Match the names of the structures given in column-I with the functions given in column-II, choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the two columns :
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| (Structure) | (Function) |
| A. Stomata | I. Protection of stem |
| B. Bark | II. Plant movement |
| C. Cambium | III. Secondary growth |
| D. Cuticle | IV. Transpiration |
| V. Prevent the loss of water | ... |
A V, B III, C I, D IV
A I, B IV, C V, D III
A II, B IV, C I, D III
A IV, B I, C III, D V
Correct Answer :
D. A IV, B I, C III, D V
A - Stomata: They are minute aperture structures on plants found typically on the outer leaf skin layer, also known as the epidermis. They consist of two specialized cells, called guard cells that surround a tiny pore called a stoma. It helps in transpiration and gaseous exchange. Transpiration is the transport of water through an actual, vegetated plant into the atmosphere. Transpiration is an important part of the evapotranspiration process, and a major mechanism of the water cycle in the atmosphere.
B - Bark: Bark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines, and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside of the vascular cambium. It serves as protection of stem against damage from parasites, herbivorous animals and diseases, as well as dehydration and fire.
C - Cambium: It is a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening.
D - Cuticle: It is a protecting film covering the epidermis of leaves, young shoots and other aerial plant organs without periderm. It consists of lipid and hydrocarbon polymers impregnated with wax, and are synthesized exclusively by the epidermal cells. In addition to its function as permeability barrier for water and other molecules (prevent water loss), the micro and nano-structure of the cuticle confer specialised surface properties that prevent contamination of plant tissues with external water, dirt and microorganisms.
Related Questions
A student was given a tissue to observe under the microscope. He observes the tissue and concludes that the tissue is a type of simple plant tissue and provides mechanical support to young stem and petiole of leaf.
Identify the tissue.
Parenchyma
Collenchyma
Sclerenchyma
Xylem parenchyma
In land plants, the guard cells differ from other epidermal cells in having
cytoskeleton.
mitochondria.
endoplasmic reticulum.
chloroplasts.
The given figure shows T.S. of monocot stem. Identify the correct labelling of A to F marked in the given figure.
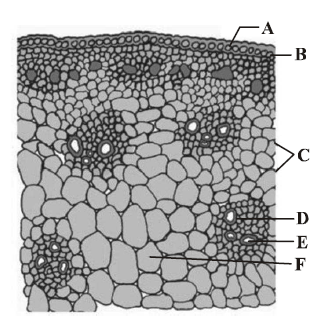
A Epidermis, B Hypodermis, C Vascular bundles, D Phloem, E Xylem, F Ground tissue
A Cuticle, B Epidermis, C Sclerenchymatous sheath, D Sclerenchymatous hypodermis, E Parenchymatous sheath, F Phloem
A Cuticle, B Epidermis, C Sclerenchymatous hypodermis, D Sclerenchymatous sheath, E Parenchymatous sheath, F Phloem
A Cuticle, B Epidermis, C Sclerenchymatous hypodermis, D Sclerenchymatous sheath, E Parenchymatous sheath, F Protoxylem
Trees at sea do not have annual rings because
soil is sandy.
there is climatic variation.
there is no marked climatic variation.
there is enough moisture in the atmosphere.
Which one of the following statement is incorrect ?
- Epidermal cell has small amount of cytoplasm and a large vacuole.
- Waxy cuticle layer is absent in roots.
- Root hairs are unicellular, while stem hairs / trichomes are multicellular.
- Trichomes may be branched or unbranched, soft or stiff and prevent transpiration.
- Guard cells are dumbell shaped in dicots and beanshaped in monocots (e.g. grass).
Only (i)
Only (iv)
Only (iii)
Only (v)
Apical and intercalary meristems are primary meristems because
they occur in the mature region of roots and shoots of many plants.
they made up of different kinds of tissues.
they involved in secondary growth.
they appear early in life of a plant and contribute to the formation of the primary plant body.
In the given columns, column I contain structures of female reproductive system and column II contain its feature. Select the correct match.
