IBPS SO - Applied Mechanics and Graphic Statics 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. For a given velocity of a projectile, the range is maximum when the angle of projection is
A. 30°
B. 45°
C. 90°
D. 0°
Answer : B
A. 30°
B. 45°
C. 90°
D. 0°
Answer : B
2. The force which produces an acceleration of 1 m/sec2 in a mass of one kg, is called
A. Dyne
B. Newton
C. Joule
D. Erg
Answer : B
A. Dyne
B. Newton
C. Joule
D. Erg
Answer : B
3. A block in the shape of a parallelepiped of sides 1m × 2m × 3m lies on the surface. Which of the faces gives maximum stable block?
A. 1 m × 2 m
B. 2 m × 3 m
C. 1 m × 3 m
D. Equally stable on all faces
Answer : B
A. 1 m × 2 m
B. 2 m × 3 m
C. 1 m × 3 m
D. Equally stable on all faces
Answer : B
4. In a lifting machine a weight of 5 kN is lifted through 200 mm by an effort of 0.1 kN moving through 15 m. The mechanical advantage and velocity ratio of the machine are respectively
A. 50 and 75
B. 75 and 50
C. 75 and 75
D. 50 and 50
Answer : A
A. 50 and 75
B. 75 and 50
C. 75 and 75
D. 50 and 50
Answer : A
5. The characteristic of a couple is:
A. Algebraic sum of forces, constituting a couple is zero
B. Algebraic sum of moments of forces, constituting a couple, about any point, is same
C. A couple can be never the balanced by a single force
D. All the above
Answer : D
A. Algebraic sum of forces, constituting a couple is zero
B. Algebraic sum of moments of forces, constituting a couple, about any point, is same
C. A couple can be never the balanced by a single force
D. All the above
Answer : D
6. On a ladder resisting on a smooth ground and leaning against a rough vertical wall, the force of friction acts
A. Towards the wall at its upper end
B. Away from the wall at its upper end
C. Upwards at its upper end
D. Downwards at its upper end
Answer : C
A. Towards the wall at its upper end
B. Away from the wall at its upper end
C. Upwards at its upper end
D. Downwards at its upper end
Answer : C
7. A load of 500 kg was lifted through a distance of 13 cm. by an effort of 25 kg which moved through a distance of 650 cm. The efficiency of the lifting machine is
A. 50 %
B. 40 %
C. 55 %
D. 30 %
Answer : A
A. 50 %
B. 40 %
C. 55 %
D. 30 %
Answer : A
8. If the angle between the applied force and the direction of motion of a body, is between 90° and 180°, the work done, is called
A. Virtual work
B. Imaginary work
C. Zero work
D. Negative work
Answer : D
A. Virtual work
B. Imaginary work
C. Zero work
D. Negative work
Answer : D
9. For a body moving with simple harmonic motion, the number of cycles per second, is known as its
A. Oscillation
B. Amplitude
C. Periodic time
D. Frequency
Answer : D
A. Oscillation
B. Amplitude
C. Periodic time
D. Frequency
Answer : D
10. One end of a light string 4 m in length is fixed to a point on a smooth wall and the other end fastened to a point on the surface of a smooth sphere of diameter 2.25 m and of weight 100 kg. The tension in the string is
A. 17.5 kg
B. 19.5 kg
C. 22.5 kg
D. 25 kg
Answer : C
A. 17.5 kg
B. 19.5 kg
C. 22.5 kg
D. 25 kg
Answer : C
11. The direction of projection should bisect the angle between the inclined plane and the vertical for a range of a projectile on inclined plane
A. To be zero
B. To be maximum
C. To be minimum
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. To be zero
B. To be maximum
C. To be minimum
D. None of these
Answer : B
12. A rod 5 m in length is moving in a vertical plane. When it is inclined at 60° to horizontal, its lower end is moving horizontally at 3 m/sec and upper end is moving in vertical direction. The velocity of its upper end, is
A. 0.5 m/sec
B. 1.0 m/sec
C. 1.5 m/sec
D. 2.5 m/sec
Answer : B
A. 0.5 m/sec
B. 1.0 m/sec
C. 1.5 m/sec
D. 2.5 m/sec
Answer : B
13. One Newton is equivalent to
A. 1 kg. wt
B. 9.81 kg. wt
C. 981 dyne
D. 1/9.81 kg. wt
Answer : D
A. 1 kg. wt
B. 9.81 kg. wt
C. 981 dyne
D. 1/9.81 kg. wt
Answer : D
14. One Joule is equivalent to
A. 9.81 Newton metre
B. 1 Newton metre
C. 1 kg wt metre
D. 1 dyne metre
Answer : B
A. 9.81 Newton metre
B. 1 Newton metre
C. 1 kg wt metre
D. 1 dyne metre
Answer : B
15. 0.For maximum range of a projectile, the angle of projection should be
A. 30°
B. 45°
C. 60°
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. 30°
B. 45°
C. 60°
D. None of these
Answer : B
16. Kinetic friction may be defined as
A. Friction force acting when the body is just about to move
