Strength of Materials MCQ Solved Paper for SSC CHSL
Thursday 9th of March 2023

Sharing is caring
1. If in the equation pvn = C, the value of n = ?, then the process is called
A. Constant volume process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Constant pressure process
D. Isothermal process
Answer : A
A. Constant volume process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Constant pressure process
D. Isothermal process
Answer : A
2. Modulus of rigidity may be defined as the ratio of
A. Linear stress to lateral strain
B. Lateral strain to linear strain
C. Linear stress to linear strain
D. Shear stress to shear strain
Answer : D
A. Linear stress to lateral strain
B. Lateral strain to linear strain
C. Linear stress to linear strain
D. Shear stress to shear strain
Answer : D
3. The value of shear stress which is induced in the shaft due to the applied couple varies
A. From maximum at the centre to zero at the circumference
B. From zero at the centre to maximum at the circumference
C. From maximum at the centre to minimum at the circumference
D. From minimum at the centre to maximum at the circumference
Answer : B
A. From maximum at the centre to zero at the circumference
B. From zero at the centre to maximum at the circumference
C. From maximum at the centre to minimum at the circumference
D. From minimum at the centre to maximum at the circumference
Answer : B
4. The extension of a circular bar tapering uniformly from diameter d? at one end to diameter d? at the other end and subjected to an axial pull of P is given by
A. ?l = 4PE/ ?l²
B. ?l = 4?ld²/PE
C. ?l = 4Pl/?Ed?d?
D. ?l = 4PlE/ ?d?d?
Answer : C
A. ?l = 4PE/ ?l²
B. ?l = 4?ld²/PE
C. ?l = 4Pl/?Ed?d?
D. ?l = 4PlE/ ?d?d?
Answer : C
5. Charles' law states that all perfect gases change in volume by __________ of its original volume at 0°C for every 1°C change in temperature, when pressure remains constant.
A. 1/27th
B. 1/93th
C. 1/173th
D. 1/273th
Answer : D
A. 1/27th
B. 1/93th
C. 1/173th
D. 1/273th
Answer : D
6. An open cycle gas turbine works on
A. Carnot cycle
B. Otto cycle
C. Joule's cycle
D. Stirling cycle
Answer : C
A. Carnot cycle
B. Otto cycle
C. Joule's cycle
D. Stirling cycle
Answer : C
7. In order to know whether a column is long or short, we must know its
A. Ultimate shear stress of the column
B. Factor of safety
C. Torque resisting capacity
D. Slenderness ratio
Answer : D
A. Ultimate shear stress of the column
B. Factor of safety
C. Torque resisting capacity
D. Slenderness ratio
Answer : D
8. The strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft in torsion, subjected to shear stress (?), is: (Where, G = Modulus of rigidity for the shaft material)
A. ?²/ 2G × Volume of shaft
B. ?/ 2G × Volume of shaft
C. ?²/ 4G × Volume of shaft
D. ?/ 4G × Volume of shaft
Answer : C
A. ?²/ 2G × Volume of shaft
B. ?/ 2G × Volume of shaft
C. ?²/ 4G × Volume of shaft
D. ?/ 4G × Volume of shaft
Answer : C
9. The natural solid fuel is
A. Wood
B. Coke
C. Anthracite coal
D. Pulverised coal
Answer : A
A. Wood
B. Coke
C. Anthracite coal
D. Pulverised coal
Answer : A
10. The lower layer of the beam as shown in the below figure, will be
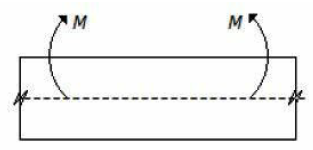
A. In tension
B. In compression
C. Neither in tension nor in compression
D. None of these
Answer : A

