1000+ Applied Mechanics and Graphic Statics Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. The force acting on a point on the surface of a rigid body may be considered to act
A. At the centre of gravity of the body
B. On the periphery of the body
C. On any point on the line of action of the force
D. At any point on the surface normal to the line of action of the force
Answer : C
A. At the centre of gravity of the body
B. On the periphery of the body
C. On any point on the line of action of the force
D. At any point on the surface normal to the line of action of the force
Answer : C
2. Parallelogram Law of Forces states, if two forces acting simultaneously on a particle be represented in magnitude and direction by two adjacent sides of a parallelogram, their resultant may be represented in magnitude and direction by
A. Its longer side
B. Its shorter side
C. The diagonal of the parallelogram which does not pass through the point of intersection of the forces
D. The diagonal of the parallelogram which passes through the point of intersection of the forces
Answer : D
A. Its longer side
B. Its shorter side
C. The diagonal of the parallelogram which does not pass through the point of intersection of the forces
D. The diagonal of the parallelogram which passes through the point of intersection of the forces
Answer : D
3. A smooth cylinder lying on its convex surface remains
A. In stable equilibrium
B. In unstable equilibrium
C. In neutral equilibrium
D. Out of equilibrium
Answer : B
A. In stable equilibrium
B. In unstable equilibrium
C. In neutral equilibrium
D. Out of equilibrium
Answer : B
4. The shape of a suspended cable for a uniformly distributed load over it is
A. Circular
B. Parabolic
C. Catenary
D. Cubic parabola
Answer : B
A. Circular
B. Parabolic
C. Catenary
D. Cubic parabola
Answer : B
5. Periodic time of a particle moving with simple harmonic motion is the time taken by the particle for
A. Half oscillation
B. Quarter oscillation
C. Complete oscillation
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Half oscillation
B. Quarter oscillation
C. Complete oscillation
D. None of these
Answer : C
6. The load shared by the member BC of the structure shown in below figure is
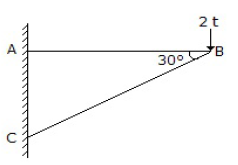
A. 23 t
B. 32 t
C. 4 t
D. 3 t
Answer : C

A. 23 t
B. 32 t
C. 4 t
D. 3 t
Answer : C
7. A uniform pyramid and a uniform prism of same height lie with their base on the surface. Which is more stable?
A. Pyramid
B. Prism
C. Both equally stable
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Pyramid
B. Prism
C. Both equally stable
D. None of the above
Answer : A
8. The rate of change of displacement of a body with respect to its surrounding, is known
A. Velocity
B. Acceleration
C. Speed
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Velocity
B. Acceleration
C. Speed
D. None of these
Answer : C
9. According to Law of Triangle of Forces
A. Three forces acting at a point, can be rep-resented by the sides of a triangle, each side being in proportion to the force
B. Three forces acting along the sides of a triangle are always in equilibrium
C. If three forces acting on a, point can be represented in magnitude and direction, by the sides of a triangle taken in order, these will be in equilibrium
D. If the forces acting on a particle be represented in magnitude and direction by the two sides of a triangle taken in order, their resultant will be represented in magnitude and direction by the third side of the triangle, taken in opposite order
Answer : D