B. Friction force acting when the body is in motion
C. Angle between normal reaction and resultant of normal reaction and limiting friction
D. Ratio of limiting friction and normal reaction
Answer : B
A. Friction force acting when the body is just about to move
B. Friction force acting when the body is in motion
C. Angle between normal reaction and resultant of normal reaction and limiting friction
D. Ratio of limiting friction and normal reaction
Answer : B
17. If the tension in a cable supporting a lift moving upwards is twice the tension when the lift is moving downwards, the acceleration of the lift, is
A. g/2
B. g/3
C. g/4
D. g/5
Answer : B
A. g/2
B. g/3
C. g/4
D. g/5
Answer : B
18. A ball is dropped from a height of 2.25 m on a smooth floor and rises to a height of 1.00 m after the bounce. The coefficient of restitution between the ball and the floor is
A. 0.33
B. 0.44
C. 0.57
D. 0.67
Answer : D
A. 0.33
B. 0.44
C. 0.57
D. 0.67
Answer : D
19. When a body moves round a fixed axis, it has
A. A rotary motion
B. A circular motion
C. A translatory
D. A rotary motion and translatory motion
Answer : B
A. A rotary motion
B. A circular motion
C. A translatory
D. A rotary motion and translatory motion
Answer : B
20. Free body diagram is an
A. Isolated joint with only body forces acting on it
B. Isolated joint with internal forces acting on it
C. Isolated joint with all the forces, internal as well as external, acting on it
D. None of the above
Answer : C
A. Isolated joint with only body forces acting on it
B. Isolated joint with internal forces acting on it
C. Isolated joint with all the forces, internal as well as external, acting on it
D. None of the above
Answer : C
21. The angle of friction is:
A. The ratio of the friction and the normal reaction
B. The force of friction when the body is in motion
C. The angle between the normal reaction and the resultant of normal reaction and limiting friction
D. The force of friction at which the body is just about to move
Answer : C
A. The ratio of the friction and the normal reaction
B. The force of friction when the body is in motion
C. The angle between the normal reaction and the resultant of normal reaction and limiting friction
D. The force of friction at which the body is just about to move
Answer : C
22. The necessary condition of equilibrium of a body is:
A. Algebraic sum of horizontal components of all the forces must be zero
B. Algebraic sum of vertical components of all the forces must be zero
C. Algebraic sum of the moments of the forces about a point must be zero
D. All (a), (b) and (c)
Answer : D
A. Algebraic sum of horizontal components of all the forces must be zero
B. Algebraic sum of vertical components of all the forces must be zero
C. Algebraic sum of the moments of the forces about a point must be zero
D. All (a), (b) and (c)
Answer : D
23. A 2 m long ladder rests against a wall and makes an angle of 30° with the horizontal floor. Where will be the instantaneous center of rotation when the ladder starts slipping? (i) 1.0 in from the wall (ii) 1.732 m from the wall (iii) 1.0 m above the floor (iv) 1.732 m above the floor The correct answer is
A. (i) and (iii)
B. (i) and (iv)
C. (ii) and (iii)
D. (ii) and (iv)
Answer : D
A. (i) and (iii)
B. (i) and (iv)
C. (ii) and (iii)
D. (ii) and (iv)
Answer : D
24. A 50 kg boy climbs up a 8 m rope in gymnasium in 10 sec. The average power developed by the boy is approximately
A. 400 watts
B. 500 watts
C. 4000 watts
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. 400 watts
B. 500 watts
C. 4000 watts
D. None of these
Answer : A
25. On a ladder resting on a rough ground and leaning against a smooth vertical wall, the force of friction acts
A. Downwards at its upper end
B. Upwards at its upper end
C. Perpendicular to the wall at its upper end
D. Zero at its upper end
Answer : D
A. Downwards at its upper end
B. Upwards at its upper end
C. Perpendicular to the wall at its upper end
D. Zero at its upper end
Answer : D
26. For a particle moving with a simple harmonic motion, the frequency is
A. Directly proportional to periodic time
B. Inversely proportional to periodic time
C. Inversely proportional to its angular velocity
D. Directly proportional to its angular velocity
Answer : B
A. Directly proportional to periodic time
B. Inversely proportional to periodic time
C. Inversely proportional to its angular velocity