A. In tension
B. In compression
C. Neither in tension nor in compression
D. None of these
Answer : A
11. Elasticity of Mild Steel specimen is defined by
A. Hookes law
B. Yield point
C. Plastic flow
D. Proof stress
Answer : C
A. Hookes law
B. Yield point
C. Plastic flow
D. Proof stress
Answer : C
12. The general law of expansion or compression is pvn = C, The process is said to be hyperbolic, if n is equal to
A. 0
B. 1
C. ?
D. ?
Answer : B
A. 0
B. 1
C. ?
D. ?
Answer : B
13. The variables which control the physical properties of a perfect gas are
A. Pressure exerted by the gas
B. Volume occupied by the gas
C. Temperature of the gas
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. Pressure exerted by the gas
B. Volume occupied by the gas
C. Temperature of the gas
D. All of these
Answer : D
14. A material obeys hooks law up to
A. Plastic limit
B. Elastic limit
C. Yield point
D. Limit of proportionality
Answer : B
A. Plastic limit
B. Elastic limit
C. Yield point
D. Limit of proportionality
Answer : B
15. The property of a material by virtue of which a body returns to its original, shape after removal of the load is called
A. Plasticity
B. Elasticity
C. Ductility
D. Malleability
Answer : B
A. Plasticity
B. Elasticity
C. Ductility
D. Malleability
Answer : B
16. The value of one bar (in S. I. units) is equal to
A. 1 × 102 N/m2
B. 1 × 103 N/m2
C. 1 × 104 N/m2
D. 1 × 105 N/m2
Answer : D
A. 1 × 102 N/m2
B. 1 × 103 N/m2
C. 1 × 104 N/m2
D. 1 × 105 N/m2
Answer : D
17. The ratio of root mean square velocity to average velocity of gas molecules at a particular temperature is
A. 0.086
B. 1.086
C. 1.086
D. 4.086
Answer : B
A. 0.086
B. 1.086
C. 1.086
D. 4.086
Answer : B
18. The ideal efficiency of a Brayton cycle with regeneration, with increase in pressure ratio will
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain unchanged
D. Increase/decrease depending on application
Answer : B
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain unchanged
D. Increase/decrease depending on application
Answer : B
19. The deformation of a bar under its own weight is _________ the deformation, if the same body is subjected to a direct load equal to weight of the body.
A. Equal to
B. Half
C. Double
D. Quadruple
Answer : B
A. Equal to
B. Half
C. Double
D. Quadruple
Answer : B
20. Carbonisation of coal consists of
A. Drying and crushing the coal to a fine powder
B. Moulding the finely ground coal under pressure with or without a binding material
C. Heating the wood with a limited supply of air to temperature not less than 280°C
D. None of the above
Answer : D
A. Drying and crushing the coal to a fine powder
B. Moulding the finely ground coal under pressure with or without a binding material
C. Heating the wood with a limited supply of air to temperature not less than 280°C
D. None of the above
Answer : D
21. When coal is strongly heated continuously for 42 to 48 hours in the absence of air in a closed vessel, the process is known as __________ of fuel.
A. Atomisation
B. Carbonisation C. Combustion
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Atomisation
B. Carbonisation C. Combustion
D. None of these
Answer : B
22. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of the unit mass of gas through one degree at constant volume, is called
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. Kilo Joule
D. None of these
Answer : A
A. Specific heat at constant volume
B. Specific heat at constant pressure
C. Kilo Joule
D. None of these
Answer : A
23. The ratio of the largest load in a test to the original cross-sectional area of the test piece is called
A. Elastic limit
B. Yield stress
C. Ultimate stress
D. Breaking stress
Answer : C
A. Elastic limit
B. Yield stress
C. Ultimate stress
D. Breaking stress
Answer : C
24. True stress strain-curve for materials is plotted between
A. Load/original cross-sectional area and change in length/original length
B. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and loge (original area/ instantaneous area)
C. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and change in length/ original length
D. Load/ instantaneous area and instantaneous area/original area
Answer : B
A. Load/original cross-sectional area and change in length/original length
B. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and loge (original area/ instantaneous area)
C. Load/ instantaneous cross-sectional area and change in length/ original length
D. Load/ instantaneous area and instantaneous area/original area
Answer : B
25. The buckling load for a given column depends upon
A. Area of cross-section of the column
B. Length and least radius of gyration of the column
C. Modulus of elasticity for the material of the column
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. Area of cross-section of the column