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| A. Lateral meristem | (i) Fascicular vascular cambium, interfascicular cambium and cork cambium. |
| B. Apical meristem | (ii) Produces dermal tissue, ground tissues and vascular tissue. |
| C. Bast fibres | (iii) Generally absent in primary phloem but found in secondary phloem. |
| D. Sap wood | (iv) Involved in the conduction of water and minerals from the root to leaf. |
A - (i), B - (ii), C - (iii), D - (iv)
A - (iii), B - (i), C - (ii), D - (iv)
A - (i), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (ii)
A - (ii), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (i)
Match the terms given in column I with their features given in column II and choose the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| (Terms) | (Features) |
| A. Fibres | (i) Cells are living and thin walled with cellulosic cell wall, store food materials in the form of starch or fat |
| B. Sclereids | (ii) Main water conductive cells of the pteridophytes and the gymnosperms |
| C. Tracheids | (iii) Thick walled, elongated and pointed cells, generally occurring in groups |
| D. Vessels | (iv) Long cylindrical tube like structure and cells are devoid of protoplasm. Characteristic feature of angiosperms |
| E. Xylem parenchyma | (v) Reduced form of sclerenchyma cells with highly thickened lignified cellular walls that form small bundles of durable layers of tissue in most plants. |
A - (i), B - (ii), C - (iii), D - (iv), E - (v)
A - (iii), B - (v), C - (ii), D - (iv), E - (i)
A - (iii), B - (i), C - (v), D - (ii), E - (iv)
A - (v), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (i), E - (ii)
The given figure shows apical meristem of root apex with few part marked as A, B and C. Identify the correct labelling of A, B and C.
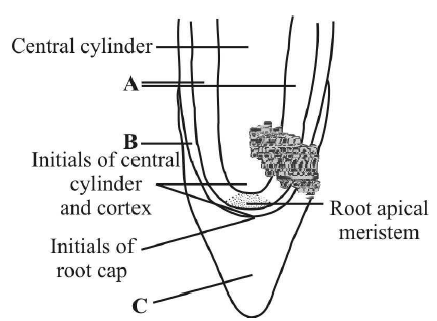
A Vascular structure, B Protoderm, C Root cap
A Cortex, B Endodermis, C Root cap
A Cortex, B Protoderm, C Root cap
A Tunica, B Protoderm, C Root cap
Phellogen and phellem respectively denote
cork and cork cambium,
cork cambium and cork,
secondary cortex and cork,
cork and secondary cortex,
Match column-I with column-II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
| Column-I | Column-II |
|---|---|
| A. Stele | I. Innermost layer of cortex |
| B. Endodermis | II. Suberin |
| C. Casparian strips | III. All the tissues exterior to vascular cambium |
| D. Bark | IV. All the tissues inner to endodermis |
A IV, B I, C II, D III
A III, B II, C I, D IV
A I, B II, C III, D IV
A IV, B II, C I, D III
In an experiment, a student cut a transverse section of young stem of a plant which he has taken from his school garden.
After observing it under the microscope how would he ascertain whether it is a monocot stem or a dicot stem?
With the help of bulliform cells.
With the help of casparian strips.
With the help of vascular bundles.
With the help of stomatal apparatus.
A narrow layer of thin walled cells found between phloem/ bark and wood of a dicot is
cork cambium
vascular cambium
endodermis
both (a) & (c)
Match column-I with column-II and choose the correct option.
| Column -I | Column -II |
|---|---|
| A. Bulliform cells | I. Initiation of lateral roots |
| B. Pericycle | II. Root |
| C. Endarch xylem | III. Grasses |
| D. Exarch xylem | IV. Dicot leaf |
| E. Bundle sheath cells | V. Stem |
A III, B V, C IV, D I, E II
A II, B V, C I, D III, E IV
A II, B IV, C I, D III, E V
A III, B I, C V, D II, E IV
Tissue(s) present in an annual ring is/are
secondary xylem and phloem.
primary xylem and phloem.
secondary xylem only.
primary phloem and secondary xylem.
Choose the correct labelling of (A J) in the given figure of T.S. of monocot root.

A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pericycle, G Pith, H Phloem, I Metaxylem.
A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Passage cell, F Pith, G Pericycle, H Metaxylem, I Phloem.
A Root hair, B Epiblema, C Cortex, D Endodermis, E Pericycle, F Phloem, G Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
A Root hair, B Cortex, C Epiblema, D Pericycle, E Endodermis, F Pith, G Phloem, H Protoxylem, I Metaxylem
Cells of permanent tissues are specialized
functionally.
only structurally.
both structurally and functionally.
for mitosis.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct ?
- Uneven thickening of cell wall is characteristic of sclerenchyma.
- Periblem forms cortex of the stem and the root.
- Tracheids are the chief water transporting elements in gymnosperms.
- Companion cell is devoid of nucleus at maturity.
- The commercial cork is obtained from Quercus suber.
(i) and (iv) only
(ii) and (v) only
(iii) and (iv) only
(ii), (iii) and (v) only
Some vascular bundles are described as open because these
are surrounded by pericycle but not endodermis.
are capable of producing secondary xylem and phloem.
possess conjunctive tissue between xylem and phloem.
are not surrounded by pericycle.