D. Directly proportional to its angular velocity
Answer : B
27. The diagram showing the point of application and line of action of forces in their plane is called
A. Vector diagram
B. Space diagram
C. Force diagram
D. Funicular diagram
Answer : B
A. Vector diagram
B. Space diagram
C. Force diagram
D. Funicular diagram
Answer : B
28. Moment of inertia of a squares of side b about an axis through its centre of gravity, is
A. b3/4
B. b4/12
C. b4/3
D. b4/8
Answer : B
A. b3/4
B. b4/12
C. b4/3
D. b4/8
Answer : B
29. The piston of a steam engine moves with a simple harmonic motion. The crank rotates 120 r.p.m. and the stroke length is 2 metres. The linear velocity of the piston when it is at a distance of 0.5 metre from the centre, is
A. 5.88 m/sec
B. 8.88 m/sec
C. 10.88 m/sec
D. 12.88 m/sec
Answer : C
A. 5.88 m/sec
B. 8.88 m/sec
C. 10.88 m/sec
D. 12.88 m/sec
Answer : C
30. The maximum frictional force which comes into play, when a body just begins to slide over the surface of a another body, is known
A. Sliding friction
B. Rolling friction
C. Limiting friction
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Sliding friction
B. Rolling friction
C. Limiting friction
D. None of these
Answer : C
31. Two forces act an angle of 120°. If the greater force is 50 kg and their resultant is perpendicular to the smaller force, the smaller force is
A. 20 kg
B. 25 kg
C. 30 kg
D. 35 kg
Answer : B
A. 20 kg
B. 25 kg
C. 30 kg
D. 35 kg
Answer : B
32. If a body is lying on a plane whose inclination with the horizontal is less than the angle of friction, then? (i) A force is required to move the body upwards (ii) A force is required to move the body downward (iii) The body will not be in equilibrium The correct answer is
A. Only (i)
B. Only (ii)
C. Both (i) and (ii)
D. Both (i) and (iii)
Answer : C
A. Only (i)
B. Only (ii)
C. Both (i) and (ii)
D. Both (i) and (iii)
Answer : C
33. The acceleration of a particle moving along the circumference of a circle with a uniform speed, is directed
A. Radially
B. Tangentially at that point
C. Away from the centre
D. Towards the centre
Answer : B
A. Radially
B. Tangentially at that point
C. Away from the centre
D. Towards the centre
Answer : B
34. A string of length 90 cm is fastened to two points A and B at the same level 60 cm apart. A ring weighing 120 g is slided on the string. A horizontal force P is applied to the ring such that it is in equilibrium vertically below B. The value of P is:
A. 40 g
B. 60 g
C. 80 g
D. 100 g
Answer : C
A. 40 g
B. 60 g
C. 80 g
D. 100 g
Answer : C
35. If two forces each equal to T in magnitude act at right angles, their effect may be neutralised by a third force acting along their bisector in opposite direction whose magnitude will be
A. 2 T
B. 1/2 T
C. ?2 T
D. 3 T
Answer : C
A. 2 T
B. 1/2 T
C. ?2 T
D. 3 T
Answer : C
36. For a self-locking machine, the efficiency should be
A. Less than 60%
B. 50 %
C. More than 50%
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Less than 60%
B. 50 %
C. More than 50%
D. None of these
Answer : A
37. If G is the Gauge of track, v is velocity of the moving vehicle, g is the acceleration due to gravity and r is the radius of a circular path, the required super elevation is
A. gv²/Gr
B. Gr²/gr
C. Gr²/gv²
D. Gv²/gv
Answer : D
A. gv²/Gr
B. Gr²/gr
C. Gr²/gv²
D. Gv²/gv
Answer : D
38. For perfectly elastic bodies, the value of coefficient of restitution is
A. Zero
B. 0.5
C. 1.0
D. Between 0 and 1
Answer : C
A. Zero
B. 0.5
C. 1.0
D. Between 0 and 1
Answer : C
39. A Second's pendulum gains 2 minutes a day. To make it to keep correct time its length
A. Must be decreased
B. Must be increased
C. Is not changed but weight of the bob is increased
D. Is not changed but weight of the bob is decreased
Answer : B
A. Must be decreased
B. Must be increased
C. Is not changed but weight of the bob is increased
D. Is not changed but weight of the bob is decreased
Answer : B
40. Three forces which act on a rigid body to keep it in equilibrium. The forces must be coplanar and
A. Concurrent
B. Parallel
C. Concurrent parallel
D. Nne of these
Answer : A
A. Concurrent
B. Parallel
C. Concurrent parallel
D. Nne of these
Answer : A
41. If two forces of 3 kg and 4 kg act at right angles to each other, their resultant force will be equal to
A. 7 kg
B. 1 kg
C. 5 kg
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. 7 kg
B. 1 kg
C. 5 kg
D. None of these