B. Length and least radius of gyration of the column
C. Modulus of elasticity for the material of the column
D. All of the above
Answer : D
26. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
A. The liquid fuels have higher calorific value than solid fuels
B. The solid fuels have higher calorific value than liquid fuels
C. A good fuel should have low ignition point
D. The liquid fuels consist of hydrocarbons
Answer : B
A. The liquid fuels have higher calorific value than solid fuels
B. The solid fuels have higher calorific value than liquid fuels
C. A good fuel should have low ignition point
D. The liquid fuels consist of hydrocarbons
Answer : B
27. A riveted joint in which every rivet of a row is opposite to other rivet of the outer row, is known as
A. Chain riveted joint
B. Diamond riveted joint
C. Crisscross riveted joint
D. Zigzag riveted joint
Answer : A
A. Chain riveted joint
B. Diamond riveted joint
C. Crisscross riveted joint
D. Zigzag riveted joint
Answer : A
28. The bending moment at a point on a beam is the algebraic ________ of all the moments on either side of the point.
A. Sum
B. Difference
C. Multiplication
D. None of the above
Answer : A
A. Sum
B. Difference
C. Multiplication
D. None of the above
Answer : A
29. During a tensile test on a specimen of 1 cm cross-section, maximum load observed was 8 tonnes and area of cross-section at neck was 0.5 cm². Ultimate tensile strength of specimen is
A. 4 tonnes/ cm²
B. 8 tonnes/ cm²
C. 16 tonnes/ cm²
D. 22 tonnes/ cm²
Answer : B
A. 4 tonnes/ cm²
B. 8 tonnes/ cm²
C. 16 tonnes/ cm²
D. 22 tonnes/ cm²
Answer : B
30. Coke is produced
A. When coal is first dried and then crushed to a fine powder by pulverising machine
B. From the finely ground coal by moulding under pressure with or without a binding material
C. When coal is strongly heated continuously for 42 to 48 hours in the absence of air in a closed vessel
D. By heating wood with a limited supply of air to a temperature not less than 280°C
Answer : C
A. When coal is first dried and then crushed to a fine powder by pulverising machine
B. From the finely ground coal by moulding under pressure with or without a binding material
C. When coal is strongly heated continuously for 42 to 48 hours in the absence of air in a closed vessel
D. By heating wood with a limited supply of air to a temperature not less than 280°C
Answer : C
31. The ratio of specific heat at constant pressure (cp) and specific heat at constant volume (cv) is
A. Equal to one
B. Less than one
C. Greater than one
D. None of these
Answer : C
A. Equal to one
B. Less than one
C. Greater than one
D. None of these
Answer : C
32. In case of an under-reinforced beam, the depth of actual neutral axis is __________ that of the critical neutral axis.
A. Same as
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Same as
B. Less than
C. Greater than
D. None of these
Answer : B
33. The standard value of atmospheric pressure taken at sea level is
A. 1.013 bar
B. 760 mm of Hg
C. 1013 × 102 N/m2
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. 1.013 bar
B. 760 mm of Hg
C. 1013 × 102 N/m2
D. All of these
Answer : D
34. Brayton cycle consists' of following four processes
A. Two isothermals and two isentropic
B. Two isentropic and two constant volumes
C. Two isentropic, one constant volume and one constant pressure
D. Two isentropic and two constant pressures
Answer : D
A. Two isothermals and two isentropic
B. Two isentropic and two constant volumes
C. Two isentropic, one constant volume and one constant pressure
D. Two isentropic and two constant pressures
Answer : D
35. The assumption made in Euler's column theory is that
A. The failure of column occurs due to buckling alone
B. The length of column is very large as compared to its cross-sectional dimensions
C. The column material obeys Hooke's law
D. All of the above
Answer : D
A. The failure of column occurs due to buckling alone
B. The length of column is very large as compared to its cross-sectional dimensions
C. The column material obeys Hooke's law
D. All of the above
Answer : D
36. The bending moment of a cantilever beam of length l and carrying a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length is __________ at the fixed end.