A. Three forces acting at a point, can be rep-resented by the sides of a triangle, each side being in proportion to the force
B. Three forces acting along the sides of a triangle are always in equilibrium
C. If three forces acting on a, point can be represented in magnitude and direction, by the sides of a triangle taken in order, these will be in equilibrium
D. If the forces acting on a particle be represented in magnitude and direction by the two sides of a triangle taken in order, their resultant will be represented in magnitude and direction by the third side of the triangle, taken in opposite order
Answer : D
10. The equation of motion of a particle starting from rest along a straight line is x = t3 - 3l2 + 5. The ratio of the velocities after 5 sec and 3 sec will be
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Answer : D
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Answer : D
11. A body is said to move with Simple Harmonic Motion if its acceleration, is
A. Always directed away from the centre, the point of reference
B. Proportional to the square of the distance from the point of reference
C. Proportional to the distance from the point of reference and directed towards it
D. Inversely proportion to the distance from the point of reference
Answer : C
A. Always directed away from the centre, the point of reference
B. Proportional to the square of the distance from the point of reference
C. Proportional to the distance from the point of reference and directed towards it
D. Inversely proportion to the distance from the point of reference
Answer : C
12. A block of weight 50 kg is placed on a horizontal plane. When a horizontal force of 18 kg is applied, the block is just on the point of motion. The angle of friction is
A. 17° 48'
B. 18° 48'
C. 19° 48'
D. 20° 48'
Answer : C
A. 17° 48'
B. 18° 48'
C. 19° 48'
D. 20° 48'
Answer : C
13. The resultant of two forces acting at right angles is 5 kgf and if they act at an angle of 60°, it is 37 kgf. The magnitudes of the forces are:
A. 2 kgf, 3 kgf
B. 3 kgf, 4 kgf
C. 4 kgf, 5 kgf
D. 5 kgf, 3 kgf
Answer : B
A. 2 kgf, 3 kgf
B. 3 kgf, 4 kgf
C. 4 kgf, 5 kgf
D. 5 kgf, 3 kgf
Answer : B
14. Pick up the correct statement from the following. A rubber ball when strikes a wall rebounds but a lead ball of same mass and velocity when strikes the same wall, falls down
A. Rubber and lead balls undergo equal changes in momentum
B. Change in momentum suffered by lead ball is less that of rubber ball
C. Momentum of rubber ball is less than that of lead ball
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Rubber and lead balls undergo equal changes in momentum
B. Change in momentum suffered by lead ball is less that of rubber ball
C. Momentum of rubber ball is less than that of lead ball
D. None of these
Answer : D
15. Pick up the incorrect statement from the following. In a simple harmonic motion
A. Velocity is maximum at its mean position
B. Velocity is minimum at the end of the stroke
C. Acceleration is minimum at the end of the stroke
D. Acceleration is zero at the mean position
Answer : C
A. Velocity is maximum at its mean position
B. Velocity is minimum at the end of the stroke
C. Acceleration is minimum at the end of the stroke
D. Acceleration is zero at the mean position
Answer : C
16. When a body falls freely under gravitational force, it possesses
A. Maximum weight
B. Minimum weight
C. No weight
D. No effect on its weight
Answer : C
A. Maximum weight
B. Minimum weight
C. No weight
D. No effect on its weight
Answer : C
17. Centre of gravity of a thin hollow cone lies on the axis of symmetry at a height of
