process
Answer : D
A. Isothermal process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Free expansion process
D. Throttling process
Answer : D
22. When both ends of a column are fixed, the effective length is
A. Its own length
B. Twice its length
C. Half its length
D. 1/?2 × its length
Answer : C
A. Its own length
B. Twice its length
C. Half its length
D. 1/?2 × its length
Answer : C
23. The unit of energy is S. I. units is
A. Joule (J)
B. Joule metre (Jm)
C. Watt (W)
D. Joule/metre (J/m)
Answer : A
A. Joule (J)
B. Joule metre (Jm)
C. Watt (W)
D. Joule/metre (J/m)
Answer : A
24. In the below figure, curve D represents_________.
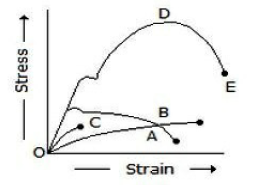
A. Mild steel
B. Cast iron
C. Concrete
D. Bone of these
Answer : A

A. Mild steel
B. Cast iron
C. Concrete
D. Bone of these
Answer : A
25. The extension of a circular bar tapering uniformly from diameter d? at one end to diameter d? at the other end and subjected to an axial pull of P is given by
A. ?l = 4PE/ ?l²
B. ?l = 4?ld²/PE
C. ?l = 4Pl/?Ed?d?
D. ?l = 4PlE/ ?d?d?
Answer : C
A. ?l = 4PE/ ?l²
B. ?l = 4?ld²/PE
C. ?l = 4Pl/?Ed?d?
D. ?l = 4PlE/ ?d?d?
Answer : C
26. The molecular mass expressed in gram (i.e. 1 g - mole) of all gases, at N. T. P., occupies a volume of
A. 0.224 litres
B. 2.24 litres
C. 22.4 litres
D. 224 litres
Answer : C
A. 0.224 litres
B. 2.24 litres
C. 22.4 litres
D. 224 litres
Answer : C
27. The energy stored in a body when strained within elastic limit is known as
A. Resilience
B. Proof resilience
C. Strain energy
D. Impact energy
Answer : C
A. Resilience
B. Proof resilience
C. Strain energy
D. Impact energy
Answer : C
28. Young's modulus is defined as the ratio of
A. Volumetric stress and volumetric strain
B. Lateral stress and lateral strain
C. Longitudinal stress and longitudinal strain
D. Shear stress to shear strain
Answer : C
A. Volumetric stress and volumetric strain
B. Lateral stress and lateral strain
C. Longitudinal stress and longitudinal strain
D. Shear stress to shear strain
Answer : C
29. When coal is strongly heated continuously for 42 to 48 hours in the absence of air in a closed vessel, the process is known as __________ of fuel.
A. Atomisation
B. Carbonisation
C. Combustion
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Atomisation
B. Carbonisation
C. Combustion
D. None of these
Answer : B
30. Strain energy is the
A. Energy stored in a body when strained within elastic limits
B. Energy stored in a body when strained up to the breaking of a specimen
C. Maximum strain energy which can be stored in a body
D. Proof resilience per unit volume of a material
Answer : A
A. Energy stored in a body when strained within elastic limits
B. Energy stored in a body when strained up to the breaking of a specimen
C. Maximum strain energy which can be stored in a body
D. Proof resilience per unit volume of a material
Answer : A
31. The value of modulus of elasticity for mild steel is of the order of
A. 2.1 × 10? kg/cm²
B. 2.1 × 10? kg/cm²
C. 2.1 × 10? kg/cm²
D. 0.1 × 10? kg/cm²
Answer : B
A. 2.1 × 10? kg/cm²
B. 2.1 × 10? kg/cm²
C. 2.1 × 10? kg/cm²
D. 0.1 × 10? kg/cm²
Answer : B
32. The deformation of a bar under its own weight compared to the deformation of same body subjected to a direct load equal to weight of the body is
A. Same
B. Double
C. Half
D. Four times
Answer : C
A. Same
B. Double
C. Half
D. Four times
Answer : C
33. A circular shaft fixed at, A has diameter D for half of its length and diameter D/2 over the other half, as shown in the below figure. If the rotation of B relative to A is 0.1 radian, the rotation of C relative to B will be
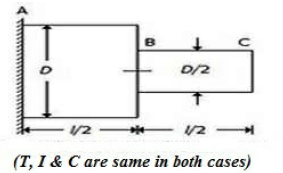
A. 0.4 radian
B. 0.8 radian
C. 1.6 radian
D. 3.2 radian
Answer : C