A. wl/4
B. wl/2
C. wl
D. wl²/2
Answer : D
A. wl/4
B. wl/2
C. wl
D. wl²/2
Answer : D
37. When a system changes its state from one equilibrium state to another equilibrium state, then the path of successive states through which the system has passed, is known as
A. Thermodynamic law
B. Thermodynamic process
C. Thermodynamic cycle
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Thermodynamic law
B. Thermodynamic process
C. Thermodynamic cycle
D. None of these
Answer : B
38. The stress necessary to initiate yielding is
A. Considerably greater than that necessary to continue it
B. Considerably lesser than that necessary to continue it
C. Greater than that necessary to stop it
D. Lesser than that necessary to stop it
Answer : A
A. Considerably greater than that necessary to continue it
B. Considerably lesser than that necessary to continue it
C. Greater than that necessary to stop it
D. Lesser than that necessary to stop it
Answer : A
39. The __________ is obtained when carbonisation of coal is carried out at 500° to 700° C.
A. Soft coal
B. Hard coal
C. Pulverised coal
D. Bituminous coal
Answer : A
A. Soft coal
B. Hard coal
C. Pulverised coal
D. Bituminous coal
Answer : A
40. The unit of Young's modulus is
A. mm/mm
B. kg/cm
C. Kg
D. kg/cm²
Answer : D
A. mm/mm
B. kg/cm
C. Kg
D. kg/cm²
Answer : D
41. In a tensile test on mild steel specimen, the breaking stress as compared to ultimate tensile stress i
A. More
B. Less
C. Same
D. More/less depending on composition
Answer : B
A. More
B. Less
C. Same
D. More/less depending on composition
Answer : B
42. When a body is subjected to biaxial stress i.e. direct stresses (?x) and (?y) in two mutually perpendicular planes accompanied by a simple shear stress (?xy), then minimum normal stress is
A. (?x + ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
B. (?x + ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
C. (?x - ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
D. (?x - ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
Answer : B
A. (?x + ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
B. (?x + ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x - ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
C. (?x - ?y)/2 + (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
D. (?x - ?y)/2 - (1/2) × ?[(?x + ?y)² + 4 ?²xy]
Answer : B
43. Strain re-setters are used to
A. Measure shear strain
B. Measure linear strain
C. Measure volumetric strain
D. Relieve strain
Answer : B
A. Measure shear strain
B. Measure linear strain
C. Measure volumetric strain
D. Relieve strain
Answer : B
44. According to Regnault's law, the specific heat at constant pressure (cp) and specific heat at constant volume (cv) _________ with the change in pressure and temperature of the gas.
A. Change
B. Do not change
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : B
A. Change
B. Do not change
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. None of these
Answer : B
45. The point of contraflexure is a point where
A. Shear force changes sign
B. Bending moment changes sign
C. Shear force is maximum
D. Bending moment is maximum
Answer : B
A. Shear force changes sign
B. Bending moment changes sign
C. Shear force is maximum
D. Bending moment is maximum
Answer : B
46. In an extensive property of a thermodynamic system
A. Extensive heat is transferred
B. Extensive work is done
C. Extensive energy is utilised
D. None of these
Answer : D
A. Extensive heat is transferred
B. Extensive work is done
C. Extensive energy is utilised
D. None of these
Answer : D
47. The behaviour of a perfect gas, undergoing any change in the variables which control physical properties, is governed by
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. All of these
Answer : D
A. Boyle's law
B. Charles' law
C. Gay-Lussac law
D. All of these
Answer : D
48. If a material expands freely due to heating it will develop
A. Thermal stresses
B. Tensile stress
C. Bending
D. No stress
Answer : D
A. Thermal stresses
B. Tensile stress
C. Bending
D. No stress
Answer : D
49. A composite bar made up of steel and copper bars of equal lengths are heated through 100°C. The stresses developed shall be
A. Tensile in both the material
B. Tensile in steel and compressive in copper
C. Compressive in steel and tensile in copper
D. Compressive in both the materials
Answer : D
A. Tensile in both the material
B. Tensile in steel and compressive in copper
C. Compressive in steel and tensile in copper
D. Compressive in both the materials
Answer : D
50. The fuel mostly used in cement industry and in metallurgical processes is
A. Wood charcoal
B. Bituminous coke
C. Pulverised coal
D. Coke
Answer : C
A. Wood charcoal
B. Bituminous coke
C. Pulverised coal
D. Coke
Answer : C
Sharing is caring
Related Post
CTET - Transformation of Sentences 1000+ MCQ [Solved] PDF Download
1000+ Design of Steel Structures Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Microsoft PowerPoint Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
1000+ Microsoft PowerPoint Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]
Line Graph MCQ Solved Paper for RRB ALP
1000+ WAN Multiple Choice Question Answer [Solved]