A. One-half of the total height above base
B. One-third of the total height above base
C. One-fourth of the total height above base
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. One-half of the total height above base
B. One-third of the total height above base
C. One-fourth of the total height above base
D. None of these
Answer : B
18. Energy may be defined as
A. Power of doing work
B. Capacity of doing work
C. Rate of doing work
D. All the above
Answer : B
A. Power of doing work
B. Capacity of doing work
C. Rate of doing work
D. All the above
Answer : B
19. The masses of two balls are in the ratio of 2 : 1 and their respective velocities are in the ratio of 1 : 2 but in opposite direction before impact. If the coefficient of restitution is ½, the velocities of separation of the balls will be equal to
A. Original velocity in the same direction
B. Half the original velocity in the same direction
C. Half the original velocity in the opposite direction
D. Original velocity in the opposite direction
Answer : D
A. Original velocity in the same direction
B. Half the original velocity in the same direction
C. Half the original velocity in the opposite direction
D. Original velocity in the opposite direction
Answer : D
20. The vertical reaction at the support A of the structure shown in below figure, is 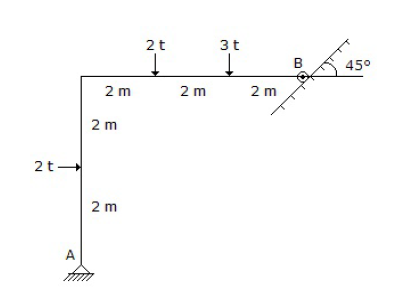
A. 1 t
B. 2 t
C. 3 t
D. 3.5 t
Answer : C

A. 1 t
B. 2 t
C. 3 t
D. 3.5 t
Answer : C
21. The rotational velocity of a satellite is increased by 450 m per second if its launch is done from equator
A. Eastward
B. Northward
C. Westward
D. Southward
Answer : A
A. Eastward
B. Northward
C. Westward
D. Southward
Answer : A
22. The graphical method of determining the forces in the members of a truss is based on
A. Method of joint
B. Method of section
C. Either method
D. None of the two methods
Answer : A
A. Method of joint
B. Method of section
C. Either method
D. None of the two methods
Answer : A
23. The total kinetic energy of a hoop of mass 2 kg and radius 4 m sliding with linear velocity 8 m/sec and angular velocity 5 radian/sec is
A. 64 J
B. 400 J
C. 464 J
D. 89 J
Answer : C
A. 64 J
B. 400 J
C. 464 J
D. 89 J
Answer : C
24. A particle moves with a velocity of 2 m/sec in a straight line with a negative acceleration of 0.1 m/sec2. Time required to traverse a distance of 1.5 m, is
A. 40 sec
B. 30 sec
C. 20 sec
D. 15 sec
Answer : C
A. 40 sec
B. 30 sec
C. 20 sec
D. 15 sec
Answer : C
25. The member which does not carry zero force in the structure shown in below figure, is
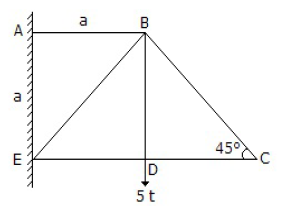
A. ED
B. DC
C. BC
D. BD
Answer : D

A. ED
B. DC
C. BC
D. BD
Answer : D
26. A body of weight w placed on an inclined plane is acted upon by a force P parallel to the plane which causes the body just to move up the plane. If the angle of inclination of the plane is ? and angle of friction is ?, the minimum value of P, is
A. w sin (? - ?)/cos ?
B. w sin (? - ?)/cos ?
C. w cos (? + ?)/cos ?
D. w sin? cos(? - ?)/sin ?
Answer : B
A. w sin (? - ?)/cos ?
B. w sin (? - ?)/cos ?
C. w cos (? + ?)/cos ?
D. w sin? cos(? - ?)/sin ?
Answer : B
27. Rate of change of angular momentum is equal to
A. Force
B. Torque
C. Linear momentum
D. Impulse
Answer : B
A. Force
B. Torque
C. Linear momentum
D. Impulse
Answer : B
28. Ball A of mass 250 g moving on a smooth horizontal table with a velocity of 10 m/s hits an identical stationary ball B on the table. If the impact is perfectly elastic, the velocity of the ball B just after impact would be