A piece of wood having no vessels (trachea) must be belonged to
teak
mango
pine
palm
Main function of lenticel is
transpiration
guttation
gaseous exchange
both (a) & (c)
Apical, intercalary and lateral meristems are differentiated on the basis of
origin
function
position
development
Identify A, B and C in the given figure of shoot apical meristem
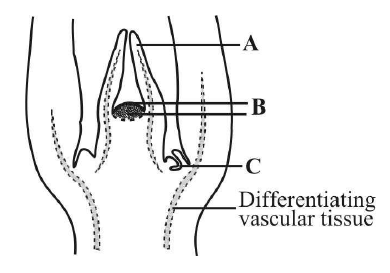
A Leaf primordium, B Shoot apical meristem, C Axillary bud
A Leaf primordium, B Shoot apical meristem, C Apical bud
A Root hair primordium, B Root apical meristem, C Axillary bud
A Root hair primordium, B Root apical meristem, C Terminal bud
The length of different internodes in a culm of sugarcane is variable because of
size of leaf lamina at the node below each internode
intercalary meristem
shoot apical meristem
position of axillary buds
Read the following statements and answer the question.
- Cambium is very active and produces a large number of xylary elements having vessels with wider cavities.
- It is also called early wood.
- It is lighter in colour and has lower density.
Which type of wood is described by the above statements?
Sap wood
Heart wood
Spring wood
Autumn wood
T.S. of dicot leaf passing through the midrib is given below. Certain parts have been marked by alphabets (A to H). Choose the option showing their correct labelling.
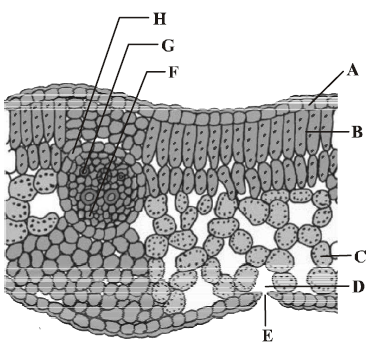
A Epidermis, B Spongy mesophyll, C Palisade mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Sub-stomatal cavity, E Stoma, F Phloem, G Xylem, H Bundle sheath
A Epidermis, B Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Epidermis, G Xylem, H Phloem
A Epidermis, C Palisade mesophyll, C Spongy mesophyll, D Stomata, E Guard cells, F Phloem, G Metaxylem, H Protoxylem
Tissues are classified into two main groups, namely meristematic and permanent tissues on the basis of
whether the cells being able to divide or not.
position of the cells.
whether they are living or dead.
none of the above
Identify types of vascular bundles in given figures A, B and C.
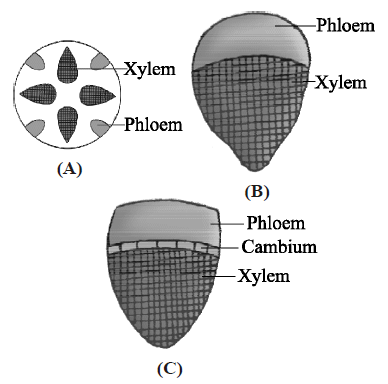
Radial; Conjoint closed; Conjoint open
Conjoint closed; Conjoint open; Radial
Conjoint open; Conjoint closed; Radial
Bicollateral; Concentric; Radial
The given figure shows the secondary growth in a dicot stem. Their parts are marked as A, B, C, D, E & F. Choose the correct labelling of the parts marked as A to F.
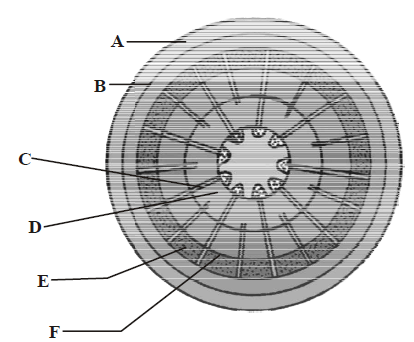
A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Medullary rays, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Cambium ring
A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Medullary rays, D Secondary phloem, E Secondary xylem, F Cambium ring
A Phellogen, B Phellem, C Medullary rays, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Cambium ring
A Phellem, B Phellogen, C Cambium ring, D Secondary xylem, E Secondary phloem, F Medullary rays
Which type of plant tissue is being described by the given statements?
- It consists of long, narrow cells with thick and lignified cell walls having a few or numerous pits.
- They are dead and without protoplasts.
- On the basis of variation in form, structure, origin and development, it may be either fibres or sclereids.
- It provides mechanical support to organs.
Parenchyma
Sclerenchyma
Collenchyma
Chlorenchyma