A. 0.4 radian
B. 0.8 radian
C. 1.6 radian
D. 3.2 radian
Answer : C
34. A beam which is fixed at one end and free at the other is called
A. Simply supported beam
B. Fixed beam
C. Overhanging beam
D. Cantilever beam
Answer : D
A. Simply supported beam
B. Fixed beam
C. Overhanging beam
D. Cantilever beam
Answer : D
35. Select the wrong statement
A. A Joule cycle consists of two constant volume and two isentropic processes.
B. An Otto cycle consists of two constant volume and two isentropic processes.
C. An Ericsson cycle consists of two constant pressure and two isothermal processes.
D. All of the above
Answer : A
A. A Joule cycle consists of two constant volume and two isentropic processes.
B. An Otto cycle consists of two constant volume and two isentropic processes.
C. An Ericsson cycle consists of two constant pressure and two isothermal processes.
D. All of the above
Answer : A
36. If in the equation pvn = C, the value of n = ?, then the process is called
A. Constant volume process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Constant pressure process
D. Isothermal process
Answer : A
A. Constant volume process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Constant pressure process
D. Isothermal process
Answer : A
37. True stress strain-curve for materials is plotted between
A. Load/original cross-sectional area and change in length/original length
B. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and loge (original area/ instantaneous area)
C. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and change in length/ original length
D. Load/ instantaneous area and instantaneous area/original area
Answer : B
A. Load/original cross-sectional area and change in length/original length
B. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and loge (original area/ instantaneous area)
C. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and change in length/ original length
D. Load/ instantaneous area and instantaneous area/original area
Answer : B
38. The shape of cantilever for uniformly distributed load will be
A. Straight line
B. Parabolic
C. Elliptical
D. Cubic
Answer : B
A. Straight line
B. Parabolic
C. Elliptical
D. Cubic
Answer : B
39. The efficiency of Diesel cycle with decrease in cut-off
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. First increases and then decreases
D. First decreases and then increases
Answer : A
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. First increases and then decreases
D. First decreases and then increases
Answer : A
40. The maximum tangential stress in a thick cylindrical shell is always _________ the internal pressure acting on the shell.
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Equal to
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : C
41. The amount of heat generated per kg of fuel is known as
A. Calorific value
B. Heat energy
C. Lower calorific value
D. Higher calorific value
Answer : A
A. Calorific value
B. Heat energy
C. Lower calorific value
D. Higher calorific value
Answer : A
42. The heat and work are mutually conertible. This statement is called __________ law of thermodynamics.
A. Zeroth
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
Answer : B
A. Zeroth
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
Answer : B
43. The reading of the pressure gauge fitted on a vessel is 25 bar. The atmospheric pressure is 1.03 bar and the value of 'g' is 9.81 m/s2. The absolute pressure in the vessel is
A. 23.97 bar
B. 25 bar
C. 26.03 bar
D. 34.81 bar
Answer : C
A. 23.97 bar
B. 25 bar
C. 26.03 bar
D. 34.81 bar
Answer : C
44. A composite bar made up of steel and copper bars of equal lengths are heated through 100°C. The stresses developed shall be
A. Tensile in both the material
B. Tensile in steel and compressive in copper
C. Compressive in steel and tensile in copper
D. Compressive in both the materials
Answer : D
A. Tensile in both the material
B. Tensile in steel and compressive in copper
C. Compressive in steel and tensile in copper
D. Compressive in both the materials
Answer : D
45. The volumetric or molar specific heat at constant pressure is the product of
A. Molecular mass of the gas and the specific heat at constant volume
B. Atomic mass of the gas and the gas constant
C. Molecular mass of the gas and the gas constant
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. Molecular mass of the gas and the specific heat at constant volume
B. Atomic mass of the gas and the gas constant
C. Molecular mass of the gas and the gas constant
D. None of the above
Answer : D
46. The value of 1 mm of Hg is equal to
A. 1.333 N/m2
B. 13.33 N/m2
C. 133.3 N/m2
D. 1333 N/m2
Answer : C
A. 1.333 N/m2
B. 13.33 N/m2
C. 133.3 N/m2
D. 1333 N/m2
Answer : C
47. In an irreversible process, there is a
A. Loss of heat
B. No loss of heat
C. Gain of heat
D. No gain of heat
Answer : A
A. Loss of heat
B. No loss of heat
C. Gain of heat
D. No gain of heat
Answer : A
48. The value of shear stress which is induced in the shaft due to the applied couple varies
A. From maximum at the centre to zero at the circumference
B. From zero at the centre to maximum at the circumference
C. From maximum at the centre to minimum at the circumference
D. From minimum at the centre to maximum at the circumference
Answer : B
A. From maximum at the centre to zero at the circumference
B. From zero at the centre to maximum at the circumference
C. From maximum at the centre to minimum at the circumference
D. From minimum at the centre to maximum at the circumference
Answer : B
49. Charles' law states that all perfect gases change in volume by __________ of its original volume at 0°C for every 1°C change in temperature, when pressure remains constant.
A. 1/27th
B. 1/93th
C. 1/173th
D. 1/273th
Answer : D
A. 1/27th
B. 1/93th
C. 1/173th
D. 1/273th
Answer : D
50. The maximum bending moment for the beam shown in the below figure, is
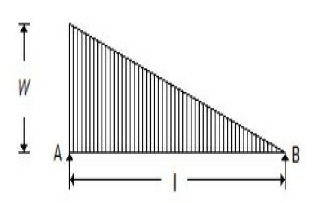
A. wl²/3?3
B. wl²/6?3
C. wl²/9?3
D. wl²/12?3
Answer : C

A. wl²/3?3
B. wl²/6?3
C. wl²/9?3
D. wl²/12?3
Answer : C
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Direct and Indirect Speech Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Current Affairs November 2022 Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Internal Combustion Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Electrical Circuits MCQ Solved Paper for GMAT
1000+ Basics of Neurology MCQ for SBI Clerk [Solved]
1000+ Advanced Surveying MCQ for IBPS PO [Solved]