A. Zero
B. 5 m/sec
C. 10 m/sec
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Zero
B. 5 m/sec
C. 10 m/sec
D. None of these
Answer : C
29. In SI units, the units of force and energy are respectively
A. Newton and watt
B. Dyne and erg
C. Newton and joule
D. kg wt and joule
Answer : C
A. Newton and watt
B. Dyne and erg
C. Newton and joule
D. kg wt and joule
Answer : C
30. According to Kennedy's theorem, if three bodies have plane motions, their instantaneous centres lie on
A. A point
B. A straight line
C. Two straight lines
D. A triangle
Answer : B
A. A point
B. A straight line
C. Two straight lines
D. A triangle
Answer : B
31. 0.For maximum range of a projectile, the angle of projection should be
A. 30°
B. 45°
C. 60°
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. 30°
B. 45°
C. 60°
D. None of these
Answer : B
32. The resultant of two forces P and Q is R. If Q is doubled, the new resultant is perpendicular to P. Then,
A. P = R
B. Q = R
C. P = Q
D. None of the above is correct
Answer : B
A. P = R
B. Q = R
C. P = Q
D. None of the above is correct
Answer : B
33. Which of the following represents the state of neutral equilibrium?
A. A cube resting on one edge
B. A smooth cylinder lying on a curved surface
C. A smooth cylinder lying on a convex surface
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. A cube resting on one edge
B. A smooth cylinder lying on a curved surface
C. A smooth cylinder lying on a convex surface
D. None of the above
Answer : D
34. ? rad/sec is the angular velocity of a crank whose radius is r. If it makes ?° with inner dead centre and obliquity of the connecting rod l is ?, the velocity v of the piston, is given by the equation
A. ?2 (l cos ? + r sin ? tan ?)
B. ?2 (l sin ? + r cos ? tan ?)
C. ? (l sin ? + r cos ? tan ?)
D. ?2 (l sin ? - r cos ? tan ?)
Answer : C
A. ?2 (l cos ? + r sin ? tan ?)
B. ?2 (l sin ? + r cos ? tan ?)
C. ? (l sin ? + r cos ? tan ?)
D. ?2 (l sin ? - r cos ? tan ?)
Answer : C
35. Two forces act an angle of 120°. If the greater force is 50 kg and their resultant is perpendicular to the smaller force, the smaller force is
A. 20 kg
B. 25 kg
C. 30 kg
D. 35 kg
Answer : B
A. 20 kg
B. 25 kg
C. 30 kg
D. 35 kg
Answer : B
36. In a simple harmonic motion, the position of equilibrium is always
A. Stable
B. Unstable
C. Neutral
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Stable
B. Unstable
C. Neutral
D. None of the above
Answer : A
37. A particle of mass 2 kg executes simple harmonic motion of frequency 6/71 Hz and amplitude 0.25 m. Its maximum kinetic energy is
A. 4.5 J
B. 9.0 J
C. 12.0 J
D. 18.0 J
Answer : B
A. 4.5 J
B. 9.0 J
C. 12.0 J
D. 18.0 J
Answer : B
38. A ball is dropped from a height of 16 m on a horizontal floor. If it rebounds to a height of 9 m after striking the floor, the coefficient of restitution between ball and floor is
A. 1/4
B. 2/3
C. 3/4
D. 4/3
Answer : C
A. 1/4
B. 2/3
C. 3/4
D. 4/3
Answer : C
39. A load of 500 kg was lifted through a distance of 13 cm. by an effort of 25 kg which moved through a distance of 650 cm. The efficiency of the lifting machine is
A. 50 %
B. 40 %
C. 55 %
D. 30 %
Answer : A
A. 50 %
B. 40 %
C. 55 %
D. 30 %
Answer : A
40. A 2 m long ladder rests against a wall and makes an angle of 30° with the horizontal floor. Where will be the instantaneous center of rotation when the ladder starts slipping? (i) 1.0 in from the wall (ii) 1.732 m from the wall (iii) 1.0 m above the floor (iv) 1.732 m above the floor The correct answer is
A. (i) and (iii)
B. (i) and (iv)
C. (ii) and (iii)
D. (ii) and (iv)
Answer : D
A. (i) and (iii)
B. (i) and (iv)
C. (ii) and (iii)
D. (ii) and (iv)
Answer : D
41. Varingons theorem of moments states
A. Arithmetical sum of the moments of two forces about any point, is equal to the moments of their resultant about that point