Answer : C
42. A force P of 50 N and another force Q of unknown magnitude act at 90° to each other. They are balanced by a force of 130 N. The magnitude of Q is
A. 60 N
B. 80 N
C. 100 N
D. 120 N
Answer : D
A. 60 N
B. 80 N
C. 100 N
D. 120 N
Answer : D
43. Lami's theorem states that
A. Three forces acting at a point are always in equilibrium
B. If three forces acting on a point can be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a triangle, the point will be in the state of equilibrium
C. Three coplanar forces acting at a point will be in equilibrium, if each force is proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two
D. Three coplanar forces acting at a point will be in equilibrium if each force is inversely proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two
Answer : C
A. Three forces acting at a point are always in equilibrium
B. If three forces acting on a point can be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a triangle, the point will be in the state of equilibrium
C. Three coplanar forces acting at a point will be in equilibrium, if each force is proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two
D. Three coplanar forces acting at a point will be in equilibrium if each force is inversely proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two
Answer : C
44. If the given forces P?, P?, P? and P? are such that the force polygon does not close, then the system will
A. Be in equilibrium
B. Always reduce to a resultant force
C. Always reduce to a couple
D. Both (A) and (C)
Answer : B
A. Be in equilibrium
B. Always reduce to a resultant force
C. Always reduce to a couple
D. Both (A) and (C)
Answer : B
45. If two bodies of masses M1 and M2(M1 > M2) are connected by alight inextensible string passing over a smooth pulley, the tension in the string, will be given by
A. T = g(M1 - M2)/(M1 + M2)
B. T = g(M1 + M2)/(M1 × M2)
C. T = g(M2 - M1)/(M1 + M2)
D. T = g(M2 + M1)/(M2 - M1)
Answer : A
A. T = g(M1 - M2)/(M1 + M2)
B. T = g(M1 + M2)/(M1 × M2)
C. T = g(M2 - M1)/(M1 + M2)
D. T = g(M2 + M1)/(M2 - M1)
Answer : A
46. The member forces in a statically in determinate truss
A. Can be obtained by graphic statics
B. Cannot be obtained by graphic statics
C. May be obtained by graphic statics
D. Can be obtained by graphic statics by trial and error
Answer : B
A. Can be obtained by graphic statics
B. Cannot be obtained by graphic statics
C. May be obtained by graphic statics
D. Can be obtained by graphic statics by trial and error
Answer : B
47. A rigid body is in a stable equilibrium if the application of any force
A. Can raise the CG of the body but cannot lower it
B. Tends to lower the CG of the body
C. Neither raises nor lowers the CG of the body
D. None of above
Answer : A
A. Can raise the CG of the body but cannot lower it
B. Tends to lower the CG of the body
C. Neither raises nor lowers the CG of the body
D. None of above
Answer : A
48. The centre of gravity of the trapezium as shown in below figure from the side is at a distance of
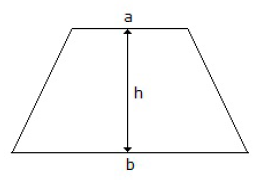
A. (h/3) × [(b + 2a)/(b + a)]
B. (h/3) × [(2b + a)/(b + a)]
C. (h/2) × [(b + 2a)/(b + a)]
D. (h/2) × [(2b + a)/(b + a)]
Answer : A

A. (h/3) × [(b + 2a)/(b + a)]
B. (h/3) × [(2b + a)/(b + a)]
C. (h/2) × [(b + 2a)/(b + a)]
D. (h/2) × [(2b + a)/(b + a)]
Answer : A
49. A particle moves with a velocity of 2 m/sec in a straight line with a negative acceleration of 0.1 m/sec2. Time required to traverse a distance of 1.5 m, is
A. 40 sec
B. 30 sec
C. 20 sec
D. 15 sec
Answer : C
A. 40 sec
B. 30 sec
C. 20 sec
D. 15 sec
Answer : C
50. Two objects moving with uniform speeds are 5 m apart after 1 second when they move towards each other and are 1 m apart when they move in the same direction. The speeds of the objects are
A. 2 m/sec and 2 m/sec
B. 3 m/sec and 2 m/sec
C. 3 m/sec and 3 m/sec
D. 4 m/sec and 6 m/sec
Answer : B
A. 2 m/sec and 2 m/sec
B. 3 m/sec and 2 m/sec
C. 3 m/sec and 3 m/sec
D. 4 m/sec and 6 m/sec
Answer : B
Sharing is caring
Related Post
Microsoft Word MCQ Solved Paper for SSC CHSL
Urologic infections and inflammations MCQ Solved Paper for RRB NTPC
1000+ Asp Programming Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Visual Basic .NET Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Operating System Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
WAN 1000+ MCQ with answer for SBI PO