B. Algebraic sum of the moments of two forces about any point, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
C. Arithmetical sum of the moments of the forces about any point in their plane, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
D. Algebraic sum of the moments of the forces about any point in their plane, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
Answer : D
A. Arithmetical sum of the moments of two forces about any point, is equal to the moments of their resultant about that point
B. Algebraic sum of the moments of two forces about any point, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
C. Arithmetical sum of the moments of the forces about any point in their plane, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
D. Algebraic sum of the moments of the forces about any point in their plane, is equal to the moment of their resultant about that point
Answer : D
42. The units of moment of inertia of an area are
A. kg/m
B. kg/m2
C. m4
D. m3
Answer : C
A. kg/m
B. kg/m2
C. m4
D. m3
Answer : C
43. If a spherical body is symmetrical about its perpendicular axes, the moment of inertia of the body about an axis passing through its centre of gravity as given by Routh's rule is obtained by dividing the product of the mass and the sum of the squares of two semi-axes by n. Where, n is
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Answer : D
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Answer : D
44. A particle is executing simple harmonic motion in a line 1.0 m long. If the time of one complete vibration is 1 sec, then the maximum velocity of the particle is
A. 1.00 m/sec
B. 1.57 m/sec
C. 3.14 m/sec
D. 6.28 m/sec
Answer : C
A. 1.00 m/sec
B. 1.57 m/sec
C. 3.14 m/sec
D. 6.28 m/sec
Answer : C
45. If a body is lying on a plane whose inclination with the horizontal is less than the angle of friction, then? (i) A force is required to move the body upwards (ii) A force is required to move the body downward (iii) The body will not be in equilibrium The correct answer is
A. Only (i)
B. Only (ii)
C. Both (i) and (ii)
D. Both (i) and (iii)
Answer : C
A. Only (i)
B. Only (ii)
C. Both (i) and (ii)
D. Both (i) and (iii)
Answer : C
46. A ball moving on a smooth horizontal table hits a rough vertical wall, the coefficient of restitution between ball and wall being 1/3. The ball rebounds at the same angle. The fraction of its kinetic energy lost is
A. 1/3
B. 2/3
C. 1/9
D. 8/9
Answer : D
A. 1/3
B. 2/3
C. 1/9
D. 8/9
Answer : D
47. The beam shown in below figure is supported by a hinge at A and a roller at B. The reaction RA of the hinged support A of the beam, is 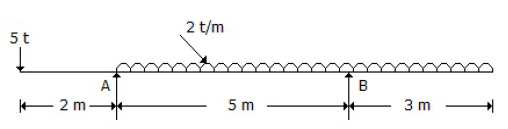
A. 10.8 t
B. 10.6 t
C. 10.4 t
D. 10.2 t
Answer : D

A. 10.8 t
B. 10.6 t
C. 10.4 t
D. 10.2 t
Answer : D
48. The instantaneous centre of a member lies at the point of intersection of two lines drawn at the ends of the member such that the lines are inclined to the direction of motion of the ends at
A. 30°
B. 45°
C. 60°
D. 90°
Answer : D
A. 30°
B. 45°
C. 60°
D. 90°
Answer : D
49. In simple harmonic motion, acceleration of a particle is proportional to
A. Rate of change of velocity
B. Displacement
C. Velocity
D. Direction
Answer : B
A. Rate of change of velocity
B. Displacement
C. Velocity
D. Direction
Answer : B
50. Angular acceleration of a particle may be expressed as
A. Radians/sec2
B. Degrees/sec2
C. Revolutions/sec
D. All the above
Answer : D
A. Radians/sec2
B. Degrees/sec2
C. Revolutions/sec
D. All the above
Answer : D
Sharing is caring
Related Post
1000+ Atomic Structure MCQ for SSC Scientific Assistant [Solved]
Microsoft Access 1000+ MCQ with answer for UPSC CSE
Microsoft Excel 1000+ MCQ with answer for SSC Stenographer
1000+ Senile enlargement of the prostate Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Human reproductive system 1000+ MCQ with answer for NEET PG
WAN 1000+ MCQ with answer for GMAT